Abstract
Genetic mutations in the isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) gene that result in a pathological enzymatic activity to produce oncometabolite have been detected in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients. While specific inhibitors that target mutant IDH enzymes and normalize intracellular oncometabolite level have been developed, refractoriness and resistance has been reported. Since acquisition of pathological enzymatic activity is accompanied by the abrogation of the crucial WT IDH enzymatic activity in IDH mutant cells, aberrant metabolism in IDH mutant cells can potentially persist even after the normalization of intracellular oncometabolite level. Comparisons of isogenic AML cell lines with and without IDH2 gene mutations revealed two mutually exclusive signalings for growth advantage of IDH2 mutant cells, STAT phosphorylation associated with intracellular oncometabolite level and phospholipid metabolic adaptation. The latter came to light after the oncometabolite normalization and increased the resistance of IDH2 mutant cells to arachidonic acid‐mediated apoptosis. The release of this metabolic adaptation by FDA‐approved anti‐inflammatory drugs targeting the metabolism of arachidonic acid could sensitize IDH2 mutant cells to apoptosis, resulting in their eradication in vitro and in vivo. Our findings will contribute to the development of alternative therapeutic options for IDH2 mutant AML patients who do not tolerate currently available therapies.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia, apoptosis, arachidonic acid, drug repositioning, phospholipid
Phospholipid metabolic adaptation in IDH2 mutant acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells underlies their resistance to apoptosis. Food and Drug Administration‐approved anti‐inflammatory drugs targeting the metabolism of arachidonic acid can sensitize IDH2 mutant AML cells to apoptosis.
Abbreviations
- 2‐HG
2‐hydroxyglutarate
- AML
acute myeloid leukemia
- BM
bone marrow
- EPO
erythropoietin
- GM‐CSF
granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor
- GO
Gene Ontology
- IDH
isocitrate dehydrogenase
- LOX
lipoxygenase
- mut
mutant
- PLC
phospholipase C
- STAT
signal transducer and activator of transcription
- TPO
thrombopoietin
- α‐KG
α‐ketoglutarate
1. INTRODUCTION
The IDH gene is one of the genes responsible for the pathogenesis of AML, 1 and the frequencies of IDH1 and IDH2 gene mutations in adult AML patients were previously reported to be approximately 8% and 12%, respectively. 2 IDH is an enzyme that catalyzes the redox reaction converting isocitrate to α‐KG, while reducing NADP to NADPH. IDH 1 and IDH2 are highly homologous enzymes with a different intracellular localization. IDH 1 localizes to the cytoplasm and peroxisomes, while IDH2 functions within mitochondria to regulate the tricarboxylic acid cycle. 3 Mutations occurring at conserved arginine residues in enzymatic active sites result in the acquisition of pathological enzymatic activity, which converts α‐KG to 2‐HG. 4 , 5 2‐HG is a cancer‐specific metabolite, a so‐called “oncometabolite”, which competitively inhibits α‐KG‐dependent demethylation enzymes, such as TET2, and results in DNA and histone hypermethylation. 6 These epigenetic changes impair normal cellular differentiation and induce malignant transformation.
Small molecule inhibitors targeting the mut IDH enzymes, which specifically bind to allosteric sites in the mutant forms of IDH enzymes, have been reported. 7 , 8 , 9 These inhibitors strongly suppress the production of 2‐HG and induce the myeloid differentiation of AML blasts. Among them, AG‐221 (enasidenib) is the first‐in‐class, selective, and orally available mut IDH2‐specific inhibitor, 9 that successfully normalized 2‐HG levels and induced myeloid differentiation both in vitro and in vivo in preclinical studies, and has been currently evaluated in a clinical trial. 10 , 11 In the clinical trial, the overall response rate for AG‐221 monotherapy in relapsed or refractory AML patients was approximately 40%, while more than half of the patients were nonresponders. 11 Moreover, relapse cases under the mut IDH‐specific inhibitors treatment have been reported to be caused by clonal heterogeneity, 12 second mutation in IDH genes, 13 , 14 mutant isoform switching, 15 or co‐occurring genetic mutations in hematopoietic transcription factors or the RAS‐RTK pathway. 16 These findings indicate that development of novel therapy combined with the mut IDH‐specific inhibitors is required to improve prognosis of IDH mut AML patients.
Given the crucial role of IDH in cell metabolism, metabolic changes derived from IDH mutation have been well studied, especially in IDH1 mut cancers. 17 For example, IDH1 mut glioma cells are less glycolytic and rely more on oxidative phosphorylation. 18 Production of 2‐HG competes with antioxidant production, which requires NADPH in IDH1 mut colon cancer. 19 Alterations of amino acid 20 and lipid 21 metabolism are reported in IDH1 mut glioma. As IDH gene mutations result in pathological enzymatic activity in exchange for normal IDH enzymatic activity, aberrant metabolic features in IDH mut cells irrespective of the mut IDH‐specific inhibitors treatment can be assumed, but has drawn limited attention to date. Indeed, metabolic changes under the mut IDH1‐specific inhibitor treatment in IDH1 mut glioma, 22 colon cancer, 23 and recently in AML 24 have been reported, whereas no studies have been carried out in IDH2 mut cancers.
In the present study, we focused on the metabolic features in IDH2 mut AML cells. A metabolome analysis and drug screening revealed phospholipid metabolic adaptation followed by the resistance of IDH2 mut AML cells to apoptosis, which was not canceled by AG‐221 treatment. Anti‐inflammatory drugs targeting the arachidonic acid metabolism in combination with AG‐221 successfully induced apoptosis in IDH2 mut AML cells. These findings will contribute to the development of alternative therapeutic options for AML patients with IDH2 gene mutations.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Patient samples
Samples derived from nine newly diagnosed AML patients with/without IDH gene mutations were analyzed by mass cytometry. Whole BM mononuclear cells or magnetically CD3/CD19‐depleted BM cells were used for Ab staining. Detailed information on patient samples is shown in Table S1.
2.2. Cell culture
TF‐1 cells (CRL‐2003; ATCC) and TF‐1 IDH2 mut cells (CRL‐2003IG; ATCC), in which the homozygous c.419G > A knock‐in mutation encoding the IDH2R140Q protein was induced by CRISPR/Cas9 technology, were purchased from the ATCC. These cells and THP‐1 cells were maintained in RPMI‐1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. The following reagents were added to the culture: 2 ng/mL human GM‐CSF (PeproTech), 1 μM AG‐221 (enasidenib; Selleck Chemicals), 10 μM m‐3M3FBS (Merck), 100 nM U‐73122 (Selleck Chemicals), 2 IU/mL erythropoietin (Kissei Pharmaceutical), 20 μM celecoxib (Selleck Chemicals), and 50 μM zileuton (Selleck Chemicals). The same concentration of DMSO was added as a vehicle control. Regarding live cell counting, dead cells were excluded by Trypan blue dye staining.
