Abstract
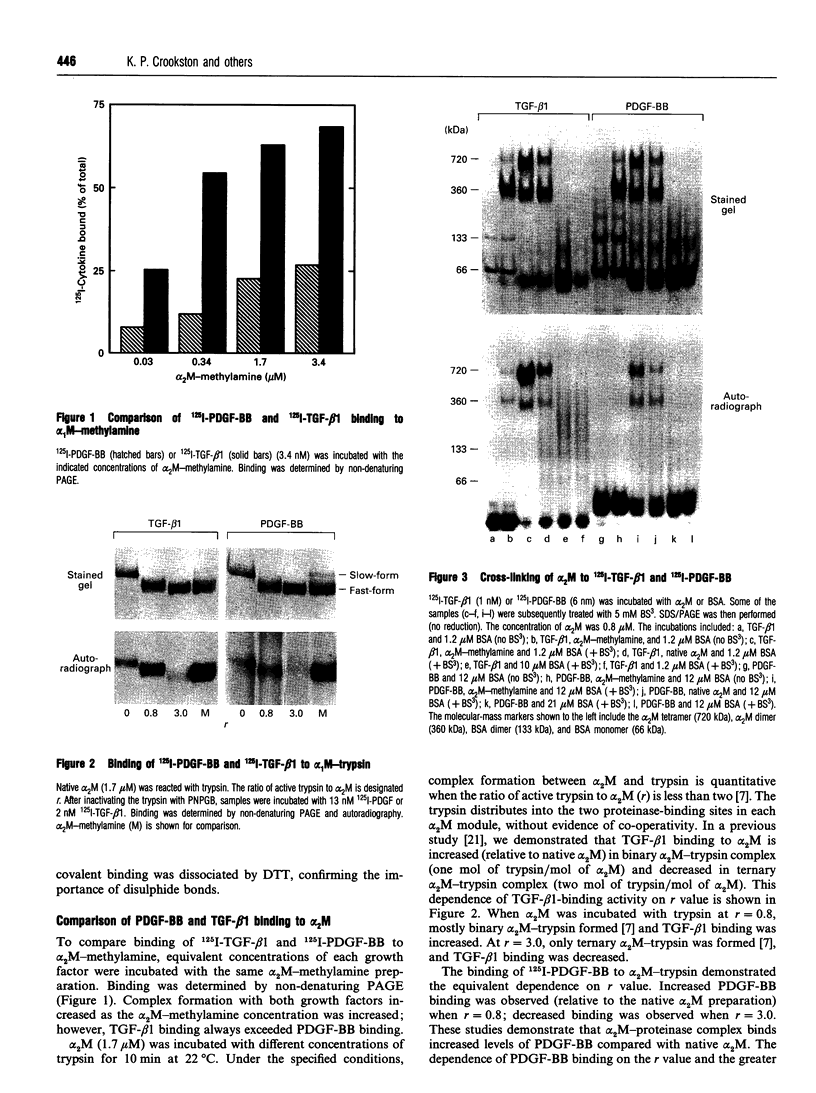
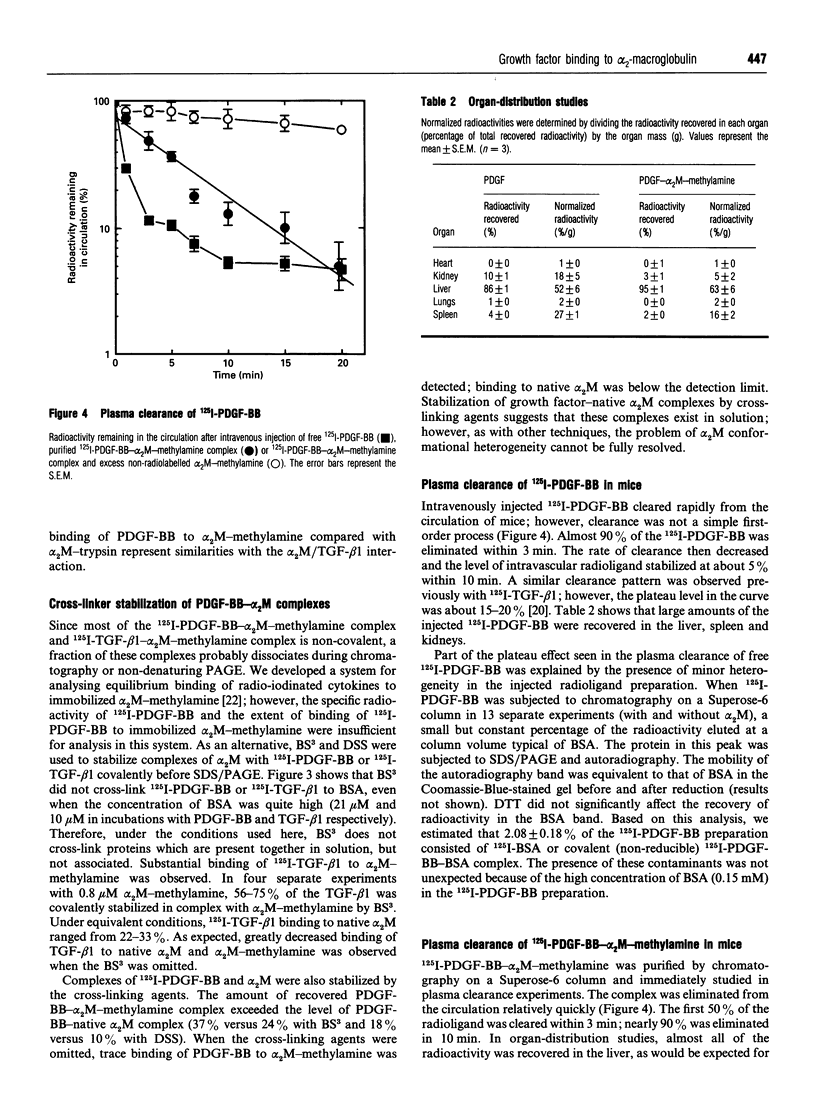
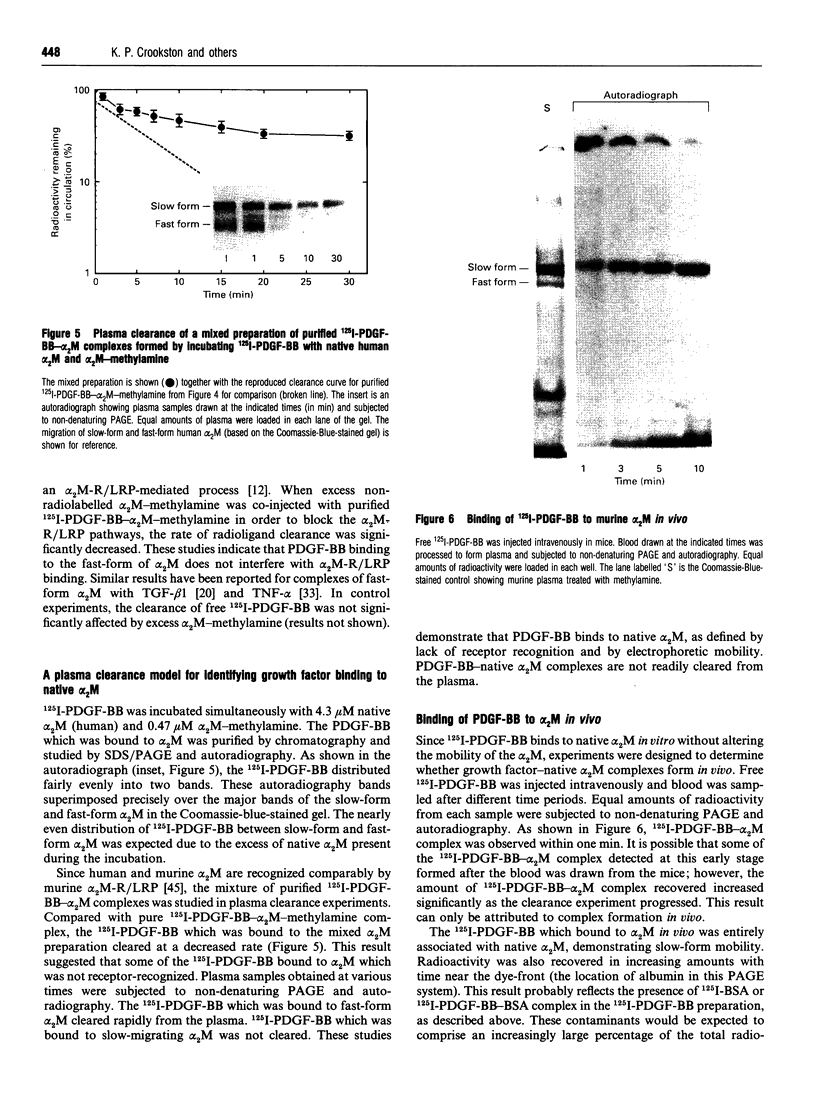
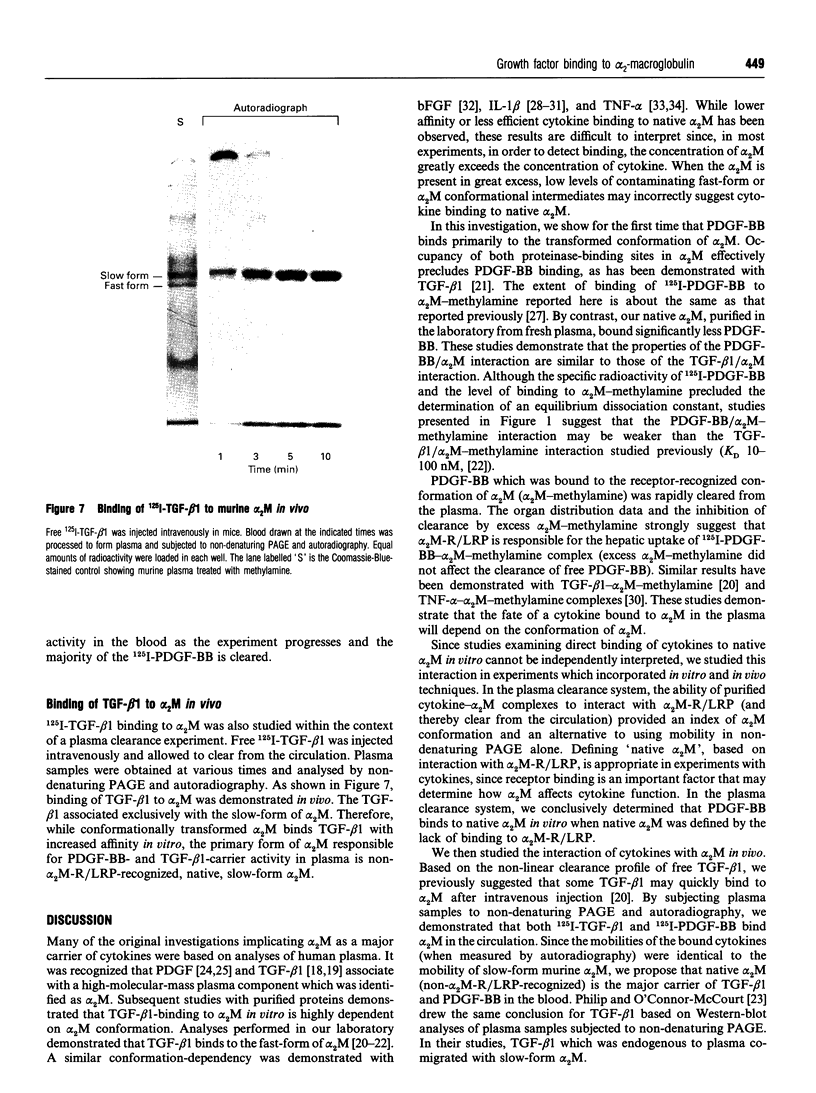
alpha 2-Macroglobulin (alpha 2M) undergoes a major conformational change when reacting with proteinases or primary amines. This conformational change has been referred to as the 'slow' to 'fast' transformation based on the increase in alpha 2M mobility shown by non-denaturing PAGE. Previous studies demonstrated that many cytokines, including transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) and interleukin-1 beta, bind preferentially or exclusively to alpha 2M which has undergone conformational change. In this study, we demonstrate that platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) also binds preferentially to conformationally transformed alpha 2M (alpha 2M-methylamine, alpha 2M-trypsin) in vitro. Purified 125I-PDGF-BB-alpha 2M-methylamine complex cleared rapidly from the circulation of mice via the alpha 2M receptor/low-density-lipoprotein-receptor-related protein (alpha 2M-R/LRP). In order to determine whether PDGF-BB or TGF-beta 1 binds to native alpha 2M, we defined the native conformation by lack of interaction with alpha 2M-R/LRP instead of electrophoretic mobility. 125I-PDGF-BB was incubated with 4.3 microM native alpha 2M and 0.47 microM alpha 2M-methylamine. The 125I-PDGF-BB distributed evenly between slow-form and fast-form alpha 2M without shifting the electrophoretic mobility of either species. When the mixed preparation was injected intravenously in mice, 125I-PDGF-BB-fast-form-alpha 2M cleared rapidly and selectively from the circulation; 125I-PDGF-BB which was bound to slow-form alpha 2M was stable in the blood (apparently not recognized by alpha 2M-R/LRP). Therefore, while conformationally transformed alpha 2M binds PDGF-BB preferentially in vitro, non-alpha 2M-R/LRP-recognized alpha 2M binds PDGF-BB as well. Binding of 125I-PDGF-BB and 125I-TGF-beta 1 to alpha 2M was demonstrated in vivo by injecting the free growth factors intravenously into mice. Plasma samples which were subjected to non-denaturing PAGE and autoradiography demonstrated binding of both growth factors exclusively to the slow-form of alpha 2M. Therefore, under normal physiological conditions, native alpha 2M (non-alpha 2M-R/LRP-recognized) is the primary form of the proteinase inhibitor functioning as a carrier of PDGF-BB and TGF-beta 1 in the blood.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assoian R. K. Purification of type-beta transforming growth factor from human platelets. Methods Enzymol. 1987;146:153–163. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)46017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Brown M. A., Sayers C. A. The electrophoretically 'slow' and 'fast' forms of the alpha 2-macroglobulin molecule. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):401–418. doi: 10.1042/bj1810401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Starkey P. M. The interaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin with proteinases. Characteristics and specificity of the reaction, and a hypothesis concerning its molecular mechanism. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):709–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1330709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk I., Fish W. W. Evidence for similar conformational changes in alpha 2-macroglobulin on reaction with primary amines or proteolytic enzymes. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 1;207(2):347–356. doi: 10.1042/bj2070347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. C., Badgett A., Osornio-Vargas A. R., Hoffman M., Brody A. R. PDGF-stimulated fibroblast proliferation is enhanced synergistically by receptor-recognized alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Oct;145(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041450102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. C., Goodell A. L., Lasky J. A., Hoffman M. R. Reversible binding of platelet-derived growth factor-AA, -AB, and -BB isoforms to a similar site on the "slow" and "fast" conformations of alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12837–12844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borth W. Alpha 2-macroglobulin, a multifunctional binding protein with targeting characteristics. FASEB J. 1992 Dec;6(15):3345–3353. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.15.1281457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borth W., Luger T. A. Identification of alpha 2-macroglobulin as a cytokine binding plasma protein. Binding of interleukin-1 beta to "F" alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5818–5825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borth W., Scheer B., Urbansky A., Luger T. A., Sottrup-Jensen L. Binding of IL-1 beta to alpha-macroglobulins and release by thioredoxin. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3747–3754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borth W., Urbanski A., Prohaska R., Susanj M., Luger T. A. Binding of recombinant interleukin-1 beta to the third complement component and alpha 2-macroglobulin after activation of serum by immune complexes. Blood. 1990 Jun 15;75(12):2388–2395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T., Jr, Shaw E. p-Nitrophenyl-p'-guanidinobenzoate HCl: a new active site titrant for trypsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 30;29(4):508–514. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O. Inhibition of plasmin activity by alpha-2-macroglobulin. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 May;16(2):328–329. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L. Alpha 2-macroglobulin: a protein at the interface of fibrinolysis and cellular growth regulation. Exp Hematol. 