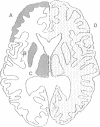
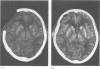
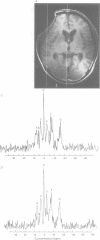
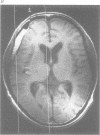
Abstract
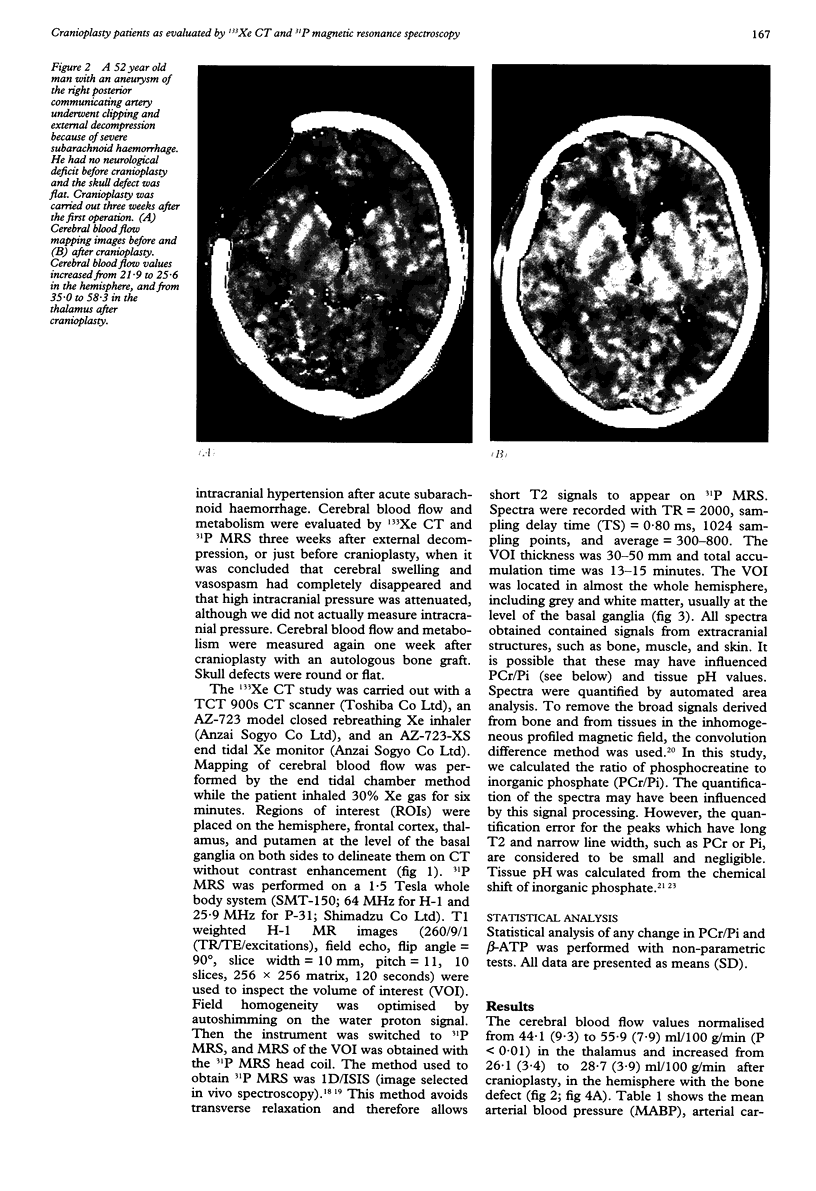
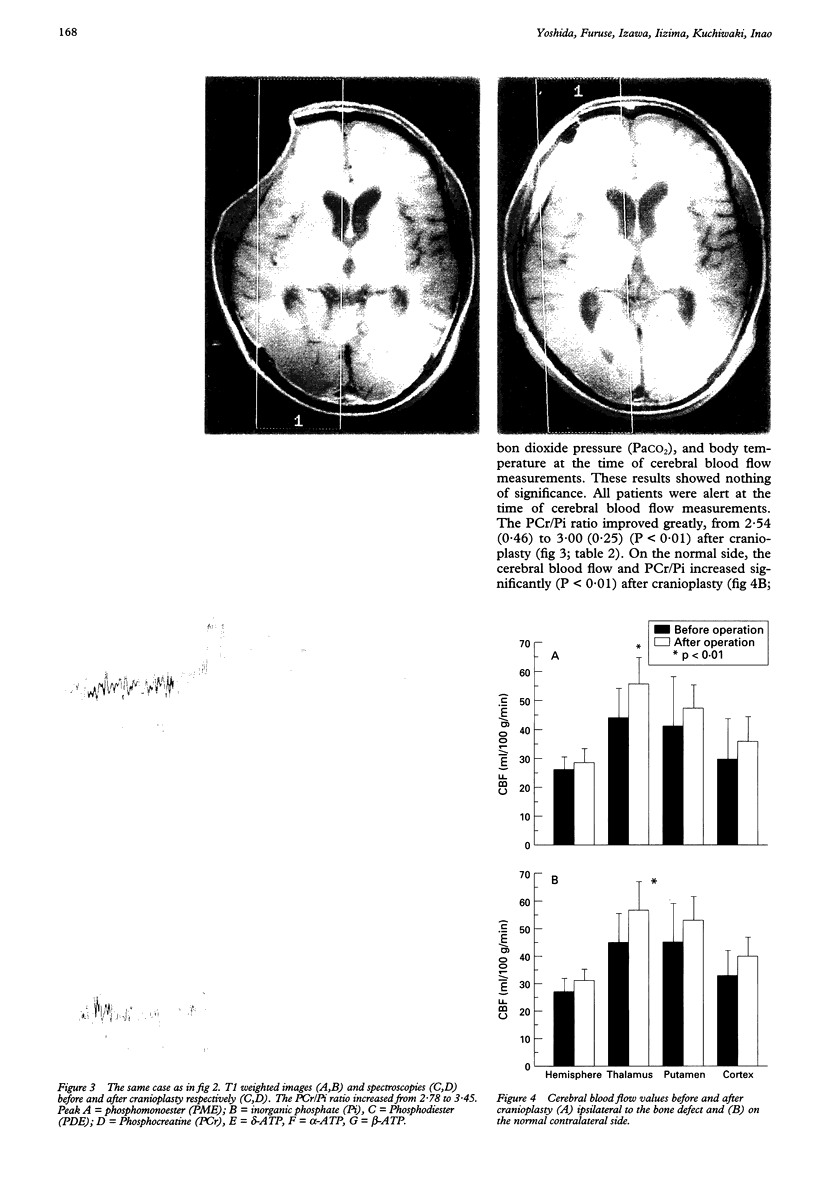
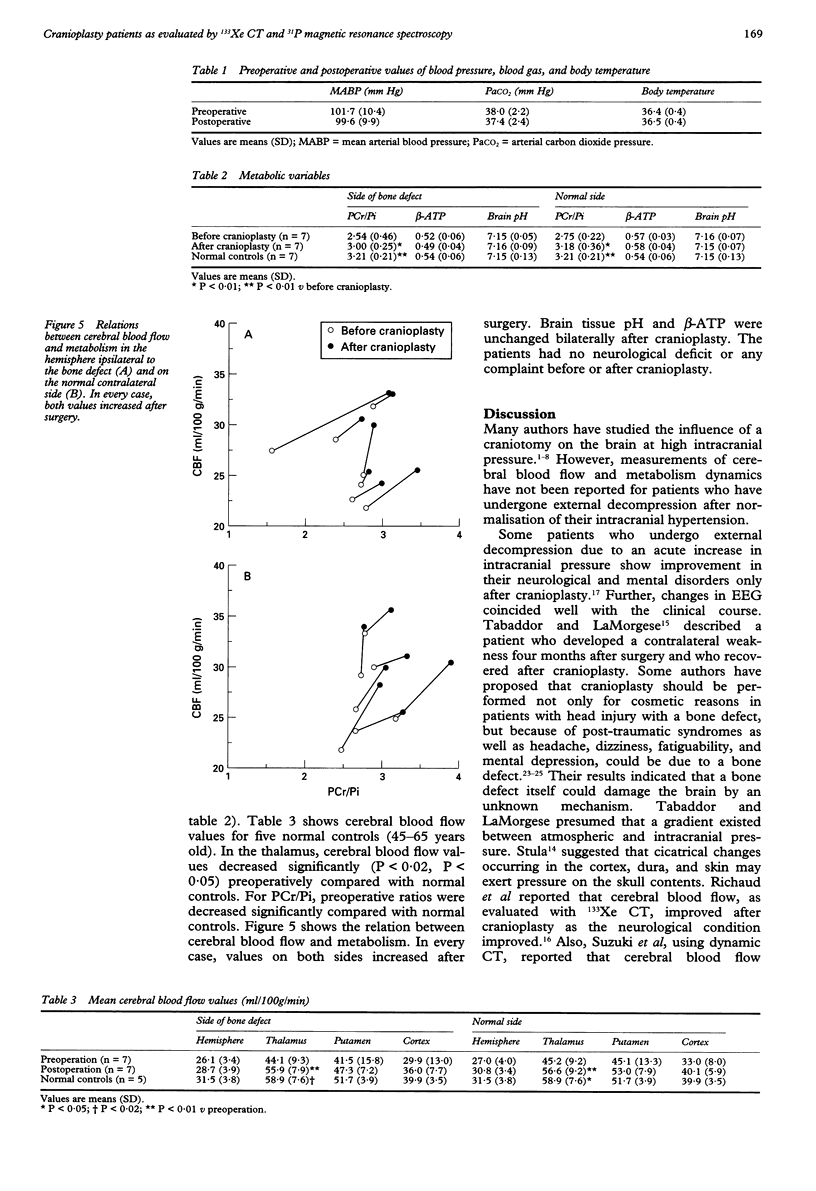
OBJECTIVE--Prolonged improvement in neurological and mental disorders has been seen after only cranioplasty in patients initially treated with external decompression for high intracranial pressure. The objective was to evaluate, using 133Xe CT and 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), how restoring the bone itself can influence cerebral blood flow and cerebral energy metabolism after high intracranial pressure is attenuated. METHODS--Seven patients (45-65 years old) who had undergone external decompression to prevent uncontrollable intracranial hypertension after acute subarachnoid haemorrhage were evaluated. Cerebral blood flow and metabolic changes were evaluated before and after cranioplasty. RESULTS--The ratio of phosphocreatine to inorganic phosphate (PCr/Pi), which is a sensitive index of cerebral energy depletion, was calculated and beta-ATP was measured. The cerebral blood flow value in the thalamus was normalised, from 44 (SD 9) to 56 (SD 8) ml/100 g/min (P < 0.01) and the value in the hemisphere increased from 26 (SD 3) to 29 (SD 4) ml/100 g/min on the side with the bone defect. The PCr/Pi ratio improved greatly from 2.53 (SD 0.45) to 3.01 (SD 0.24) (P < 0.01). On the normal side, the values of cerebral blood flow and PCr/Pi increased significantly (P < 0.01) after cranioplasty, possibly due to transneural suppression. The pH of brain tissue was unchanged bilaterally after cranioplasty. CONCLUSION--Cranioplasty should be carried out as soon as oedema has disappeared, because a bone defect itself may decrease cerebral blood flow and disturb energy metabolism.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottomley P. A., Drayer B. P., Smith L. S. Chronic adult cerebral infarction studied by phosphorus NMR spectroscopy. Radiology. 1986 Sep;160(3):763–766. doi: 10.1148/radiology.160.3.3737915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britt R. H., Hamilton R. D. Large decompressive craniotomy in the treatment of acute subdural hematoma. Neurosurgery. 1978 May-Jun;2(3):195–200. doi: 10.1227/00006123-197805000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. R., Hagler H., Clark W. K., Barnett P. Enhancement of experimental cerebral edema after decompressive craniectomy: implications for the management of severe head injuries. Neurosurgery. 1979 Apr;4(4):296–300. doi: 10.1227/00006123-197904000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. R., Rovit R. L., Ransohoff J. Hemicraniectomy in the treatment of acute subdural hematoma: a re-appraisal. Surg Neurol. 