Abstract
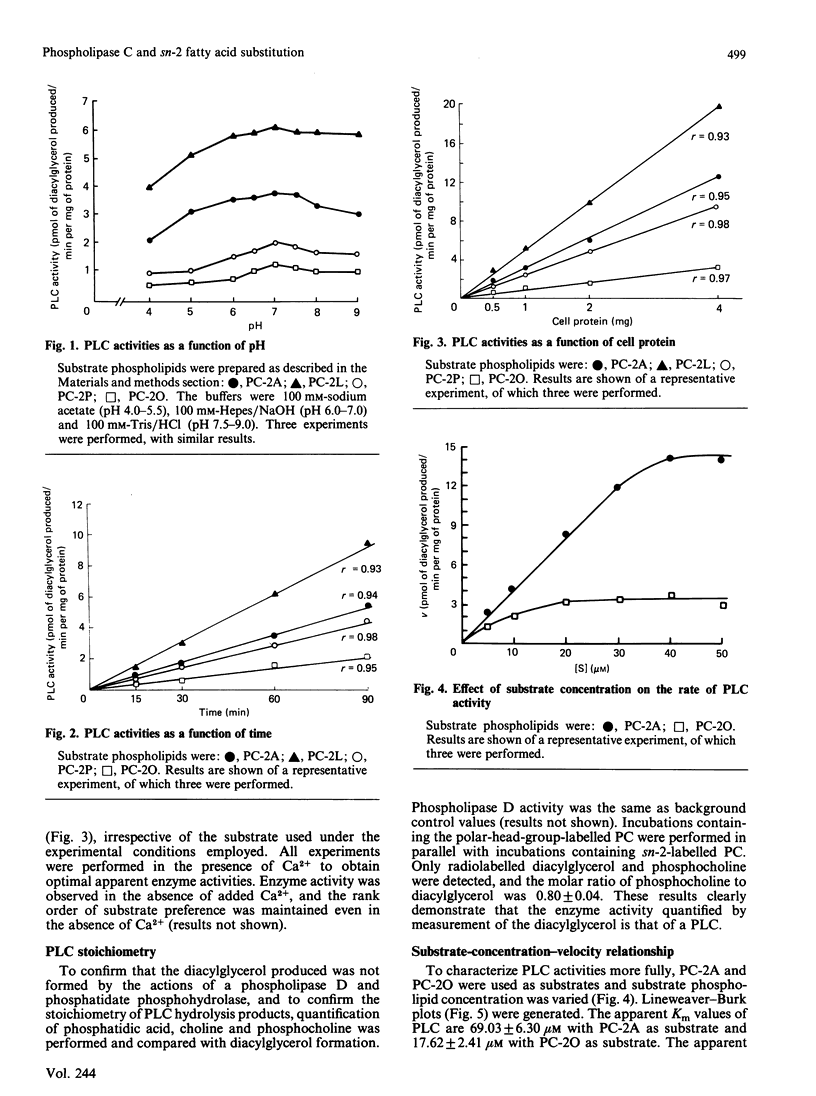
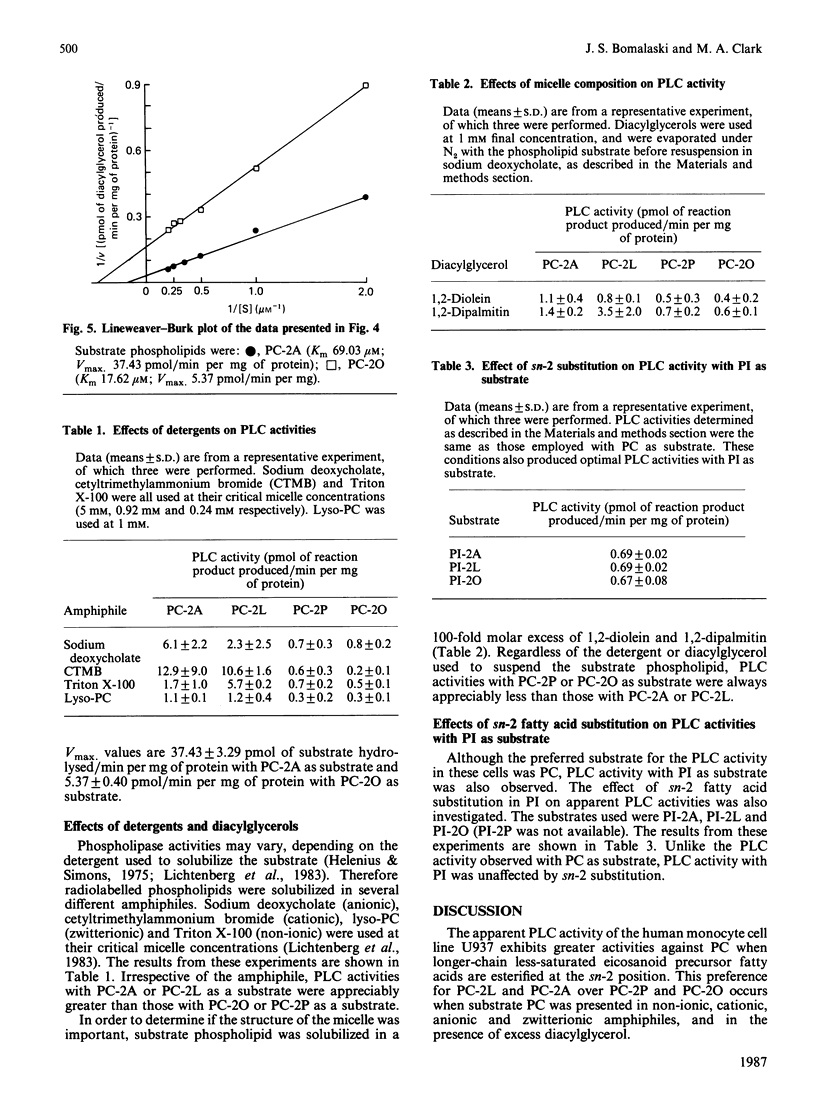
The human monocyte cell line U937 expresses phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C activities and produces eicosanoids. The phospholipase C (PLC) activity exhibits substrate preference for phosphatidyl-choline (PC), rather than phosphatidylinositol or phosphatidylethanolamine. In order to characterize the PLC activity found in these cells, the effects of substitution of the sn-2 fatty acid on this activity were examined. PC substrates with palmitic acid (PC-2P), oleic acid (PC-2O), arachidonic acid (PC-2A) and linoleic acid (PC-2L) at the sn-2 position were used. The sn-1 fatty acid was palmitic acid. PC-2L and PC-2A with the longer-chain less-saturated fatty acids linoleic acid and arachidonic acid esterified at sn-2 were found to be better substrates for PLC activity than PC-2P or PC-2O in these cells. This preference was maintained even when substrate phospholipid was solubilized in non-ionic, anionic, cationic and zwitterionic amphiphiles. Furthermore, when a 500-fold excess of 1,2-diolein or 1,2-dipalmitin was added to the reaction, the specificity of the PLC activity for PC-2A and PC-2L remained unchanged. When similar experiments were performed with phosphatidylinositol as a substrate, we did not observe any effect when the sn-2 position was altered. These data show that the fatty acid constituent at the sn-2 position affects the observed PLC activity when phosphatidylcholine, but not phosphatidylinositol, is used as a substrate by these cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bomalaski J. S., Clark M. A., Douglas S. D., Zurier R. B. Enhanced phospholipase A2 and C activities of peripheral blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Nov;38(5):649–654. doi: 10.1002/jlb.38.5.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomalaski J. S., Clark M. A., Zurier R. B. Enhanced phospholipase activity in peripheral blood monocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Mar;29(3):312–318. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomalaski J. S., Goldstein C. S., Dailey A. T., Douglas S. D., Zurier R. B. Uptake of fatty acids and their mobilization from phospholipids in cultured monocyte-macrophages from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 May;39(2):198–212. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomalaski J. S., Hirata F., Clark M. A. Aspirin inhibits phospholipase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 29;139(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonney R. J., Naruns P., Davies P., Humes J. L. Antigen-antibody complexes stimulate the synthesis and release of prostaglandins by mouse peritoneal macrophages. Prostaglandins. 1979 Oct;18(4):605–616. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(79)90027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau L. Y., Tai H. H. Resolution into two different forms and study of the properties of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from human platelet cytosol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 12;713(2):344–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. A., Hsueh W., Pachman L. M., Barnes W. T. Prostaglandin biosynthesis by a human macrophage-like cell line, U937. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Mar;33(3):197–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen D., Bartolf M., Franson R. C. Inhibition of lysosomal phospholipases C and A in rabbit alveolar macrophages, polymorphonuclear leukocytes and rat liver by sodium bisulfite. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Mar 27;793(1):10–17. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Drugs which inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Mar;26(1):33–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. Steroidal antiinflammatory drugs as inhibitors of phospholipase A2. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1978;3:105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirasawa K., Irvine R. F., Dawson R. M. Heterogeneity of the calcium-dependent phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase in rat brain. Biochem J. 1982 Aug 1;205(2):437–442. doi: 10.1042/bj2050437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirasawa K., Irvine R. F., Dawson R. M. Heterogeneity of the calcium-dependent phosphatidylinositol-phosphodiesterase of rat liver kidney, as revealed by column chromatofocusing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 30;107(2):533–537. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91524-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann S. L., Majerus P. W. Identification and properties of two distinct phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C enzymes from sheep seminal vesicular glands. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6461–6469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann S. L., Majerus P. W. Modulation of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity by phospholipid interactions, diglycerides, and calcium ions. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14359–14364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holub B. J., Celi B. Evaluation of the fatty acid selectivity of a phosphatidylinositol-specific cytosolic phospholipase C from pig and human platelets. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Feb-Mar;62(2-3):115–120. doi: 10.1139/o84-017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Hemington N., Dawson R. M. The calcium-dependent phosphatidylinositol-phosphodiesterase of rat brain. Mechanisms of suppression and stimulation. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(3):525–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenstra R., Mauco G., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Studies on enzymes related to diacylglycerol production in activated platelets. I. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C: further characterization using a simple method for determination of activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Feb 9;792(2):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg D., Robson R. J., Dennis E. A. Solubilization of phospholipids by detergents. Structural and kinetic aspects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):285–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C. Phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Action on some artificial lecithins. Acta Chem Scand B. 1977;31(4):267–272. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.31b-0267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Carroll R. C., Weglicki W. B. Multiple forms of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C of different relative molecular masses in animal tissues. Evidence for modification of the platelet enzyme by Ca2+-dependent proteinase. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):813–820. doi: 10.1042/bj2210813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Weglicki W. B. Resolution of myocardial phospholipase C into several forms with distinct properties. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):325–334. doi: 10.1042/bj2150325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. F., Siegel M. I. The appearance of phospholipase activity in the human macrophage-like cell line U937 during dimethyl sulfoxide induced differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 13;118(1):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otnaess A. B., Little C., Sletten K., Wallin R., Johnsen S., Flengsrud R., Prydz H. Some characteristics of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 3;79(2):459–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowski N. A., Kaplan G., Hamill A. L., Cohn Z. A., Scott W. A. Arachidonic acid metabolism by human monocytes. Studies with platelet-depleted cultures. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):393–412. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. F., Otnaess A. B., Kensil C. A., Dennis E. A. The specificity of phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C in a mixed micellar system. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1252–1257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M. I., Deems R. A., Jesaitis A. J., Dennis E. A., Ulevitch R. J. Phospholipase activities of the P388D1 macrophage-like cell line. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Apr;238(1):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Pawlowski N. A., Andreach M., Cohn Z. A. Resting macrophages produce distinct metabolites from exogenous arachidonic acid. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):535–547. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Pawlowski N. A., Murray H. W., Andreach M., Zrike J., Cohn Z. A. Regulation of arachidonic acid metabolism by macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1148–1160. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Zrike J. M., Hamill A. L., Kempe J., Cohn Z. A. Regulation of arachidonic acid metabolites in macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):324–335. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite M. Approaches to the study of mammalian cellular phospholipases. J Lipid Res. 1985 Dec;26(12):1379–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wightman P. D., Dahlgren M. E., Hall J. C., Davies P., Bonney R. J. Identification and characterization of a phospholipase C activity in resident mouse peritoneal macrophages. Inhibition of the enzyme by phenothiazines. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):523–526. doi: 10.1042/bj1970523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf R. A., Gross R. W. Identification of neutral active phospholipase C which hydrolyzes choline glycerophospholipids and plasmalogen selective phospholipase A2 in canine myocardium. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7295–7303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Sayed M. Y., DeBose C. D., Coury L. A., Roberts M. F. Sensitivity of phospholipase C (Bacillus cereus) activity to phosphatidylcholine structural modifications. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 4;837(3):325–335. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Sayed M. Y., Roberts M. F. Charged detergents enhance the activity of phospholipase C (Bacillus cereus) towards micellar short-chain phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 20;831(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90160-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


