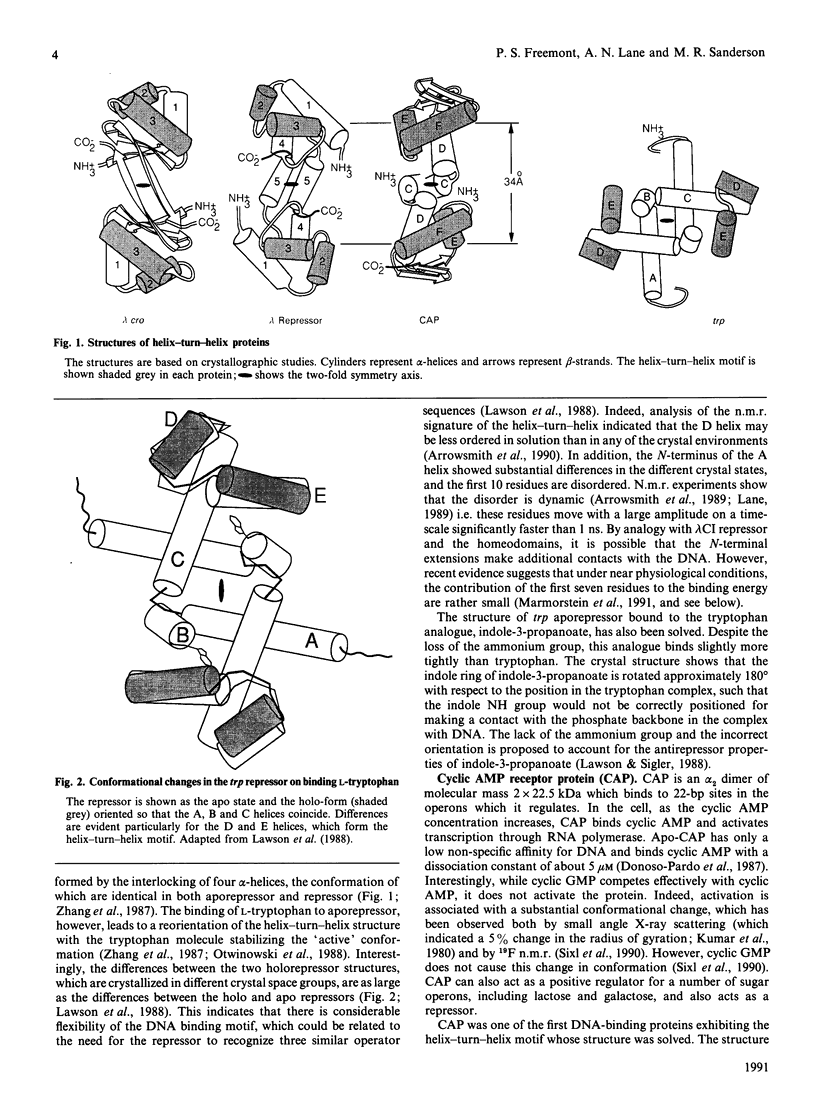
Full text
PDF




















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Meguid S. S., Grindley N. D., Templeton N. S., Steitz T. A. Cleavage of the site-specific recombination protein gamma delta resolvase: the smaller of two fragments binds DNA specifically. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2001–2005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Affolter M., Percival-Smith A., Müller M., Leupin W., Gehring W. J. DNA binding properties of the purified Antennapedia homeodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4093–4097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal A. K., Rodgers D. W., Drottar M., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Recognition of a DNA operator by the repressor of phage 434: a view at high resolution. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):899–907. doi: 10.1126/science.3187531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. E., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Structure of the repressor-operator complex of bacteriophage 434. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):846–852. doi: 10.1038/326846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. F., Ohlendorf D. H., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. Structure of the cro repressor from bacteriophage lambda and its interaction with DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):754–758. doi: 10.1038/290754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. F. Proposed alpha-helical super-secondary structure associated with protein-dna recognition. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 25;159(4):745–751. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrowsmith C. H., Carey J., Treat-Clemons L., Jardetzky O. NMR assignments for the amino-terminal residues of trp repressor and their role in DNA binding. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3875–3879. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrowsmith C. H., Pachter R., Altman R. B., Iyer S. B., Jardetzky O. Sequence-specific 1H NMR assignments and secondary structure in solution of Escherichia coli trp repressor. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 10;29(27):6332–6341. doi: 10.1021/bi00479a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass S., Sorrells V., Youderian P. Mutant Trp repressors with new DNA-binding specificities. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):240–245. doi: 10.1126/science.3140377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beese L. S., Steitz T. A. Structural basis for the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I: a two metal ion mechanism. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):25–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
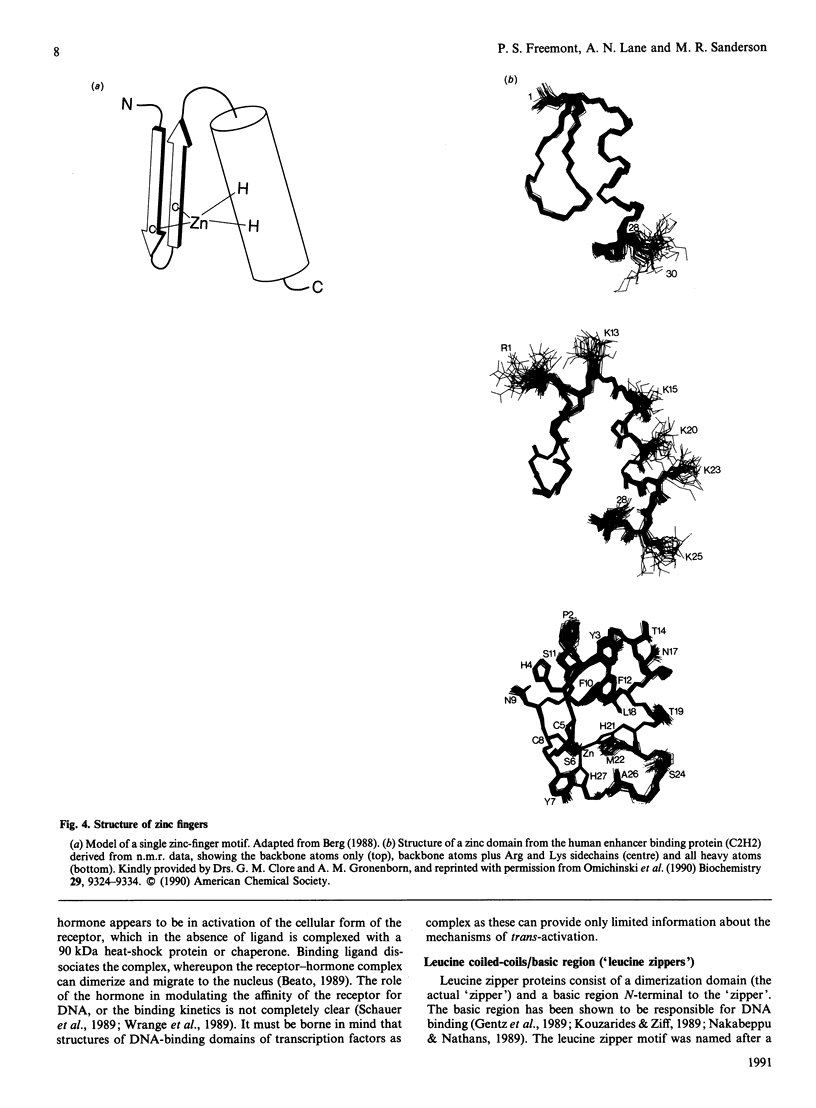
- Berg J. M. Proposed structure for the zinc-binding domains from transcription factor IIIA and related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):99–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M., Qian Y., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Determination of the three-dimensional structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain from Drosophila in solution by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):183–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90155-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breg J. N., Boelens R., George A. V., Kaptein R. Sequence-specific 1H NMR assignment and secondary structure of the Arc repressor of bacteriophage P22, as determined by two-dimensional 1H NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 12;28(25):9826–9833. doi: 10.1021/bi00451a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breg J. N., van Opheusden J. H., Burgering M. J., Boelens R., Kaptein R. Structure of Arc repressor in solution: evidence for a family of beta-sheet DNA-binding proteins. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):586–589. doi: 10.1038/346586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Matthews B. W. Structural basis of DNA-protein recognition. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Jul;14(7):286–290. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Matthews B. W. The helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):1903–1906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Roderick S. L., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. Protein-DNA conformational changes in the crystal structure of a lambda Cro-operator complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8165–8169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. M., Bowie J. U., Sauer R. T. Arc repressor is tetrameric when bound to operator DNA. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 25;29(51):11189–11195. doi: 10.1021/bi00503a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame R. W., Love W. E., Wang B. C., Hamlin R., Nguyen H. X., Moudrianakis E. N. Crystallographic structure of the octameric histone core of the nucleosome at a resolution of 3.3 A. Science. 