1976 Jan;5(1):25–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpy D. T., Gordon R. E., Hope P. L., Parker D., Reynolds E. O., Shaw D., Whitehead M. D. Noninvasive investigation of cerebral ischemia by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance. Pediatrics. 1982 Aug;70(2):310–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germano I. M., Pitts L. H., Berry I., De Armond S. J. High energy phosphate metabolism in experimental permanent focal cerebral ischemia: an in vivo 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988 Feb;8(1):24–31. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1988.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant F. C., Norcross N. C. REPAIR OF CRANIAL DEFECTS BY CRANIOPLASTY. Ann Surg. 1939 Oct;110(4):488–512. doi: 10.1097/00000658-193910000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatashita S., Hoff J. T. The effect of craniectomy on the biomechanics of normal brain. J Neurosurg. 1987 Oct;67(4):573–578. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.67.4.0573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatashita S., Koike J., Sonokawa T., Ishii S. Cerebral edema associated with craniectomy and arterial hypertension. Stroke. 1985 Jul-Aug;16(4):661–668. doi: 10.1161/01.str.16.4.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilberman M., Subramanian V. H., Haselgrove J., Cone J. B., Egan J. W., Gyulai L., Chance B. In vivo time-resolved brain phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1984 Sep;4(3):334–342. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1984.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inao S., Kuchiwaki H., Kanaiwa H., Sugito K., Banno M., Furuse M. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of brainstem distortion associated with a supratentorial mass. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1993 Mar;56(3):280–285. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.56.3.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishige N., Pitts L. H., Pogliani L., Hashimoto T., Nishimura M. C., Bartkowski H. M., James T. L. Effect of hypoxia on traumatic brain injury in rats: Part 2. Changes in high energy phosphate metabolism. Neurosurgery. 1987 Jun;20(6):854–858. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198706000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondziolka D., Fazl M. Functional recovery after decompressive craniectomy for cerebral infarction. Neurosurgery. 1988 Aug;23(2):143–147. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198808000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse S., Horikawa Y., Tanaka C., Hirakawa K., Nishikawa H., Watari H. In vivo measurement of energy metabolism and the concomitant monitoring of electroencephalogram in experimental cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 2;296(2):370–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordidge R. J., Bowley R. M., McHale G. A general approach to selection of multiple cubic volume elements using the ISIS technique. Magn Reson Med. 1988 Nov;8(3):323–331. