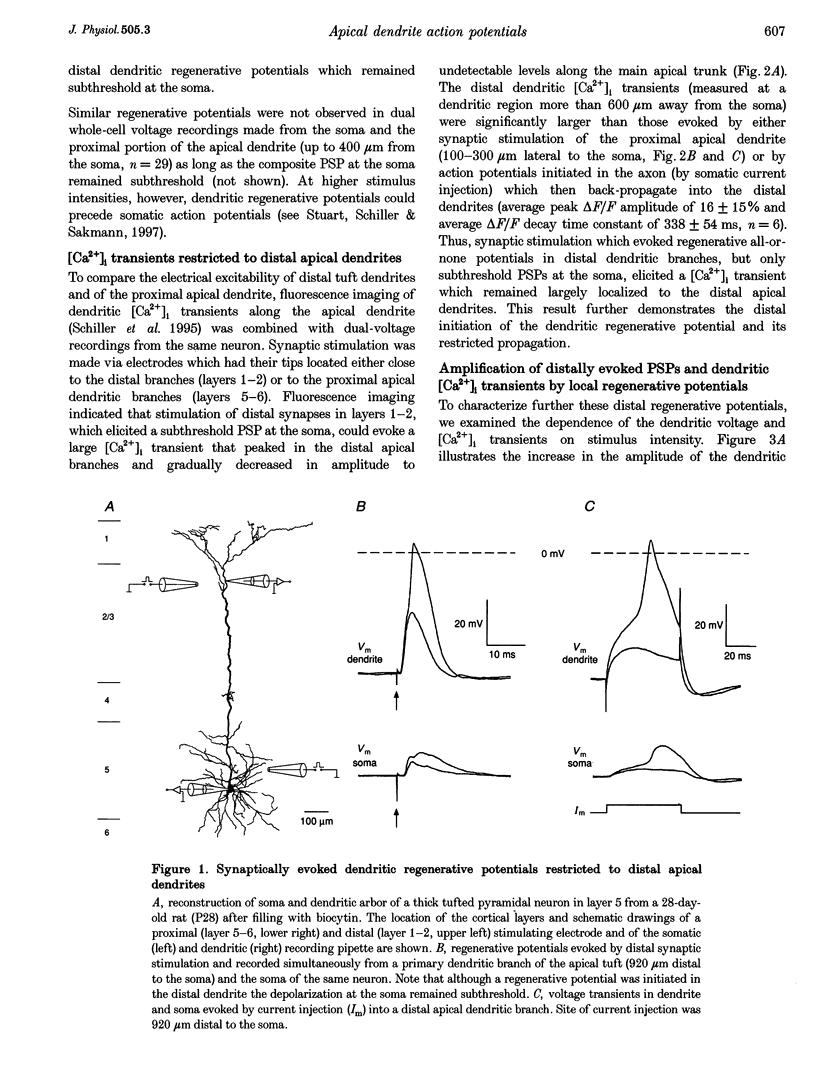
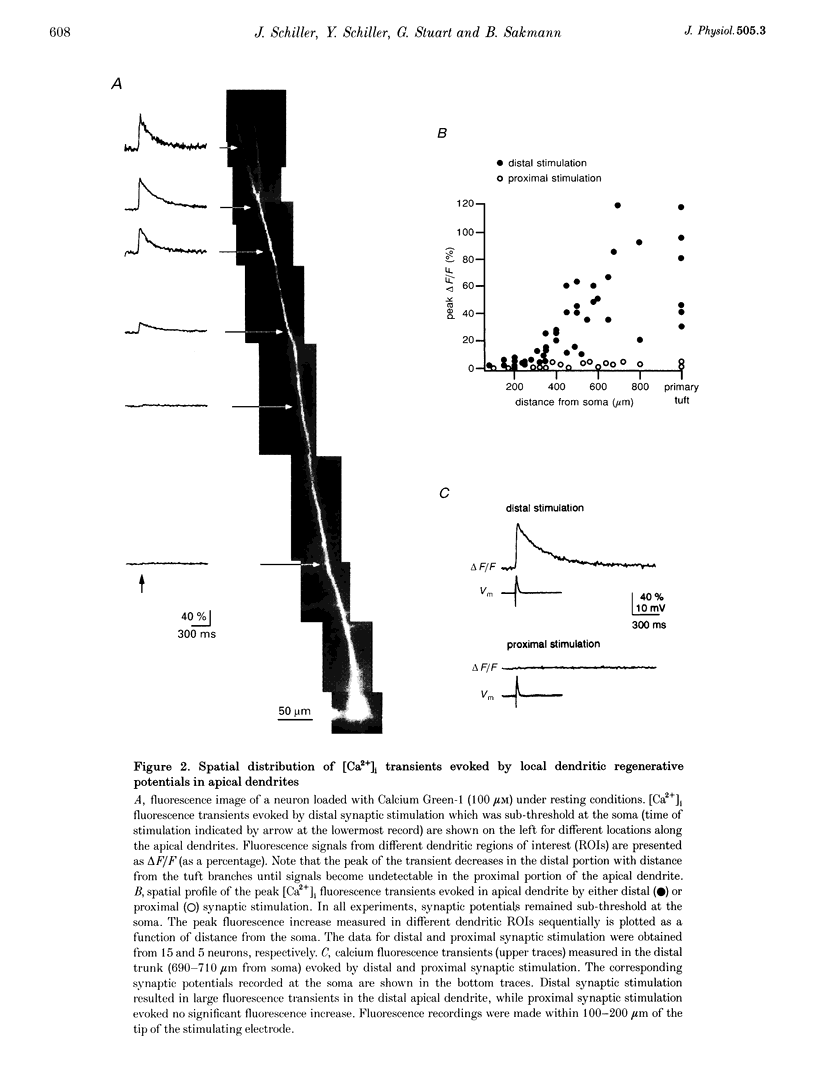
