Abstract
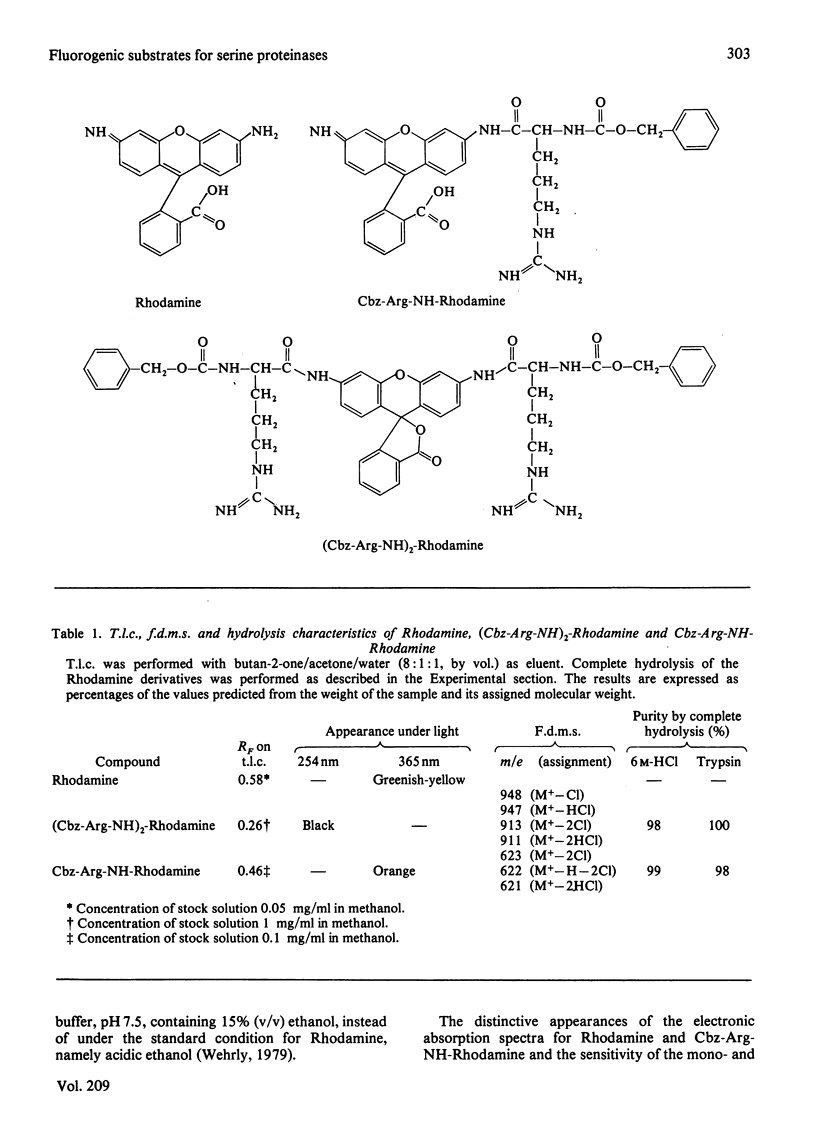
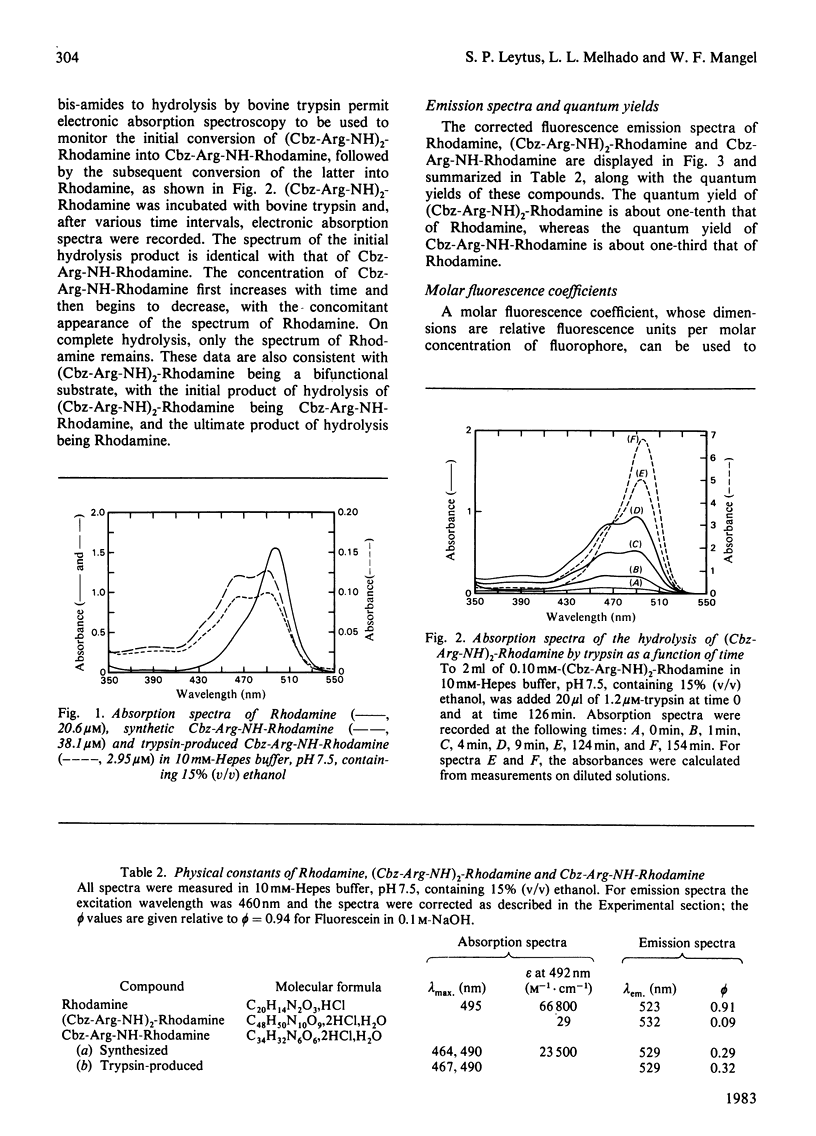
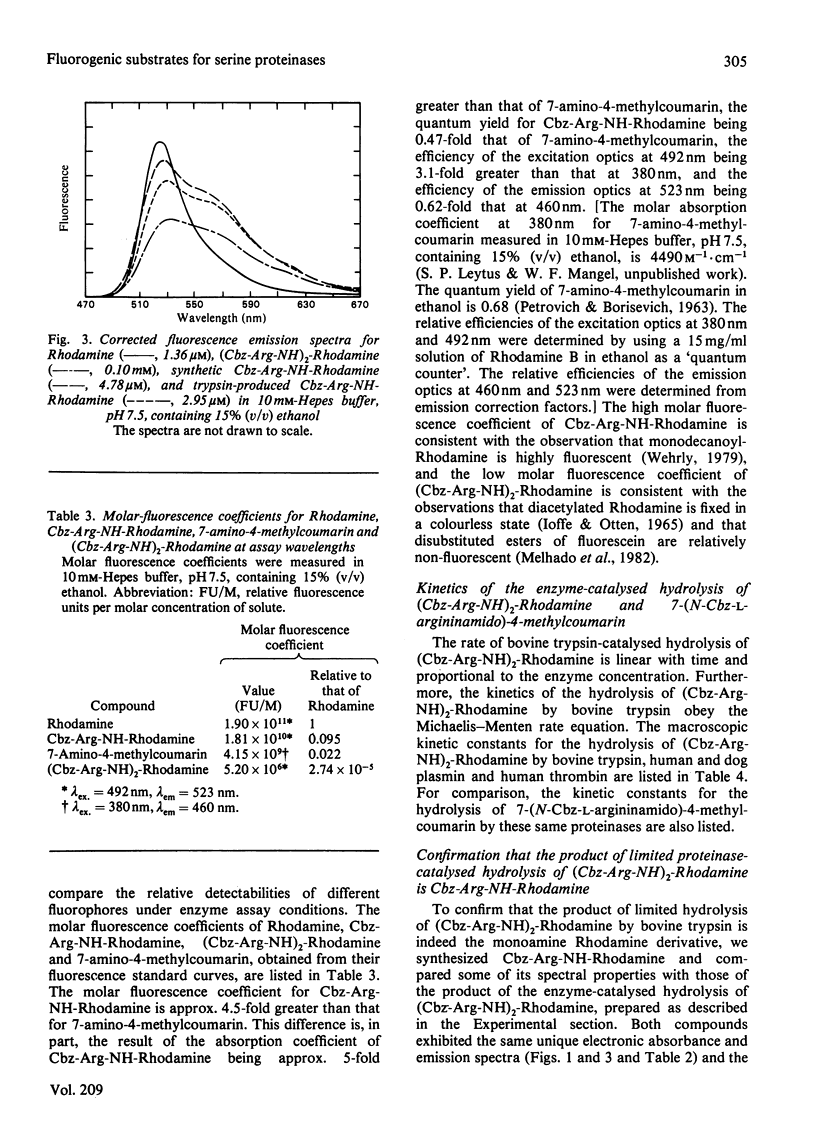
A new fluorogenic substrate for serine proteinases, bis(N-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-argininamido)Rhodamine [(Cbz-Arg-NH)2-Rhodamine], was synthesized, purified and chemically and enzymically characterized. This compound, which employs Rhodamine as a fluorophoric leaving group, is the first in a series of substrates designed to measure the amidase activity of proteinases. Cleavage of one of the amide bonds of (Cbz-Arg-NH)2-Rhodamine by a trypsin-like serine proteinase converts the non-fluorescent bisamide substrate into a highly fluorescent monoamide product. Significant differences in the electronic absorption and fluorescence emission spectra and quantum yields of bis-, mono- and un-substituted Rhodamine are reported. Macroscopic kinetic constants for the interaction of (Cbz-Arg-NH)2-Rhodamine with bovine trypsin, human and dog plasmin and human thrombin were determined. Compared with the corresponding 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin-based analogue, (Cbz-Arg-NH)2-Rhodamine exhibits an increase in sensitivity with these enzymes of 50--300-fold. The physical basis for this increase in sensitivity is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bigbee W. L., Weintraub H. B., Jensen R. H. Sensitive fluorescence assays for urokinase using synthetic peptide 4-methoxy-beta-naphthylamide substrates. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jul 15;88(1):114–122. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90403-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellino F. J., Sodetz J. M. Rabbit plasminogen and plasmin isozymes. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:273–286. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo M. J., Nakajima K., Zimmerman M., Powers J. C. Sensitive substrates for human leukocyte and porcine pancreatic elastase: a study of the merits of various chromophoric and fluorogenic leaving groups in assays for serine proteases. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;99(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T., Jr, Shaw E. Comparison of the esterase activities of trypsin, plasmin, and thrombin on guanidinobenzoate esters. Titration of the enzymes. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):2212–2224. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:1–32. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leytus S. P., Peltz G. A., Liu H. Y., Cannon J. F., Peltz S. W., Livingston D. C., Brocklehurst J. R., Mangel W. F. A quantitative assay for the activation of plasminogen by transformed cells in situ and by urokinase. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4307–4314. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Kato H., Iwanaga S., Takada K., Kimura T. New fluorogenic substrates for alpha-thrombin, factor Xa, kallikreins, and urokinase. J Biochem. 1977 Nov;82(5):1495–1498. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuizen W., Wijngaards G., Groeneveld E. Flourogenic peptide amide substrates for the estimation of plasminogen activators and plasmin. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90519-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierzchala P. A., Dorn C. P., Zimmerman M. A new fluorogenic substrate for plasmin. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):555–559. doi: 10.1042/bj1830555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pochron S. P., Mitchell G. A., Albareda I., Huseby R. M., Gargiulo R. J. A fluorescent substrate assay for plasminogen. Thromb Res. 1978 Nov;13(5):733–739. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Bissell E. R., Mitchell A. R., Pearson K. W. Direct photometric or fluorometric assay of proteinases using substrates containing 7-amino-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin. Thromb Res. 1980 Feb 1;17(3-4):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. C., Shaw E. Inactivation of trypsin-like proteases by active-site-directed sulfonylation. Ability of the departing group to confer selectivity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Sep;176(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M., Ashe B., Yurewicz E. C., Patel G. Sensitive assays for trypsin, elastase, and chymotrypsin using new fluorogenic substrates. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M., Yurewicz E., Patel G. A new fluorogenic substrate for chymotrypsin. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):258–262. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