1985 May 3;228(4699):546–553. doi: 10.1126/science.3983639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey J. trp repressor arms contribute binding energy without occupying unique locations on DNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):1941–1945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. D., Pastore A., Gausepohl H., Frank R., Roesch P. NMR and molecular dynamics studies of the mKr2 'zinc finger'. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Mar 10;188(2):455–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. W., Jr, Kraut J. A proposed model for interaction of polypeptides with RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):283–287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler L. R., Lane A. N. Interaction of the trp repressor from Escherichia coli with a constitutive trp operator. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):925–928. doi: 10.1042/bj2500925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Sussman J. L., Kim S. H. Secondary structural complementarity between DNA and proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1458–1462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Joyce C. M., Beardsley G. P. Novel blunt-end addition reactions catalyzed by DNA polymerase I of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 5;198(1):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowart M., Gibson K. J., Allen D. J., Benkovic S. J. DNA substrate structural requirements for the exonuclease and polymerase activities of procaryotic and phage DNA polymerases. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):1975–1983. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusack S., Berthet-Colominas C., Härtlein M., Nassar N., Leberman R. A second class of synthetase structure revealed by X-ray analysis of Escherichia coli seryl-tRNA synthetase at 2.5 A. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):249–255. doi: 10.1038/347249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire V., Freemont P. S., Sanderson M. R., Beese L., Friedman J. M., Joyce C. M., Steitz T. A. Genetic and crystallographic studies of the 3',5'-exonucleolytic site of DNA polymerase I. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):199–201. doi: 10.1126/science.2832946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire V., Grindley N. D., Joyce C. M. The 3'-5' exonuclease of DNA polymerase I of Escherichia coli: contribution of each amino acid at the active site to the reaction. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):17–24. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07916.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Improved detection of helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motifs in protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5019–5026. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoso-Pardo J. L., Turner P. C., King R. W. Cyclic nucleotide binding to cAMP receptor protein from Escherichia coli. Optical and ligand-binding studies. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Nov 2;168(3):687–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA bending and its relation to nucleosome positioning. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederick C. A., Grable J., Melia M., Samudzi C., Jen-Jacobson L., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Rosenberg J. M. Kinked DNA in crystalline complex with EcoRI endonuclease. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):327–331. doi: 10.1038/309327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S., Friedman J. M., Beese L. S., Sanderson M. R., Steitz T. A. Cocrystal structure of an editing complex of Klenow fragment with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8924–8928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S., Hanson I. M., Trowsdale J. A novel cysteine-rich sequence motif. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):483–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90229-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S., Ollis D. L., Steitz T. A., Joyce C. M. A domain of the Klenow fragment of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I has polymerase but no exonuclease activity. Proteins. 1986 Sep;1(1):66–73. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto B. S., Schurr J. M. Dependence of the torsional rigidity of DNA on base composition. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):175–177. doi: 10.1038/344175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. DNA sequence determinants of CAP-induced bending and protein binding affinity. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):824–829. doi: 10.1038/333824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Isolation of amino-terminal fragment of lactose repressor necessary for DNA binding. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):938–943. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C., Aggarwal A. K. DNA recognition by proteins with the helix-turn-helix motif. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:933–969. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman J., Model P. Substrate recognition by the EcoRI endonuclease. Proteins. 1990;7(2):185–197. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J. C., O'Shea E. K., Kim P. S., Sauer R. T. Sequence requirements for coiled-coils: analysis with lambda repressor-GCN4 leucine zipper fusions. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1400–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.2147779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härd T., Dahlman K., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A., Rigler R. Cooperativity and specificity in the interactions between DNA and the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 5;29(22):5358–5364. doi: 10.1021/bi00474a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härd T., Kellenbach E., Boelens R., Kaptein R., Dahlman K., Carlstedt-Duke J., Freedman L. P., Maler B. A., Hyde E. I., Gustafsson J. A. 1H NMR studies of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain: sequential assignments and identification of secondary structure elements. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 25;29(38):9015–9023. doi: 10.1021/bi00490a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härd T., Kellenbach E., Boelens R., Maler B. A., Dahlman K., Freedman L. P., Carlstedt-Duke J., Yamamoto K. R., Gustafsson J. A., Kaptein R. Solution structure of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):157–160. doi: 10.1126/science.2115209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. Transcriptional regulation by dimerization: two sides to an incestuous relationship. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90207-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S. R., Pabo C. O. Structure of the lambda complex at 2.5 A resolution: details of the repressor-operator interactions. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):893–899. doi: 10.1126/science.3187530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S. R., Whitcombe T. V., Berg J. M., Pabo C. O. Systematic variation in DNA length yields highly ordered repressor-operator cocrystals. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1383–1385. doi: 10.1126/science.3906896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaptein R., Zuiderweg E. R., Scheek R. M., Boelens R., van Gunsteren W. F. A protein structure from nuclear magnetic resonance data. lac repressor headpiece. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 5;182(1):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karslake C., Schroeder S., Wang P. L., Gorenstein D. G. 31P NMR spectra of an oligodeoxyribonucleotide duplex lac operator-repressor headpiece complex. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6578–6584. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. L., Yanofsky C. Mutational studies with the trp repressor of Escherichia coli support the helix-turn-helix model of repressor recognition of operator DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):483–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. C., Grable J. C., Love R., Greene P. J., Rosenberg J. M. Refinement of Eco RI endonuclease crystal structure: a revised protein chain tracing. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1307–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.2399465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpichnikov M. P., Hahn K. D., Buck F., Rüterjans H., Chernov B. K., Kurochkin A. V., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A. 1H NMR study of the interaction of bacteriophage lambda Cro protein with the OR3 operator. Evidence for a change of the conformation of the OR3 operator on binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3551–3561. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpichnikov M. P., Kurochkin A. V., Chernov B. K., Skryabin K. G. Interactions between cro repressor and the model specific binding site. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 1;175(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80759-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klevit R. E., Herriott J. R., Horvath S. J. Solution structure of a zinc finger domain of yeast ADR1. Proteins. 1990;7(3):215–226. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klig L. S., Carey J., Yanofsky C. trp repressor interactions with the trp aroH and trpR operators. Comparison of repressor binding in vitro and repression in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):769–777. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90557-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostrewa D., Granzin J., Koch C., Choe H. W., Raghunathan S., Wolf W., Labahn J., Kahmann R., Saenger W. Three-dimensional structure of the E. coli DNA-binding protein FIS. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):178–180. doi: 10.1038/349178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koudelka G. B., Harbury P., Harrison S. C., Ptashne M. DNA twisting and the affinity of bacteriophage 434 operator for bacteriophage 434 repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4633–4637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. Leucine zippers of fos, jun and GCN4 dictate dimerization specificity and thereby control DNA binding. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):568–571. doi: 10.1038/340568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S. A., Murthy N. S., Krakow J. S. Ligand-induced change in the radius of gyration of cAMP receptor protein from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 1;109(1):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamerichs R. M., Boelens R., Van der Marel G. A., Van Boom J. H., Kaptein R. Assignment of the 1H-NMR spectrum of a lac repressor headpiece-operator complex in H2O and identification of NOEs. Consequences for protein-DNA interaction. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 12;194(2):629–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane A. N. The influence of tryptophan on mobility of residues in the trp repressor of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jun 1;182(1):95–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latchman D. S. Eukaryotic transcription factors. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):281–289. doi: 10.1042/bj2700281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson C. L., Sigler P. B. The structure of trp pseudorepressor at 1.65A shows why indole propionate acts as a trp 'inducer'. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):869–871. doi: 10.1038/333869a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson C. L., Zhang R. G., Schevitz R. W., Otwinowski Z., Joachimiak A., Sigler P. B. Flexibility of the DNA-binding domains of trp repressor. Proteins. 1988;3(1):18–31. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Gippert G. P., Soman K. V., Case D. A., Wright P. E. Three-dimensional solution structure of a single zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):635–637. doi: 10.1126/science.2503871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton P., Lu P. Lambda cro repressor complex with OR3 DNA: 15N NMR observations. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7262–7271. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S., Riggs A. D. The general affinity of lac repressor for E. coli DNA: implications for gene regulation in procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1975 Feb;4(2):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90116-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Sigler P. B. The stereochemistry and biochemistry of the trp repressor-operator complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 6;1048(2-3):113–126. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmorstein R. Q., Joachimiak A., Sprinzl M., Sigler P. B. The structural basis for the interaction between L-tryptophan and the Escherichia coli trp aporepressor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4922–4927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmorstein R. Q., Sigler P. B. Stereochemical effects of L-tryptophan and its analogues on trp repressor's affinity for operator-DNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9149–9154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmorstein R. Q., Sprinzl M., Sigler P. B. An alkaline phosphatase protection assay to investigate trp repressor/operator interactions. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 29;30(4):1141–1148. doi: 10.1021/bi00218a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W. Protein-DNA interaction. No code for recognition. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):294–295. doi: 10.1038/335294a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClarin J. A., Frederick C. A., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Grable J., Rosenberg J. M. Structure of the DNA-Eco RI endonuclease recognition complex at 3 A resolution. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1526–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.3024321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9 A resolution suggests binding to left-handed B-DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):744–749. doi: 10.1038/290744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9-A resolution. Incorporation of amino acid sequence and interactions with cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9518–9524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondragón A., Subbiah S., Almo S. C., Drottar M., Harrison S. C. Structure of the amino-terminal domain of phage 434 repressor at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):189–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90375-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondragón A., Wolberger C., Harrison S. C. Structure of phage 434 Cro protein at 2.35 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Affolter M., Leupin W., Otting G., Wüthrich K., Gehring W. J. Isolation and sequence-specific DNA binding of the Antennapedia homeodomain. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4299–4304. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Nathans D. The basic region of Fos mediates specific DNA binding. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3833–3841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T. J., Vesque C., Charnay P. Base sequence discrimination by zinc-finger DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):175–178. doi: 10.1038/349175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H. C., Finch J. T., Luisi B. F., Klug A. The structure of an oligo(dA).oligo(dT) tract and its biological implications. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):221–226. doi: 10.1038/330221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus D., Nakaseko Y., Nagai K., Klug A. Sequence-specific [1H]NMR resonance assignments and secondary structure identification for 1- and 2-zinc finger constructs from SW15. A hydrophobic core involving four invariant residues. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80184-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oas T. G., McIntosh L. P., O'Shea E. K., Dahlquist F. W., Kim P. S. Secondary structure of a leucine zipper determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 27;29(12):2891–2894. doi: 10.1021/bi00464a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oefner C., Suck D. Crystallographic refinement and structure of DNase I at 2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):605–632. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90280-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Fisher R. G., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. The molecular basis of DNA-protein recognition inferred from the structure of cro repressor. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):718–723. doi: 10.1038/298718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollis D. L., Brick P., Hamlin R., Xuong N. G., Steitz T. A. Structure of large fragment of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I complexed with dTMP. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):762–766. doi: 10.1038/313762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omichinski J. G., Clore G. M., Appella E., Sakaguchi K., Gronenborn A. M. High-resolution three-dimensional structure of a single zinc finger from a human enhancer binding protein in solution. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 9;29(40):9324–9334. doi: 10.1021/bi00492a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Protein--DNA contacts in the structure of a homeodomain--DNA complex determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3085–3092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otwinowski Z., Schevitz R. W., Zhang R. G., Lawson C. L., Joachimiak A., Marmorstein R. Q., Luisi B. F., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of trp repressor/operator complex at atomic resolution. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):321–329. doi: 10.1038/335321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Aggarwal A. K., Jordan S. R., Beamer L. J., Obeysekare U. R., Harrison S. C. Conserved residues make similar contacts in two repressor-operator complexes. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.2315694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Lewis M. The operator-binding domain of lambda repressor: structure and DNA recognition. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):443–447. doi: 10.1038/298443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace H. C., Lu P., Lewis M. lac repressor: crystallization of intact tetramer and its complexes with inducer and operator DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1870–1873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Abate C., Curran T. Altered protein conformation on DNA binding by Fos and Jun. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):572–575. doi: 10.1038/347572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. E., Manfield I., Parsons I., Davidson B. E., Rafferty J. B., Somers W. S., Margarita D., Cohen G. N., Saint-Girons I., Stockley P. G. Cooperative tandem binding of met repressor of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1989 Oct 26;341(6244):711–715. doi: 10.1038/341711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. The structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain determined by NMR spectroscopy in solution: comparison with prokaryotic repressors. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafferty J. B., Somers W. S., Saint-Girons I., Phillips S. E. Three-dimensional crystal structures of Escherichia coli met repressor with and without corepressor. Nature. 1989 Oct 26;341(6244):705–710. doi: 10.1038/341705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen R., Benvegnu D., O'Shea E. K., Kim P. S., Alber T. X-ray scattering indicates that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):561–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A., Goldman A., Steitz T. A. A helix-turn-strand structural motif common in alpha-beta proteins. Proteins. 1990;8(4):334–340. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Helix lap-joints as ion-binding sites: DNA-binding motifs and Ca-binding "EF hands" are related by charge and sequence reversal. Proteins. 1988;4(4):229–239. doi: 10.1002/prot.340040402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J. M., Boyer H. W., Greene P. The structure and function of the Eco RI restriction endonuclease. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;1:131–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson M. R., Freemont P. S., Rice P. A., Goldman A., Hatfull G. F., Grindley N. D., Steitz T. A. The crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the site-specific recombination enzyme gamma delta resolvase at 2.7 A resolution. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1323–1329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90427-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saudek V., Pasley H. S., Gibson T., Gausepohl H., Frank R., Pastore A. Solution structure of the basic region from the transcriptional activator GCN4. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 5;30(5):1310–1317. doi: 10.1021/bi00219a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saudek V., Pastore A., Castiglione Morelli M. A., Frank R., Gausepohl H., Gibson T., Weih F., Roesch P. Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of the yeast transcriptional activator protein GCN4. Protein Eng. 1990 Oct;4(1):3–10. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Yocum R. R., Doolittle R. F., Lewis M., Pabo C. O. Homology among DNA-binding proteins suggests use of a conserved super-secondary structure. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):447–451. doi: 10.1038/298447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer M., Chalepakis G., Willmann T., Beato M. Binding of hormone accelerates the kinetics of glucocorticoid and progesterone receptor binding to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1123–1127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheek R. M., Zuiderweg E. R., Klappe K. J., van Boom J. H., Kaptein R., Rüterjans H., Beyreuther K. lac Repressor headpiece binds specifically to half of the lac operator: a proton nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):228–235. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schevitz R. W., Otwinowski Z., Joachimiak A., Lawson C. L., Sigler P. B. The three-dimensional structure of trp repressor. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):782–786. doi: 10.1038/317782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystallization of Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein with its DNA binding site. The use of modular DNA. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 5;213(1):159–166. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe J. W., Neuhaus D., Rhodes D. Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of the oestrogen receptor. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):458–461. doi: 10.1038/348458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senear D. F., Ackers G. K. Proton-linked contributions to site-specific interactions of lambda cI repressor and OR. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6568–6577. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa M., Lee S. J., Akutsu H., Kyogoku Y., Kitano K., Shin M., Ohtsuka E., Ikehara M. Photo CIDNP study on the complex formation of lambda cro protein with OR3. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 25;181(2):286–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixl F., King R. W., Bracken M., Feeney J. 19F-n.m.r. studies of ligand binding to 5-fluorotryptophan- and 3-fluorotyrosine-containing cyclic AMP receptor protein from Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):545–552. doi: 10.1042/bj2660545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staacke D., Walter B., Kisters-Woike B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. How Trp repressor binds to its operator. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1963–1967. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A., Ohlendorf D. H., McKay D. B., Anderson W. F., Matthews B. W. Structural similarity in the DNA-binding domains of catabolite gene activator and cro repressor proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3097–3100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stob S., Scheek R. M., Boelens R., Kaptein R. Photo-CIDNP study of the interaction between lac repressor headpiece and lac operator DNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 24;239(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Helix-turn-helix, zinc-finger, and leucine-zipper motifs for eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Apr;14(4):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90145-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Lahm A., Oefner C. Structure refined to 2A of a nicked DNA octanucleotide complex with DNase I. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):464–468. doi: 10.1038/332464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Oefner C., Kabsch W. Three-dimensional structure of bovine pancreatic DNase I at 2.5 A resolution. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2423–2430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02149.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Oefner C. Structure of DNase I at 2.0 A resolution suggests a mechanism for binding to and cutting DNA. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):620–625. doi: 10.1038/321620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talanian R. V., McKnight C. J., Kim P. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding by a short peptide dimer. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):769–771. doi: 10.1126/science.2389142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka I., Appelt K., Dijk J., White S. W., Wilson K. S. 3-A resolution structure of a protein with histone-like properties in prokaryotes. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):376–381. doi: 10.1038/310376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. D., Halford S. E. Discrimination between DNA sequences by the EcoRV restriction endonuclease. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6198–6207. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade-Jardetzky N., Bray R. P., Conover W. W., Jardetzky O., Geisler N., Weber K. Differential mobility of the N-terminal headpiece in the lac-repressor protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 25;128(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warwicker J., Engelman B. P., Steitz T. A. Electrostatic calculations and model-building suggest that DNA bound to CAP is sharply bent. Proteins. 1987;2(4):283–289. doi: 10.1002/prot.340020404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Gilliland G. L., Harman J. G., Peterkofsky A. Crystal structure of a cyclic AMP-independent mutant of catabolite gene activator protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5630–5636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Structure of a complex of catabolite gene activator protein and cyclic AMP refined at 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. A., Ellenberger T., Wobbe C. R., Lee J. P., Harrison S. C., Struhl K. Folding transition in the DNA-binding domain of GCN4 on specific binding to DNA. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):575–578. doi: 10.1038/347575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. A. Thermal unfolding studies of a leucine zipper domain and its specific DNA complex: implications for scissor's grip recognition. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 4;29(35):8020–8024. doi: 10.1021/bi00487a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton R. P., Ptashne M. A new-specificity mutant of 434 repressor that defines an amino acid-base pair contact. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):888–891. doi: 10.1038/326888a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. W., Appelt K., Wilson K. S., Tanaka I. A protein structural motif that bends DNA. Proteins. 1989;5(4):281–288. doi: 10.1002/prot.340050405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. W. Prediction of DNA-binding regulatory proteins in bacteriophage T7. Protein Eng. 1987 Oct-Nov;1(5):373–376. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.5.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler F. K., D'Arcy A., Blöcker H., Frank R., van Boom J. H. Crystallization of complexes of EcoRV endonuclease with cognate and non-cognate DNA fragments. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jan 20;217(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90536-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Dong Y. C., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Structure of a phage 434 Cro/DNA complex. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):789–795. doi: 10.1038/335789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Eriksson P., Perlmann T. The purified activated glucocorticoid receptor is a homodimer. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5253–5259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagorski M. G., Bowie J. U., Vershon A. K., Sauer R. T., Patel D. J. NMR studies of Arc repressor mutants: proton assignments, secondary structure, and long-range contacts for the thermostable proline-8----leucine variant of Arc. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 12;28(25):9813–9825. doi: 10.1021/bi00451a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang R. G., Joachimiak A., Lawson C. L., Schevitz R. W., Otwinowski Z., Sigler P. B. The crystal structure of trp aporepressor at 1.8 A shows how binding tryptophan enhances DNA affinity. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):591–597. doi: 10.1038/327591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. Comparative gel electrophoresis measurement of the DNA bend angle induced by the catabolite activator protein. Biopolymers. 1990 Jan;29(1):29–38. doi: 10.1002/bip.360290106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuiderweg E. R., Kaptein R., Wüthrich K. Secondary structure of the lac repressor DNA-binding domain by two-dimensional 1H nuclear magnetic resonance in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5837–5841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vlieg J., Scheek R. M., van Gunsteren W. F., Berendsen H. J., Kaptein R., Thomason J. Combined procedure of distance geometry and restrained molecular dynamics techniques for protein structure determination from nuclear magnetic resonance data: application to the DNA binding domain of lac repressor from Escherichia coli. Proteins. 1988;3(4):209–218. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Berg O. G. On the specificity of DNA-protein interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1608–1612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Revzin A., Gross C. A., Wang A. C. Non-specific DNA binding of genome regulating proteins as a biological control mechanism: I. The lac operon: equilibrium aspects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4808–4812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]