2.3. Western blot analysis
One million cells were directly lysed in 200 μL Laemmli Sample Buffer (Bio‐Rad Laboratories) and denatured at 95°C for 10 min. Cytosolic fraction was separated by Cell Fractionation Kit ‐ Standard (#ab109719; Abcam) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Proteins were separated on 4%–20% gradient SDS‐PAGE gels and transferred to PVDF membranes. Transferred membranes were probed with the primary Ab at 4°C overnight, followed by an incubation with the secondary Ab at room temperature for 1 h. The protein signal was detected with Pierce ECL western blotting substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The following Abs were used: rabbit mAb to Stat5 (#25656; Cell Signaling Technology), rabbit mAb to phospho‐Stat5 (#4322; Cell Signaling Technology), rabbit mAb to PLCγ1 (#5690; Cell Signaling Technology), rabbit mAb to PLCB1 (#ab182359; Abcam), rabbit mAb to β‐actin (#4970; Cell Signaling Technology), Cytochrome c Apoptosis WB Antibody Cocktail (#ab110415; Abcam), secondary anti‐mouse IgG, HRP‐linked Ab (#7076; Cell Signaling Technology), and secondary anti‐rabbit IgG, HRP‐linked Ab (#7074; Cell Signaling Technology).
2.4. Cytokine measurement in the cell culture supernatant
Concentration of GM‐CSF in the cell culture supernatant was measured by Legendplex Human Hematopoietic Stem Cell Panel (#740610; BioLegend) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
2.5. Drug screening
IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells were maintained with 2 ng/mL human TPO and used for screening. In total, 2500 cells were seeded on each well of a 384‐well plate and compounds from a metabolic inhibitor library (MedChemExpress) were added at 1 μM using Bravo liquid handler (Agilent Technologies). After a 7‐day culture, 10 μL CellTiter‐Glo reagent (Promega) was added and luminescence signals were measured. The same concentration of DMSO was added as a vehicle control and cell growth relative to the DMSO control was analyzed. The compound list is shown in Table S2.
2.6. Lentiviral transduction
Total RNA was extracted and purified from IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells with the RNeasy Micro Kit (Qiagen). RNA was reverse transcribed and mutant form of IDH2 and PLCB1 genes were amplified using the PrimeScript High Fidelity RT‐PCR Kit (Takara Bio Inc.). The PCR product was gel‐purified and cloned into pENTR/D‐TOPO vector using the pENTR/D‐TOPO Cloning Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The target gene sequences were further cloned into pMAL (a gift from John Dick and Peter van Galen [Addgene plasmid #161783; http://n2t.net/addgene:161783; RRID:Addgene_161,783]) 25 using Gateway LR Clonase II Enzyme Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The generated lentiviral vector plasmids were cotransfected with lentiviral packaging vectors into HEK293 T cells using Lipofectamine 3000 Transfection Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and viral supernatants were harvested and concentrated by Lenti‐X Concentrator (Takara Bio Inc.). The lentiviral supernatant was added to IDH2 mut TF‐1 or THP‐1 cell cultures in the presence of 8 μg/mL protamine sulfate and centrifuged at 800 g for 1 h at room temperature, followed by incubation at 37°C for 16 h. The transduced cells were expanded and GFP‐positive cells were used for subsequent experiments. Empty lentiviral vector‐transduced cells were used as control.
2.7. Mitochondrial membrane potential
Cultured cells were collected and stained with MitoProbe JC‐1 Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Stained cells were analyzed on a FACSCanto II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences). All data were analyzed using FlowJo (BD Biosciences).
2.8. Apoptosis assay
Cultured cells were collected and stained with Pacific Blue‐conjugated annexin V (BioLegend) in binding buffer for annexin V (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at room temperature for 15 min. Stained cells were washed once with binding buffer and resuspended in binding buffer containing 7‐AAD (Thermo Fisher Scientific) before being analyzed on a FACSCanto II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences). All data were analyzed using FlowJo (BD Biosciences).
2.9. Quantitative RT‐PCR
Total RNA was extracted and purified with the RNeasy Micro Kit (Qiagen). Total RNA was then reverse transcribed to cDNA using the PrimeScript RT Master Mix (Takara Bio Inc.) following the manufacturer's instructions. A quantitative real‐time PCR was carried out using SYBR green master mix (Thunderbird qPCR Mix; Toyobo Life Sciences). Quantitative PCR was run on the LightCycler‐96 real‐time PCR instrument (Roche Life Science). The ACTB gene was used as an internal control. Primer sequences are shown in Table S3.
2.10. Xenotransplantation
Six‐ to 12‐week‐old MSTRG mice, in which the human M‐CSF, SIRPα, and TPO genes were knocked into an immunodeficient mouse strain on the mouse Rag2 −/− Il2rg −/− background, 26 were used as hosts for xenotransplantation studies. All mice were conditioned with 2.5 Gy of radiation before transplantation. IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells were precultured in cytokine‐free medium for 10 days. After the preculture, 1 × 106 cells were collected, resuspended in PBS, and transplanted into the left femur of MSTRG mice by an intrafemoral injection. All mice were maintained at the Center for Animal Resources and Development at Kumamoto University.
2.11. In vivo drug treatment
AG‐221, celecoxib, and zileuton were purchased from Selleck Chemicals. All drugs were resuspended in 0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Nacalai Tesque). Drugs were administered by oral gavage at the following dose for 3 weeks on a 5‐days‐on, 2‐days‐off schedule: AG‐221, 45 mg/kg b.i.d.; celecoxib, 100 mg/kg b.i.d.; and zileuton, 50 mg/kg b.i.d. The drug treatment was started 7 weeks after the transplantation of IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells into MSTRG mice.
2.12. Hematological parameter analysis
Peripheral blood was obtained from the tail vein once a week during the drug treatment. Hematological parameters were assessed using the hematology analyzer, Celltac α MEK‐6358 (Nihon Kohden).
2.13. Mouse BM FACS analysis
At the end of the drug treatment, mice were killed and BM cells were isolated from the left femur. Isolated BM cells were stained with the anti‐mouse CD45.2 PE Ab and anti‐human CD45 APC‐Cy7 Ab (both from BioLegend) on ice for 30 min. Cells were then washed in FACS buffer followed by annexin V staining. Stained cells were analyzed on a FACSCanto II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences). All data were analyzed using FlowJo (BD Biosciences).
2.14. Supplementary methods
The methods of mass cytometry, metabolite extraction, metabolome analysis, gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis, and RNA sequencing are shown in Appendix S1.
2.15. Quantification and statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 6 software and statistical analyses were undertaken with an unpaired Student's t‐test (two‐tailed t‐test) to compare two groups unless specified otherwise. ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Data are shown as the mean ± SD unless specified otherwise.
3. RESULTS
3.1. Intracellular 2‐HG‐dependent STAT phosphorylation promoted cell proliferation in IDH mut AML cells
As mutations in the IDH gene markedly alter its enzymatic activity, resulting in pathological enzymatic activity that produces 2‐HG in exchange for normal enzymatic activity in redox reactions, cellular homeostasis is expected to be compromised in IDH mut AML cells. To identify the molecular mechanisms conferring the growth advantage to IDH mut AML cells, we analyzed intracellular signaling pathways in the lineage‐negative cell fraction of IDH WT, IDH1 mut, and IDH2 mut AML patient BM cells by mass cytometry (Figure S1A, Table S4). Among the signaling pathways tested, such as energy metabolism, iron metabolism, and mitochondria‐related pathways, we detected higher phosphorylation levels of STAT in IDH mut AML patient cells than in IDH WT AML patient cells (Figure 1A).
FIGURE 1.
