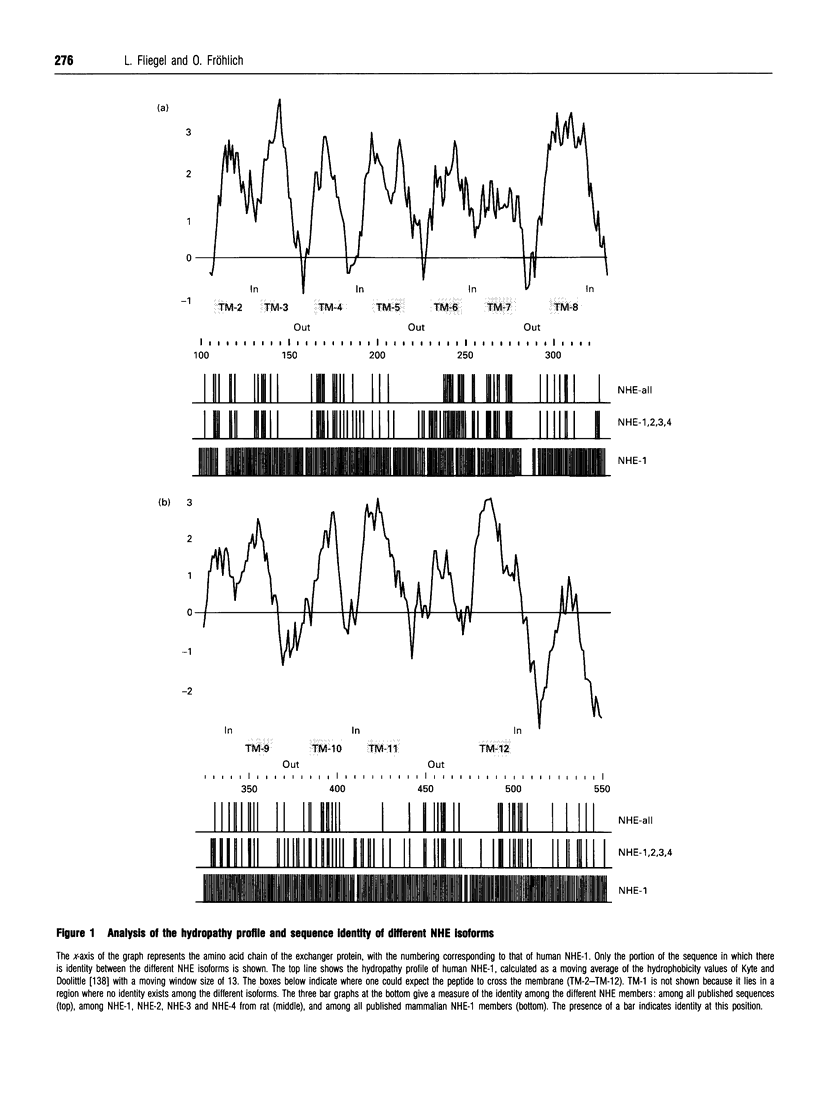
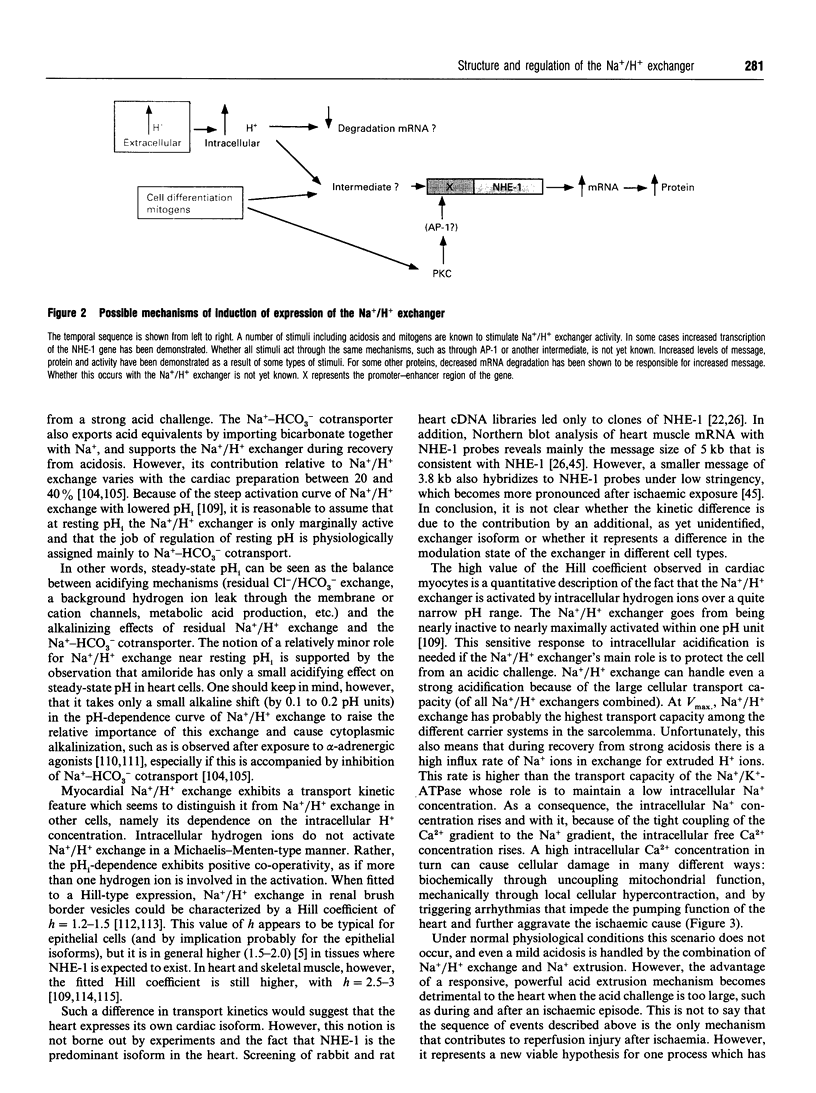
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
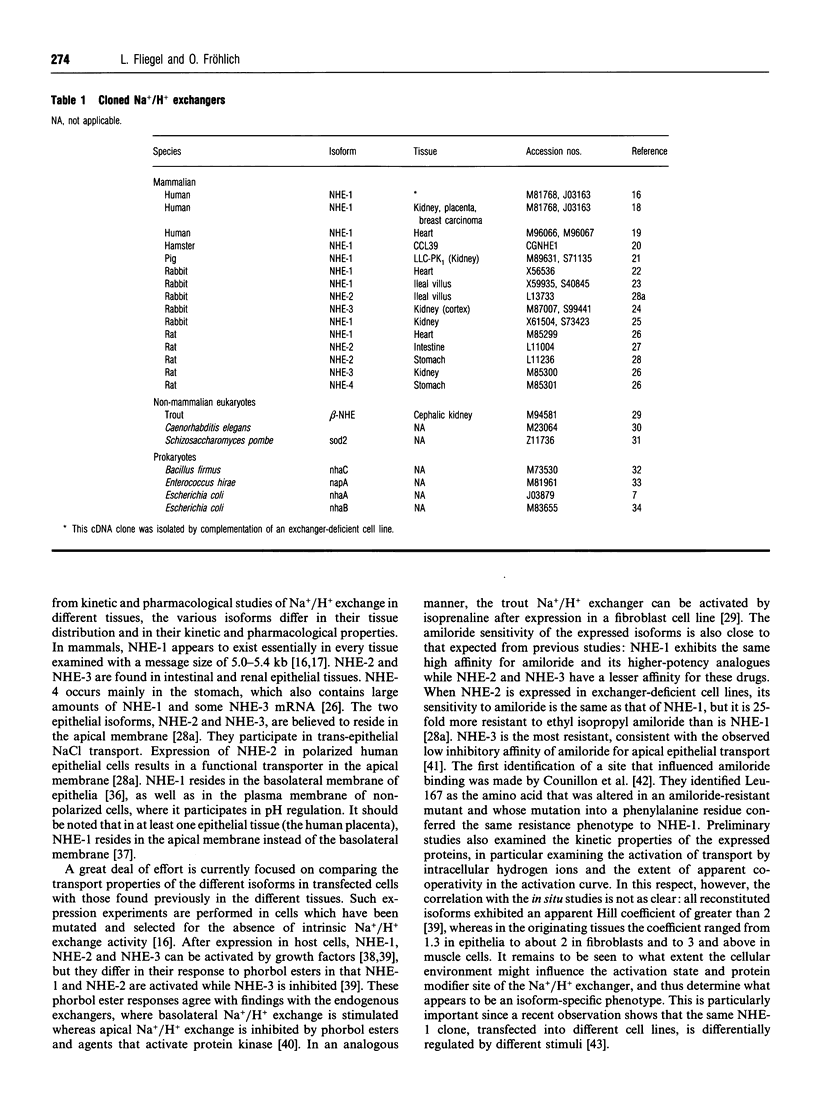
- Akiba T., Rocco V. K., Warnock D. G. Parallel adaptation of the rabbit renal cortical sodium/proton antiporter and sodium/bicarbonate cotransporter in metabolic acidosis and alkalosis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):308–315. doi: 10.1172/JCI113074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. E., Murphy E., Steenbergen C., London R. E., Cala P. M. Na-H exchange in myocardium: effects of hypoxia and acidification on Na and Ca. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):C940–C948. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.6.C940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S. Kinetic properties of the plasma membrane Na+-H+ exchanger. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:545–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Nee J., Suhm M. A. Modifier role of internal H+ in activating the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):161–163. doi: 10.1038/299161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avkiran M., Ibuki C. Reperfusion-induced arrhythmias. A role for washout of extracellular protons? Circ Res. 1992 Dec;71(6):1429–1440. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.6.1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker L. C., Ambrosio G. Myocardial consequences of reperfusion. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1987 Jul-Aug;30(1):23–44. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(87)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Canessa M., Vallega G., Alexander R. W. Agonist-mediated changes in intracellular pH: role in vascular smooth muscle cell function. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988;12 (Suppl 5):S104–S114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Elder E., Mitsuka M. Hypertrophy and hyperplasia cause differing effects on vascular smooth muscle cell Na+/H+ exchange and intracellular pH. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19632–19637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini L., Woodside M., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Takai A., Grinstein S. Okadaic acid, a phosphatase inhibitor, induces activation and phosphorylation of the Na+/H+ antiport. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15406–15413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidet M., Merot J., Tauc M., Poujeol P. Na+-H+ exchanger in proximal cells isolated from kidney. II. Short-term regulation by glucocorticoids. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):F945–F951. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.5.F945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biemesderfer D., Reilly R. F., Exner M., Igarashi P., Aronson P. S. Immunocytochemical characterization of Na(+)-H+ exchanger isoform NHE-1 in rabbit kidney. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 2):F833–F840. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.5.F833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgese F., Sardet C., Cappadoro M., Pouyssegur J., Motais R. Cloning and expression of a cAMP-activated Na+/H+ exchanger: evidence that the cytoplasmic domain mediates hormonal regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6765–6769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casavola V., Helmle-Kolb C., Murer H. Separate regulatory control of apical and basolateral Na+/H+ exchange in renal epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 15;165(2):833–837. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casavola V., Reshkin S. J., Murer H., Helmle-Kolb C. Polarized expression of Na+/H+ exchange activity in LLC-PK1/PKE20 cells: II. Hormonal regulation. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Mar;420(3-4):282–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00374460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. H., Rich D. P., Marshall J., Gregory R. J., Welsh M. J., Smith A. E. Phosphorylation of the R domain by cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulates the CFTR chloride channel. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):1027–1036. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90446-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. E., Wesolek J., McCullen J., Rys-Sikora K., Pandol S., Rood R. P., Sharp G. W., Donowitz M. Carbachol- and elevated Ca(2+)-induced translocation of functionally active protein kinase C to the brush border of rabbit ileal Na+ absorbing cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):855–863. doi: 10.1172/JCI115387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. F., Honda T., Knobel S., Bulus N. M., Conary J., DuBois R., Ghishan F. K. Molecular cloning, sequencing, tissue distribution, and functional expression of a Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE-2). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3938–3942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counillon L., Pouysségur J. Nucleotide sequence of the Chinese hamster Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Mar 20;1172(3):343–345. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis S. C., Coetzee W. A., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Opie L. H. Effects of proton buffering and of amiloride derivatives on reperfusion arrhythmias in isolated rat hearts. Possible evidence for an arrhythmogenic role of Na(+)-H+ exchange. Circ Res. 1990 Apr;66(4):1156–1159. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.4.1156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan J., Karmazyn M. Protective effects of amiloride on the ischemic reperfused rat heart. Relation to mitochondrial function. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;210(2):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90665-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck J. R., Lopaschuk G. D., Fliegel L. Identification of a small Na+/H+ exchanger-like message in the rabbit myocardium. FEBS Lett. 1992 Oct 5;310(3):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81343-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasman G. D., Gilbert W. A. The prediction of transmembrane protein sequences and their conformation: an evaluation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90187-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel L., Haworth R. S., Dyck J. R. Characterization of the placental brush border membrane Na+/H+ exchanger: identification of thiol-dependent transitions in apparent molecular size. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):101–107. doi: 10.1042/bj2890101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel L., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Barr A. Identification of the protein and cDNA of the cardiac Na+/H+ exchanger. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 11;279(1):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80241-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel L., Walsh M. P., Singh D., Wong C., Barr A. Phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of the Na+/H+ exchanger by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 15;282(Pt 1):139–145. doi: 10.1042/bj2820139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freiberg J. M., Kinsella J., Sacktor B. Glucocorticoids increase the Na+-H+ exchange and decrease the Na+ gradient-dependent phosphate-uptake systems in renal brush border membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4932–4936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelin C., Vigne P., Lazdunski M. The role of the Na+/H+ exchange system in the regulation of the internal pH in cultured cardiac cells. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 15;149(1):1–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlid K. D., Shariat-Madar Z., Nath S., Jezek P. Reconstitution and partial purification of the Na(+)-selective Na+/H+ antiporter of beef heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6518–6523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E., Nosek T. M. Changes of intracellular milieu with fatigue or hypoxia depress contraction of skinned rabbit skeletal and cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:155–180. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Cohen S., Rothstein A. Cytoplasmic pH regulation in thymic lymphocytes by an amiloride-sensitive Na+/H+ antiport. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):341–369. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rothstein A. Mechanisms of regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01869680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rotin D., Mason M. J. Na+/H+ exchange and growth factor-induced cytosolic pH changes. Role in cellular proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):73–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Woodside M., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Rotin D. Activation of the Na+/H+ antiporter during cell volume regulation. Evidence for a phosphorylation-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23823–23828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guizouarn H., Borgese F., Pellissier B., Garcia-Romeu F., Motais R. Role of protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in activation and desensitization of the cAMP-dependent Na+/H+ antiport. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8632–8639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty J. G., Agarwal N., Reilly R. F., Adelberg E. A., Slayman C. W. Pharmacologically different Na/H antiporters on the apical and basolateral surfaces of cultured porcine kidney cells (LLC-PK1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6797–6801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth R. S., Fröhlich O., Fliegel L. Multiple carbohydrate moieties on the Na+/H+ exchanger. Biochem J. 1993 Feb 1;289(Pt 3):637–640. doi: 10.1042/bj2890637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearse D. J. Reperfusion of the ischemic myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1977 Aug;9(8):605–616. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(77)80357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensley C. B., Bradley M. E., Mircheff A. K. Parathyroid hormone-induced translocation of Na-H antiporters in rat proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 1):C637–C645. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.4.C637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Moore J. P., Morris J. D., Taylor M. V., Rogers J., Smith G. A., Metcalfe J. C. A common sequence of calcium and pH signals in the mitogenic stimulation of eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):481–484. doi: 10.1038/313481a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt F., Pizzonia J. H., Reilly R. F., Rebouças N. A., Sardet C., Pouysségur J., Slayman C. W., Aronson P. S., Igarashi P. Cloning, sequence, and tissue distribution of a rabbit renal Na+/H+ exchanger transcript. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 2;1129(1):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90221-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann E. K., Simonsen L. O. Membrane mechanisms in volume and pH regulation in vertebrate cells. Physiol Rev. 1989 Apr;69(2):315–382. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie S., Moe O., Miller R. T., Alpern R. J. Long-term activation of protein kinase c causes chronic Na/H antiporter stimulation in cultured proximal tubule cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):365–372. doi: 10.1172/JCI115594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie S., Moe O., Tejedor A., Alpern R. J. Preincubation in acid medium increases Na/H antiporter activity in cultured renal proximal tubule cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4742–4745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie S., Moe O., Yamaji Y., Cano A., Miller R. T., Alpern R. J. Role of protein kinase C and transcription factor AP-1 in the acid-induced increase in Na/H antiporter activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5236–5240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J. J., Curthoys N. P. Effect of acute alterations in acid-base balance on rat renal glutaminase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9392–9396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi P., Freed M. I., Ganz M. B., Reilly R. F. Effects of chronic metabolic acidosis on Na(+)-H+ exchangers in LLC-PK1 renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jul;263(1 Pt 2):F83–F88. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.1.F83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivey D. M., Guffanti A. A., Bossewitch J. S., Padan E., Krulwich T. A. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a gene from alkaliphilic Bacillus firmus OF4 that functionally complements an Escherichia coli strain carrying a deletion in the nhaA Na+/H+ antiporter gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23483–23489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins A. D., Dousa T. P., Smith L. H. Transport of citrate across renal brush border membrane: effects of dietary acid and alkali loading. Am J Physiol. 1985 Oct;249(4 Pt 2):F590–F595. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.4.F590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia Z. P., McCullough N., Martel R., Hemmingsen S., Young P. G. Gene amplification at a locus encoding a putative Na+/H+ antiporter confers sodium and lithium tolerance in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1631–1640. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05209.