Abstract
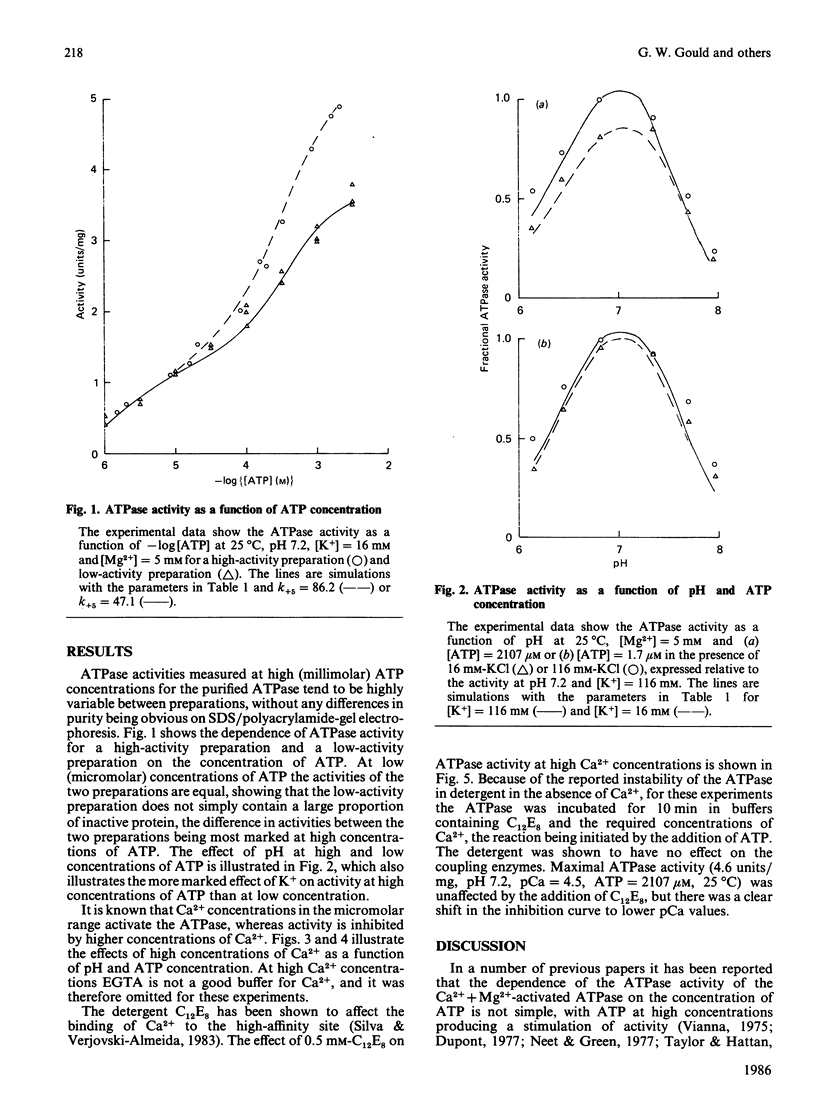
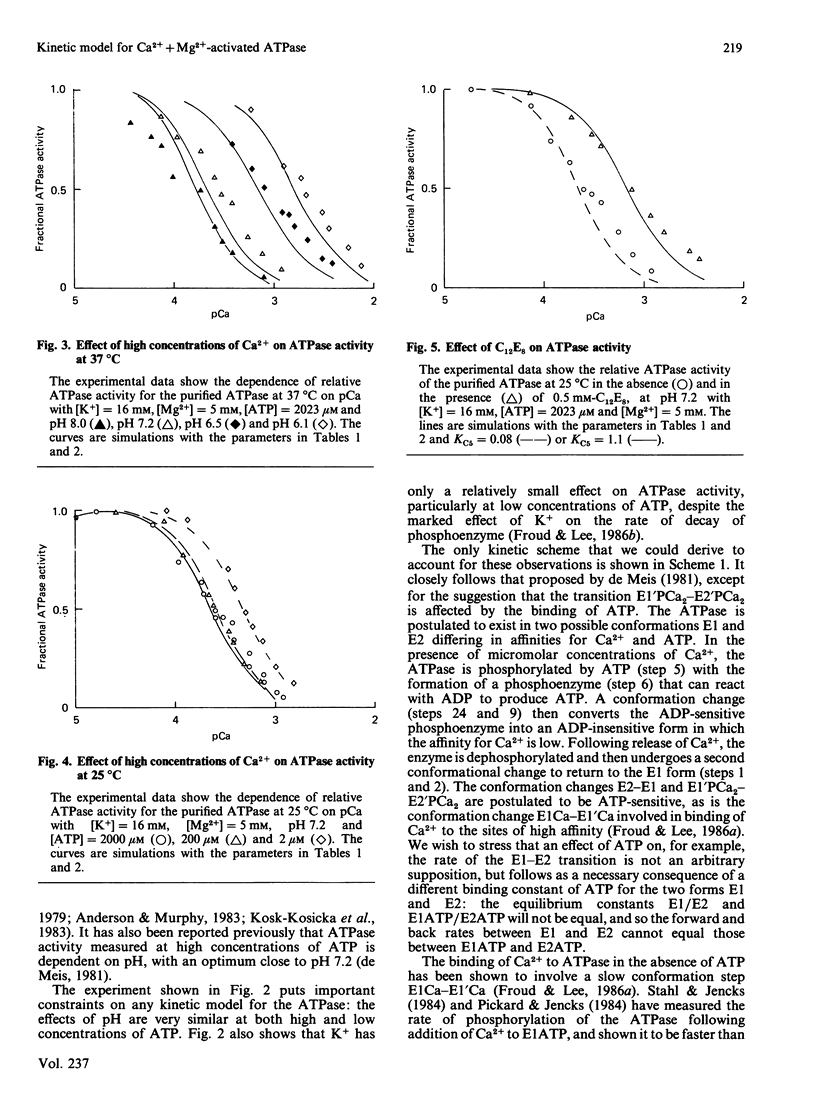
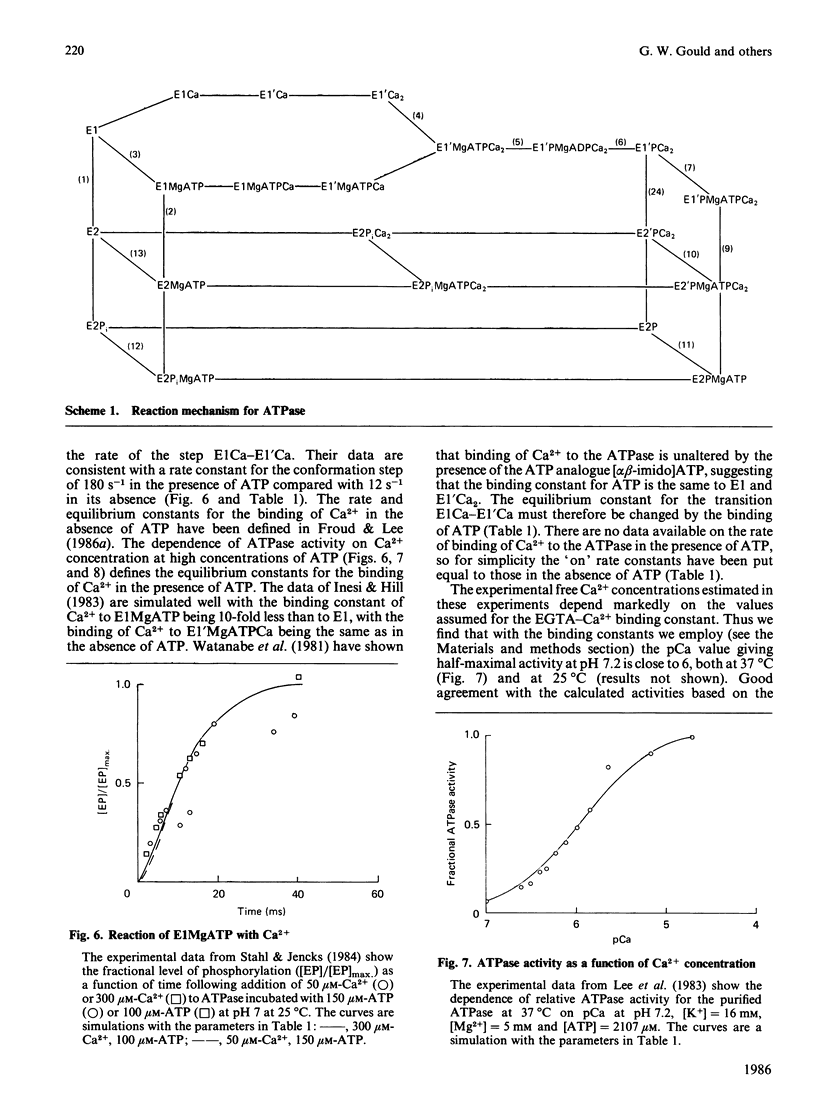
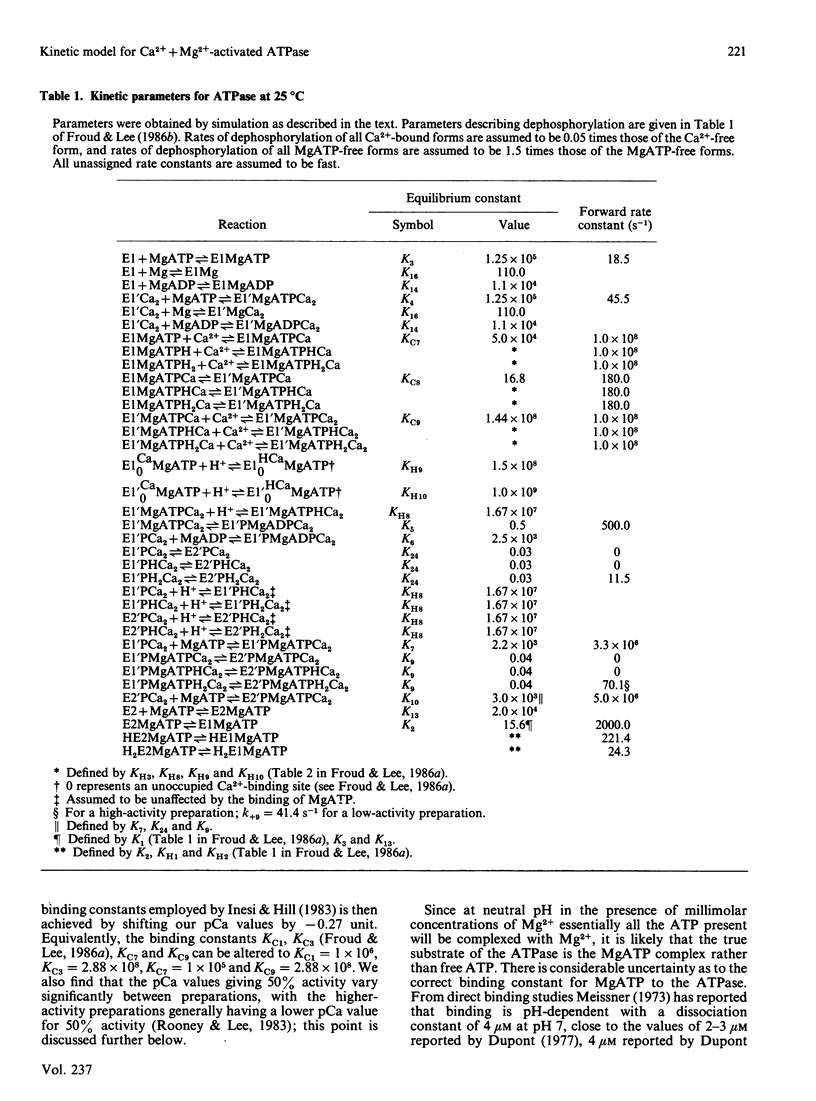
The Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum exhibits complex kinetics of activation with respect to ATP. ATPase activity is pH-dependent, with similar pH-activity profiles at high and low concentrations of ATP. Low concentrations of Ca2+ in the micromolar range activate the ATPase, whereas activity is inhibited by Ca2+ at millimolar concentrations. The pH-dependence of this Ca2+ inhibition and the effect of the detergent C12E8 (dodecyl octaethylene glycol monoether) on Ca2+ inhibition are similar to those observed on activation by low concentrations of Ca2+. On the basis of these and other studies we present a kinetic model for the ATPase. The ATPase is postulated to exist in one of two conformations: a conformation (E1) of high affinity for Ca2+ and MgATP and a conformation (E2) of low affinity for Ca2+ and MgATP. Ca2+ binding to E2 and to the phosphorylated form E2P are equal. Proton binding at the Ca2+-binding sites in the E1 and E2 conformations explains the pH-dependence of Ca2+ effects. Binding of MgATP to the phosphorylated intermediate E1'PCa2 and to E2 modulate the rates of the transport step E1'PCa-E2'PCa2 and the return of the empty Ca2+ sites to the outside surface of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, as well as the rate of dephosphorylation of E2P. Only a single binding site for MgATP is postulated.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J. P., Lassen K., Møller J. V. Changes in Ca2+ affinity related to conformational transitions in the phosphorylated state of soluble monomeric Ca2+-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):371–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J. P., Møller J. V., Jørgensen P. L. The functional unit of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Active site titration and fluorescence measurements. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8300–8307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J. P., Møller J. V. The role of Mg2+ and Ca2+ in the simultaneous binding of vanadate and ATP at the phosphorylation site of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 26;815(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. W., Murphy A. J. Alterations in the structure of the ribose moiety of ATP reduce its effectiveness as a substrate for the sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14276–14278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. E., Johnson J. D., Berman M. C. Transient kinetic analysis of turnover-dependent fluorescence of 2',3'-O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-ATP bound to Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15163–15171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho-Alves P. C., Oliveira C. R., Verjovski-Almeida S. Stoichiometric photolabeling of two distinct low and high affinity nucleotide sites in sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4282–4287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A. An automatic method for deriving steady-state rate equations. Biochem J. 1977 Jul 1;165(1):55–59. doi: 10.1042/bj1650055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Y., Chapron Y., Pougeois R. Titration of the nucleotide binding sites of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ -ATPase with 2',3'-O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) adenosine 5'-triphosphate and 5'-diphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1272–1279. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91250-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Y. Kinetics and regulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan 3;72(1):185–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
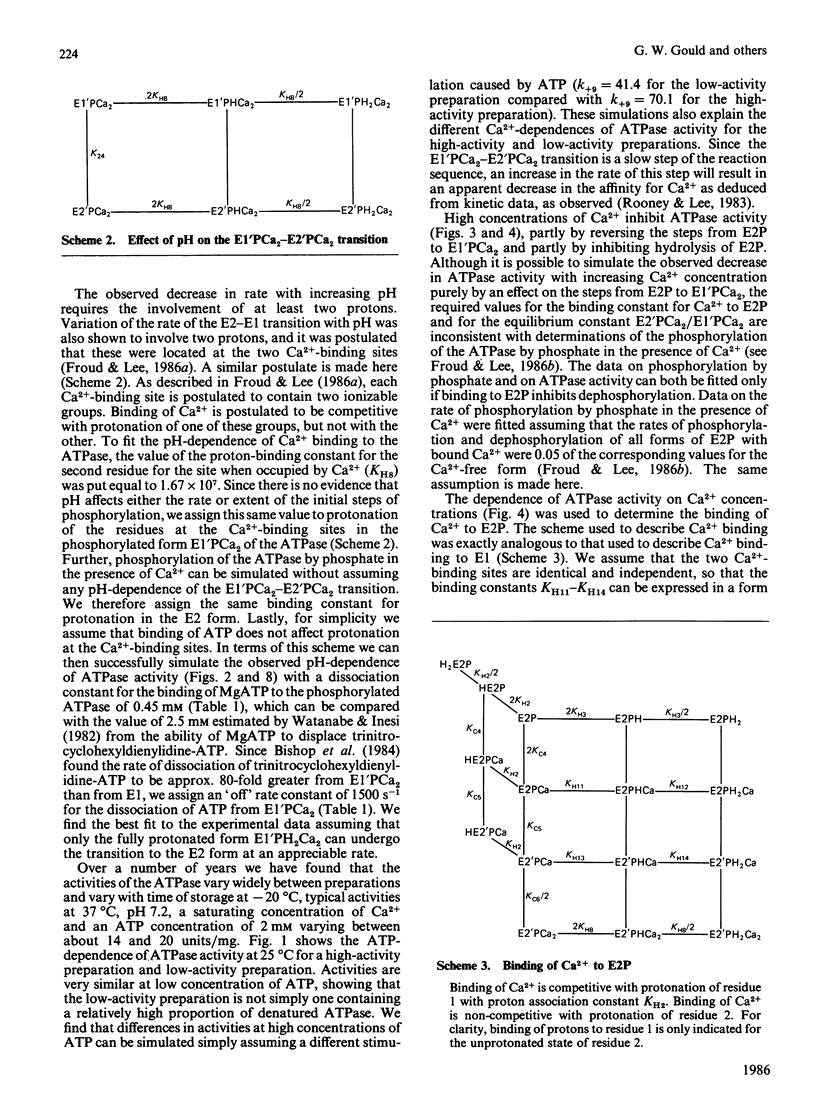
- Fernandez-Belda F., Kurzmack M., Inesi G. A comparative study of calcium transients by isotopic tracer, metallochromic indicator, and intrinsic fluorescence in sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9687–9698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehlich J. P., Heller P. F. Transient-state kinetics of the ADP-insensitive phosphoenzyme in sarcoplasmic reticulum: implications for transient-state calcium translocation. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):126–136. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
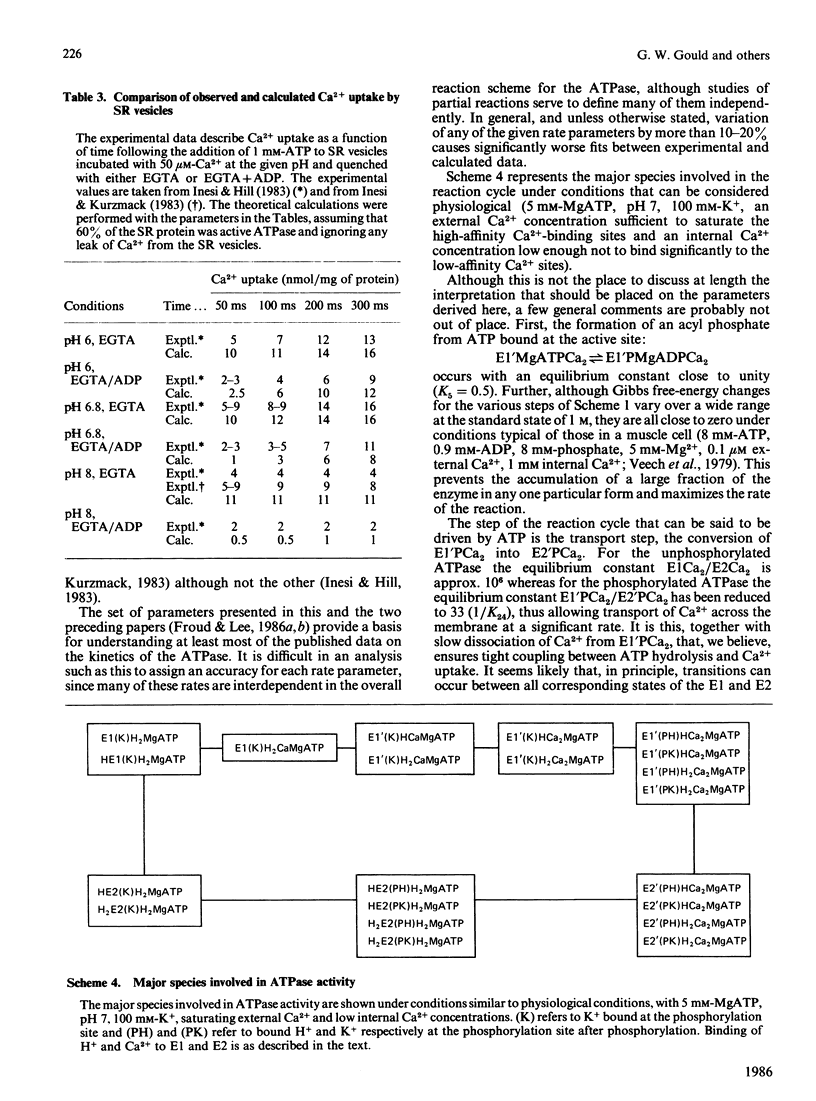
- Froud R. J., Lee A. G. A model for the phosphorylation of the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase by phosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):207–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2370207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froud R. J., Lee A. G. Conformational transitions in the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase and the binding of Ca2+ ions. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):197–206. doi: 10.1042/bj2370197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Rega A. F., Alonso G. L. The interaction of magnesium ions with the calcium pump of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 21;448(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruys K. J., Urbauer J. L., Schuster S. M. Metal-nucleotide structural characteristics during catalysis by beef heart mitochondrial F1. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6533–6540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillain F., Champeil P., Boyer P. D. Sarcoplasmic reticulum adenosinetriphosphatase phosphorylation from inorganic phosphate. Theoretical and experimental reinvestigation. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 25;23(20):4754–4761. doi: 10.1021/bi00315a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith S. Evidence that the ATP binding site of sarcoplasmic reticulum CaATPase has a Mg(2+) ion binding sub-site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 15;124(1):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90934-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
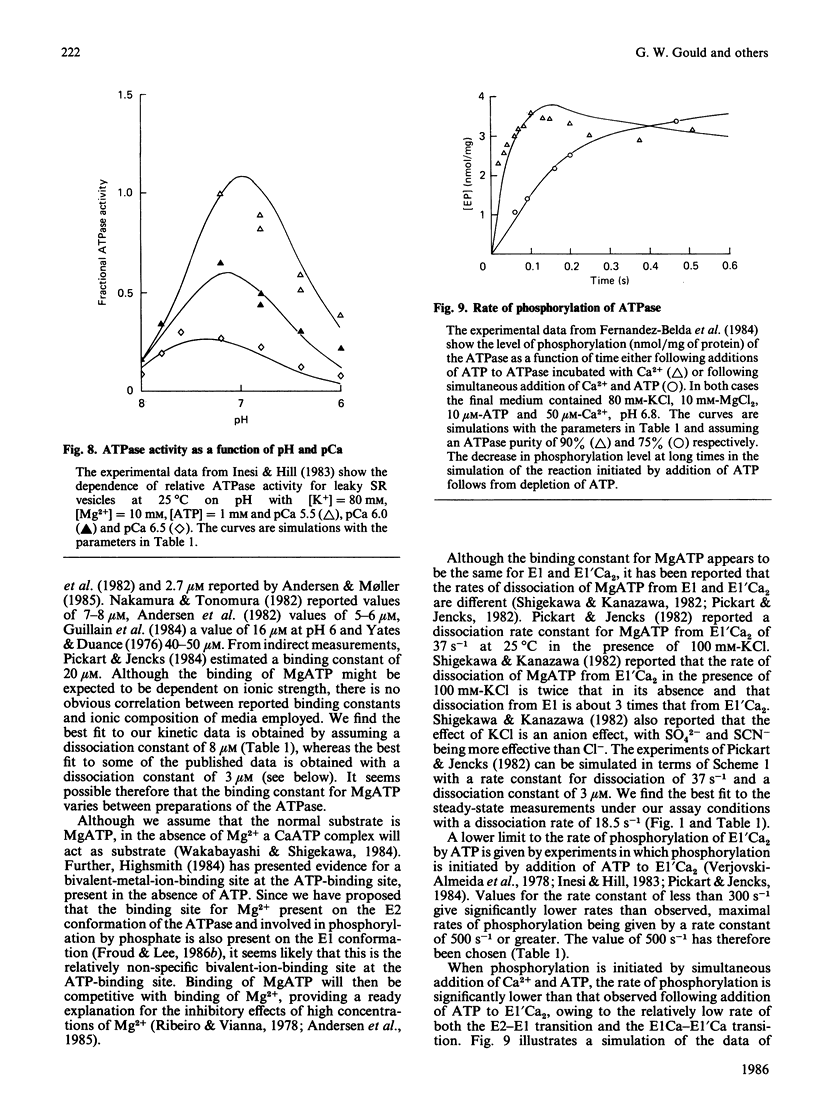
- Inesi G., Hill T. L. Calcium and proton dependence of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. Biophys J. 1983 Nov;44(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84299-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosk-Kosicka D., Kurzmack M., Inesi G. Kinetic characterization of detergent-solubilized sarcoplasmic reticulum adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2559–2567. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G., East J. M., Jones O. T., McWhirter J., Rooney E. K., Simmonds A. C. Binding of dansyl propranolol to the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 27;732(2):441–454. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemasters J. J. The ATP-to-oxygen stoichiometries of oxidative phosphorylation by rat liver mitochondria. An analysis of ADP-induced oxygen jumps by linear nonequilibrium thermodynamics. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13123–13130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh D. B., Boyer P. D. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate modulation of catalytic intermediates of calcium ion activated adenosinetriphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum subsequent to enzyme phosphorylation. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):2867–2875. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. ATP and Ca2+ binding by the Ca2+ pump protein of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 16;298(4):906–926. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamoto R. K., Inesi G. Studies of the interactions of 2',3'-O-(2,4,6-trinitrocyclohexyldienylidine)adenosine nucleotides with the sarcoplasmic reticulum (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase active site. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):2961–2970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Tonomura Y. The binding of ATP to the catalytic and the regulatory site of Ca2+, Mg2+-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1982 Dec;14(5-6):307–318. doi: 10.1007/BF00743060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y. Two alternate kinetic routes for the decomposition of the phosphorylated intermediate of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neet K. E., Green N. M. Kinetics of the cooperativity of the Ca2+-transporting adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum and the mechanism of the ATP interaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 30;178(2):588–597. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90230-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickart C. M., Jencks W. P. Energetics of the calcium-transporting ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1629–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickart C. M., Jencks W. P. Slow dissociation of ATP from the calcium ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5319–5322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M., Vianna A. L. Allosteric modification by K+ of the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-dependent ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Interaction with Mg2+. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3153–3157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney E. K., Lee A. G. Binding of hydrophobic drugs to lipid bilayers and to the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 27;732(2):428–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scofano H. M., Vieyra A., de Meis L. Substrate regulation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. Transient kinetic studies. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10227–10231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigekawa M., Kanazawa T. Phosphoenzyme formation from ATP in the ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Effect of KCl or ATP and slow dissociation of ATP from precursor enzyme-ATP complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7657–7665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigekawa M., Wakabayashi S., Nakamura H. Effect of divalent cation bound to the ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Activation of phosphoenzyme hydrolysis by Mg2+. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14157–14161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. L., Verjovski-Almeida S. Self-association and modification of calcium binding in solubilized sarcoplasmic reticulum adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):707–716. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Jencks W. P. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate at the active site accelerates binding of calcium to calcium adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5389–5392. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takisawa H., Tonomura Y. Factors affecting the transient phase of the Ca2+, Mg2+-dependent ATPase reaction of sarcoplasmic reticulum from skeletal muscle. J Biochem. 1978 May;83(5):1275–1284. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. S., Hattan D. Biphasic kinetics of ATP hydrolysis by calcium-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal muscle. Evidence for a nucleoside triphosphate effector site. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4402–4407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veech R. L., Lawson J. W., Cornell N. W., Krebs H. A. Cytosolic phosphorylation potential. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6538–6547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verjovski-Almeida S., Kurzmack M., Inesi G. Partial reactions in the catalytic and transport cycle of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):5006–5013. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Shigekawa M. Role of divalent cation bound to phosphoenzyme intermediate of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4427–4436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Inesi G. The use of 2',3'-O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) adenosine 5'-triphosphate for studies of nucleotide interaction with sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11510–11516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Lewis D., Nakamoto R., Kurzmack M., Fronticelli C., Inesi G. Modulation of calcium binding in sarcoplasmic reticulum adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 10;20(23):6617–6625. doi: 10.1021/bi00526a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Fialho de Mello M. C. Substrate regulation of membrane phosphorylation and of Ca 2+ transport in the sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3691–3701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


