Abstract
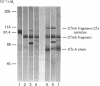
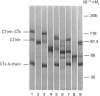
The effects of proteolysis and deglycosylation on C1 inhibitor (C1Inh) were tested with respect to both its ability to form complexes with C1s and its capacity to block C1 autoactivation. Limited proteolysis of C1Inh by Staphylococcus aureus V8 proteinase, proline-specific endopeptidase or elastase generated a major high-Mr (approximately 86,000) fragment. In contrast with the fragment produced by elastase, which was inactive, the fragments resulting from V8 proteinase and proline-specific endopeptidase treatment retained activity. Deglycosylation with N-glycanase or O-glycanase, or both, had no major effect on the functional activity of C1Inh.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlaud G. J., Sim R. B., Duplaa A. M., Colomb M. G. Differential elution of Clq, Clr and Cls from human Cl bound to immune aggregates. Use in the rapid purification of Cl subcomponents. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jul;16(7):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlaud G. J., Villiers C. L., Chesne S., Colomb M. G. Purified proenzyme C1r. Some characteristics of its activation and subsequent proteolytic cleavage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 6;616(1):116–129. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensa J. C., Reboul A., Colomb M. G. Biosynthesis in vitro of complement subcomponents C1q, C1s and C1 inhibitor by resting and stimulated human monocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 15;216(2):385–392. doi: 10.1042/bj2160385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock S. C., Skriver K., Nielsen E., Thøgersen H. C., Wiman B., Donaldson V. H., Eddy R. L., Marrinan J., Radziejewska E., Huber R. Human C1 inhibitor: primary structure, cDNA cloning, and chromosomal localization. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4292–4301. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower M. S., Harpel P. C. Proteolytic cleavage and inactivation of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor and C1 inactivator by human polymorphonuclear leukocyte elastase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9849–9854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catanese J., Kress L. F. Enzymatic inactivation of human plasma C1-inhibitor and alpha 1-antichymotrypsin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteinase and elastase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 28;789(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., EVANS R. R. A BIOCHEMICAL ABNORMALITY IN HEREDIATRY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: ABSENCE OF SERUM INHIBITOR OF C' 1-ESTERASE. Am J Med. 1963 Jul;35:37–44. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. E., 3rd, Whitehead A. S., Harrison R. A., Dauphinais A., Bruns G. A., Cicardi M., Rosen F. S. Human inhibitor of the first component of complement, C1: characterization of cDNA clones and localization of the gene to chromosome 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3161–3165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Angiotensinogen is related to the antitrypsin-antithrombin-ovalbumin family. Science. 1983 Oct 28;222(4622):417–419. doi: 10.1126/science.6604942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes C. D., Pensky J., Ratnoff O. D. Inhibition of activated Hageman factor and activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent by purified serum C1 inactivator. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Nov;76(5):809–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Mason J. W., Colman R. W., Austen K. F. Interaction of plasma kallikrein with the C1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):574–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Cooper N. R. Studies on human plasma C1 inactivator-enzyme interactions. I. Mechanisms of interaction with C1s, plasmin, and trypsin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):593–604. doi: 10.1172/JCI107967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. A. Human C1 inhibitor: improved isolation and preliminary structural characterization. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 11;22(21):5001–5007. doi: 10.1021/bi00290a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt H., Heimburger N., Kranz T., Schwick H. G. Ein Beitrag zur Isolierung und Charakterisierung des Cl-Inaktivators aus Humanplasma. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):254–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houmard J., Drapeau G. R. Staphylococcal protease: a proteolytic enzyme specific for glutamoyl bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3506–3509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odermatt E., Berger H., Sano Y. Size and shape of human C1-inhibitor. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 31;131(2):283–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80385-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pensky J., Schwick H. G. Human serum inhibitor of C'1 esterase: identity with alpha-2-neuraminoglycoprotein. Science. 1969 Feb 14;163(3868):698–699. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3868.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J. Molecular modelling of human complement subcomponent C1q and its complex with C1r2C1s2 derived from neutron-scattering curves and hydrodynamic properties. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):13–26. doi: 10.1042/bj2280013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer T. H., Jr, Elder J. H., Alexander S., Phelan A. W., Tarentino A. L. Demonstration of peptide:N-glycosidase F activity in endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F preparations. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10700–10704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prandini M. H., Reboul A., Colomb M. G. Biosynthesis of complement C1 inhibitor by Hep G2 cells. Reactivity of different glycosylated forms of the inhibitor with C1s. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):93–98. doi: 10.1042/bj2370093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reboul A., Arlaud G. J., Sim R. B., Colomb M. G. A simplified procedure for the purification of C1-inactivator from human plasma. Interaction with complement subcomponents C1r and C1s. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reboul A., Prandini M. H., Bensa J. C., Colomb M. G. Characterization of C1q, C1s and C-1 Inh synthesized by stimulated human monocytes in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 7;190(1):65–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Lowe D. M., Porter R. R. Isolation and characterization of C1q, a subcomponent of the first component of complement, from human and rabbit sera. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):749–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1300749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Porter R. R., Reid K. B., Gigli I. The structure and enzymic activities of the C1r and C1s subcomponents of C1, the first component of human serum complement. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):219–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1630219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Reboul A., Arlaud G. J., Villiers C. L., Colomb M. G. Interaction of 125I-labelled complement subcomponents C-1r and C-1s with protease inhibitors in plasma. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 1;97(1):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Frank M. M. Activator-bound C1 is less susceptible to inactivation by C1 inhibition than is fluid-phase C1. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):625–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Duponchel C., Bourgarel P., Colomb M., Meo T. Molecular cloning of human C1 inhibitor: sequence homologies with alpha 1-antitrypsin and other members of the serpins superfamily. Gene. 1986;42(3):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umemoto J., Bhavanandan V. P., Davidson E. A. Purification and properties of an endo-alpha-N-acetyl-D-galactosaminidase from Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8609–8614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villiers C. L., Arlaud G. J., Colomb M. G. Diamine-induced dissociation of the first component of human complement, C1. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Apr 16;140(2):421–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Walter R., Tsuru D. Proline-specific endopeptidase from Flavobacterium. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4786–4792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J. A new role for C-1-inhibitor in homeostasis: control of activation of the first component of human complement. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2505–2508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]