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser S., Curthoys N. P. Effect of pH and bicarbonate on phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and glutaminase mRNA levels in cultured renal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9397–9402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmazyn M. Amiloride enhances postischemic ventricular recovery: possible role of Na+-H+ exchange. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 2):H608–H615. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.3.H608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmazyn M. Na+/H+ exchange inhibitors reverse lactate-induced depression in postischaemic ventricular recovery. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;108(1):50–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpel R., Olami Y., Taglicht D., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Sequencing of the gene ant which affects the Na+/H+ antiporter activity in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10408–10414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandoudi N., Bernard M., Cozzone P., Feuvray D. Intracellular pH and role of Na+/H+ exchange during ischaemia and reperfusion of normal and diabetic rat hearts. Cardiovasc Res. 1990 Nov;24(11):873–878. doi: 10.1093/cvr/24.11.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Cujdik T., Sacktor B. Kinetic studies on the stimulation of Na+-H+ exchange activity in renal brush border membranes isolated from thyroid hormone-treated rats. J Membr Biol. 1986;91(2):183–191. doi: 10.1007/BF01925795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J., Cujdik T., Sacktor B. Na+-H+ exchange in isolated renal brush-border membrane vesicles in response to metabolic acidosis. Kinetic effects. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13224–13227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyman T. R., Cragoe E. J., Jr Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J Membr Biol. 1988 Oct;105(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01871102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R., Pearce D., Lynch C., Xi X. P., Reudelhuber T. L., Pouysségur J., Rector F. C., Jr Expression of rat renal Na/H antiporter mRNA levels in response to respiratory and metabolic acidosis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):747–751. doi: 10.1172/JCI115057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulanthaivel P., Furesz T. C., Moe A. J., Smith C. H., Mahesh V. B., Leibach F. H., Ganapathy V. Human placental syncytiotrophoblast expresses two pharmacologically distinguishable types of Na(+)-H+ exchangers, NHE-1 in the maternal-facing (brush border) membrane and NHE-2 in the fetal-facing (basal) membrane. Biochem J. 1992 May 15;284(Pt 1):33–38. doi: 10.1042/bj2840033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulanthaivel P., Leibach F. H., Mahesh V. B., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Ganapathy V. The Na(+)-H+ exchanger of the placental brush-border membrane is pharmacologically distinct from that of the renal brush-border membrane. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1249–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagadic-Gossmann D., Buckler K. J., Vaughan-Jones R. D. Role of bicarbonate in pH recovery from intracellular acidosis in the guinea-pig ventricular myocyte. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:361–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagadic-Gossmann D., Vaughan-Jones R. D., Buckler K. J. Adrenaline and extracellular ATP switch between two modes of acid extrusion in the guinea-pig ventricular myocyte. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:385–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malloy C. R., Matthews P. M., Smith M. B., Radda G. K. In vivo phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance study of the regional metabolic response to cardiac ischemia. Adv Myocardiol. 1985;6:461–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason M. J., Smith J. D., Garcia-Soto J. J., Grinstein S. Internal pH-sensitive site couples Cl-(-)HCO3- exchange to Na+-H+ antiport in lymphocytes. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):C428–C433. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.2.C428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng H. P., Lonsberry B. B., Pierce G. N. Influence of perfusate pH on the postischemic recovery of cardiac contractile function: involvement of sodium-hydrogen exchange. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Sep;258(3):772–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng H. P., Pierce G. N. Protective effects of 5-(N,N-dimethyl)amiloride on ischemia-reperfusion injury in hearts. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):H1615–H1619. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.5.H1615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng H., Pierce G. N. Involvement of sodium in the protective effect of 5-(N,N-dimethyl)-amiloride on ischemia-reperfusion injury in isolated rat ventricular wall. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Mar;256(3):1094–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. T., Counillon L., Pages G., Lifton R. P., Sardet C., Pouysségur J. Structure of the 5'-flanking regulatory region and gene for the human growth factor-activatable Na/H exchanger NHE-1. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10813–10819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina T., Scholer D. W., Edelman I. S. Glucocorticoid receptors in rat kidney cortical tubules enriched in proximal and distal segments. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):F38–F45. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.1.F38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe O. W., Miller R. T., Horie S., Cano A., Preisig P. A., Alpern R. J. Differential regulation of Na/H antiporter by acid in renal epithelial cells and fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1703–1708. doi: 10.1172/JCI115487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Perlman M., London R. E., Steenbergen C. Amiloride delays the ischemia-induced rise in cytosolic free calcium. Circ Res. 1991 May;68(5):1250–1258. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.5.1250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuccitelli R., Webb D. J., Lagier S. T., Matson G. B. 31P NMR reveals increased intracellular pH after fertilization in Xenopus eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4421–4425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orchard C. H., Kentish J. C. Effects of changes of pH on the contractile function of cardiac muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C967–C981. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski J., Kandasamy R. A., Shull G. E. Molecular cloning of putative members of the Na/H exchanger gene family. cDNA cloning, deduced amino acid sequence, and mRNA tissue expression of the rat Na/H exchanger NHE-1 and two structurally related proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9331–9339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: versatile transducers for cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jun;17(6):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinner E., Padan E., Schuldiner S. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the nhaB gene, encoding a Na+/H+ antiporter in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11064–11068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock A. S., Long J. A. The 5'region of the rat phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene confers pH sensitivity to chimeric genes expressed in renal and liver cell lines capable of expressing PEPCK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 16;164(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91685-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poronnik P., Young J. A., Cook D. I. Na(+)-H+ exchange in sheep parotid endpieces. Apparent insensitivity to amiloride. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 11;315(3):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Sardet C., Franchi A., L'Allemain G., Paris S. A specific mutation abolishing Na+/H+ antiport activity in hamster fibroblasts precludes growth at neutral and acidic pH. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad S. S., Baillie D. L. Evolutionarily conserved coding sequences in the dpy-20-unc-22 region of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):185–198. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig P. A., Alpern R. J. Chronic metabolic acidosis causes an adaptation in the apical membrane Na/H antiporter and basolateral membrane Na(HCO3)3 symporter in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1445–1453. doi: 10.1172/JCI113750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raley-Susman K. M., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Sapolsky R. M., Kopito R. R. Regulation of intracellular pH in cultured hippocampal neurons by an amiloride-insensitive Na+/H+ exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2739–2745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao G. N., Sardet C., Pouysségur J., Berk B. C. Na+/H+ antiporter gene expression increases during retinoic acid-induced granulocytic differentiation of HL60 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 May;151(2):361–366. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041510217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao G. N., de Roux N., Sardet C., Pouysségur J., Berk B. C. Na+/H+ antiporter gene expression during monocytic differentiation of HL60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13485–13488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly R. F., Hildebrandt F., Biemesderfer D., Sardet C., Pouysségur J., Aronson P. S., Slayman C. W., Igarashi P. cDNA cloning and immunolocalization of a Na(+)-H+ exchanger in LLC-PK1 renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 2):F1088–F1094. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.6.F1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rood R. P., Emmer E., Wesolek J., McCullen J., Husain Z., Cohen M. E., Braithwaite R. S., Murer H., Sharp G. W., Donowitz M. Regulation of the rabbit ileal brush-border Na+/H+ exchanger by an ATP-requiring Ca++/calmodulin-mediated process. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1091–1097. doi: 10.1172/JCI113665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein A. The Na+/H+ exchange system in cell pH and volume control. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1989;112:235–257. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabolić I., Brown D. Na+(Li+)-H+ exchange in rat renal cortical vesicles with endosomal characteristics. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1245–F1253. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salihagić A., Macković M., Banfić H., Sabolić I. Short-term and long-term stimulation of Na+-H+ exchange in cortical brush-border membranes during compensatory growth of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Dec;413(2):190–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00582530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Counillon L., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Growth factors induce phosphorylation of the Na+/H+ antiporter, glycoprotein of 110 kD. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):723–726. doi: 10.1126/science.2154036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Fafournoux P., Pouysségur J. Alpha-thrombin, epidermal growth factor, and okadaic acid activate the Na+/H+ exchanger, NHE-1, by phosphorylating a set of common sites. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19166–19171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and expression of the human growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ antiporter. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90901-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz W., Albus U., Linz W., Martorana P., Lang H. J., Schölkens B. A. Effects of Na+/H+ exchange inhibitors in cardiac ischemia. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1992 Jul;24(7):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(92)93387-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifter J. L., Aronson P. S. Properties and physiologic roles of the plasma membrane sodium-hydrogen exchanger. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):859–864. doi: 10.1172/JCI112671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani M., Bizal G. L., McKinney T. D., Hattabaugh Y. J. Effect of in vitro metabolic acidosis on luminal Na+/H+ exchange and basolateral Na+:HCO3- cotransport in rabbit kidney proximal tubules. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):211–218. doi: 10.1172/JCI115838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taglicht D., Padan E., Schuldiner S. Proton-sodium stoichiometry of NhaA, an electrogenic antiporter from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5382–5387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaichi K., Balkovetz D. F., Van Meir E., Warnock D. G. Cytosolic pH sensitivity of an expressed human NHE-1 Na(+)-H+ exchanger. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 1):C944–C950. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.4.C944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani M., Neely J. R. Role of intracellular Na+ in Ca2+ overload and depressed recovery of ventricular function of reperfused ischemic rat hearts. Possible involvement of H+-Na+ and Na+-Ca2+ exchange. Circ Res. 1989 Oct;65(4):1045–1056. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.4.