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910080309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petroff O. A., Prichard J. W., Behar K. L., Alger J. R., Shulman R. G. In vivo phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in status epilepticus. Ann Neurol. 1984 Aug;16(2):169–177. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petroff O. A., Prichard J. W., Behar K. L., Alger J. R., den Hollander J. A., Shulman R. G. Cerebral intracellular pH by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurology. 1985 Jun;35(6):781–788. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.6.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard J. W., Alger J. R., Behar K. L., Petroff O. A., Shulman R. G. Cerebral metabolic studies in vivo by 31P NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2748–2751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richaud J., Boetto S., Guell A., Lazorthes Y. Incidence des crânioplasties sur la fonction neurologique et le débit sanguin cérébral. Neurochirurgie. 1985;31(3):183–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnall M. D., Yoshizaki K., Chance B., Leigh J. S., Jr Triple nuclear NMR studies of cerebral metabolism during generalized seizure. Magn Reson Med. 1988 Jan;6(1):15–23. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910060103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutta H. S., Kassell N. F., Langfitt T. W. Brain swelling produced by injury and aggravated by arterial hypertension. A light and electron microscopic study. Brain. 1968 Jun;91(2):281–294. doi: 10.1093/brain/91.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro K., Fried A., Takei F., Kohn I. Effect of the skull and dura on neural axis pressure-volume relationships and CSF hydrodynamics. J Neurosurg. 1985 Jul;63(1):76–81. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.63.1.0076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stula D. Intrakranielle Druckmessung bei grossen Schädelkalottendefekten. Neurochirurgia (Stuttg) 1985 Jul;28(4):164–169. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1054190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Suzuki S., Iwabuchi T. Neurological improvement after cranioplasty. Analysis by dynamic CT scan. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1993;122(1-2):49–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01446986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaddor K., LaMorgese J. Complication of a large cranial defect. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1976 Apr;44(4):506–508. doi: 10.3171/jns.1976.44.4.0506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Yoshinaga S., Kimura M. Xenon-enhanced computed tomographic measurement of cerebral blood flow in patients with chronic subdural hematomas. Neurosurgery. 