Abstract
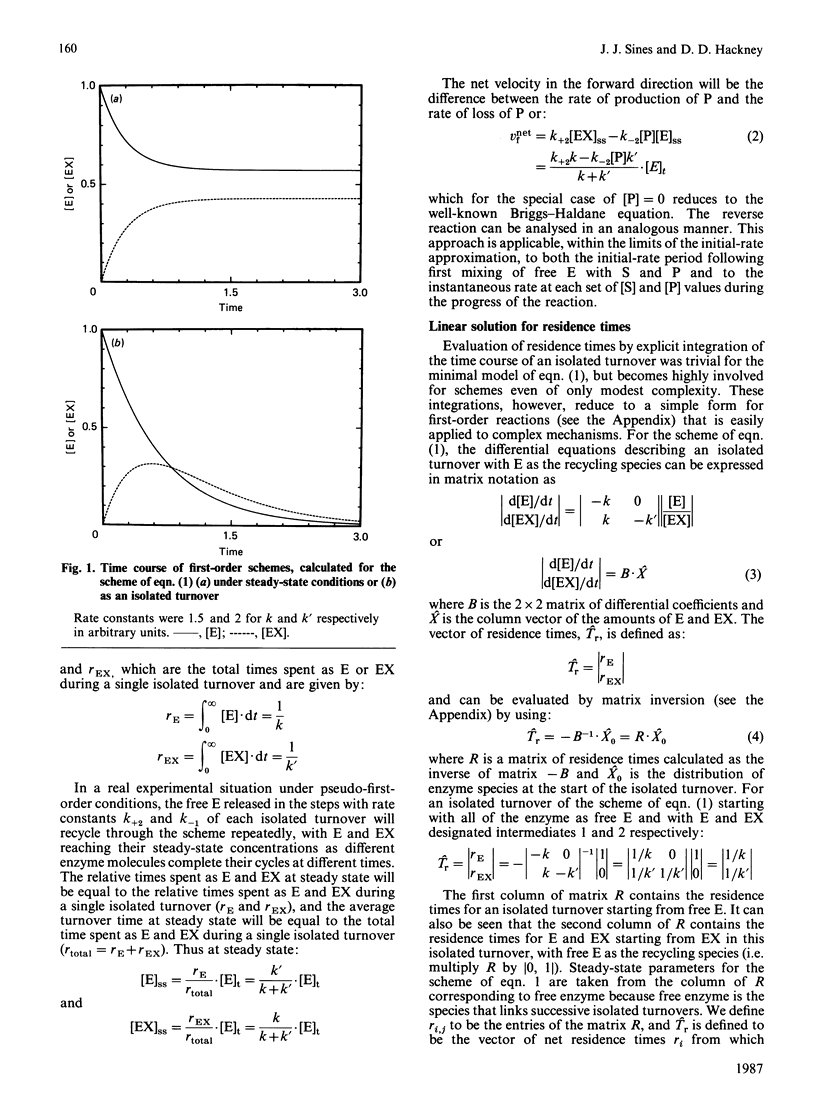
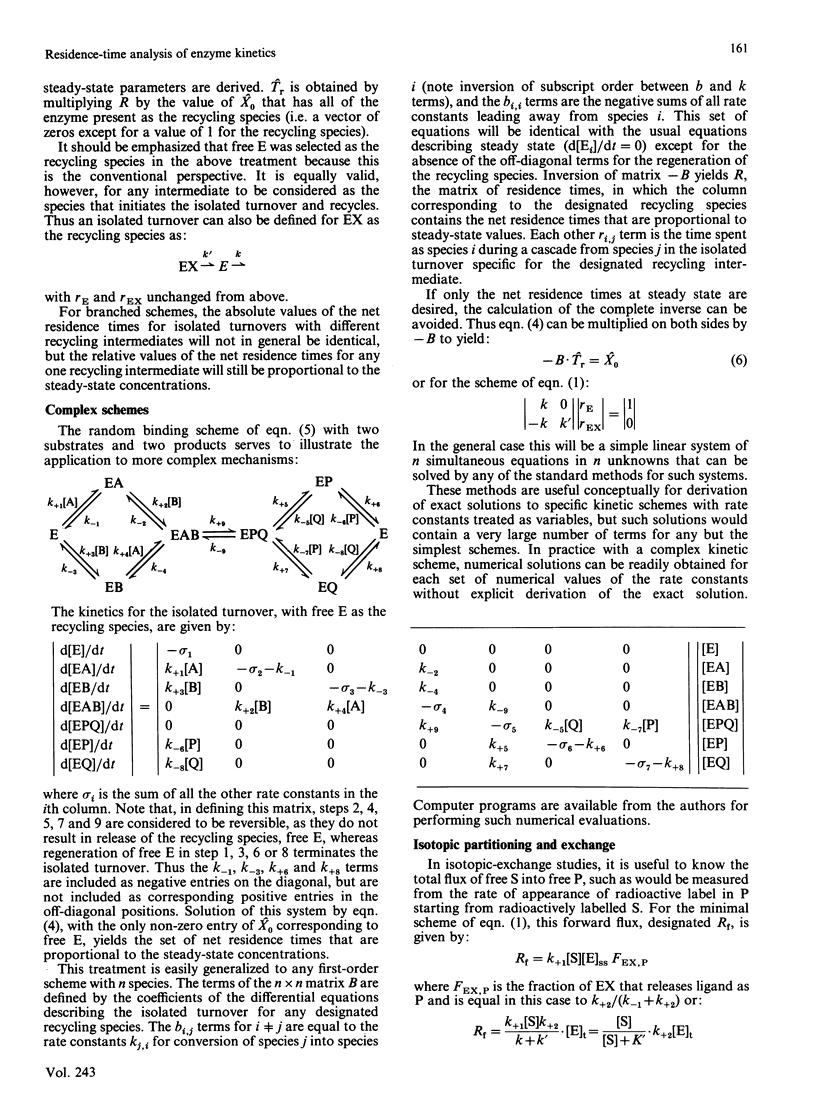
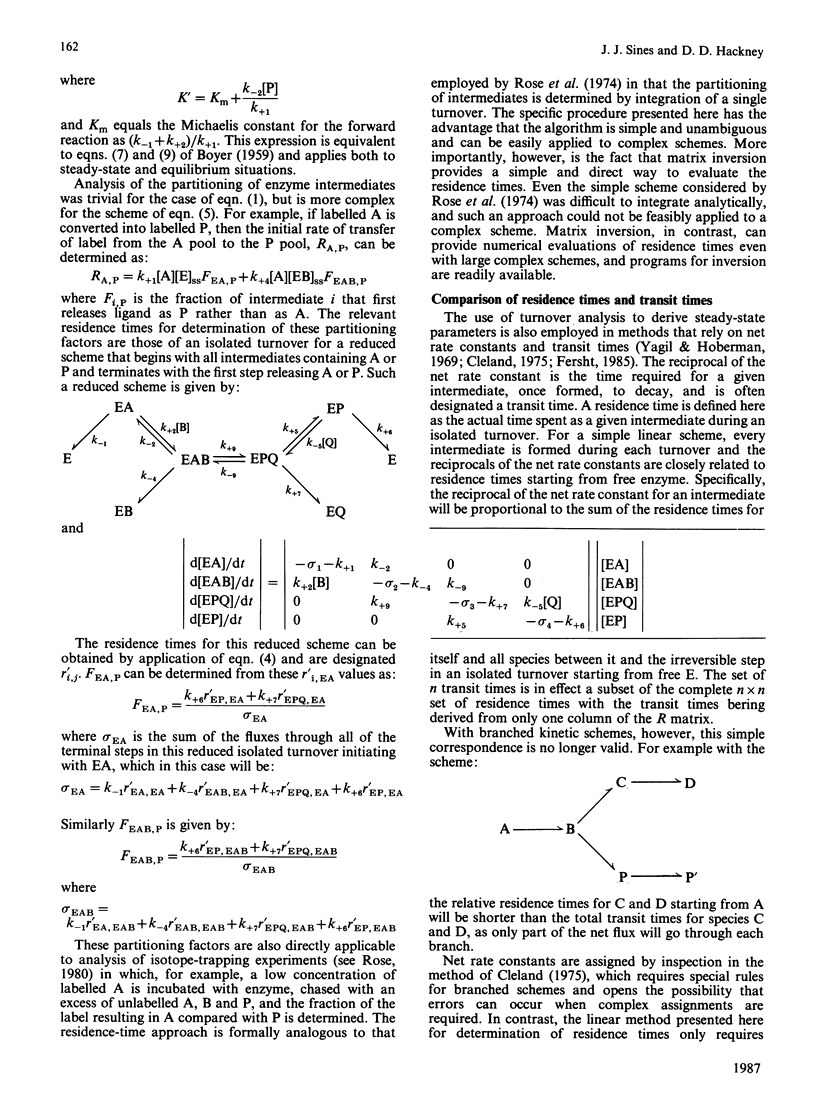
A 'first-passage-time' analysis is applied to enzyme kinetics. It is shown that the residence times determined in this way are directly related to the steady-state parameters and are particularly useful in analysis of isotopic exchange. A simple linear means is used for the calculation of these residence times that makes this method easily applicable to the numerical evaluation of complex models. This stochastic type of approach provides an alternative that avoids the classical steady-state approximation that the concentrations of enzyme intermediates are constant. Instead, steady state is defined as the randomization of the states of the enzyme following initial mixing due to completion of the turnovers of individual enzyme molecules at different times.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYER P. D. Uses and limitations of measurements of rates of isotopic exchange and incorporation in catalyzed reactions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Jun;82(2):387–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. Partition analysis and the concept of net rate constants as tools in enzyme kinetics. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3220–3224. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. Y. Derivation and initial velocity and isotope exchange rate equations. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:54–84. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose I. A., O'Connell E. L., Litwin S. Determination of the rate of hexokinase-glucose dissociation by the isotope-trapping method. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5163–5168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose I. A. The isotope trapping method: desorption rates of productive E.S complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1980;64:47–59. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)64004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagil G., Hoberman H. D. Rate of isotope exchange in enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):352–360. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


