Abstract
The activity of the template-engaged form of RNA polymerase I from livers of adrenalectomized rats was about 50-60% of that of normal control rats, and increased about 2-fold at 6 h after the administration of dexamethasone. However, no change was found in the activity of the 'free' form of RNA polymerase I or the template-engaged form of RNA polymerase II. Immunochemical studies using guinea-pig anti-(RNA polymerase I) serum disclosed that the total number of RNA polymerase I molecules did not vary during the treatment with dexamethasone. Cycloheximide caused a rapid decrease in the template-engaged form of RNA polymerase I activity in normal rats and in dexamethasone-treated (6 h) adrenalectomized rats, to the value in adrenalectomized rats, but affected it only slightly in adrenalectomized rats. The elongation rate of rRNA-precursor synthesis in liver nuclei was not affected by a change in the concentration of circulating dexamethasone. From these results, it is concluded that about half the rRNA-precursor synthesis in rat liver is regulated by glucocorticoids, probably through the synthesis of short-lived protein(s) which may play a role in conversion of the 'dormant' form of RNA polymerase I into the 'engaged' form.
Full text
PDF

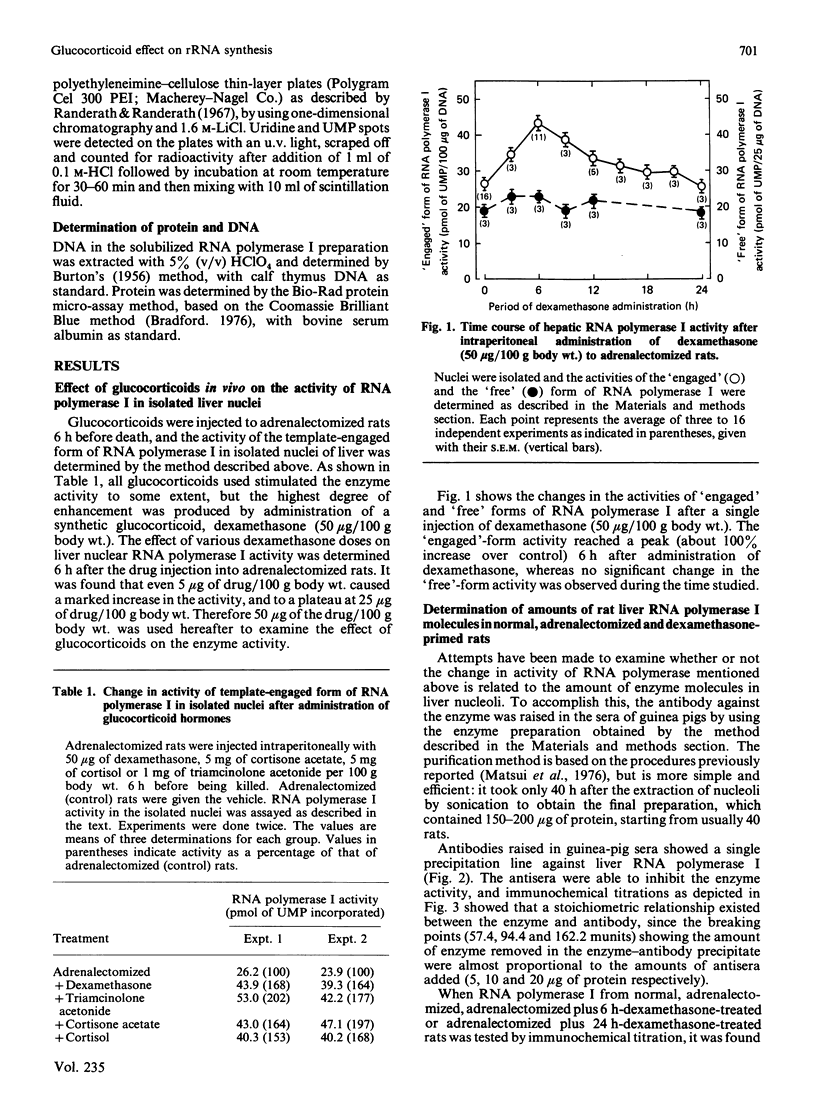
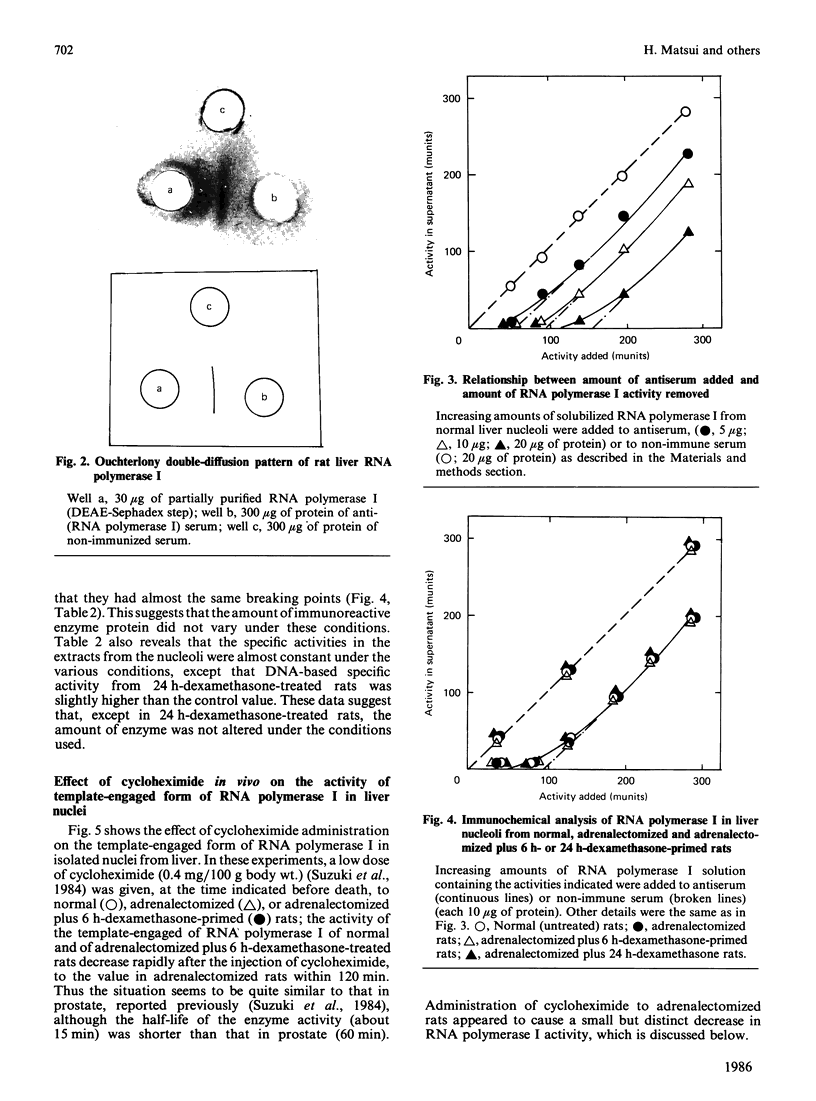
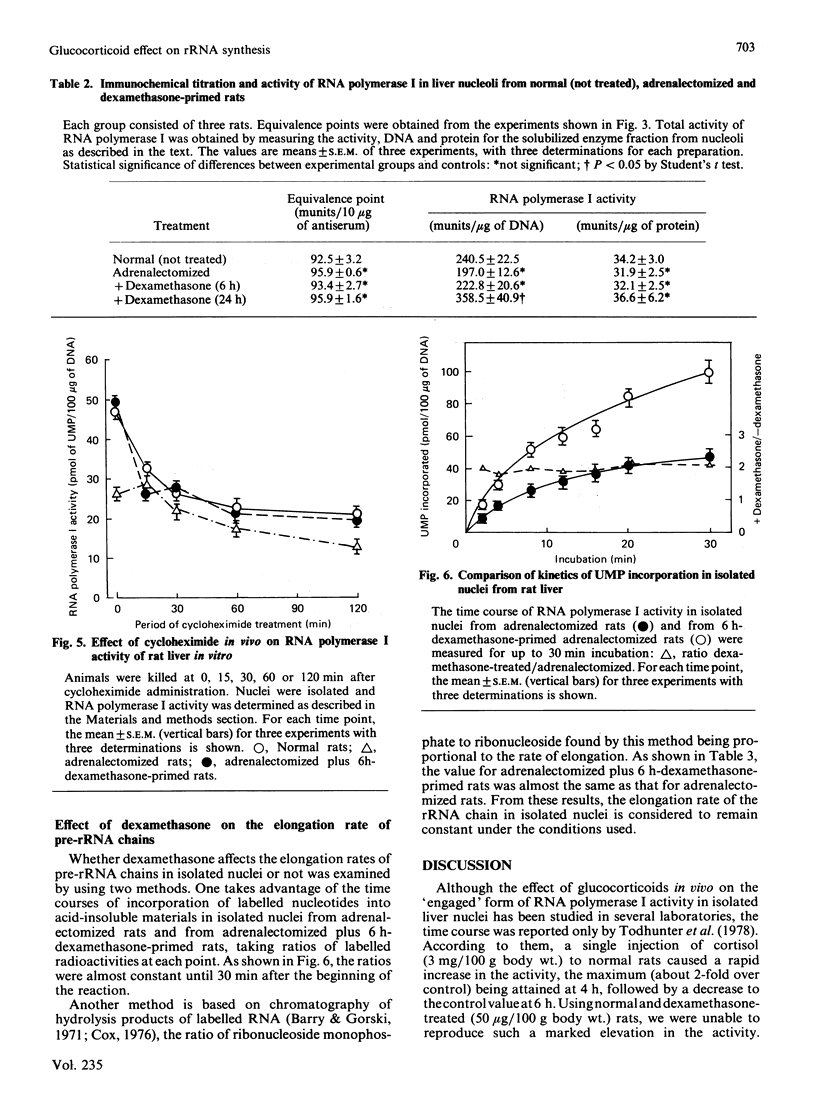


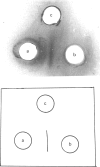
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen M. W., Ballal N. R., Busch H. Nucleoli of thioacetamide-treated liver as a model for studying regulation of preribosomal RNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry J., Gorski J. Uterine ribonucleic acid polymerase. Effect of estrogen on nucleotide incorporation into 3' chain termini. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 8;10(12):2384–2390. doi: 10.1021/bi00788a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell P. A., Borthwick N. M. Regulation of transcription in rat thymus cells by glucocorticoids. J Steroid Biochem. 1979 Jul;11(1B):381–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(79)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benecke B. J., Ferencz A., Seifart K. H. Resistance of hepatic RNA polymerases to compounds effecting RNA and protein synthesis in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1973 Apr 1;31(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthwick N. M., Bell P. A. Early glucocorticoid-dependent stimulation of RNA polymerase B in rat thymus cells. FEBS Lett. 1975 Dec 15;60(2):396–399. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80757-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthwick N. M., Bell P. A. Glucocorticoid regulation of rat thymus RNA polymerase activity: the role of RNA and protein synthesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1978 Jan;9(3):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(78)90069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh A. H., Thompson E. A., Jr Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA: glucocorticoid effects upon initiation and elongation in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3357–3369. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavannaugh A. H., Thompson E. A., Jr Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA. Inhibition of transcription during glucocorticoid-mediated inhibition of proliferation of lymphosarcoma P1798 cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9768–9773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P. Eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:613–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. F. Quantitation of elongating form A and B RNA polymerases in chick oviduct nuclei and effects of estradiol. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabeva M. D., Dineva B. B., Ikonomova R. N. Ribosomal RNA synthesis in liver of adrenalectomized rats after partial hepatectomy. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1984 Mar;8(3):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(84)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabeva M. D., Ikonomova R. N. Acceleration of ribosome formation in rat liver in response to hydrocortisone. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Nov-Dec;28(3):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmus M. E., Bonner J. Increased template activity of liver chromatin, a result of hydrocortisone administration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Nov;54(5):1370–1375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.5.1370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembinski T. C., Bell P. A. Glucocorticoids modify the rate of ribosomal RNA synthesis in rat thymus cells by regulating the polymerase elongation rate. J Steroid Biochem. 1984 Nov;21(5):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. L., Farmar R. Differential effects of cycloheximide on protein and RNA synthesis as a function of dose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 2;51(3):626–630. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franze-Fernańdez M. T., Fontanive-Sengüesa A. V. Effect of amino acids on the alpha-amanitin-insensitive RNA polymerase activity in the isolated nuclei of Ehrlich ascites cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 26;331(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90420-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey A., Seifart K. H. Glucocorticoids directly affect the synthesis of ribosomal RNA in rat-liver cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Oct;28(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenman D. L., Wicks W. D., Kenney F. T. Stimulation of ribonucleic acid synthesis by steroid hormones. II. High molecular weight components. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4420–4426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K. J., Pogo A. O. Control mechanism of ribonucleic acid synthesis in eukaryotes. The effect of amino acid and glucose starvation and cycloheximide on yeast deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):568–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Grummt F. Control of nucleolar RNA synthesis by the intracellular pool sizes of ATP and GTP. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):447–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haim L., Iapalucci-Espinoza S., Conde R., Franze-Fernández M. T. Control of activation of liver RNA polymerase I occurring after re-feeding of protein-depleted mice. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):837–844. doi: 10.1042/bj2100837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallahan C., Young D. A., Munck A. Time course of early events in the action of glucocorticoids on rat thymus cells in vitro. Synthesis and turnover of a hypothetical cortisol-induced protein inhibition of glucose metabolism and of a presumed ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2922–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashinakagawa T., Muramatsu M., Sugano H. Isolation of nucleoli from rat liver in the presence of magnesium ions. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Mar;71(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoya T., Nagai Y., Inagaki T., Hayashi M. In vivo effect of androgen and cycloheximide on the RNA synthesis in isolated nuclei of rat ventral prostates. J Biochem. 1978 Dec;84(6):1519–1528. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Sajdel E. M., Munro H. N. Regulation of nucleolar RNA metabolism by hydrocortisone. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):449–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert A., Feigelson P. A short lived polypeptide component of one of two discrete functional pools of hepatic nuclear alpha-amanitin resistant RNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jun 18;58(4):1030–1038. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80247-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard T. B., Jacob S. T. Alterations in DNA-dependent RNA polymerase I and II from rat liver by thioacetamide: preferential increase in the level of chromatin-associated nucleolar RNA polymerase IB. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4538–4544. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., O'Malley A. F., Puglisi B. Inhibition of nucleoplasmic transcription and the translation of rapidly labeled nuclear proteins by low concentrations of actinomycin D in vivo. Proposed role of messenger RNA in ribosomal RNA transcription. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1154–1160. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Onishi T., Muramatsu M. Nucleolar DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from rat liver. 1. Purification and subunit structure. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):351–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Matsui T., Muramatsu M. The mechanism of decrease in nucleolar RNA synthesis by protein synthesis inhibition. J Biochem. 1979 Mar;85(3):807–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Shimada N., Higashinakagawa T. Effect of cycloheximide on the nucleolar RNA synthesis in rat liver. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):91–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Numa S. Purification of rat liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase and immunochemical studies on its synthesis and degradation. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;16(1):161–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolette J. A., Babler M. The role of protein in the estrogen-stimulated in vitro RNA synthesis of isolated rat uterine nucleoli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jul;163(1):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90476-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi T., Matsui T., Muramatsu M. Effect of cycloheximide on the nucleolar RNA synthesis in rat liver. Changes in RNA polymerase I and nucleolar template activity. J Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(4):1109–1119. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrone-Bizzozero N., Iapalucci-Espinoza S., Medrano E. E., Franze-Fernández M. T. Transcription of ribosomal RNA is differentially controlled in resting and growing BALB/c 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jul;124(1):160–164. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041240125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdel E. M., Jacob S. T. Mechanism of early effect of hydrocortisone on the transcriptional process: stimulation of the activities of purified rat liver nucleolar RNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):707–715. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoyanova B. B., Dabeva M. D. Ribosomal RNA precursor transcription in rat liver is not dependent on continuous synthesis of proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 29;608(2):358–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Hosoya T., Igarashi T., Muramatsu M. Changes in template-engaged and free RNA polymerase I activities in isolated nuclei from rat ventral prostates after treatment with testosterone and cycloheximide. J Biochem. 1984 May;95(5):1389–1398. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Matsui H., Hosoya T. Effects of androgen and polyamines on the phosphorylation of nucleolar proteins from rat ventral prostates with particular reference to 110-kDa phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8050–8055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUKADA K., LIEBERMAN I. LIVER NUCLEAR RIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE FORMED AFTER PARTIAL HEPATECTOMY. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1731–1736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Widnell C. C. Ribonucleic acid synthesis during the early action of thyroid hormones. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):604–620. doi: 10.1042/bj0980604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todhunter J. A., Weissbach H., Brot N. Modification of rat liver RNA polymerase I after in vivo stimulation by hydrocortisone or methylisobutylxanthine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4514–4516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. L., Feigelson P. A proposed model for the glucocorticoidal regulation of rat hepatic ribosomal RNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):754–760. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. L., Feigelson P. Cortisone stimulation of nucleolar RNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2177–2180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. L., Feigelson P. The rapid turnover of RNA polymerase of rat liver nucleolus, and of its messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]