Abstract
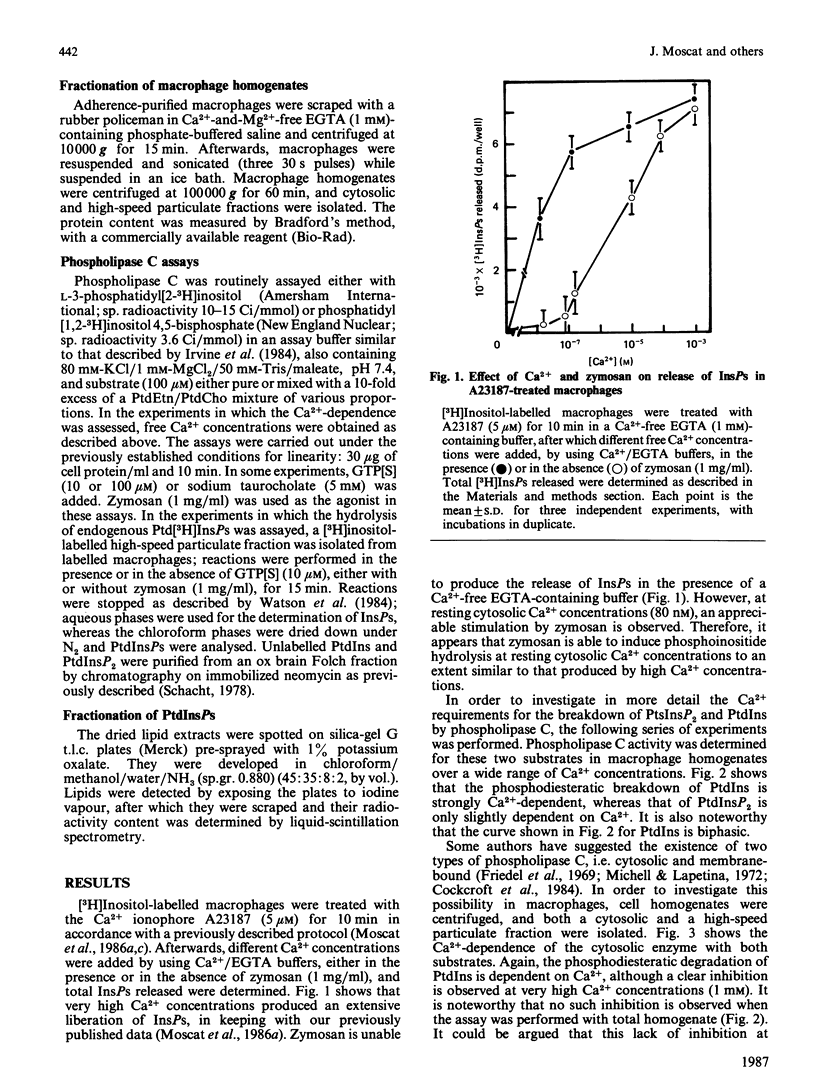
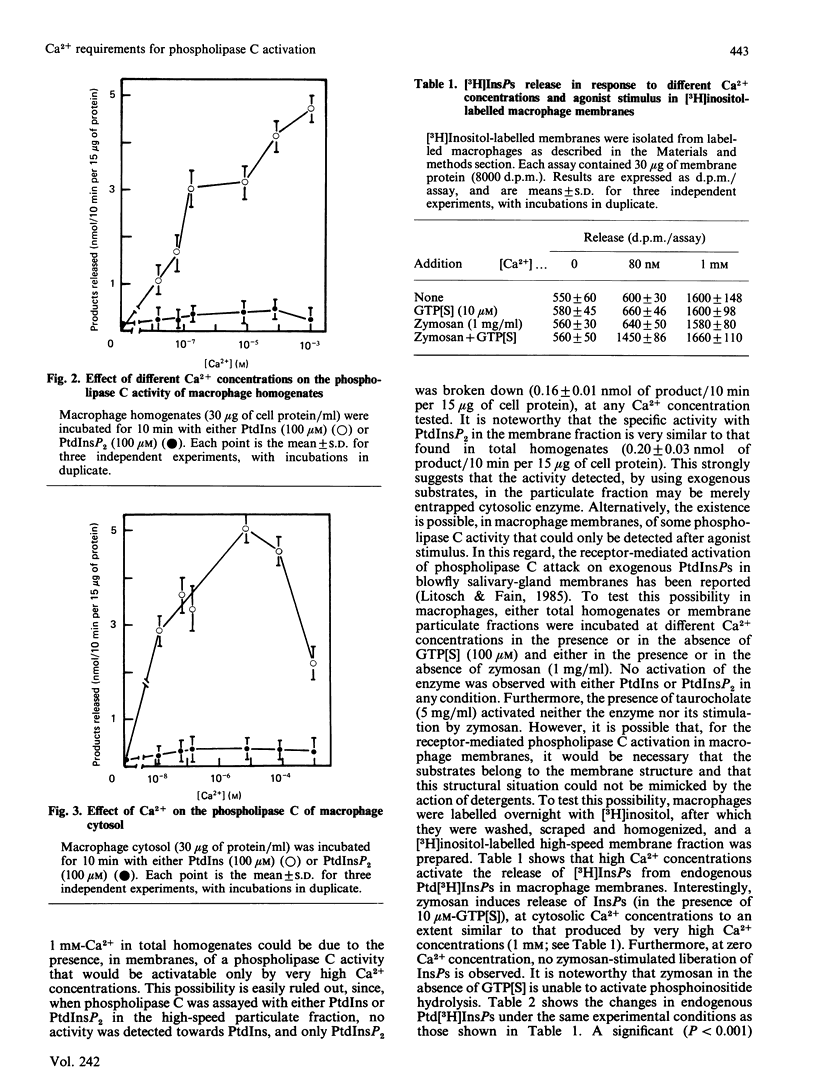
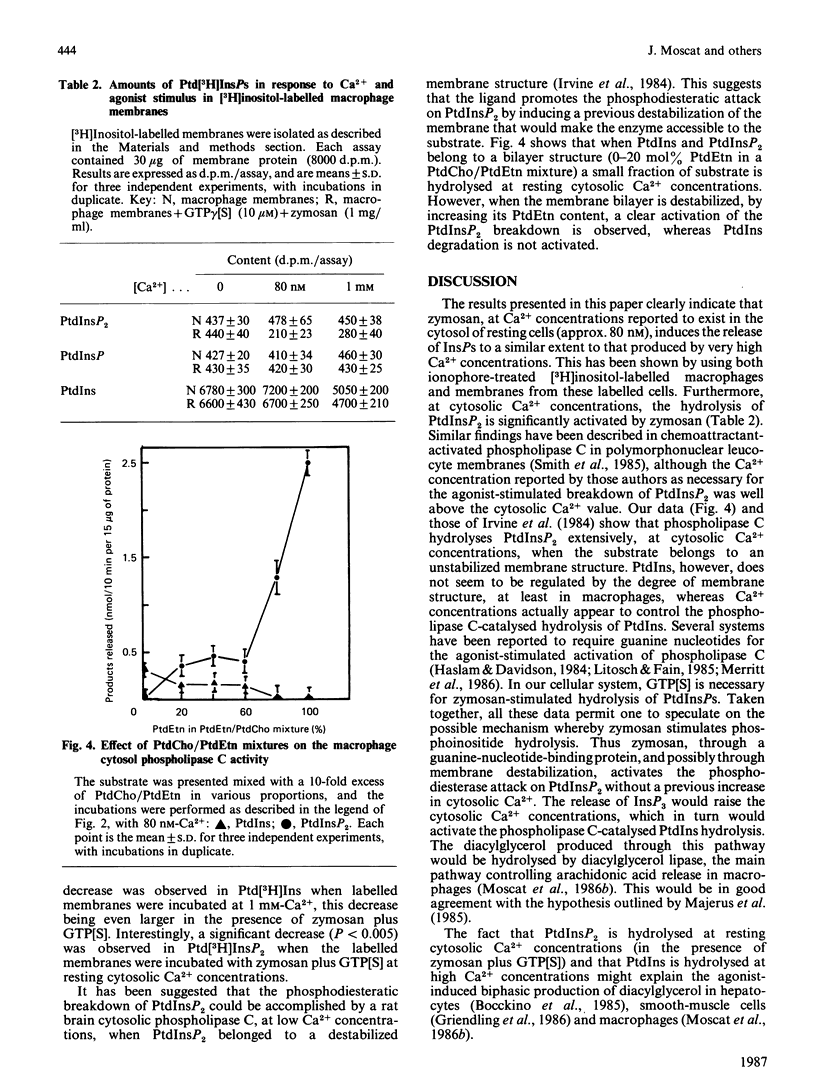
Hydrolysis of polyphosphoinositides by phosphodiesterase has been demonstrated to be involved in the control of cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations. The stimulation of Ca2+ ionophores of the release of inositol phosphates in macrophages, and other cells, together with the Ca2+ requirements for zymosan-induced phospholipase C activation, make unclear the relationship between Ca2+ mobilization and polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis. The results in the present paper strongly suggest that, for zymosan-induced phospholipase C activation, a previous increase in cytosolic Ca2+ is not a required event. These results also show that zymosan-activated release of inositol phosphates may be mediated by a guanine-nucleotide-binding protein.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. A., Scott W. A., Cohn Z. A. Evidence for sequential signals in the induction of the arachidonic acid cascade in macrophages. J Exp Med. 1986 Jan 1;163(1):139–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Kennerly D. A., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Diglyceride lipase: a pathway for arachidonate release from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3238–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Stimulation of 1,2-diacylglycerol accumulation in hepatocytes by vasopressin, epinephrine, and angiotensin II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14201–14207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BENSON B. THE DIFFERENTIATION OF MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES. MORPHOLOGY, CYTOCHEMISTRY, AND BIOCHEMISTRY. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:153–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Baldwin J. M., Allan D. The Ca2+-activated polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of human and rabbit neutrophil membranes. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 15;221(2):477–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2210477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S. Contrasting roles for receptor-stimulated inositol lipid metabolism in secretory cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 1984 Dec;12(6):966–968. doi: 10.1042/bst0120966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E., Dowling L. G., Kyger E. M., Franson R. C. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity of chromaffin granule-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7171–7173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Michell R. H. The polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1980133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emilsson A., Sundler R. Differential activation of phosphatidylinositol deacylation and a pathway via diphosphoinositide in macrophages responding to zymosan and ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3111–3116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedel R. O., Brown J. D., Durell J. The enzymic hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol by guinea pig brain: Sub-cellular distribution and hydrolysis products. J Neurochem. 1969 Mar;16(3):371–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griendling K. K., Rittenhouse S. E., Brock T. A., Ekstein L. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Sustained diacylglycerol formation from inositol phospholipids in angiotensin II-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5901–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Receptor-induced diacylglycerol formation in permeabilized platelets; possible role for a GTP-binding protein. J Recept Res. 1984;4(1-6):605–629. doi: 10.3109/10799898409042576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Dawson R. M. Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase and phosphomonoesterase activities of rat brain. Some properties and possible control mechanisms. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):177–185. doi: 10.1042/bj2180177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Fain J. N. 5-Methyltryptamine stimulates phospholipase C-mediated breakdown of exogenous phosphoinositides by blowfly salivary gland membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16052–16055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Taylor C. W., Rubin R. P., Putney J. W., Jr Evidence suggesting that a novel guanine nucleotide regulatory protein couples receptors to phospholipase C in exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):337–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2360337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Lapetina E. G. Production of cyclic inositol phosphate in stimulated tissues. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 27;240(104):258–260. doi: 10.1038/newbio240258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscat G., Moreno F., Iglesias S., Garcia-Barreno P., Municio A. M. Ionophore A23187 induces a refractory state in thrombin-activated release of inositol phosphates. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):709–714. doi: 10.1042/bj2380709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscat J., Aracil M., Diez E., Balsinde J., Garcia Barreno P., Municio A. M. Intracellular Ca2+ requirements for zymosan-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):367–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90572-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscat J., Herrero C., Garcia-Barreno P., Municio A. M. Phospholipase C-diglyceride lipase is a major pathway for arachidonic acid release in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 26;141(1):367–373. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80378-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAAFLAUB J. Applications of metal buffers and metal indicators in biochemistry. Methods Biochem Anal. 1956;3:301–325. doi: 10.1002/9780470110195.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Hasegawa-Sasaki H. Breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in a T-cell leukaemia line stimulated by phytohaemagglutinin is not dependent on Ca2+ mobilization. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):971–979. doi: 10.1042/bj2270971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht J. Purification of polyphosphoinositides by chromatography on immobilized neomycin. J Lipid Res. 1978 Nov;19(8):1063–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Lane B. C., Kusaka I., Verghese M. W., Snyderman R. Chemoattractant receptor-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in human polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes. Requirement for a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5875–5878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicentini L. M., Ambrosini A., Di Virgilio F., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J. Muscarinic receptor-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis at resting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in PC12 cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1330–1333. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., LeVine H., 3rd, May W. S., Jr, Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. A model for intracellular translocation of protein kinase C involving synergism between Ca2+ and phorbol esters. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):546–549. doi: 10.1038/317546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