1990 Oct;27(4):554–561. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199010000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thulborn K. R., du Boulay G. H., Duchen L. W., Radda G. A 31P nuclear magnetic resonance in vivo study of cerebral ischaemia in the gerbil. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1982 Sep;2(3):299–306. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1982.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venes J. L., Collins W. F. Bifrontal decompressive craniectomy in the management of head trauma. J Neurosurg. 1975 Apr;42(4):429–433. doi: 10.3171/jns.1975.42.4.0429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhall B., Spurling R. G. Tantalum Cranioplasty for War Wounds of the Skull. Ann Surg. 1945 May;121(5):649–668. doi: 10.1097/00000658-194505000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaura A., Makino H. Neurological deficits in the presence of the sinking skin flap following decompressive craniectomy. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 1977;17(1 Pt 1):43–53. doi: 10.2176/nmc.17pt1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonas H., Good W. F., Gur D., Wolfson S. K., Jr, Latchaw R. E., Good B. C., Leanza R., Miller S. L. Mapping cerebral blood flow by xenon-enhanced computed tomography: clinical experience. Radiology. 1984 Aug;152(2):435–442. doi: 10.1148/radiology.152.2.6739811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonas H., Gur D., Good B. C., Latchaw R. E., Wolfson S. K., Jr, Good W. F., Maitz G. S., Colsher J. G., Barnes J. E., Colliander K. G. Stable xenon CT blood flow mapping for evaluation of patients with extracranial-intracranial bypass surgery. J Neurosurg. 1985 Mar;62(3):324–333. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.3.0324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonas H., Wolfson S. K., Jr, Gur D., Latchaw R. E., Good W. F., Leanza R., Jackson D. L., Jannetta P. J., Reinmuth O. M. Clinical experience with the use of xenon-enhanced CT blood flow mapping in cerebral vascular disease. Stroke. 1984 May-Jun;15(3):443–450. doi: 10.1161/01.str.15.3.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Furuse M., Izawa A., Iizima N., Hirano T., Kuchiwaki H., Inao S., Sugita K. Dynamics of cerebral metabolism in patients with chronic subdural hematoma evaluated with phosphorous 31 MR spectroscopy before and after surgery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1994 Oct;15(9):1681–1686. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Marmarou A. Effects of tromethamine and hyperventilation on brain injury in the cat. J Neurosurg. 1991 Jan;74(1):87–96. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.74.1.0087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]