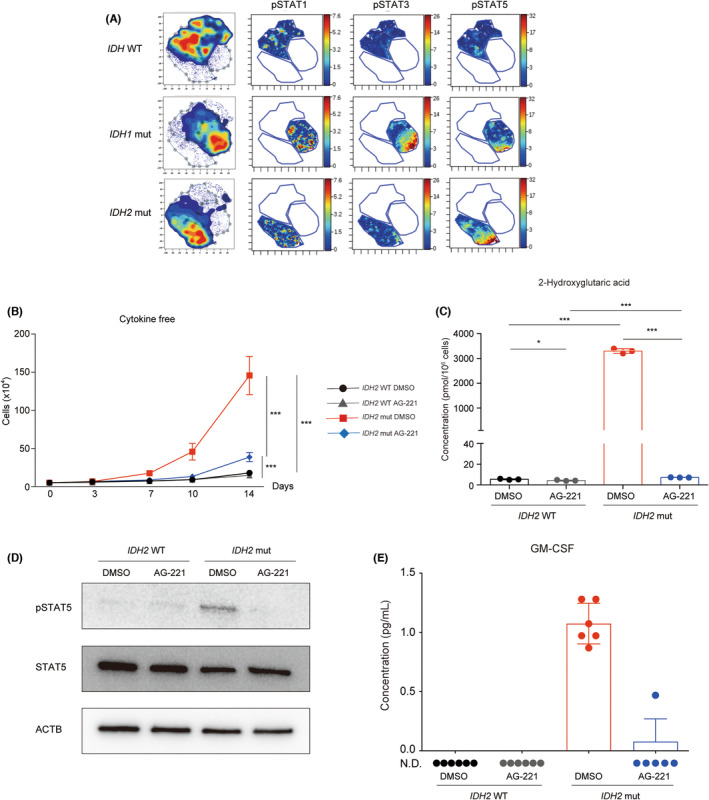
Intracellular 2‐hydroxyglutarate‐dependent signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) phosphorylation promoted cell proliferation in IDH mutant (mut) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. (A) Mass cytometric analysis of the IDH WT and IDH1/2 mut bone marrow cells of AML patients. The viSNE analysis identified genotype‐specific dominant cell populations. The phosphorylation of STAT1/3/5 proteins in each population is shown. (B) The live cell number of IDH2 WT or mut TF‐1 cells cultured under cytokine‐free conditions treated without (DMSO) or with the mut IDH2‐specific inhibitor (AG‐221) in vitro (n = 6 from two independent experiments). (C) Concentrations of intracellular 2‐hydroxyglutaric acid in IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells treated without (DMSO) or with AG‐221 for 10 days. (n = 3). (D) Western blot images of total and phosphorylated STAT5 in cell lysates of IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells treated without (DMSO) or with AG‐221 for 10 days. β‐Actin (ACTB) was used as a loading control. (E) Concentration of granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF) in the cell culture supernatant of IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells under cytokine‐free conditions treated without (DMSO) or with AG‐221 for 10 days. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (two‐tailed t‐test). N.D., not detected.
IDH gene mutations frequently coexist with other gene mutations in AML cells, 1 which makes it difficult to elucidate the precise role of IDH gene mutations in leukemogenesis. To address this issue, we utilized the cytokine‐dependent AML cell line TF‐1 27 and its isogenic cell line with the homozygous c.419G > A mutation in the IDH2 gene encoding the IDH2R140Q protein. The proliferation of these IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut cell lines in conditioned media with GM‐CSF was similar (Figure S1B). However, IDH2 mut cells showed cytokine‐independent growth under cytokine‐free culture conditions, in which the proliferation of IDH2 WT cells was negligible (Figure 1B). A treatment with 1 μM of the mut IDH2‐specific inhibitor (AG‐221), which blocks the production of 2‐HG in IDH2 mut cells, 9 significantly suppressed cell growth in IDH2 mut cells (Figure 1B,C). Similar to patient cells, phosphorylation levels of STAT5 were elevated in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells. However, this STAT5 phosphorylation was completely canceled by the AG‐221 treatment, suggesting that STAT phosphorylation in IDH mut AML cells was dependent on intracellular 2‐HG level (Figure 1D). This 2‐HG level‐dependent STAT phosphorylation was further supported by RNA sequencing data, which showed 2‐HG‐dependent upregulation of STAT5 target gene expressions in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure S1C). As STAT proteins are phosphorylated upon cytokine stimulation, we suspected that some cytokines produced by IDH2 mut cells would induce their STAT5 phosphorylation in an autocrine/paracrine manner. Among the cytokines (IL‐6, FLT3L, GM‐CSF, IL‐3, IL‐34, IL‐11, SCF, LIF, CXCL12, IL‐15, M‐CSF, and IL‐7) measured in the cell culture supernatant, GM‐CSF was detectable and found to be secreted by IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells in a 2‐HG level‐dependent manner (Figure 1E). These data indicated that 2‐HG level‐dependent autocrine GM‐CSF induced STAT phosphorylation in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells.
The growth of AG‐221‐treated IDH2 mut cells remained significantly faster than that of AG‐221‐treated IDH2 WT cells (Figure 1B). These results indicated that, in addition to STAT phosphorylation, IDH2 mut cells possessed another mechanism that could promote cell proliferation even under the AG‐221 treatment.
3.2. Downregulation of phospholipase C expression contributed to the growth advantage in IDH2 mut AML cells under AG‐221 treatment
To elucidate the molecular pathway responsible for cell proliferation under AG‐221 treatment in IDH2 mut AML cells, their metabolic status was profiled with a metabolome analysis. A principal component analysis plot clearly separated AG‐221‐treated IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells from vehicle (DMSO)‐treated IDH2 mut and AG‐221‐treated WT TF‐1 cells (Figure 2A). A metabolite set enrichment analysis of IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells treated with AG‐221 identified the glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway (−Log10 p value = 3.22) as one of the pathways that showed most significant difference between these two groups (Figure 2B), suggesting that phospholipid metabolism pathway contributed to the cell proliferation of IDH2 mut AML cells under AG‐221 treatment.
FIGURE 2.
