Abstract
The chloroplastic glutamine synthetase of spinach leaves has been purified to homogeneity using affinity chromatography. This involves a tandem `reactive blue A-agarose' and `reactive red-A-agarose' as the final step in the procedure. This procedure results in a yield of 18 milligrams of pure glutamine synthetase per kilogram of starting material. The purity of our enzyme has been demonstrated on both one- and two-dimensional polyacrylamide gels.
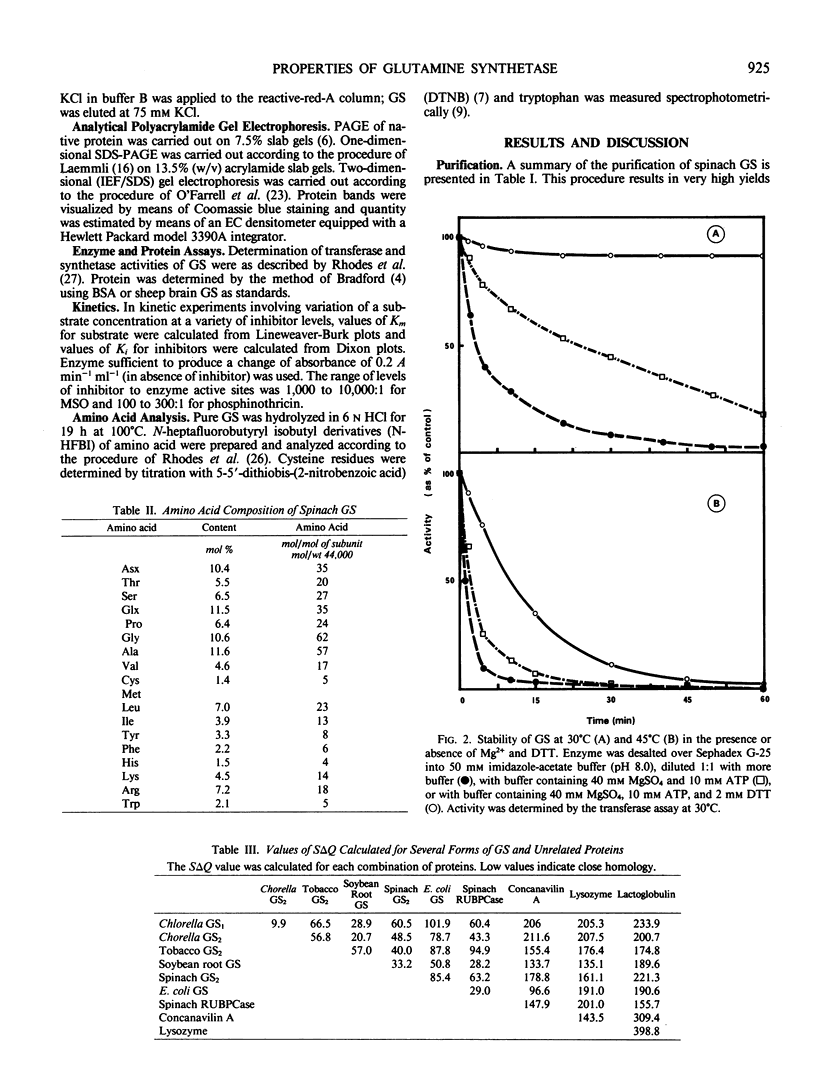
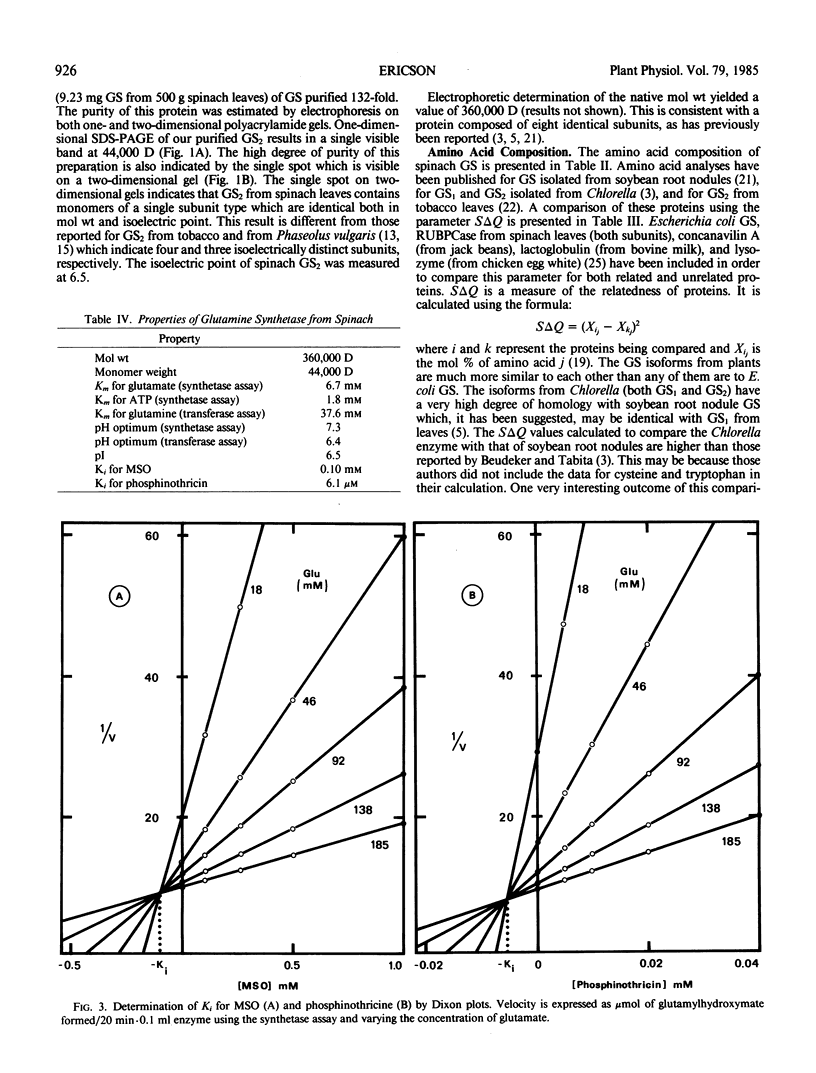
Purified glutamine synthetase has a molecular weight of 360,000 daltons and consists of eight 44,000 dalton subunits. The Km is 6.7 millimolar for glutamate, 1.8 millimolar for ATP (synthetase assay), and 37.6 millimolar for glutamine (transferase assay). The isoelectric point is 6.5 and the pH optima are 7.3 in the synthetase assay and 6.4 in the transferase assay. The irreversible, competitive inhibitors methionine sulfoxamine and phosphinothricin have Ki values of 0.1 millimolar and 6.1 micromolar, respectively. Amino acid analysis has been carried out and the results compared with published analyses for other isoforms of glutamine synthetase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akent'eva N. P., Evstigneeva Z. G., Pushkin A. V., Solov'eva N. A., Kretovich V. L. Mekhanizm ingibirovaniia glutaminsintetazy khloroplastov gorokha metioninsul'foksiminom. Biokhimiia. 1983 Jul;48(7):1209–1213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E., Gugel K. H., Hägele K., Hagenmaier H., Jessipow S., König W. A., Zähner H. Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen. 98. Phosphinothricin und Phosphinothricyl-Alanyl-Alanin. Helv Chim Acta. 1972 Jan 31;55(1):224–239. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19720550126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beudeker R. F., Tabita F. R. Characterization of glutamine synthetase isoforms from chlorella. Plant Physiol. 1985 Apr;77(4):791–794. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.4.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin T. W., Morton R. A. The spectrophotometric determination of tyrosine and tryptophan in proteins. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):628–632. doi: 10.1042/bj0400628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirel B., Gadal P. Glutamine Synthetase in Rice: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE ENZYMES FROM ROOTS AND LEAVES. Plant Physiol. 1980 Oct;66(4):619–623. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirel B., Perrot-Rechenmann C., Suzuki A., Vidal J., Gadal P. Glutamine Synthetase in Spinach Leaves : IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES AND IMMUNOCYTOCHEMICAL LOCALIZATION. Plant Physiol. 