Abstract
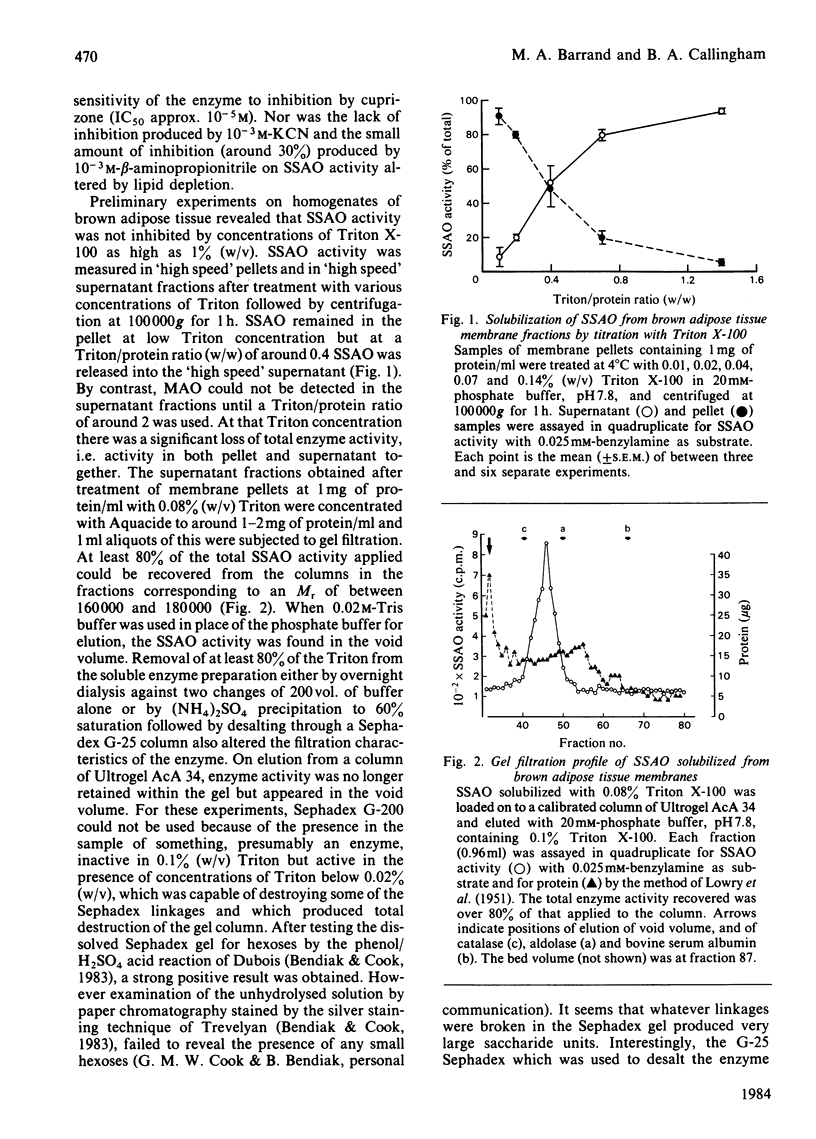
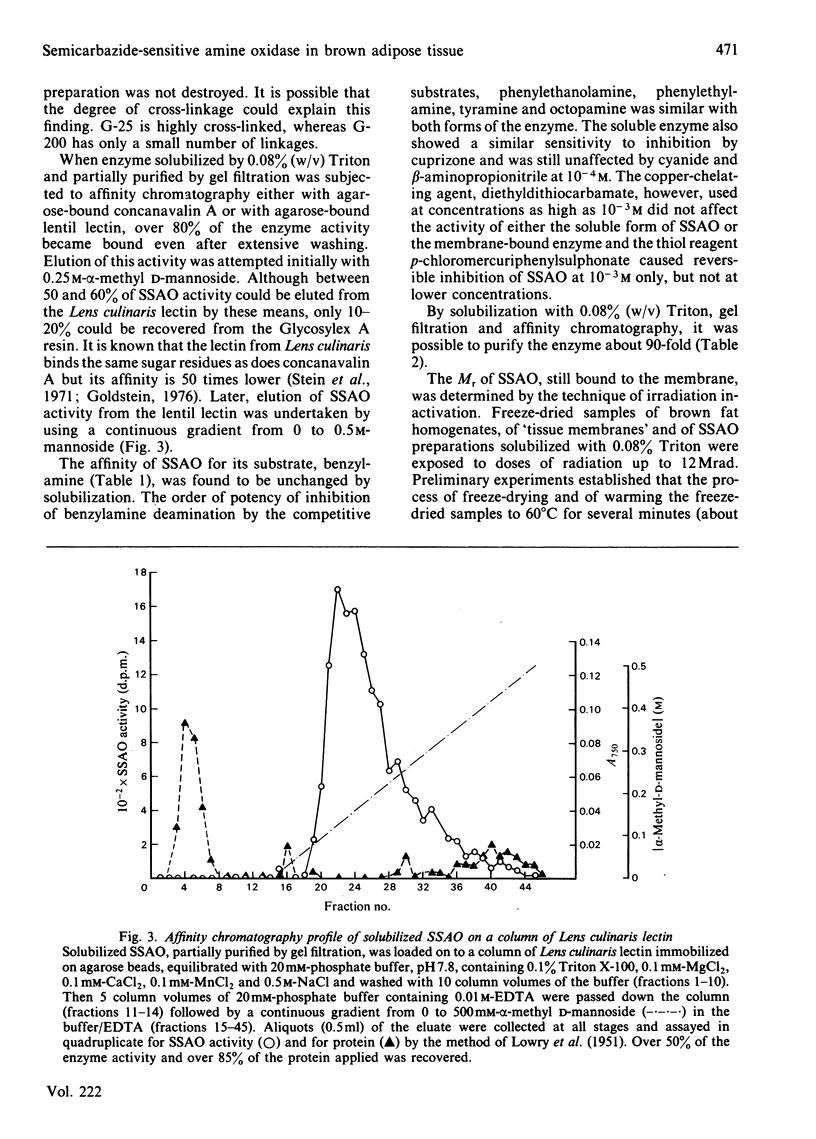
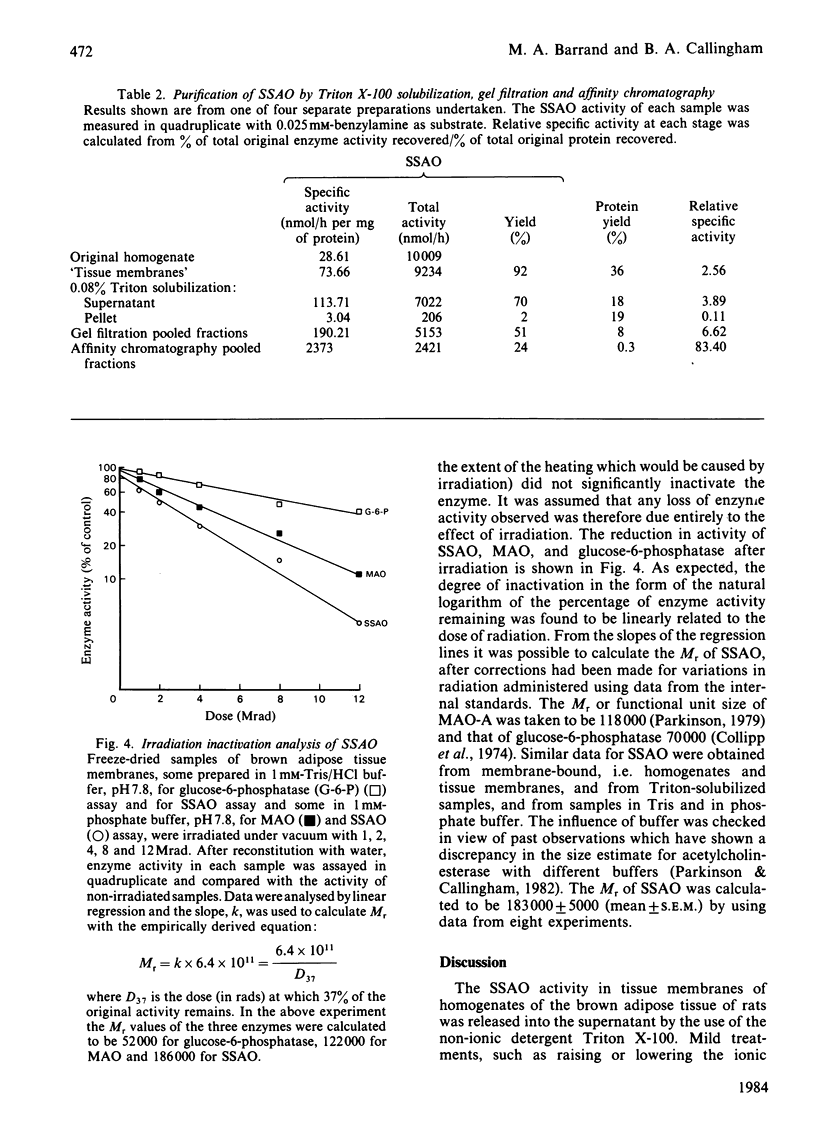
A semicarbazide-sensitive clorgyline-resistant amine oxidase (SSAO) was solubilized from membrane fractions of rat brown adipose tissue by the non-ionic detergent, Triton X-100. Alteration of ionic strength or addition of chelating agents alone failed to release the enzyme from its membrane. Lipid-depletion led to loss of enzyme activity and alteration of substrate affinity. Over 80% of the activity of the solubilized enzyme was found in gel filtration fractions corresponding to an Mr of between 160 000 and 180 000. The glycoprotein nature of SSAO was established from affinity chromatography with either immobilized concanavalin A or Lens culinaris lectin. Elution of over 50% SSAO activity from the lentil lectin was achieved with 0.25M-alpha-methyl D-mannoside to give 80-90-fold purification of the enzyme. Irradiation inactivation gave a value for Mr of around 183 000 for both soluble and membrane-bound SSAO. Substrate affinity and inhibitor sensitivity of the enzyme were unaltered by solubilization. The copper-chelating agent, diethyldithiocarbamate, did not affect the enzyme, shedding doubt on the suggestion that SSAO is a copper-requiring enzyme. The significance of these findings in relation to the nature of SSAO and to its disposition within the cell membrane is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrand M. A., Callingham B. A. Monoamine oxidase activities in brown adipose tissue of the rat: some properties and subcellular distribution. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Jun 15;31(12):2177–2184. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90511-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendiak B., Cook G. M. Comparative rates of transfer of N-acetylneuraminic acid to acceptors bearing one or more Gal(beta 1-4)GlcNAc terminus by the Gal(beta 1-4)GlcNAc(NeuAc-Gal) (alpha 2-6)-sialyltransferase from embryonic chicken liver. Utilization of oligosaccharides as acceptors in sialyltransferase assays. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 1;213(1):253–260. doi: 10.1042/bj2130253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschko H. The natural history of amine oxidases. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1974;70:83–148. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buffoni F. Some contributions to the problem of amine oxidase. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1980 Feb;12(2):101–114. doi: 10.1016/s0031-6989(80)80068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callingham B. A., Laverty R. Studies on the nature of the increased monoamine oxidase activity in the rat heart after adrenalectomy. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1973 Dec;25(12):940–947. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb09983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. E., Lyles G. A., Callingham B. A. A comparison of cardiac and vascular clorgyline-resistant amine oxidase and monoamine oxidase. Inhibition by amphetamine, mexiletine and other drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Jan 1;31(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R. Membrane-bound enzymes and membrane ultrastructure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 3;300(1):1–30. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collipp P. J., Carsten A., Chen S. Y., Thomas J., Maddaiah V. T. Molecular weight of microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase of rat and human liver. Biochem Med. 1974 Aug;10(4):312–319. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(74)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coquil J. F., Goridis C., Mack G., Neff N. H. Monoamine oxidase in rat arteries: evidence for different forms and selective localization. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Aug;48(4):590–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekstedt B., Oreland L. Effect of lipid-depletion on the different forms of monoamine oxidase in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Jan 15;25(2):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90277-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk M. C., Staton A. J., Williams T. J. Heterogeneity of pig plasma amine oxidase: molecular and catalytic properties of chromatographically isolated forms. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3746–3751. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes J. A., Neff N. H. Inhibition by pargyline of cardiovascular amine oxidase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Nov 15;26(22):2107–2112. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes B., Kloepfer H. G., Oi S., Yasunobu K. T. The reaction of sulfhydryl reagents with bovine hepatic monoamine oxidase. Evidence for the presence of two cysteine residues essential for activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 8;438(2):347–357. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. A., Evans W. H. Transverse organization of phospholipids across the bilayer of plasma-membrane subfractions of rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):563–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1740563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kepner G. R., Macey R. I. Membrane enzyme systems. Molecular size determinations by radiation inactivation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 17;163(2):188–203. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewinsohn R., Böhm K., Glover V., Sandler M. A benzylamine oxidase distinct from monoamine oxidase B--widespread distribution in man and rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(14):1857–1863. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles G. A., Garcia-Rodriguez J., Callingham B. A. Inhibitory actions of hydralazine upon monoamine oxidizing enzymes in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Sep 1;32(17):2515–2521. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makita Y. Effects of adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on smooth muscle cells and neuromuscular transmission in the guinea-pig renal artery and vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec;80(4):671–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee S. P., Mukherjee C. Similar activities of nerve growth factor and its homologue proinsulin in intracellular hydrogen peroxide production and metabolism in adipocytes. Transmembrane signalling relative to insulin-mimicking cellular effects. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;31(20):3163–3172. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90545-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano G., Harada M., Nagatsu T. Purification and properties of an amine oxidase in bovine dental pulp and its comparison with serum amine oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 25;341(2):366–377. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norqvist A., Oreland L., Fowler C. J. Some properties of monoamine oxidase and a semicarbazide sensitive amine oxidase capable of the deamination of 5-hydroxytryptamine from porcine dental pulp. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Sep 1;31(17):2739–2744. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson D., Callingham B. A. Irradiation inactivation analysis of acetylcholinesterase and the effect of buffer salts. Radiat Res. 1982 May;90(2):252–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin R., Smith R. A. Phosphoramidates. V. Probable identity of rat liver microsomal glucose 6-phosphatase, phosphoramidase, and phosphoramidate-hexose phosphotransferase. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1748–1755. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Lenard J. Membrane asymmetry. Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):743–753. doi: 10.1126/science.402030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seregi A., Serfözö P., Mergl Z. Evidence for the localization of hydrogen peroxide-stimulated cyclooxygenase activity in rat brain mitochondria: a possible coupling with monoamine oxidase. J Neurochem. 1983 Feb;40(2):407–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb11297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seregi A., Serfözö P., Mergl Z., Schaefer A. On the mechanism of the involvement of monoamine oxidase in catecholamine-stimulated prostaglandin biosynthesis in particulate fraction of rat brain homogenates: role of hydrogen peroxide. J Neurochem. 1982 Jan;38(1):20–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb10849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sourkes T. L. Copper, biogenic amines, and amine oxidases. Ciba Found Symp. 1980;79:143–156. doi: 10.1002/9780470720622.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein M. D., Howard I. K., Sage H. J. Studies on a phytohemagglutinin from the lentil. IV. Direct binding studies of Lens culinaris hand myoglobin derivatives. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Sep;146(1):353–355. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(71)80074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong J. H., Limson-Zamora M., D'Iorio A., Bégin-Heick N. Liver monoamine oxidase in the obese-hyperglycaemic (ob/ob) mouse. Biochem J. 1979 Mar 1;177(3):943–949. doi: 10.1042/bj1770943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. L., Plummer D. T. Multiple forms of acetylcholinesterase from human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):521–527. doi: 10.1042/bj1330521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMADA H., YASUNOBU K. T. Monoamine oxidase. II. Copper, one of the prosthetic groups of plasma monoamine oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3077–3082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasunobu K. T., Ishizaki H., Minamiura N. The molecular mechanistic and immunological properties of amine oxidases. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Oct 30;13(1):3–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01732392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Carmen Urdin M., Fuentes J. A. Enzyme activity of an amine oxidase to pargyline in the cardiovascular system of hypertensive rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Aug 1;32(15):2345–2347. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