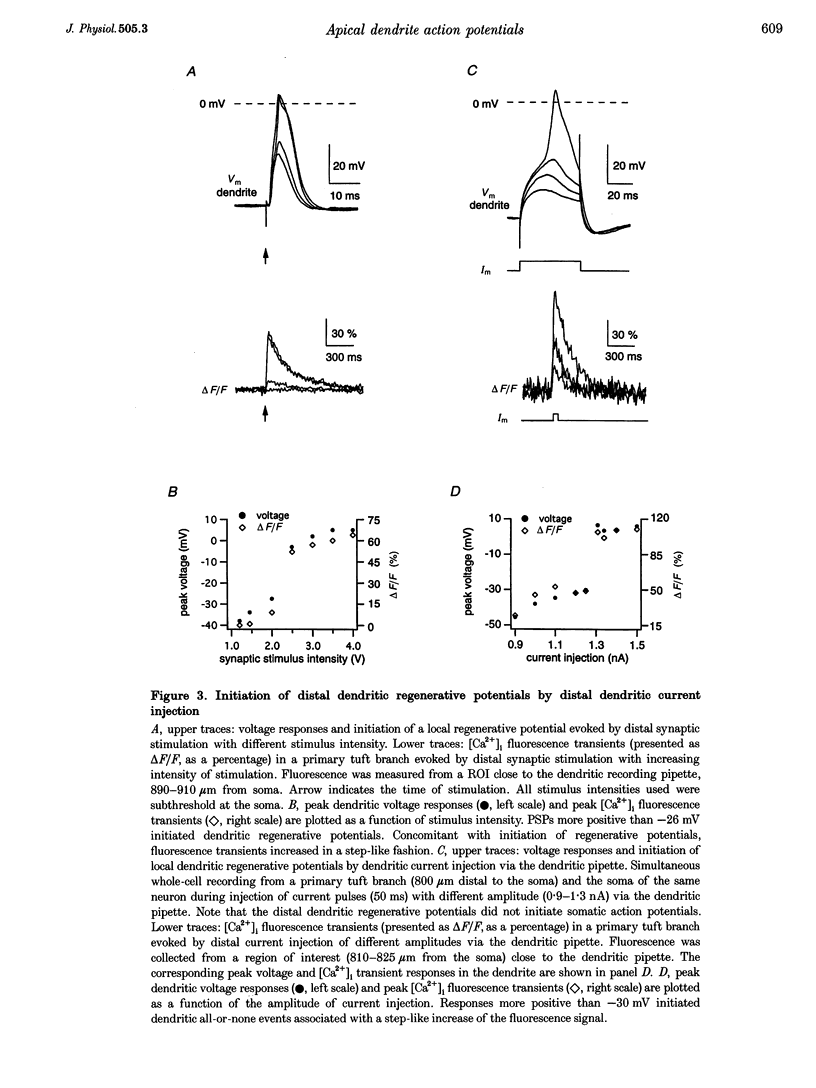
