Abstract
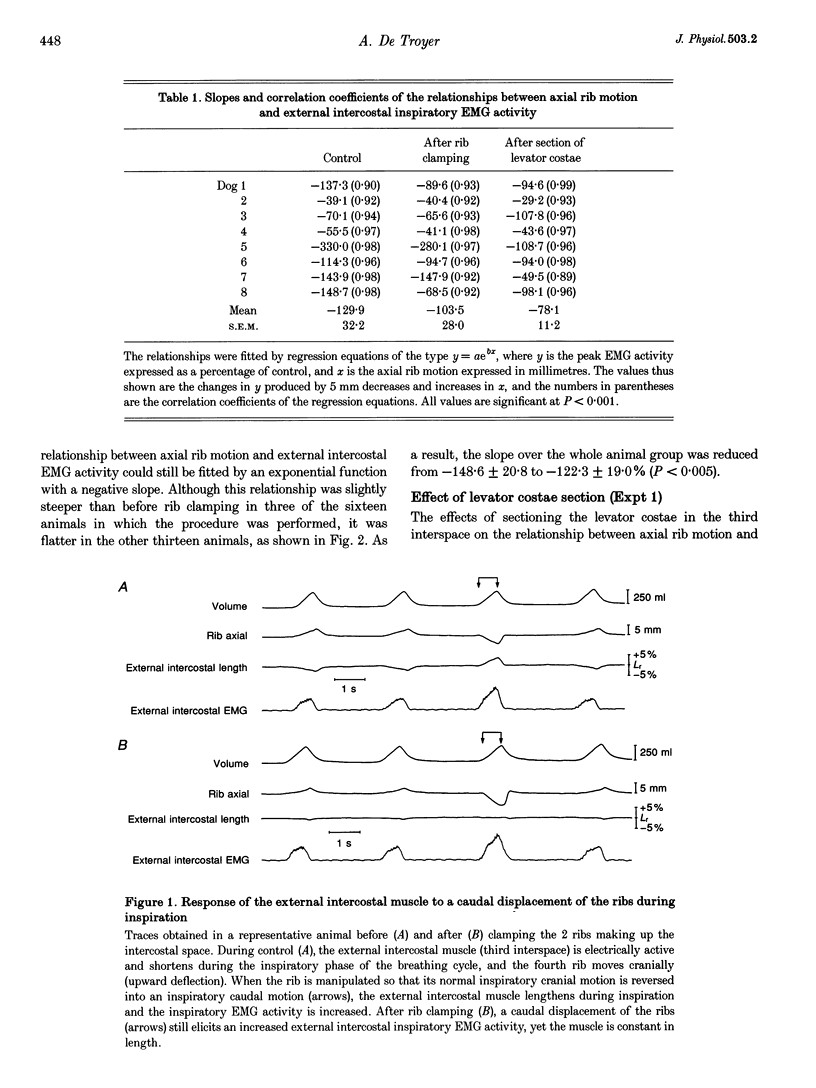
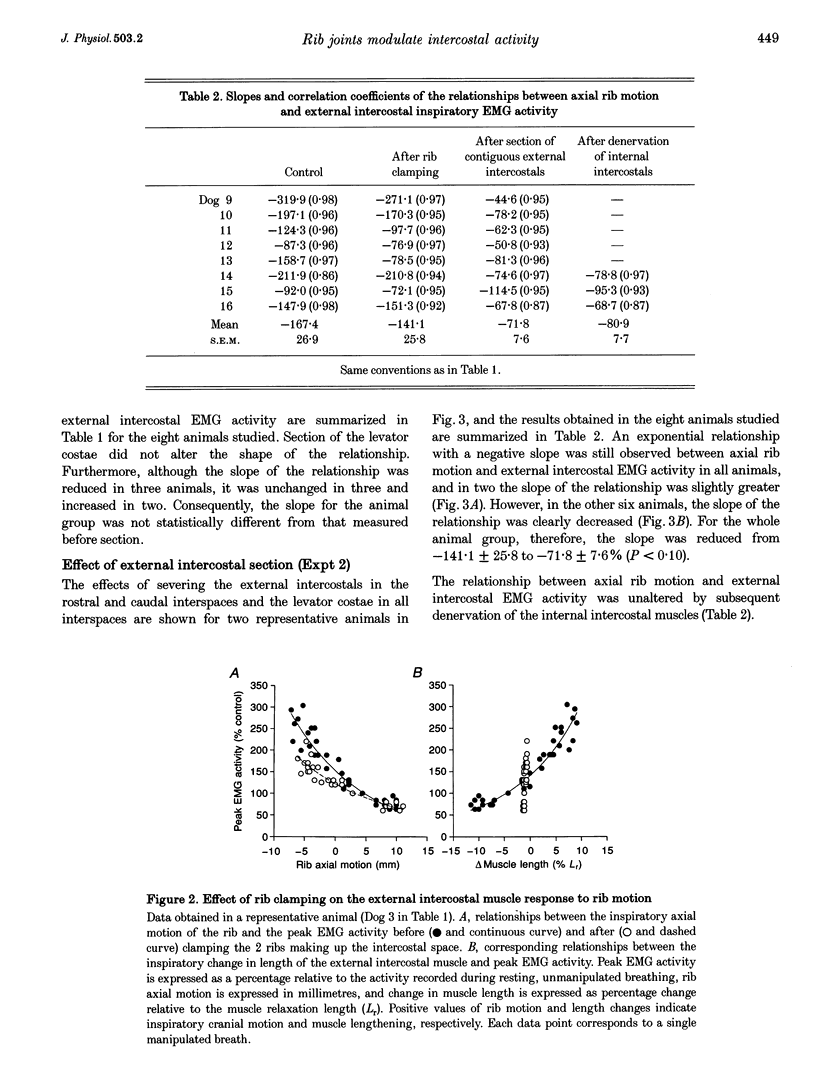
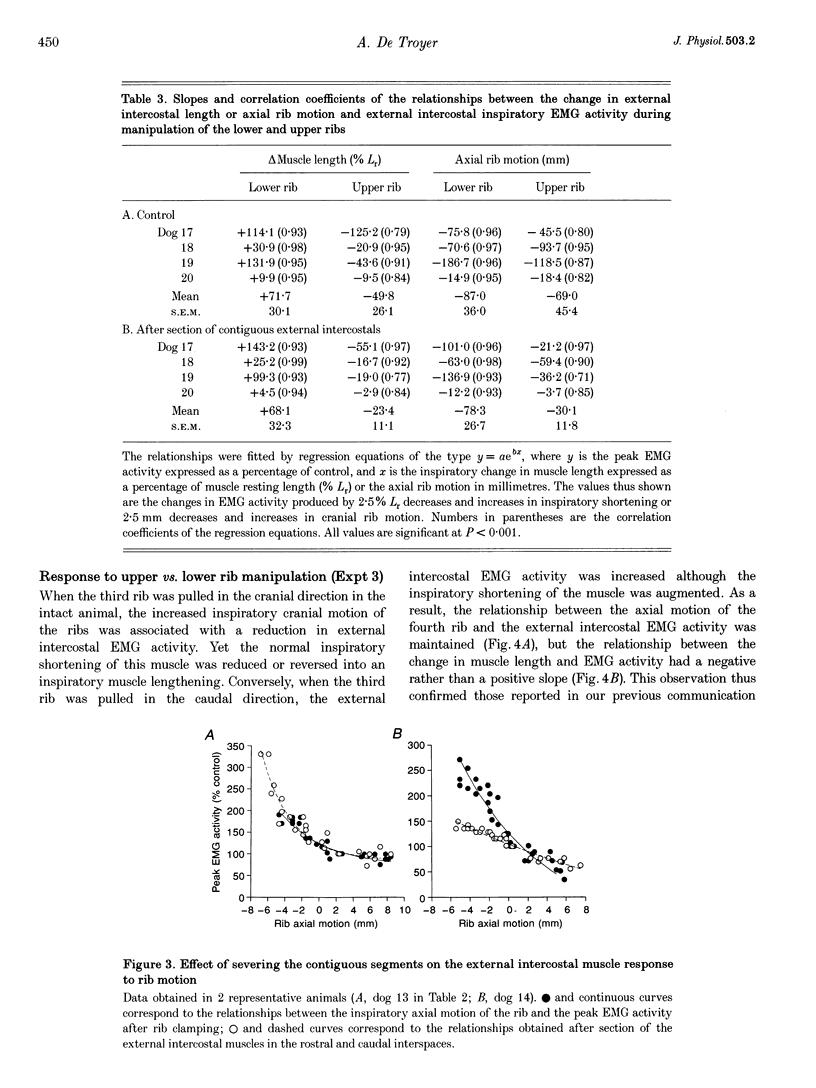
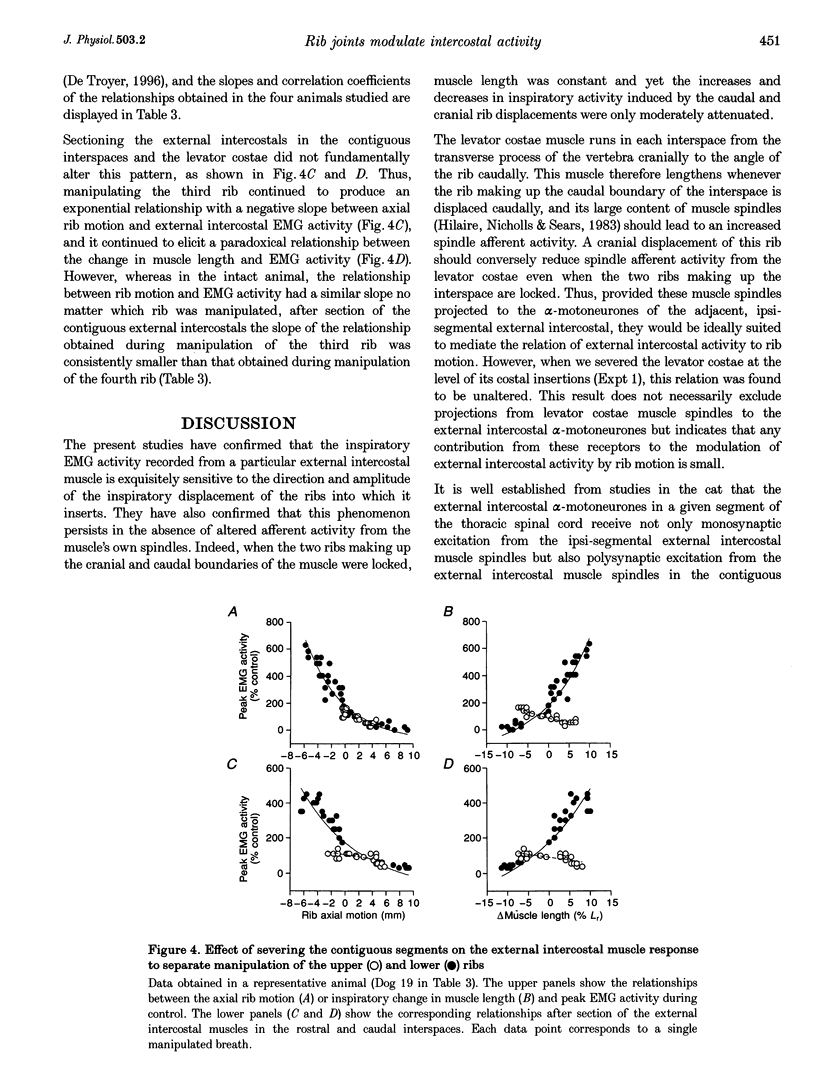
1. Inspiratory activity in the canine external intercostal muscles is exquisitely sensitive to the direction and amplitude of the inspiratory displacement of the ribs. This study was designed to investigate the role of muscle receptors, in particular the muscle spindles, in mediating this phenomenon. 2. External intercostal inspiratory activity showed a reflex increase when the normal cranial motion of the ribs and the normal shortening of the muscles was reduced, and showed a reflex decrease when the cranial motion of the ribs and the shortening of the muscles was augmented. However, clamping the two ribs making up the interspace and maintaining muscle length constant only moderately attenuated these responses. 3. These persistent responses remained unchanged after section of the levator costae muscles. 4. The responses were attenuated but still present after section of the external intercostals in the contiguous segments and denervation of the internal intercostals. 5. These reflex responses are therefore mediated in part by non-muscular receptors, which most likely lie within the costovertebral joints. These joint receptors might be a primary determinant of the load-compensating reflex.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aminoff M. J., Sears T. A. Spinal integration of segmental, cortical and breathing inputs to thoracic respiratory motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):557–575. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD I. A., ROBERTS T. D. Proprioceptive discharges from stretch-receptors in the knee-joint of the cat. J Physiol. 1953 Oct;122(1):38–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORDA M., EKLUND G., VON EULER EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL AND PHRENIC ALPHA-MOTOR RESPONSES TO CHANGES IN RESPIRATORY LOAD. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Mar;63:391–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRITCHLOW V., VON EULER INTERCOSTAL MUSCLE SPINDLE ACTIVITY AND ITS GAMMA MOTOR CONTROL. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:820–847. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A. Differential control of the inspiratory intercostal muscles during airway occlusion in the dog. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:73–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A., Kelly S. Chest wall mechanics in dogs with acute diaphragm paralysis. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Aug;53(2):373–379. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A. Rib motion modulates inspiratory intercostal activity in dogs. J Physiol. 1996 Apr 1;492(Pt 1):265–275. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A. The electro-mechanical response of canine inspiratory intercostal muscles to increased resistance: the cranial rib-cage. J Physiol. 1992;451:445–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A., Yuehua C. Intercostal muscle compensation for parasternal paralysis in the dog: central and proprioceptive mechanisms. J Physiol. 1994 Aug 15;479(Pt 1):149–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duron B., Jung-Caillol M. C., Marlot D. Myelinated nerve fiber supply and muscle spindles in the respiratory muscles of cat: quantitative study. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1978 Feb 20;152(2):171–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00315923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., SEARS T. A., SHEALY C. N. Intra-cellular recording from respiratory motoneurones of the thoracic spinal cord of the cat. Nature. 1962 Mar 3;193:844–846. doi: 10.1038/193844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godwin-Austen R. B. The mechanoreceptors of the costo-vertebral joints. J Physiol. 1969 Jun;202(3):737–753. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES R., TORRANCE R. W. Afferent fibres of the stellate ganglion. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1959 Jul;44:271–281. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1959.sp001400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilaire G. G., Nicholls J. G., Sears T. A. Central and proprioceptive influences on the activity of levator costae motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:527–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S., Road J., Bellemare F., Clozel J. P., Lavigne C. M., Grassino A. Respiratory muscle length measured by sonomicrometry. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Mar;56(3):753–764. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.3.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk J. R., Supinski G., DiMarco A. F. Relationship between parasternal and external intercostal muscle length and load compensatory responses in dogs. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:441–455. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. Activity of fusimotor fibres innervating muscle spindles in the intercostal muscles of the cat. Nature. 1963 Mar 9;197:1013–1014. doi: 10.1038/1971013a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. EFFERENT DISCHARGES IN ALPHA AND FUSIMOTOR FIBRES OF INTERCOSTAL NERVES OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:295–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. INVESTIGATIONS ON RESPIRATORY MOTONEURONES OF THE THORACIC SPINAL CORD. Prog Brain Res. 1964;12:259–273. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60627-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant'Ambrogio G., Widdicombe J. G. Respiratory reflexes acting on the diaphragm and inspiratory intercostal muscle of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):766–779. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon R., Zechman F. W. The reflex and mechanical response of the inspiratory muscles to an increased airflow resistance. Respir Physiol. 1972 Sep;16(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(72)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