1982 Apr;69(4):983–987. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.4.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirel B., Weatherley C., Cretin C., Bergounioux C., Gadal P. Multiple Subunit Composition of Chloroplastic Glutamine Synthetase of Nicotiana tabacum L. Plant Physiol. 1984 Feb;74(2):448–450. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.2.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langston-Unkefer P. L., Macy P. A., Durbin R. D. Inactivation of Glutamine Synthetase by Tabtoxinine-beta-lactam : Effects of Substrates and pH. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):71–74. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lara M., Porta H., Padilla J., Folch J., Sánchez F. Heterogeneity of Glutamine Synthetase Polypeptides in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):1019–1023. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann A. F., Fentem P. A., Stewart G. R. Identification of two forms of glutamine synthetase in barley (Hordeum vulgare). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):515–521. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally S. F., Hirel B., Gadal P., Mann A. F., Stewart G. R. Glutamine Synthetases of Higher Plants : Evidence for a Specific Isoform Content Related to Their Possible Physiological Role and Their Compartmentation within the Leaf. Plant Physiol. 1983 May;72(1):22–25. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McParland R. H., Guevara J. G., Becker R. R., Evans H. J. The purification and properties of the glutamine synthetase from the cytosol of Soya-bean root nodules. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 1;153(3):597–606. doi: 10.1042/bj1530597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neal D., Joy K. W. Glutamine synthetase of pea leaves. I. Purification, stabilization, and pH optima. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90435-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Myers A. C., Jamieson G. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry of N- Heptafluorobutyryl Isobutyl Esters of Amino Acids in the Analysis of the Kinetics of [N]H(4) Assimilation in Lemna minor L. Plant Physiol. 1981 Nov;68(5):1197–1205. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.5.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedler F. C., Horn B. R. Catalytic mechanisms of glutamine synthetase enzymes. Studies with analogs of possible intermediates and transition states. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7530–7538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