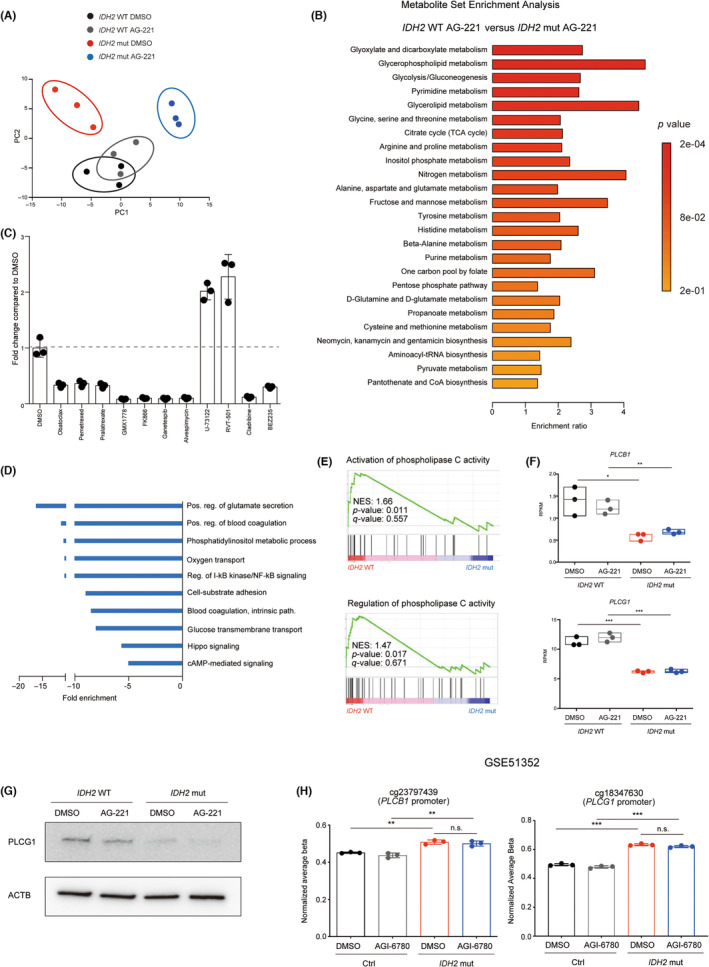
Downregulation of phospholipase C (PLC) expression contributed to the growth advantage in AG‐221‐treated IDH2 mutant (mut) acute myeloid leukemia cells. (A) Principal component (PC) analysis plot of a metabolome analysis of IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells treated without (DMSO) or with AG‐221 for 10 days. (B) Metabolite Set Enrichment Analysis plots of the metabolome dataset derived from IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells treated with AG‐221 were compared. The top 25 significantly enriched metabolite sets are shown. (C) Drug screening using a metabolic inhibitor library: IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells were maintained with 2 ng/mL thrombopoietin and treated with each drug or the DMSO control, followed by an evaluation of cell growth. Candidate drugs that suppressed or promoted cell growth (fold change >2 or <0.5 from the DMSO control) are shown (n = 3). (D) Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of biological processes significantly enriched in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells compared to IDH2 WT TF‐1 cells (p < 0.05 Fisher's test, >5‐fold enrichment; blue, downregulated). (E) Gene Set Enrichment Analysis comparing IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells in the indicated GO terms. (F) mRNA expression level of PLCB1 and PLCG1 in IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells treated without (DMSO) or with AG‐221 for 10 days. Expression level is represented in reads per kilobase of exon per million mapped reads (RPKM). (G) Western blot images of PLCG1 protein in IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells treated without (DMSO) or with AG‐221 for 10 days. β‐Actin (ACTB) was used as a loading control. (H) Methylation analysis of control (Ctrl) and IDH2 mut‐overexpressed TF‐1 cells treated without (DMSO) or with mut IDH2‐specific inhibitor (AGI‐6780) for 7 days. Published dataset (GSE51352) was reanalyzed. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (two‐tailed t‐test). n.s., not significant.
In parallel with the metabolome analysis, screening of metabolic inhibitors identified 11 drug candidates that suppressed or promoted IDH2 mut TF‐1 cell proliferation over the DMSO control (Figure 2C). Among these drugs, U‐73122, which activated IDH2 mut TF‐1 cell proliferation, was a specific inhibitor of a phospholipid degradative enzyme, PLC. Its cell proliferative activity was confirmed in IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure S2A,B). Conversely, a treatment with a PLC activator (m‐3M3FBS) canceled the growth advantage in AG‐221 treated IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure S2C). This negative correlation between cell growth and PLC activity was confirmed by PLCB1 gene overexpression that suppressed proliferation of IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure S2D,E).
These results were further supported by RNA sequencing comparing IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure S2F,G). A GO analysis showed the negative enrichment of a phosphatidylinositol‐ (which is a substrate of PLC) related GO term (phosphatidylinositol metabolic process, fold enrichment: −10.43, p value: 0.0320) in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure 2D), while a gene set enrichment analysis revealed that PLC activity‐related gene sets were negatively enriched in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure 2E). Expression of many PLC genes was suppressed in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure S2H). Especially, PLCB1 and PLCG1 gene expressions were significantly suppressed in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells irrespective of AG‐221 treatment (Figure 2F) and suppressed expression of PLCG1 was confirmed in the protein level (Figure 2G). A previous report showed that only a part of DNA methylations induced by 2‐HG were reversed by short‐term mut IDH2‐specific inhibitor treatment in IDH2 mutant‐overexpressed TF‐1 cells. 28 We reanalyzed the previously published dataset (GSE51352) 28 and found that the methylation of the promoter regions of PLCB1 and PLCG1 genes were not reversible by short‐term mut IDH2‐specific inhibitor treatment (Figure 2H). This indicated that PLCB1 and PLCG1 gene expressions were suppressed through the hypermethylation of their promoter regions, which was irreversible by short‐term mut IDH2‐specific inhibitor treatment.
Collectively, these results suggested that the downregulation of PLC expression gives IDH2 mut AML cells the growth advantage under AG‐221 treatment.
3.3. Apoptosis resistance of IDH2 mut AML cells through the downregulation of intracellular arachidonic acid
Phospholipase is a phospholipid degradative enzyme. Phospholipase C contributes to the release of arachidonic acid from the phospholipid bilayer indirectly through the release of diacylglycerol (Figure 3A). Based on this, we hypothesized a positive correlation between PLC expression and intracellular arachidonic acid level. Consistent with the suppression of PLC expression in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figures 2F,G and S2H), intracellular arachidonic acid level was significantly reduced in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells, irrespective of the AG‐221 treatment (Figure 3B). Intracellular arachidonic acid level was also significantly reduced in PLC inhibitor‐treated IDH2 WT TF‐1 cells (Figure S3A). In contrast, the PLC activator treatment restored its levels in AG‐221‐treated IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure S3B).
FIGURE 3.
