Abstract
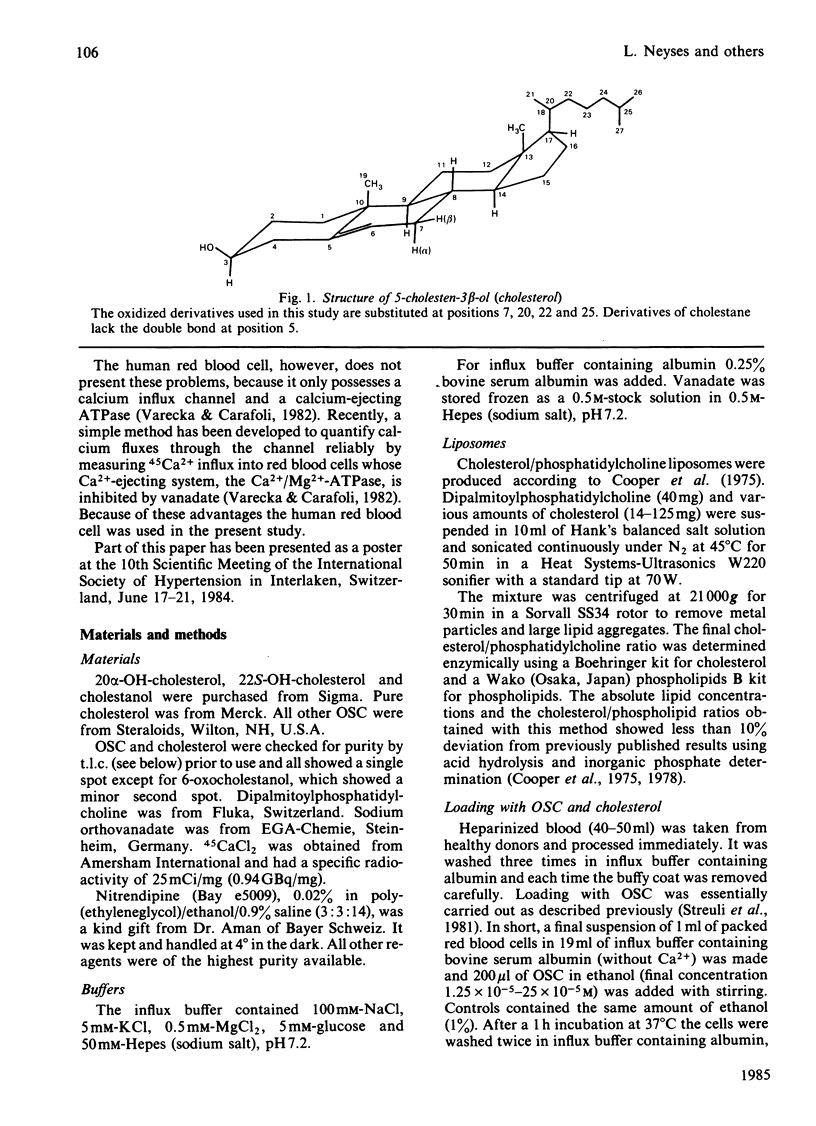
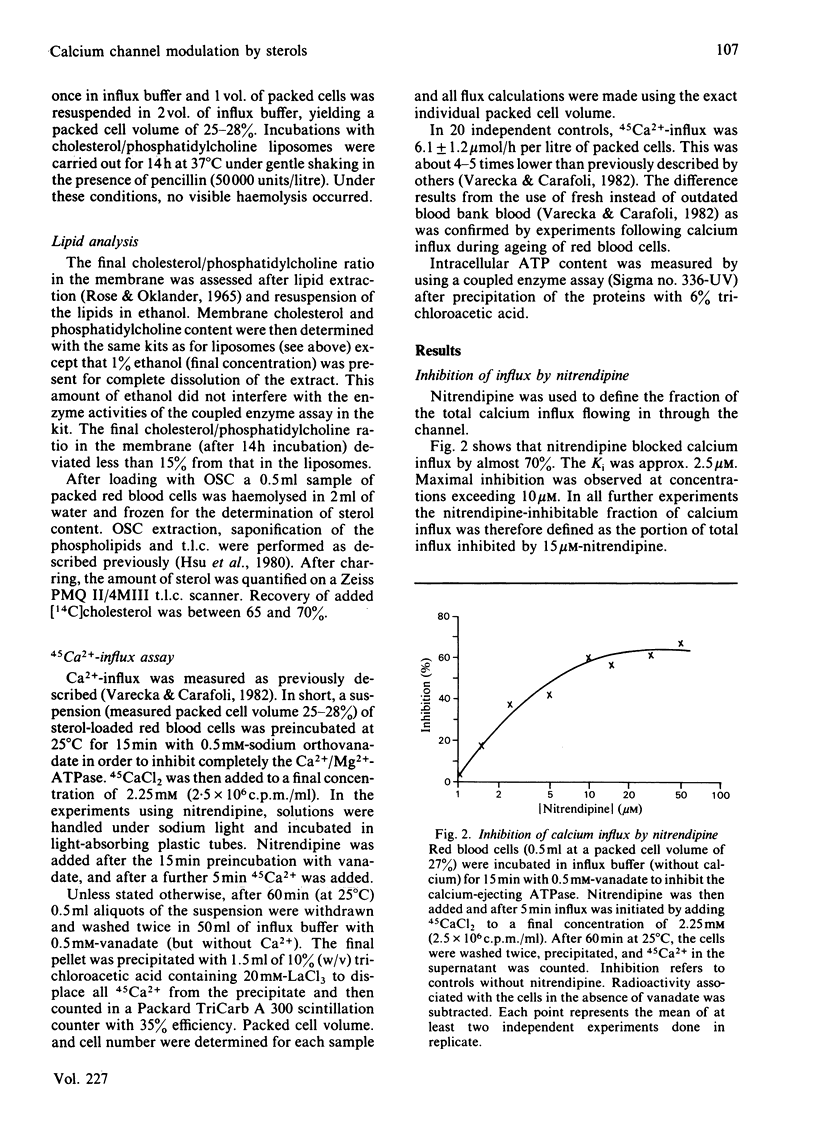
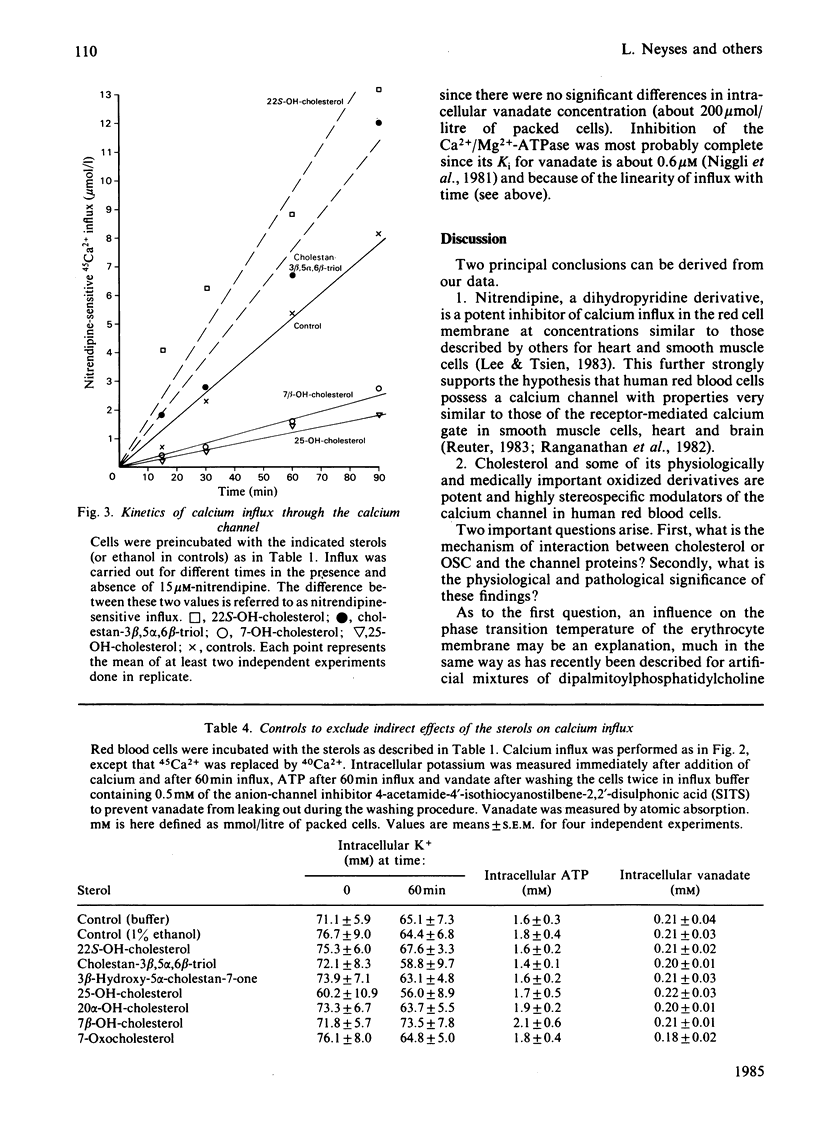
To study the effect of cholesterol and its pathophysiologically important oxidized derivatives (OSC) on the calcium entry channel, the human red blood cell was used as a model system. The calcium ejecting adenosinetriphosphatase (ATPase) was inhibited by vanadate. The cells were loaded with OSC at concentrations between 1.25 X 10(-5) and 25 X 10(-5) mol/l. 22-Hydroxycholesterol, cholestan-3 beta,5 alpha,6 beta-triol, 5 alpha-cholestan-3 beta-ol,3 beta,5 alpha-dihydroxycholestan-6-one and 3 beta-hydroxy-5 alpha-cholestan-7-one stimulated 45Ca2+ influx by up to almost 90%, whereas 25-hydroxycholesterol, 7 beta-hydroxycholesterol, 20 alpha-hydroxycholesterol and 7-oxocholesterol inhibited influx by up to 75%. Both stimulation and inhibition were dependent on the amount of OSC incorporated into the membrane. More than 90% of the total modification of calcium influx by OSC was accounted for by an influence on the nitrendipine-inhibitable part of influx. Enrichment of cholesterol in the membrane greatly stimulated, and cholesterol depletion inhibited, Ca2+ influx. These results demonstrate that cholesterol and its oxidized derivatives are able to modulate the calcium channel in human red blood cells in a highly stereospecific manner.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks C. J., Steel G., Gilbert J. D., Harland W. A. Lipids of human atheroma. 4. Characterisation of a new group of polar sterol esters from human atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis. 1971 Mar-Apr;13(2):223–237. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(71)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Arner E. C., Wiley J. S., Shattil S. J. Modification of red cell membrane structure by cholesterol-rich lipid dispersions. A model for the primary spur cell defect. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):115–126. doi: 10.1172/JCI107901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Leslie M. H., Fischkoff S., Shinitzky M., Shattil S. J. Factors influencing the lipid composition and fluidity of red cell membranes in vitro: production of red cells possessing more than two cholesterols per phospholipid. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):327–331. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egli U. H., Streuli R. A., Dubler E. Influence of oxygenated sterol compounds on phase transitions in model membranes. A study by differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 3;23(1):148–152. doi: 10.1021/bi00296a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröberg S. O. Concentration of cholesterol and triglycerides in skeletal muscle of healthy men and myocardial infarction patients. Acta Med Scand. 1973 Dec;194(6):553–558. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1973.tb19491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. H., Eanes E. D. On phase transitions in erythrocyte membranes and extracted membrane lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 24;373(3):519–522. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu R. C., Kanofsky J. R., Yachnin S. The formation of echinocytes by the insertion of oxygenated sterol compounds into red cell membranes. Blood. 1980 Jul;56(1):109–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai H., Werthessen N. T., Subramanyam V., LeQuesne P. W., Soloway A. H., Kanisawa M. Angiotoxicity of oxygenated sterols and possible precursors. Science. 1980 Feb 8;207(4431):651–653. doi: 10.1126/science.7352277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandutsch A. A., Chen H. W. Consequences of blocked sterol synthesis in cultured cells. DNA synthesis and membrane composition. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):409–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandutsch A. A., Chen H. W. Regulation of sterol synthesis in cultured cells by oxygenated derivatives of cholesterol. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Apr;85(2 Pt 2 Suppl 1):415–424. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of calcium channel blockade by verapamil, D600, diltiazem and nitrendipine in single dialysed heart cells. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):790–794. doi: 10.1038/302790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. J. Cholesterol content of the human atrium is related to plasma lipoprotein levels. Atherosclerosis. 1979 Nov;34(3):349–351. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(79)80013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Adunyah E. S., Penniston J. T., Carafoli E. Purified (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase of the erythrocyte membrane. Reconstitution and effect of calmodulin and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):395–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE H. G., OKLANDER M. IMPROVED PROCEDURE FOR THE EXTRACTION OF LIPIDS FROM HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:428–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan S., Harmony J. A., Jackson R. J. Effect of Ca2+ blocking agents on the metabolism of low density lipoproteins in human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 16;107(1):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91691-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):569–574. doi: 10.1038/301569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroepfer G. J., Jr Sterol biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:585–621. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Boss K. Band 3 protein-cholesterol interactions in erythrocyte membranes. Possible role in anion transport and dependency on membrane phospholipid. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 13;150(1):4–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81295-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli R. A., Kanofsky J. R., Gunn R. B., Yachnin S. Diminished osmotic fragility of human erythrocytes following the membrane insertion of oxygenated sterol compounds. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):317–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka R. D., Edwards P. A., Lan S. F., Fogelman A. M. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity in avian myeloblasts. Mode of action of 25-hydroxycholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13331–13339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. B., Peng S. K., Werthessen N. T., Tham P., Lee K. T. Spontaneously occurring angiotoxic derivatives of cholesterol. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):40–57. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varecka L., Carafoli E. Vanadate-induced movements of Ca2+ and K+ in human red blood cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7414–7421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yachnin S., Streuli R. A., Gordon L. I., Hsu R. C. Alteration of peripheral blood cell membrane function and morphology by oxygenated sterols; a membrane insertion hypothesis. Curr Top Hematol. 1979;2:245–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