Abstract
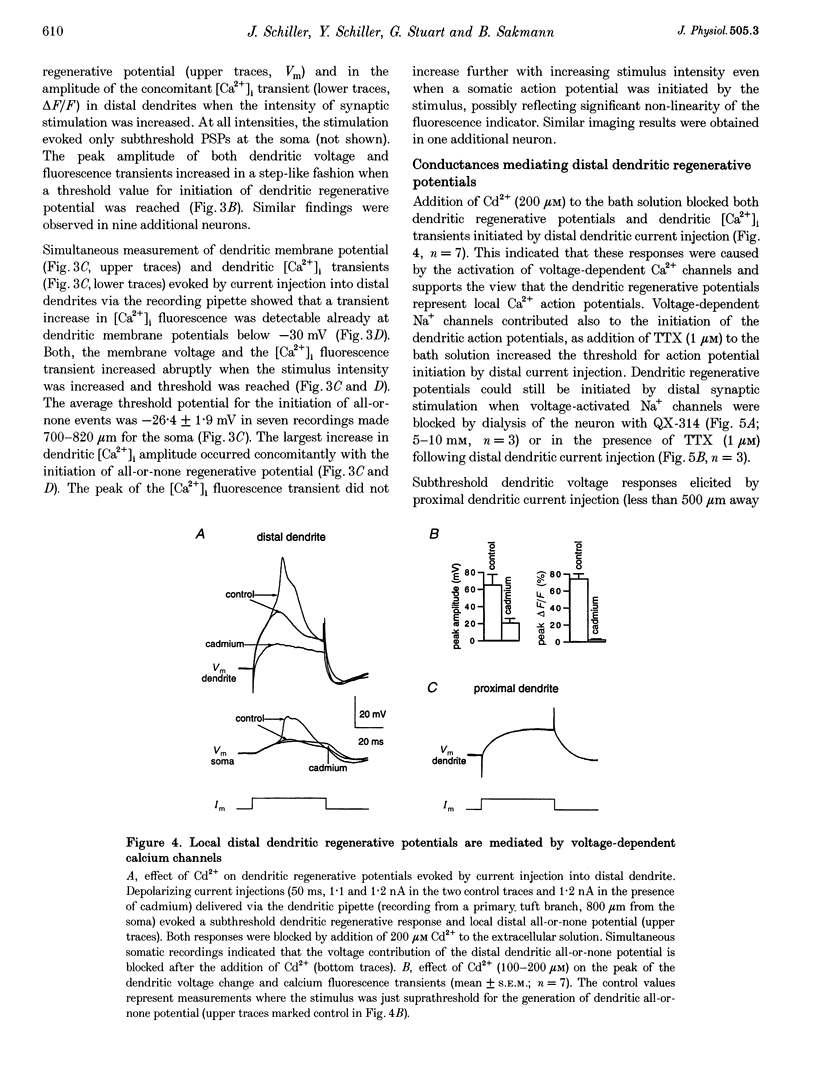