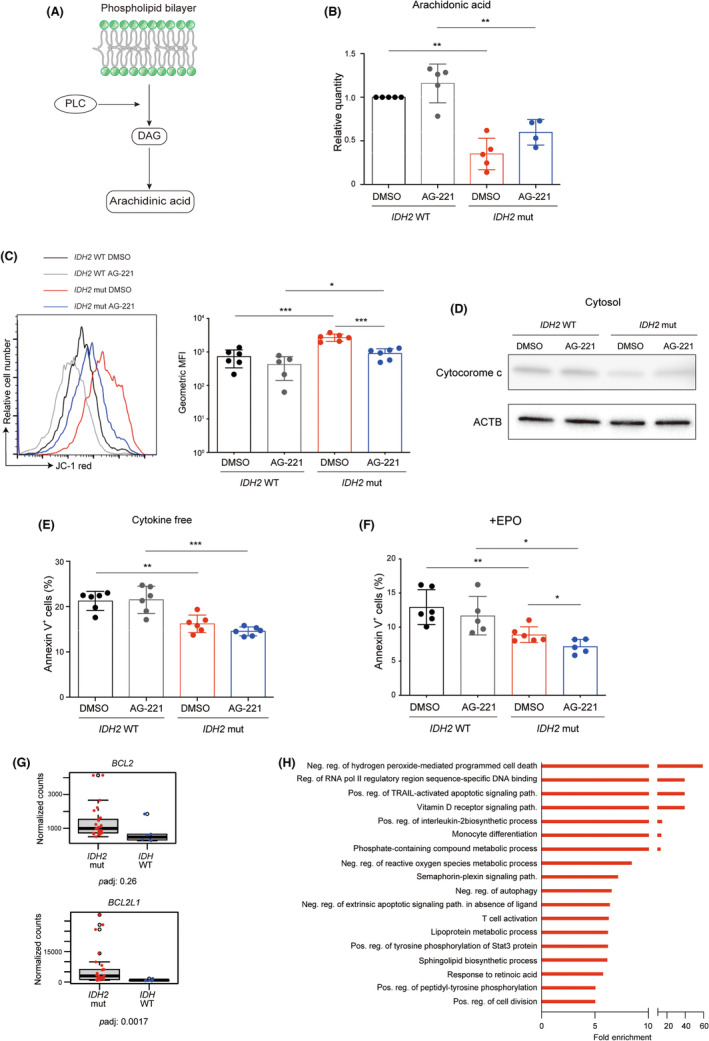
Apoptosis resistance in IDH2 mutant (mut) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells through the downregulation of intracellular arachidonic acid. (A) Scheme of phospholipase C (PLC)‐mediated arachidonic acid release from the phospholipid bilayer. DAG, diacylglycerol. (B) Quantities of intracellular arachidonic acid measured with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry in IDH2 WT and mut TF‐1 cells treated without (DMSO) or with AG‐221 for 10 days. Values relative to IDH2 WT TF‐1 cells treated with DMSO are depicted. Statistical analyses compared with DMSO‐treated IDH2 WT TF‐1 cells were carried out with the paired two‐tailed t‐test (n = 4–5 from four to five independent experiments). (C) Representative FACS histogram of JC‐1 red and geometric mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) of JC‐1 red in IDH2 WT and mut TF‐1 cells treated without (DMSO) or with AG‐221 for 10 days (n = 5–6 from two independent experiments). (D) Western blot images of cytochrome c in cytosolic fraction of IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells treated without (DMSO) or with AG‐221 for 10 days. β‐Actin (ACTB) was used as a loading control. (E) The percentage of annexin V+ cells in IDH2 WT and mut TF‐1 cells treated without (DMSO) or with AG‐221 for 3 days (n = 6 from two independent experiments). (F) The percentage of annexin V+ cells in IDH2 WT and mut TF‐1 cells cultured with erythropoietin (EPO) treated without (DMSO) or with AG‐221 for 7 days (n = 5–6 from two independent experiments). (G) mRNA expression levels of the indicated genes in the bone marrow mononuclear cells of AML patients with IDH2 gene mutations and IDH WT AML patients. padj, adjusted p value. (H) Gene Ontology analysis of biological processes significantly enriched in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells compared to IDH2 WT TF‐1 cells (p < 0.05 Fisher's test, >5‐fold enrichment; red, upregulated). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (two‐tailed t‐test).
The positive correlation between intracellular arachidonic acid level and apoptosis through the mitochondrial permeability transition, which collapses mitochondrial membrane potential and induces cytochrome c release from mitochondria, has been reported. 29 , 30 In agreement with these observations, mitochondrial membrane potential was negatively correlated with intracellular arachidonic acid level (Figure 3C), cytochrome c release was suppressed in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure 3D), and the number of annexin V+ apoptotic cells was significantly reduced in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells irrespective of the AG‐221 treatment (Figures 3E and S3C). The PLC inhibitor suppressed apoptosis in IDH WT TF‐1 cells (Figure S3D), while the PLC activator induced it in AG‐221‐treated IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure S3E). As previously reported, 7 IDH2 gene mutation blocked EPO‐induced erythroid differentiation of IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells, which was rescued by AG‐221 treatment (Figure S3F). The apoptosis resistance was also observed under the erythroid differentiation condition (Figure 3F). Previous reports showed that arachidonic acid‐induced apoptosis was mediated by production of reactive oxygen species, which suppressed Bcl‐2 gene expression. 30 , 31 These findings suggest the hypothesis that reduced intracellular arachidonic acid induces BCL2 gene expression in IDH2 mut AML cells. In support of this hypothesis, RNA sequencing with AML patient samples showed significantly higher expression of the antiapoptotic gene BCL2L1 in patients with IDH2 gene mutations than in IDH WT patients (Figure 3G). RNA sequencing data from TF‐1 cell lines also confirmed the significantly upregulated expression of the BCL2 and BCL2L1 genes in IDH2 mut cells irrespective of AG‐221 treatment (Figure S3G). Another BCL1 family gene, MCL1, also showed a similar trend (Figure S3G). In the GO analysis, anti‐cell death‐related GO terms (negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide‐mediated programmed cell death, fold enrichment 59.13, p = 0.0334; negative regulation of an extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in the absence of a ligand, fold enrichment 6.39, p = 0.0241) were positively enriched in IDH2 mut cells (Figure 3H).
Collectively, these results indicated that resistance to apoptosis was mediated by downregulation of the intracellular arachidonic acid level in IDH2 mut AML cells.
3.4. Anti‐inflammatory drug treatment combined with inhibition of mut IDH2 induced apoptosis in IDH2 mut AML cells by normalizing intracellular arachidonic acid levels
Arachidonic acid is metabolized to prostaglandin and leukotriene by COX and 5‐LOX, respectively. 32 To upregulate the intracellular arachidonic acid level in vitro, we used the COX2‐ and 5‐LOX‐specific inhibitors, celecoxib and zileuton, respectively, both of which are FDA‐approved anti‐inflammatory drugs (Figure 4A). In combination with AG‐221, celecoxib mildly suppressed cell proliferation, whereas zileuton did not exert any inhibitory effects in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure S4A). Neither of these combinations induced apoptosis (Figure S4B) and upregulated intracellular arachidonic acid level (Figure S4C) in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells. However, when all three drugs were combined, the triple drug treatment completely suppressed IDH2 mut TF‐1 cell proliferation and simultaneously induced apoptosis (Figure 4B–D). This induction of apoptosis correlated with intracellular arachidonic acid levels in triple drug‐treated IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure 4E). This apoptosis induction by the triple drug treatment was also observed in erythroid differentiation culture (Figure 4F,G) and in another AML cell line, IDH2 mutant‐overexpressed THP‐1 cells (Figure S4D,E). Celecoxib and zileuton in combination without AG‐221 could induce apoptosis in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells (Figure S4F), which indicates that 2‐HG‐induced STAT phosphorylation and PLC‐mediated resistance to apoptosis are mutually exclusive.
FIGURE 4.