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzic A., Pucéat M., Clément O., Scamps F., Vassort G. Alpha 1-adrenergic effects on intracellular pH and calcium and on myofilaments in single rat cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:275–292. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Brant S. R., Walker M. S., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Cloning and sequencing of a rabbit cDNA encoding an intestinal and kidney-specific Na+/H+ exchanger isoform (NHE-3). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9340–9346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Levine S. A., Yun C. H., Montrose M. H., Little P. J., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Cloning and expression of a rabbit cDNA encoding a serum-activated ethylisopropylamiloride-resistant epithelial Na+/H+ exchanger isoform (NHE-2). J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11917–11924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Ma A. I., Yang V. W., Watson A. J., Levine S., Montrose M. H., Potter J., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Molecular cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding the rabbit ileal villus cell basolateral membrane Na+/H+ exchanger. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):1957–1967. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07725.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vairo G., Cocks B. G., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Hamilton J. A. Selective suppression of growth factor-induced cell cycle gene expression by Na+/H+ antiport inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19043–19046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne P., Breittmayer J. P., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. Dual control of the intracellular pH in aortic smooth muscle cells by a cAMP-sensitive HCO3-/Cl- antiporter and a protein kinase C-sensitive Na+/H+ antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18023–18029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne P., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. The Na+-dependent regulation of the internal pH in chick skeletal muscle cells. The role of the Na+/H+ exchange system and its dependence on internal pH. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1865–1870. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Fafournoux P., Sardet C., Pouysségur J. The Na+/H+ antiporter cytoplasmic domain mediates growth factor signals and controls "H(+)-sensing". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Sardet C., Fafournoux P., Counillon L., Meloche S., Pagés G., Pouysségur J. Structure function of the growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE1). Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1992;119:157–186. doi: 10.1007/3540551921_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallert M. A., Fröhlich O. Alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation of Na-H exchange in cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):C1096–C1102. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.5.C1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallert M. A., Fröhlich O. Na+-H+ exchange in isolated myocytes from adult rat heart. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):C207–C213. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.2.C207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Orlowski J., Shull G. E. Primary structure and functional expression of a novel gastrointestinal isoform of the rat Na/H exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11925–11928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waser M., Hess-Bienz D., Davies K., Solioz M. Cloning and disruption of a putative NaH-antiporter gene of Enterococcus hirae. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5396–5400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkel G. K., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Ives H. E. Role of cytoplasmic domain of the Na+/H+ exchanger in hormonal activation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3396–3400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun C. H., Gurubhagavatula S., Levine S. A., Montgomery J. L., Brant S. R., Cohen M. E., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Pouyssegur J., Tse C. M., Donowitz M. Glucocorticoid stimulation of ileal Na+ absorptive cell brush border Na+/H+ exchange and association with an increase in message for NHE-3, an epithelial Na+/H+ exchanger isoform. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):206–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]