Abstract
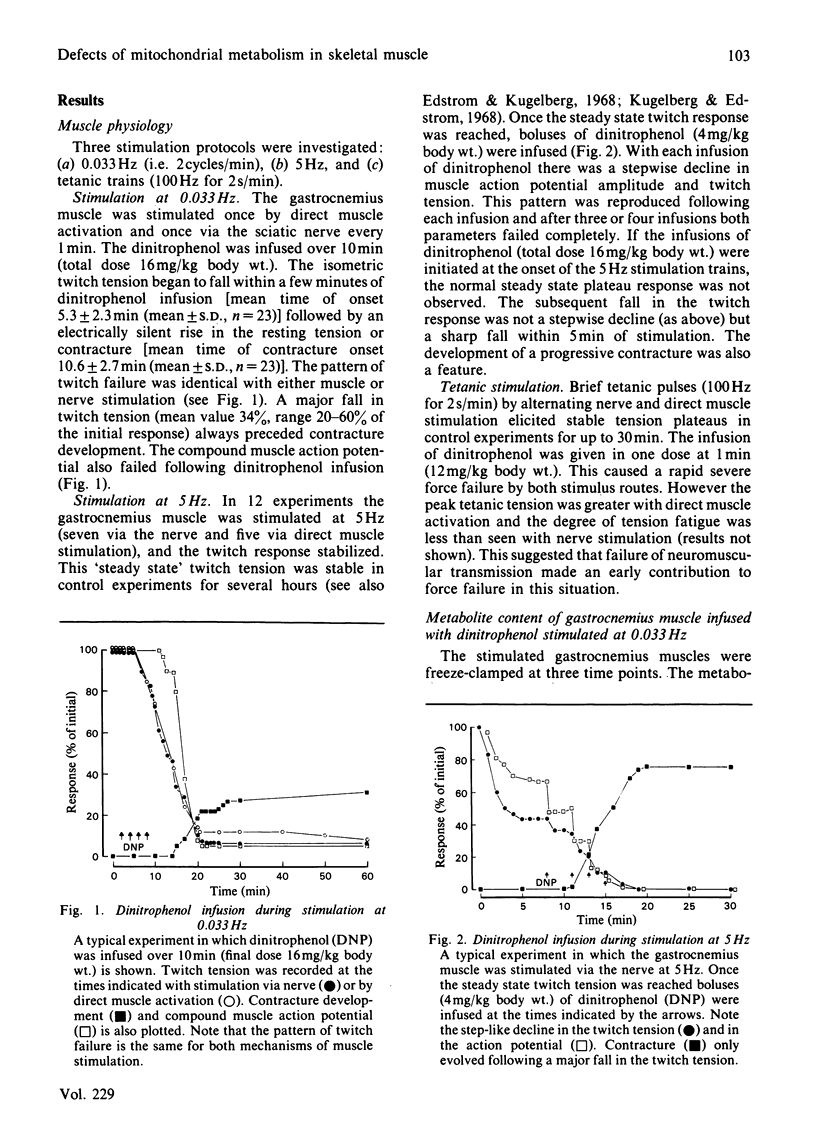
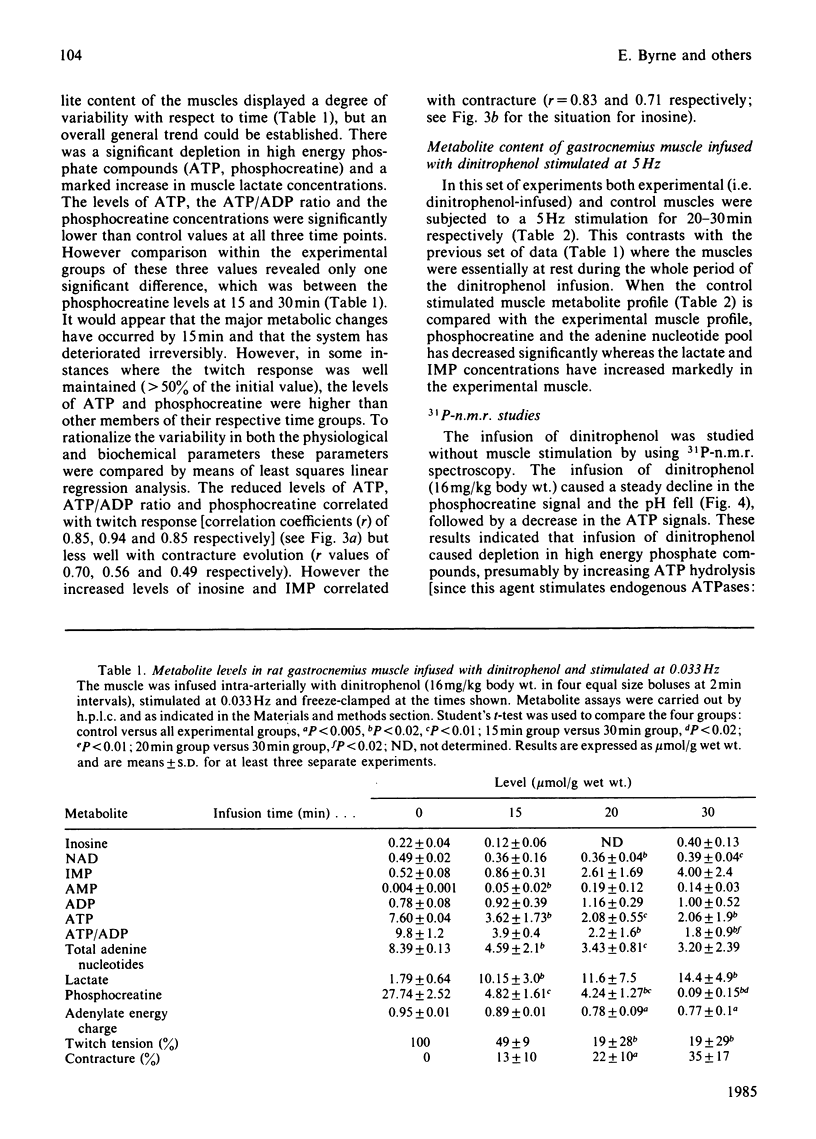
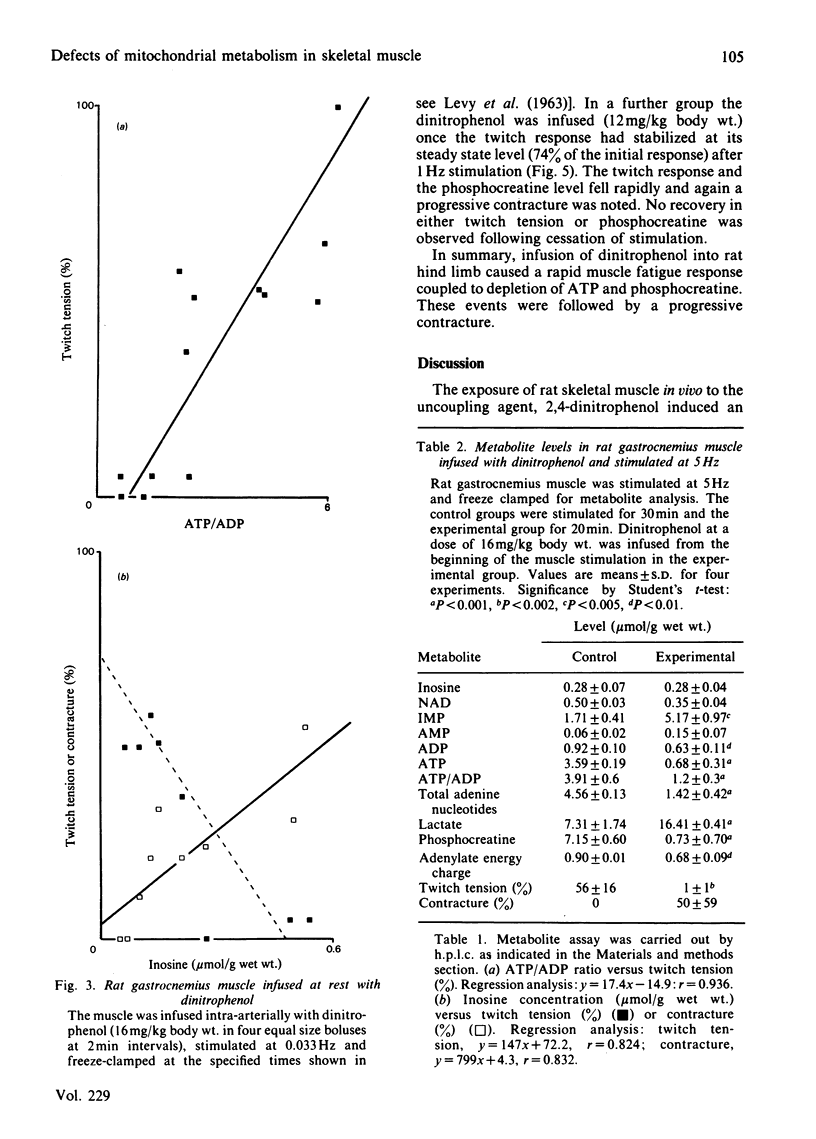
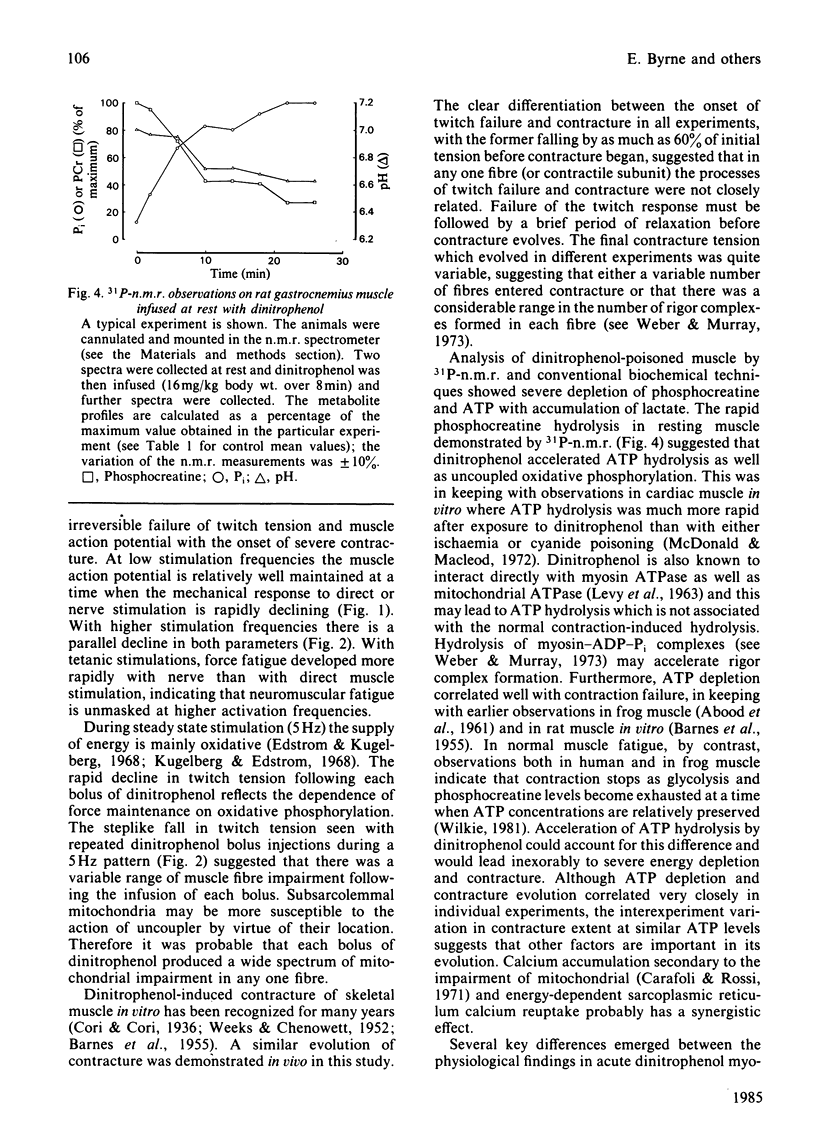
Infusion of dinitrophenol intra-arterially into rat hind limb caused an irreversible failure of isometric twitch tension and the induction of a severe progressive contracture. Metabolite analysis of muscle in which the twitch response had grossly fatigued revealed low levels of ATP and phosphocreatine together with lactate accumulation. Studies using 31P-n.m.r. confirmed the decrease in ATP and creatine phosphate concentrations and indicated a fall in intracellular pH. It is concluded that dinitrophenol-induced myopathy does not represent a good model for the human mitochondrial myopathic condition as has been previously suggested.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABOOD L. G., KOKETSU K., NODA K. Effect of dinitrophenol on phosphorylation and bioelectric phenomena of excitable tissues. Am J Physiol. 1961 Mar;200:431–436. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.3.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman J. J., Grove T. H., Wong G. G., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K. Mapping of metabolites in whole animals by 31P NMR using surface coils. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):167–170. doi: 10.1038/283167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNES J. M., DUFF J. I., THRELFALL C. J. The behaviour of mammalian striated muscle in the presence of 2:4-dinitrophenol. J Physiol. 1955 Dec 29;130(3):585–600. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson M. J., Gadian D. G., Wilkie D. R. Mechanical relaxation rate and metabolism studied in fatiguing muscle by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:465–484. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström L., Kugelberg E. Histochemical composition, distribution of fibres and fatiguability of single motor units. Anterior tibial muscle of the rat. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):424–433. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugelberg E., Edström L. Differential histochemical effects of muscle contractions on phosphorylase and glycogen in various types of fibres: relation to fatigue. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):415–423. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. M., LEBER P. D., RYAN E. M. INACTIVATION OF MYOSIN BY 2,4-DINITROPHENOL AND PROTECTION BY ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE AND OTHER PHOSPHATE COMPOUNDS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3654–3659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT R., IKKOS D., PALMIERI G., ERNSTER L., AFZELIUS B. A case of severe hypermetabolism of nonthyroid origin with a defect in the maintenance of mitochondrial respiratory control: a correlated clinical, biochemical, and morphological study. J Clin Invest. 1962 Sep;41:1776–1804. doi: 10.1172/JCI104637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lush C., Rahim Z. H., Perreitt D., Griffiths J. R. A microprocedure for extracting tissue nucleotides for analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):227–232. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. F., MacLeod D. P. The effect of 2,4-dinitrophenol on electrical and mechanical activity, metabolism and ion movements in guinea-pig ventricular muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Apr;44(4):711–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb07309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melmed C., Karpati G., Carpenter S. Experimental mitochondrial myopathy produced by in vivo uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation. J Neurol Sci. 1975 Nov;26(3):305–318. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. A., Kuchmerick M. J., Brown T. R. Application of 31P-NMR spectroscopy to the study of striated muscle metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):C1–11. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. B., Richards J. H. Determination of intracellular pH by 31P magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7276–7278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan-Hughes J. A., Darveniza P., Kahn S. N., Landon D. N., Sherratt R. M., Land J. M., Clark J. B. A mitochondrial myopathy characterized by a deficiency in reducible cytochrome b. Brain. 1977 Dec;100(4):617–640. doi: 10.1093/brain/100.4.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahgal V., Subramani V., Hughes R., Shah A., Singh H. On the pathogenesis of mitochondrial myopathies. An experimental study. Acta Neuropathol. 1979 May 15;46(3):177–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00690841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoubridge E. A., Radda G. K. A 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance study of skeletal muscle metabolism in rats depleted of creatine with the analogue beta-guanidinopropionic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 14;805(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEEKS J. R., CHENOWETH M. B. A stationary manometric respirometer for isolated rat diaphragm allowing simultaneous direct registration of mechanical activity; observations with sodium azide and dinitrophenol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1952 Feb;104(2):187–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Murray J. M. Molecular control mechanisms in muscle contraction. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jul;53(3):612–673. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.3.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles C. M., Jones D. A., Edwards R. H. Fatigue in human metabolic myopathy. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;82:264–282. doi: 10.1002/9780470715420.ch16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie D. Shortage of chemical fuel as a cause of fatigue: studies by nuclear magnetic resonance and bicycle ergometry. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;82:102–119. doi: 10.1002/9780470715420.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jesus P. V. Neuromuscular physiology in Luft's syndrome. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1974 Jan-Feb;14(1):17–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