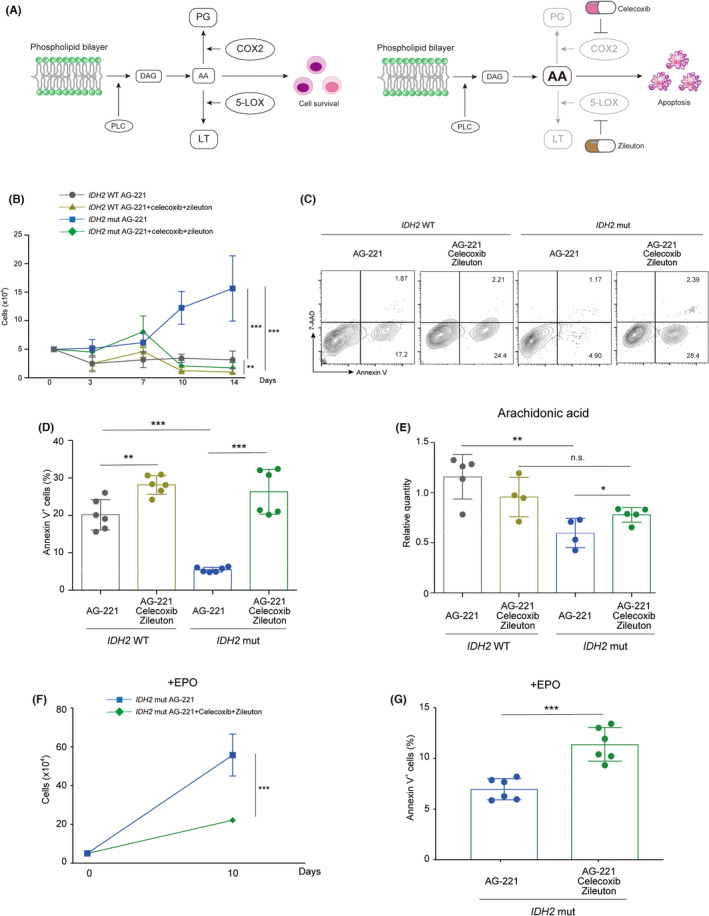
Anti‐inflammatory drug treatment combined with the inhibition of mutant (mut) IDH2 induced apoptosis in IDH2 mut acute myeloid leukemia cells by normalizing intracellular arachidonic acid levels in vitro. (A) Scheme of anti‐inflammatory drug therapy targeting the arachidonic acid metabolic pathway. The inhibition of COX2 and 5‐lipoxygenase (5‐LOX) with celecoxib and zileuton, respectively, led to the intracellular accumulation of arachidonic acid, which induced cellular apoptosis. (B) Live cell numbers of IDH2 WT or IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells cultured under cytokine‐free conditions treated with AG‐221, celecoxib, and zileuton at the indicated combinations in vitro (n = 6 from two independent experiments). (C, D) Representative FACS plots of (C) annexin V staining and (D) the percentage of annexin V+ cells in IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells treated with AG‐221, celecoxib, and zileuton at the indicated combinations for 10 days (n = 6 from two independent experiments). (E) Quantities of intracellular arachidonic acid measured with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry in IDH2 WT and IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells treated with AG‐221, celecoxib, and zileuton at the indicated combinations for 10 days. Relative values compared to IDH2 WT TF‐1 cells treated with DMSO are depicted (n = 4–5 from four or five independent experiments). (F) The live cell number and (G) the percentage of annexin V+ cells of IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells cultured with erythropoietin (EPO) treated with AG‐221, celecoxib, and zileuton at the indicated combinations in vitro for 10 days. (n = 6 from two independent experiments). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (two‐tailed t‐test). AA, arachidonic acid; DAG, diacylglycerol; LT, leukotriene; PG, prostaglandin; PLC, phospholipase C.
To test the efficacy of the triple drug treatment in vivo, we intrafemorally transplanted IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells into immunodeficient MSTRG mice, in which the human M‐CSF, SIRPα, and TPO genes were knocked in. 26 Seven weeks after transplantation, the three drugs were given by oral gavage for 3 weeks (Figure 5A). Consistent with in vitro data, the triple drug therapy successfully reduced the tumor burden by inducing apoptosis in vivo (Figures 5B,C and S5A). Mice treated with the three drugs showed no sign of cytopenia or therapy‐associated complications, securing the safety of this combination therapy (Figure S5B–D).
FIGURE 5.
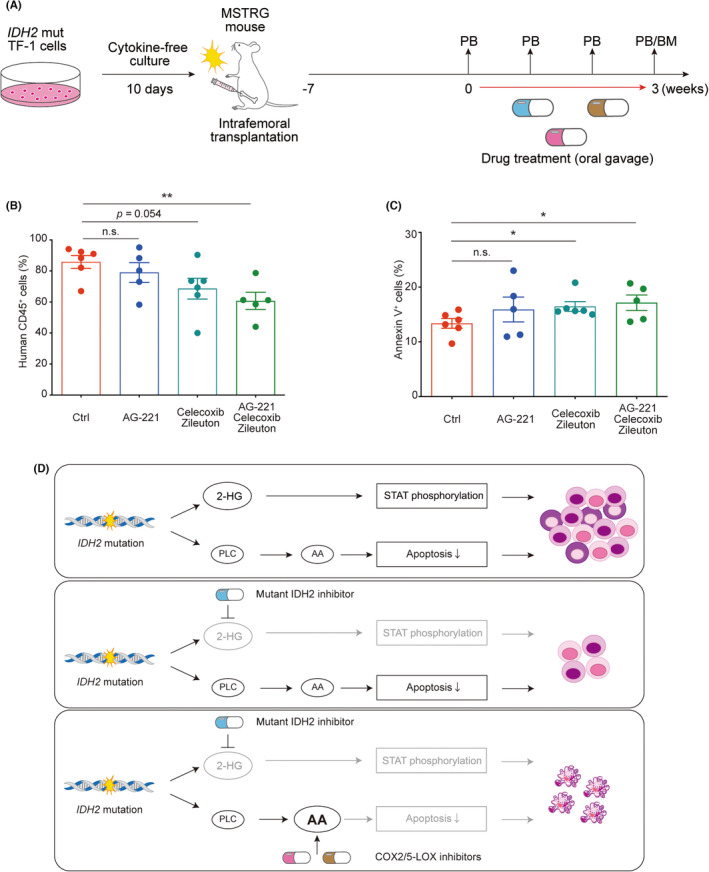
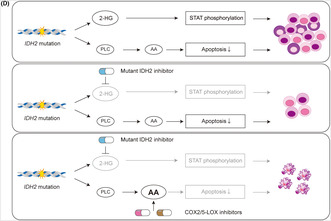
Anti‐inflammatory drug treatment combined with the inhibition of mutant (mut) IDH2 reduced tumor burden by inducing apoptosis in IDH2 mut acute myeloid leukemia cells in vivo. (A) Scheme of the in vivo drug treatment experiment on a xenograft model: IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells were precultured in cytokine‐free medium for 10 days and transplanted into the left femur of sublethally (2.5 Gy)‐irradiated MSTRG mice. Seven weeks after transplantation, transplanted mice were treated with drugs by oral gavage for 3 weeks. Peripheral blood was examined every week during the drug treatment and bone marrow (BM) was analyzed at the end of the drug treatment. (B) The chimerism of human CD45+ cells and (C) the percentage of annexin V+ cells within the human CD45+ fraction in BM cells derived from the left femur of drug‐treated mice (n = 5–6 from three independent experiments). (D) Schematic summary of the molecular basis underlying the acquisition of growth advantage by IDH2 mutant AML and its cancelation: IDH2 gene mutations induce signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) phosphorylation dependent on intracellular 2‐hydroxyglutarate level and apoptosis resistance driven by phospholipid metabolic adaptation. A treatment with a mut IDH2‐specific inhibitor blocks the STAT‐mediated growth advantage in IDH2 mut cells, while maintaining the survival advantage by resistance to apoptosis through phospholipid metabolic adaptation. An additional treatment with COX2 and 5‐lipoxygenase (5‐LOX) inhibitors targeting the metabolism of arachidonic acid cancels resistance to apoptosis and eradicates IDH2 mut AML cells. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (two‐tailed t‐test). 2‐HG , 2‐hydroxyglutarate; AA, arachidonic acid; Ctrl, control; n.s., not significant; PB, peripheral blood.
Therefore, the anti‐inflammatory drug treatment combined with the inhibition of mut IDH2 successfully eliminated IDH2 mut AML cells by apoptosis through the upregulated intracellular arachidonic acid level.