1992 Mar;20(3):302–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Balber A. E., Hubbard W. J., Pizzo S. V. Ligand binding, conformational change and plasma elimination of human, mouse and rat alpha-macroglobulin proteinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):99–105. doi: 10.1042/bj2090099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Pizzo S. V. Conformation and protease binding activity of binary and ternary human alpha 2-macroglobulin-protease complexes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14682–14685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Reynolds J. A., Pizzo S. V. Physical properties of human alpha 2-macroglobulin following reaction with methylamine and trypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 10;705(3):306–314. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. K., Roberts R. C. Physical and chemical properties of human plasma alpha2-macroglobulin. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 1;173(1):27–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1730027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall S. W., LaMarre J., Marshall L. B., Hayes M. A., Gonias S. L. Binding of transforming growth factor-beta 1 to methylamine-modified alpha 2-macroglobulin and to binary and ternary alpha 2-macroglobulin-proteinase complexes. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 15;281(Pt 2):569–575. doi: 10.1042/bj2810569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. B. Reactive site in human alpha 2-macroglobulin: circumstantial evidence for a thiolester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2235–2239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. S., Huang S. S., Deuel T. F. Specific covalent binding of platelet-derived growth factor to human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):342–346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. S., O'Grady P., Huang J. S. Human transforming growth factor beta.alpha 2-macroglobulin complex is a latent form of transforming growth factor beta. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1535–1541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imber M. J., Pizzo S. V. Clearance and binding of two electrophoretic "fast" forms of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8134–8139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James K., van den Haan J., Lens S., Farmer K. Preliminary studies on the interaction of TNF alpha and IFN gamma with alpha 2-macroglobulin. Immunol Lett. 1992 Mar;32(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(92)90198-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman N., Page J. D., Pixley R. A., Schein R., Schmaier A. H., Colman R. W. Alpha 2-macroglobulin-kallikrein complexes detect contact system activation in hereditary angioedema and human sepsis. Blood. 1991 Jun 15;77(12):2660–2667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarre J., Hayes M. A., Wollenberg G. K., Hussaini I., Hall S. W., Gonias S. L. An alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor-dependent mechanism for the plasma clearance of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in mice. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):39–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI114998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall L. B., Figler N. L., Gonias S. L. Identification of alpha 2-macroglobulin conformational intermediates by electron microscopy and image analysis. Comparison of alpha 2-macroglobulin-thrombin and alpha 2-macroglobulin reacted with cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum(II) and trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6347–6352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K., Gliemann J., Pallesen G. Distribution of the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in human tissues. Cell Tissue Res. 1992 Sep;269(3):375–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00353892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K., Gliemann J. Purification of the rat hepatic alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor as an approximately 440-kDa single chain protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15574–15577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor-McCourt M. D., Wakefield L. M. Latent transforming growth factor-beta in serum. A specific complex with alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14090–14099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip A., O'Connor-McCourt M. D. Interaction of transforming growth factor-beta 1 with alpha 2-macroglobulin. Role in transforming growth factor-beta 1 clearance. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22290–22296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines E. W., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Plasma binding proteins for platelet-derived growth factor that inhibit its binding to cell-surface receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3424–3428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Pizzo S. V. Analysis of thiolester bond cleavage-dependent conformational changes in binary alpha 2-macroglobulin-proteinase complexes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Nov 15;267(1):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff E., Rizzino A. Preparation and binding of radioactively labeled porcine transforming growth factor type beta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 31;138(2):714–719. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80555-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Gliemann J., Van Leuven F. Domain structure of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. Characterization of a receptor-binding domain obtained by digestion with papain. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 1;205(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80857-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S. A thiol-ester in alpha 2-macroglobulin cleaved during proteinase complex formation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 1;121(2):275–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80361-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner J. P., Bhattacharya P., Strickland D. K. Thrombin-induced conformational changes of human alpha 2-macroglobulin: evidence for two functional domains. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 4;24(12):2993–3001. doi: 10.1021/bi00333a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland D. K., Ashcom J. D., Williams S., Burgess W. H., Migliorini M., Argraves W. S. Sequence identity between the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein suggests that this molecule is a multifunctional receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17401–17404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland D. K., Steiner J. P., Migliorini M., Battey F. D. Identification of a monoclonal antibody specific for a neoantigenic determinant on alpha 2-macroglobulin: use for the purification and characterization of binary proteinase-inhibitor complexes. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1458–1466. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. P., Howard J. B. Structural characterization of human alpha2-macroglobulin subunits. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4452–4456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teodorescu M., McAfee M., Skosey J. L., Wallman J., Shaw A., Hanly W. C. Covalent disulfide binding of human IL-1 beta to alpha 2-macroglobulin: inhibition by D-penicillamine. Mol Immunol. 1991 Apr-May;28(4-5):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leuven F., Cassiman J. J., Van den Berghe H. Functional modifications of alpha 2-macroglobulin by primary amines. I. Characterization of alpha 2 M after derivatization by methylamine and by factor XIII. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9016–9022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leuven F., Marynen P., Sottrup-Jensen L., Cassiman J. J., Van den Berghe H. The receptor-binding domain of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. Isolation after limited proteolysis with a bacterial proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11369–11373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb D. J., Crookston K. P., Hall S. W., Gonias S. L. Binding of transforming growth factor-beta 1 to immobilized human alpha 2-macroglobulin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Feb 1;292(2):487–492. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90020-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb D. J., LaMarre J., Gonias S. L. Effect of human alpha-thrombin on the transforming growth factor-beta 1-binding activity of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1992;18(3):305–310. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. B., Lopes M. B., VandenBerg S. R., Gonias S. L. Characterization and immunohistochemical localization of alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor (low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein) in human brain. Am J Pathol. 1992 Jul;141(1):37–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenberg G. K., LaMarre J., Rosendal S., Gonias S. L., Hayes M. A. Binding of tumor necrosis factor alpha to activated forms of human plasma alpha 2 macroglobulin. Am J Pathol. 1991 Feb;138(2):265–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







