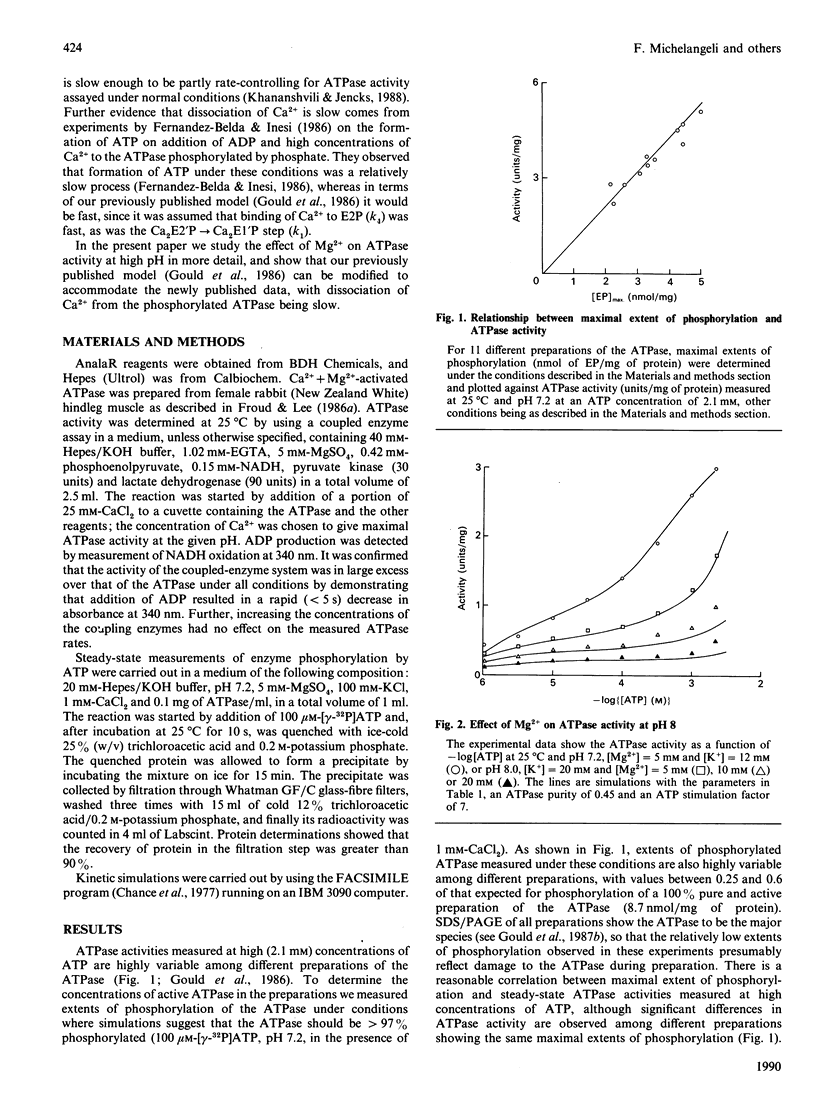
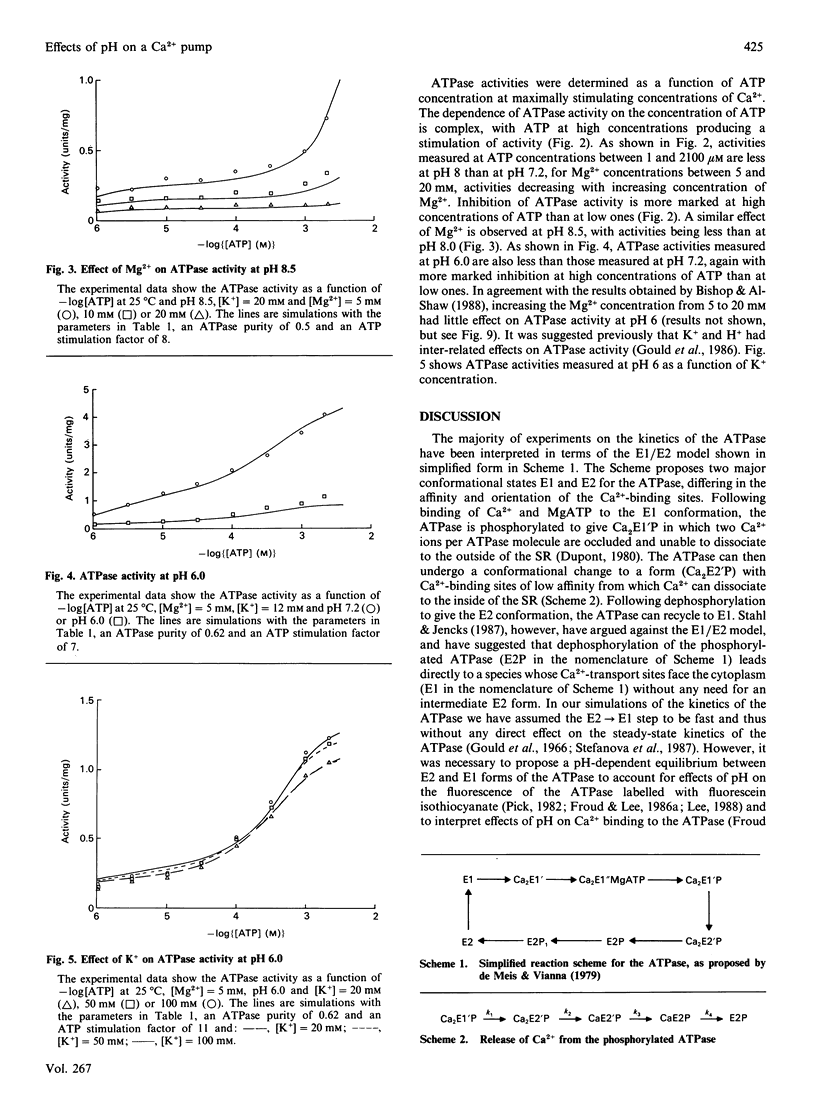
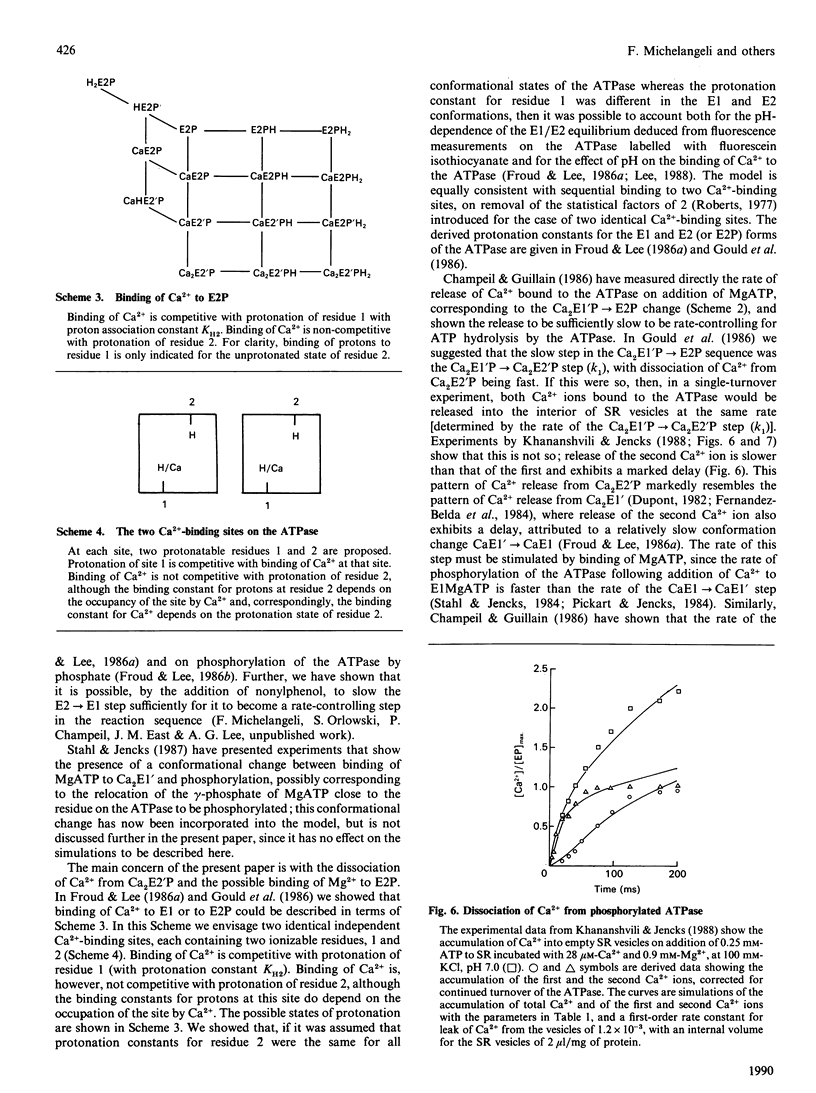
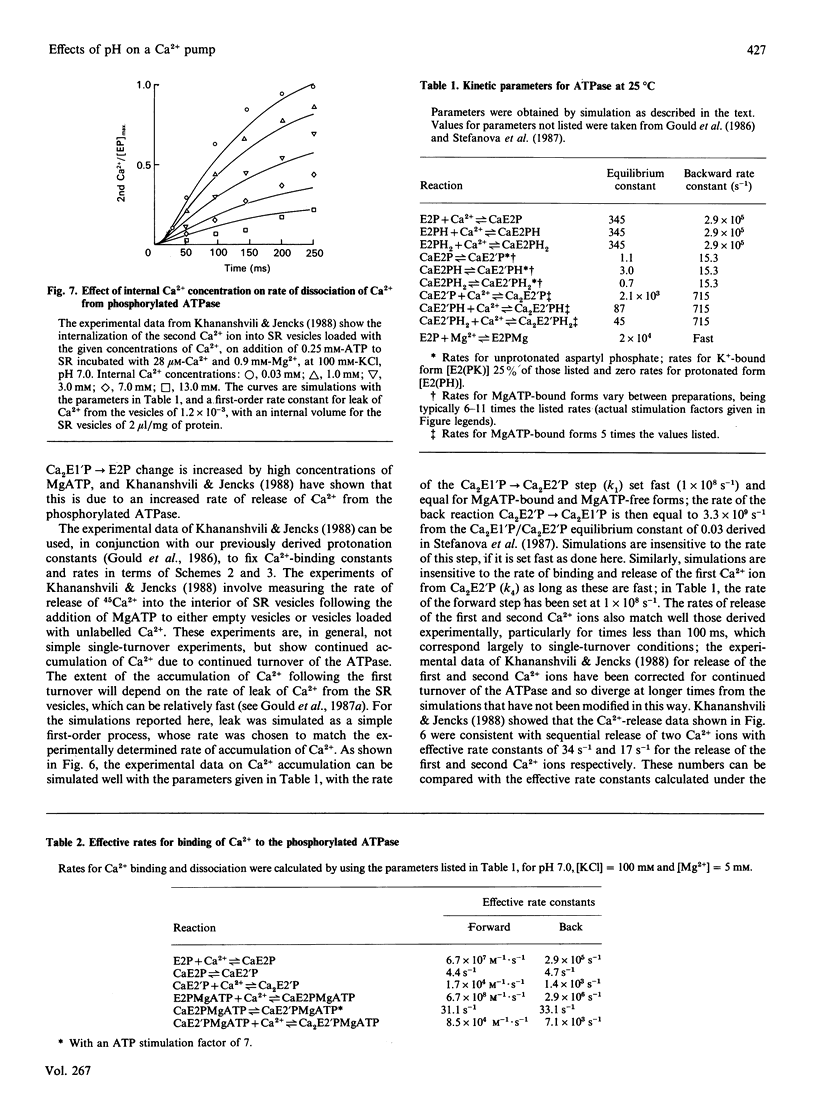
Abstract
A kinetic model for the Ca2(+) + Mg2(+)-activated ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum was presented in a previous paper [Stefanova, Napier, East & Lee (1987) Biochem. J. 245, 723-730]. Here, that model is modified to account for the pH-dependence of ATPase activity and for the effects of Mg2+ on activity at high pH. It is shown that effects of Mg2+ on measurements of ATPase activity as a function of ATP concentration at pH 8.0 and pH 8.5 are consistent with binding of Mg2+ to the Ca2(+)-binding sites on the phosphorylated ATPase, such binding inhibiting dephosphorylation of the ATPase. It is also shown that slow dissociation of Ca2+ from the phosphorylated ATPase is consistent with the previously published model.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop J. E., Al-Shawi M. K. Inhibition of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase by Mg2+ at high pH. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1886–1892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cha S. A simple method for derivation of rate equations for enzyme-catalyzed reactions under the rapid equilibrium assumption or combined assumptions of equilibrium and steady state. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 25;243(4):820–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champeil P., Guillain F. Rapid filtration study of the phosphorylation-dependent dissociation of calcium from transport sites of purified sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase and ATP modulation of the catalytic cycle. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7623–7633. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Y. Low-temperature studies of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. Mechanisms of calcium binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;688(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Y. Occlusion of divalent cations in the phosphorylated calcium pump of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(1):231–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Belda F., Inesi G. Transmembrane gradient and ligand-induced mechanisms of adenosine 5'-triphosphate synthesis by sarcoplasmic reticulum adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 2;25(24):8083–8089. doi: 10.1021/bi00372a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Belda F., Kurzmack M., Inesi G. A comparative study of calcium transients by isotopic tracer, metallochromic indicator, and intrinsic fluorescence in sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9687–9698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froud R. J., Lee A. G. A model for the phosphorylation of the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase by phosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):207–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2370207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froud R. J., Lee A. G. Conformational transitions in the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase and the binding of Ca2+ ions. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):197–206. doi: 10.1042/bj2370197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Colyer J., East J. M., Lee A. G. Silver ions trigger Ca2+ release by interaction with the (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase in reconstituted systems. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7676–7679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., East J. M., Froud R. J., McWhirter J. M., Stefanova H. I., Lee A. G. A kinetic model for the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):217–227. doi: 10.1042/bj2370217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., McWhirter J. M., East J. M., Lee A. G. A model for the uptake and release of Ca2+ by sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):739–749. doi: 10.1042/bj2450739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., Hill T. L. Calcium and proton dependence of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. Biophys J. 1983 Nov;44(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84299-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., Lewis D., Murphy A. J. Interdependence of H+, Ca2+, and Pi (or vanadate) sites in sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):996–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khananshvili D., Jencks W. P. Two-step internalization of Ca2+ from a single E approximately P.Ca2 species by the Ca2+-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2943–2952. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U. The interaction of vanadate ions with the Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6111–6119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickart C. M., Jencks W. P. Energetics of the calcium-transporting ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1629–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney E. K., Lee A. G. Binding of hydrophobic drugs to lipid bilayers and to the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 27;732(2):428–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scofano H., Barrabin H., Inesi G., Cohen J. A. Stoichiometric and electrostatic characterization of calcium binding to native and lipid-substituted adenosinetriphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 25;819(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigekawa M., Wakabayashi S., Nakamura H. Reaction mechanism of Ca2+-dependent adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. ATP hydrolysis with CaATP as a substrate and role of divalent cation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8698–8707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Jencks W. P. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate at the active site accelerates binding of calcium to calcium adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5389–5392. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Jencks W. P. Reactions of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium adenosinetriphosphatase with adenosine 5'-triphosphate and Ca2+ that are not satisfactorily described by an E1-E2 model. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7654–7667. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanova H. I., Napier R. M., East J. M., Lee A. G. Effects of Mg2+, anions and cations on the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):723–730. doi: 10.1042/bj2450723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Ogurusu T., Shigekawa M. Factors influencing calcium release from the ADP-sensitive phosphoenzyme intermediate of the sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9762–9769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Ogurusu T., Shigekawa M. Modulation of the hydrolysis rate of the ADP-insensitive phosphoenzyme of the sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase by H+ and Mg2+. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9121–9129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Fujii J., Katayama H. Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase: distinction of phosphoenzymes formed from MgATP and CaATP as substrates and interconversion of the phosphoenzymes by Mg2+ and Ca2+. J Biochem. 1986 Nov;100(5):1329–1342. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Vianna A. L. Energy interconversion by the Ca2+-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