4. DISCUSSION
As IDH gene mutations result in abnormal enzymatic activity that produces 2‐HG, the majority of studies on IDH mut cancers have focused on the oncogenic mechanisms regulated by intracellular 2‐HG level. However, refractory and relapse cases associated with mut IDH‐specific inhibitors treatment indicate the importance of the oncogenic feature in the IDH mut cancer cells under the mut IDH‐specific inhibitor treatment. In the present study, using isogenic AML cell lines with or without IDH2 gene mutation, we identified STAT phosphorylation dependent on intracellular 2‐HG level and resistance to apoptosis in the IDH2 mut cells irrespective of AG‐221 treatment, the latter of which was regulated by phospholipid metabolic adaptation, which could be canceled by anti‐inflammatory drugs targeting the metabolism of arachidonic acid (Figure 5D).
2‐HG synthesized by mutant form of IDH enzyme competitively inhibits α‐KG‐dependent demethylation enzymes and induces DNA and histone hypermethylation, which in turn block cellular differentiation and induce malignant transformation. Using IDH2 R140Q mut TF‐1 cell line model, it has been shown that IDH2 mutation induced DNA and histone hypermethylation. 28 These epigenetic changes were partially reversed with short‐term (around 1 week) mut IDH2‐specific inhibitor treatment, while majority of them were still present even after 4 weeks treatment. 28 We identified two mutually exclusive oncogenic features in IDH2 mut TF‐1 cells; STAT phosphorylation‐mediated cell proliferation, which was completely suppressed by 10‐days AG‐221 treatment, and phospholipid metabolic adaptation‐mediated apoptosis resistance, which was not canceled by 10‐days AG‐221 treatment. The contrasting reactivity to AG‐221 treatment between these two features might be explained by the variation in reversibility of epigenetic changes.
Our study identified unappreciated phospholipid adaptation through downregulation of PLC expression in IDH2 mut AML cells in the present study. PLC inactivation‐mediated oncogenic mechanism is consistent with previous reports that showed the tumor suppressive role of PLC in hematopoietic malignancies. PLCβ3‐deficient mice developed myeloproliferative disease and lymphoma and PLCβ3 expression was downregulated in human chronic lymphocytic leukemia samples. 33 A clinical study in myelodysplastic syndromes patients revealed a positive correlation between mono‐allelic deletion of the PLCB1 gene and a risk of AML development. 34 The alteration of phospholipid metabolism has been reported in IDH1 mut gliomas. 21 It is interesting that the same metabolic pathway was affected in different tumors with different IDH gene mutations, which suggested the possibility that altered phospholipid metabolism is a common metabolic feature of IDH mut cancers and promising therapeutic target for them. Further study will aim to prove this possibility in the future.
Chemotherapy against leukemia is frequently associated with severe adverse effects, which sometimes interrupt treatment in patients. A specific inhibitor of the anti‐apoptotic protein BCL‐2, venetoclax in combination with azacitidine, a hypomethylating agent, was recently approved for the treatment of AML patients who were ineligible for intensive chemotherapy, such as elderly patients. 35 Although venetoclax causes fewer adverse effects than conventional chemotherapies, it could still induce myelosuppression. 35 The present study proposes FDA‐approved anti‐inflammatory drugs as novel drug candidates of therapeutic value to the treatment of IDH2 mut AML. As these drugs already have a track record of safety in clinical practice and do not exert the adverse effect of myelosuppression, even in combination with AG‐221 in the mouse model (Figure S5B–D), they have a potential as an alternative therapeutic option for patients who do not tolerate venetoclax due to unwanted severe myelosuppression. The differentiation syndrome associated with AG‐221 is a major adverse effect upon treatment in clinic. 36 In this syndrome, IDH2 mut cells cause tissue damage and inflammation through cytokine secretion even after differentiation induced by AG‐221 treatment. The triple drug treatment proposed in the present study efficiently induced apoptosis of IDH2 mut cells even under erythroid differentiation culture condition (Figures 4F,G and S3F). These data support the idea that the triple drug combination might be able to reduce the adverse effect of AG‐221 treatment. A preclinical study using patient samples is needed for clinical applications. We attempted to develop a patient‐derived xenograft model using primary AML patient cells with IDH2 gene mutations; however, cells did not engraft in immunodeficient mice, which might have been due to the weak proliferation of IDH2 mutant cells without other genetic mutations (data not shown).
The limitation of the present study is a possible clinical application of the triple drug treatment for patients as we found a subtle differences in cell survival between IDH2 WT and mut cells, which can be easily masked by coexisting other genetic mutations in primary IDH2 mut AML samples. We speculate that not only phospholipid metabolism proposed in the present study, but also other metabolic changes might play roles in IDH2 mut AML cell survival under mut IDH2‐specific inhibitor treatment. However, the phospholipid metabolic adaptation attributed to IDH2 gene mutation that we identified in the isogenic cell line should exist in the primary AML cells carrying the same mutation, and supposed to contribute to their survival to some extent. Further study focused on metabolic changes under the mut IDH2‐specific inhibitor treatment is required to compliment the present study.
In conclusion, we herein identified a previously unappreciated antiapoptotic feature that is mediated by phospholipid metabolic adaptation in IDH2 mut AML cells, irrespective of the mut IDH2‐specific inhibitor treatment. Specific targeting of this pathway through the drug repositioning of FDA‐approved anti‐inflammatory drugs successfully eradicated IDH2 mut AML cells both in vitro and in vivo. Further studies focused on 2‐HG independent metabolic changes in IDH2 mut AML cells are required to improve patient prognosis.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Tatsuya Morishima: Conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; funding acquisition; investigation; project administration; writing – original draft. Koichi Takahashi: Data curation; formal analysis; resources. Desmond Wai Loon Chin: Data curation; formal analysis; methodology. Yuxin Wang: Data curation; methodology. Kenji Tokunaga: Resources. Yuichiro Arima: Data curation; formal analysis; methodology. Masao Matsuoka: Funding acquisition; resources. Toshio Suda: Conceptualization; writing – review and editing. Hitoshi Takizawa: Conceptualization; funding acquisition; project administration; supervision; writing – review and editing.
FUNDING INFORMATION
This work was supported by KAKENHI from the Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) (19K17833 and 21K08397 to T.M., and 18K19520 to H.T.), The Yasuda Medical Foundation (to T.M.), The Shinnihon Foundation of Advanced Medical Treatment Research (to T.M.), The Japan Research Foundation for Clinical Pharmacology (to T.M.), Takeda Science Foundation (to T.M.), The SGH Foundation (to T.M.), The Japanese Society of Hematology Research Grant (to T.M.), a clinic‐basic collaboration project support grant from Kumamoto University Hospital (to T.M., K. Takahashi, K. Tokunaga, M.M., and H.T.), KAKETSUKEN (The Chemo‐Sero‐Therapeutic Research Institute) (to T.M. and H.T.), JST FOREST (JPMJFR200O to H.T.), the Center for Metabolic Regulation of Healthy Aging at Kumamoto University (to H.T.), and Core‐to‐Core Program Advanced Research Networks “Integrative approach for normal and leukemic stem cells” (to H.T.).
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare no competing financial interests. Masao Matsuoka is an Associate Editor of Cancer Science.
ETHICS STATEMENT
Approval of the research protocol by an institutional review board: This study adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Board at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Informed consent: Written informed consent was obtained from all patients who provided samples.
Registry and the registration no. of the study/trial: N/A.
Animal Studies: All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Kumamoto University.
Supporting information
Figure S1
Figure S2
Figure S3
Figure S4
Figure S5
Table S1
Table S2
Table S3
Table S4
Appendix S1
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to thank the International Core‐facility of Advanced Life Science at Kumamoto University for their logistical and technical assistance. We also thank Dr. Sayuri Nakata for her daily technical assistance.
Morishima T, Takahashi K, Chin DWL, et al. Phospholipid metabolic adaptation promotes survival of IDH2 mutant acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Sci. 2024;115:197‐210. doi: 10.1111/cas.15994
Contributor Information
Tatsuya Morishima, Email: tatsuyam@kumamoto-u.ac.jp.
Hitoshi Takizawa, Email: htakizawa@kumamoto-u.ac.jp.
REFERENCES
- 1. Patel JP, Gonen M, Figueroa ME, et al. Prognostic relevance of integrated genetic profiling in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1079‐1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. DiNardo CD, Ravandi F, Agresta S, et al. Characteristics, clinical outcome, and prognostic significance of IDH mutations in AML. Am J Hematol. 2015;90:732‐736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Cairns RA, Mak TW. Oncogenic isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations: mechanisms, models, and clinical opportunities. Cancer Discov. 2013;3:730‐741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Dang L, White DW, Gross S, et al. Cancer‐associated IDH1 mutations produce 2‐hydroxyglutarate. Nature. 2009;462:739‐744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Ward PS, Patel J, Wise DR, et al. The common feature of leukemia‐associated IDH1 and IDH2 mutations is a neomorphic enzyme activity converting alpha‐ketoglutarate to 2‐hydroxyglutarate. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:225‐234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Figueroa ME, Abdel‐Wahab O, Lu C, et al. Leukemic IDH1 and IDH2 mutations result in a hypermethylation phenotype, disrupt TET2 function, and impair hematopoietic differentiation. Cancer Cell. 2010;18:553‐567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Wang F, Travins J, DeLaBarre B, et al. Targeted inhibition of mutant IDH2 in leukemia cells induces cellular differentiation. Science. 2013;340:622‐626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Okoye‐Okafor UC, Bartholdy B, Cartier J, et al. New IDH1 mutant inhibitors for treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Chem Biol. 2015;11:878‐886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Yen K, Travins J, Wang F, et al. AG‐221, a first‐in‐class therapy targeting acute myeloid leukemia harboring oncogenic IDH2 mutations. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:478‐493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Stein EM, DiNardo CD, Pollyea DA, et al. Enasidenib in mutant IDH2 relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2017;130:722‐731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Stein EM, DiNardo CD, Fathi AT, et al. Molecular remission and response patterns in patients with mutant‐IDH2 acute myeloid leukemia treated with enasidenib. Blood. 2019;133:676‐687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Quek L, David MD, Kennedy A, et al. Clonal heterogeneity of acute myeloid leukemia treated with the IDH2 inhibitor enasidenib. Nat Med. 2018;24:1167‐1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Intlekofer AM, Shih AH, Wang B, et al. Acquired resistance to IDH inhibition through trans or cis dimer‐interface mutations. Nature. 2018;559:125‐129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Choe S, Wang H, DiNardo CD, et al. Molecular mechanisms mediating relapse following ivosidenib monotherapy in IDH1‐mutant relapsed or refractory AML. Blood Adv. 2020;4:1894‐1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Harding JJ, Lowery MA, Shih AH, et al. Isoform switching as a mechanism of acquired resistance to mutant Isocitrate dehydrogenase inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:1540‐1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Wang F, Morita K, DiNardo CD, et al. Leukemia stemness and co‐occurring mutations drive resistance to IDH inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Commun. 2021;12:2607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Hvinden IC, Cadoux‐Hudson T, Schofield CJ, McCullagh JSO. Metabolic adaptations in cancers expressing isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations. Cell Rep Med. 2021;2:100469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Lenting K, Khurshed M, Peeters TH, et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1‐mutated human gliomas depend on lactate and glutamate to alleviate metabolic stress. FASEB J. 2019;33:557‐571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Gelman SJ, Naser F, Mahieu NG, et al. Consumption of NADPH for 2‐HG synthesis increases pentose phosphate pathway flux and sensitizes cells to oxidative stress. Cell Rep. 2018;22:512‐522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. McBrayer SK, Mayers JR, DiNatale GJ, et al. Transaminase inhibition by 2‐Hydroxyglutarate impairs glutamate biosynthesis and redox homeostasis in glioma. Cell. 2018;175:101‐116.e25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Fack F, Tardito S, Hochart G, et al. Altered metabolic landscape in IDH‐mutant gliomas affects phospholipid, energy, and oxidative stress pathways. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9:1681‐1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Molloy AR, Najac C, Viswanath P, et al. MR‐detectable metabolic biomarkers of response to mutant IDH inhibition in low‐grade glioma. Theranostics. 2020;10:8757‐8770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Grassian AR, Parker SJ, Davidson SM, et al. IDH1 mutations alter citric acid cycle metabolism and increase dependence on oxidative mitochondrial metabolism. Cancer Res. 2014;74:3317‐3331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Stuani L, Sabatier M, Saland E, et al. Mitochondrial metabolism supports resistance to IDH mutant inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia. J Exp Med. 2021;218:e20200924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. van Galen P, Kreso A, Wienholds E, et al. Reduced lymphoid lineage priming promotes human hematopoietic stem cell expansion. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14:94‐106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Rongvaux A, Willinger T, Martinek J, et al. Development and function of human innate immune cells in a humanized mouse model. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32:364‐372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Kitamura T, Tange T, Terasawa T, et al. Establishment and characterization of a unique human cell line that proliferates dependently on GM‐CSF, IL‐3, or erythropoietin. J Cell Physiol. 1989;140:323‐334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Kernytsky A, Wang F, Hansen E, et al. IDH2 mutation‐induced histone and DNA hypermethylation is progressively reversed by small‐molecule inhibition. Blood. 2015;125:296‐303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Scorrano L, Penzo D, Petronilli V, Pagano F, Bernardi P. Arachidonic acid causes cell death through the mitochondrial permeability transition. Implications for tumor necrosis factor‐alpha aopototic signaling. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:12035‐12040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Cao Y, Pearman AT, Zimmerman GA, McIntyre TM, Prescott SM. Intracellular unesterified arachidonic acid signals apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:11280‐11285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Hildeman DA, Mitchell T, Aronow B, Wojciechowski S, Kappler J, Marrack P. Control of Bcl‐2 expression by reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:15035‐15040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Harizi H, Corcuff JB, Gualde N. Arachidonic‐acid‐derived eicosanoids: roles in biology and immunopathology. Trends Mol Med. 2008;14:461‐469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Xiao W, Hong H, Kawakami Y, et al. Tumor suppression by phospholipase C‐beta3 via SHP‐1‐mediated dephosphorylation of Stat5. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:161‐171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Follo MY, Finelli C, Clissa C, et al. Phosphoinositide‐phospholipase C beta1 mono‐allelic deletion is associated with myelodysplastic syndromes evolution into acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:782‐790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. DiNardo CD, Jonas BA, Pullarkat V, et al. Azacitidine and Venetoclax in previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:617‐629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Fathi AT, DiNardo CD, Kline I, et al. Differentiation syndrome associated with Enasidenib, a selective inhibitor of mutant Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2: analysis of a phase 1/2 study. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:1106‐1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1
Figure S2
Figure S3
Figure S4
Figure S5
Table S1
Table S2
Table S3
Table S4
Appendix S1