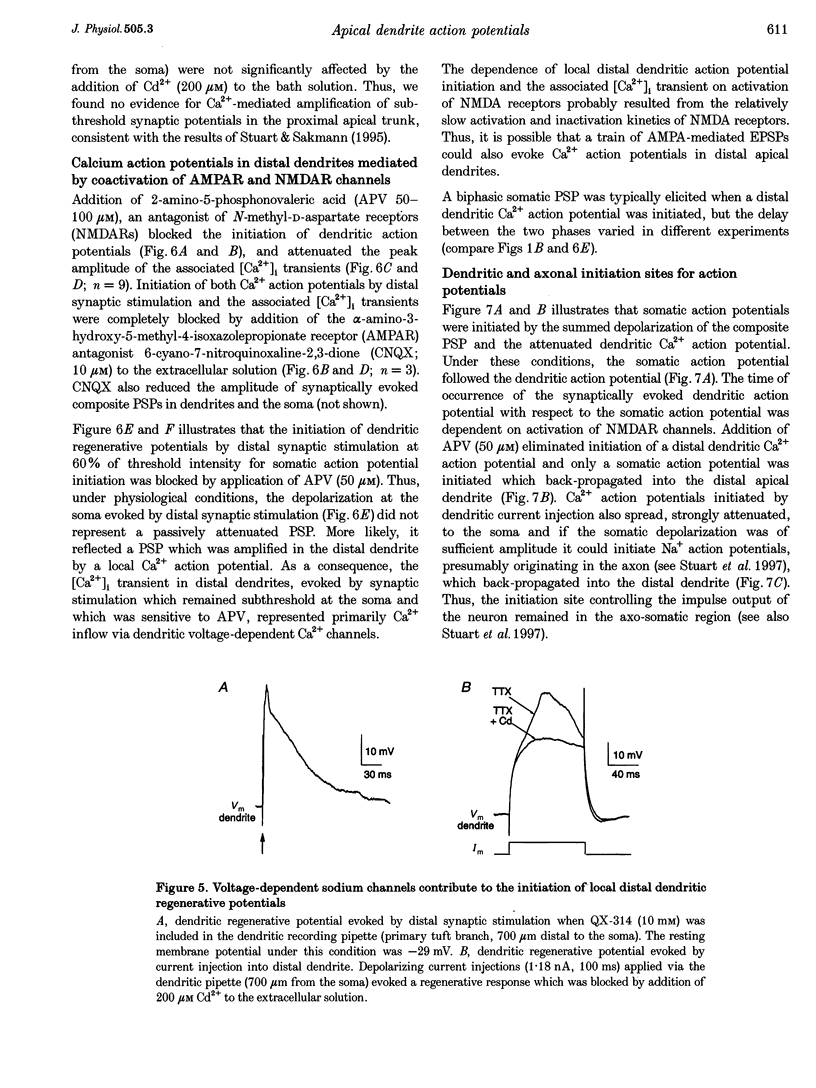
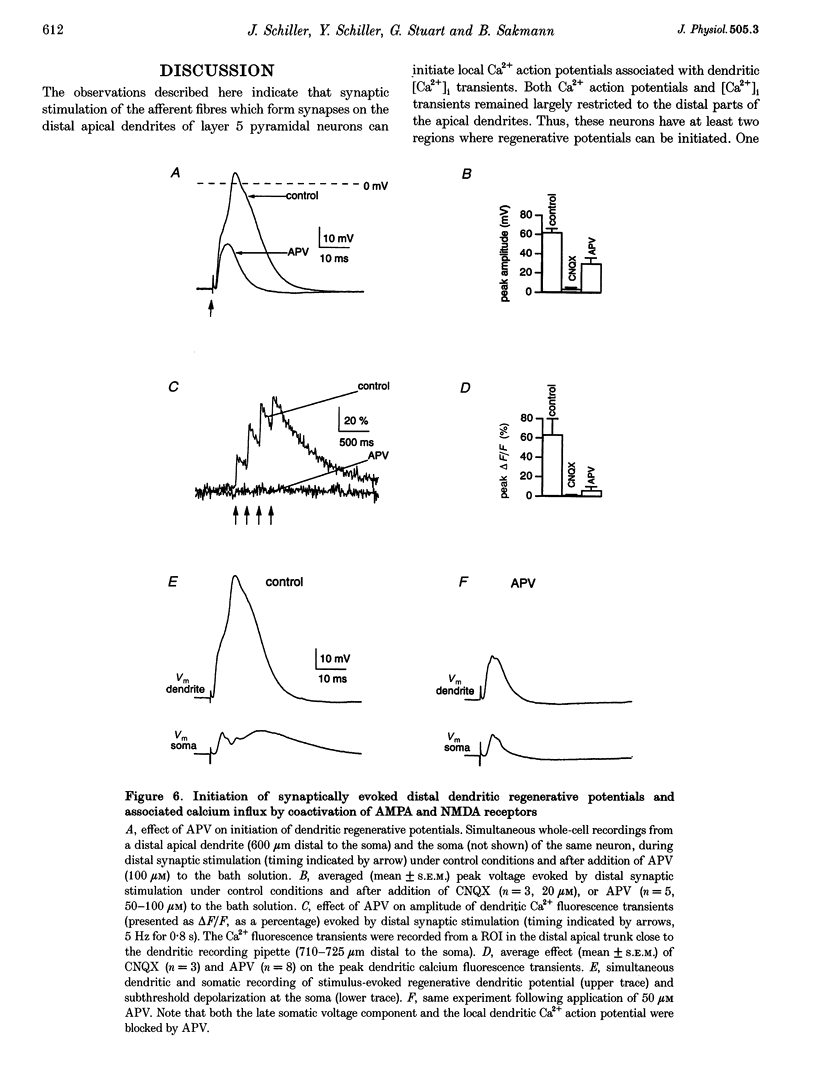
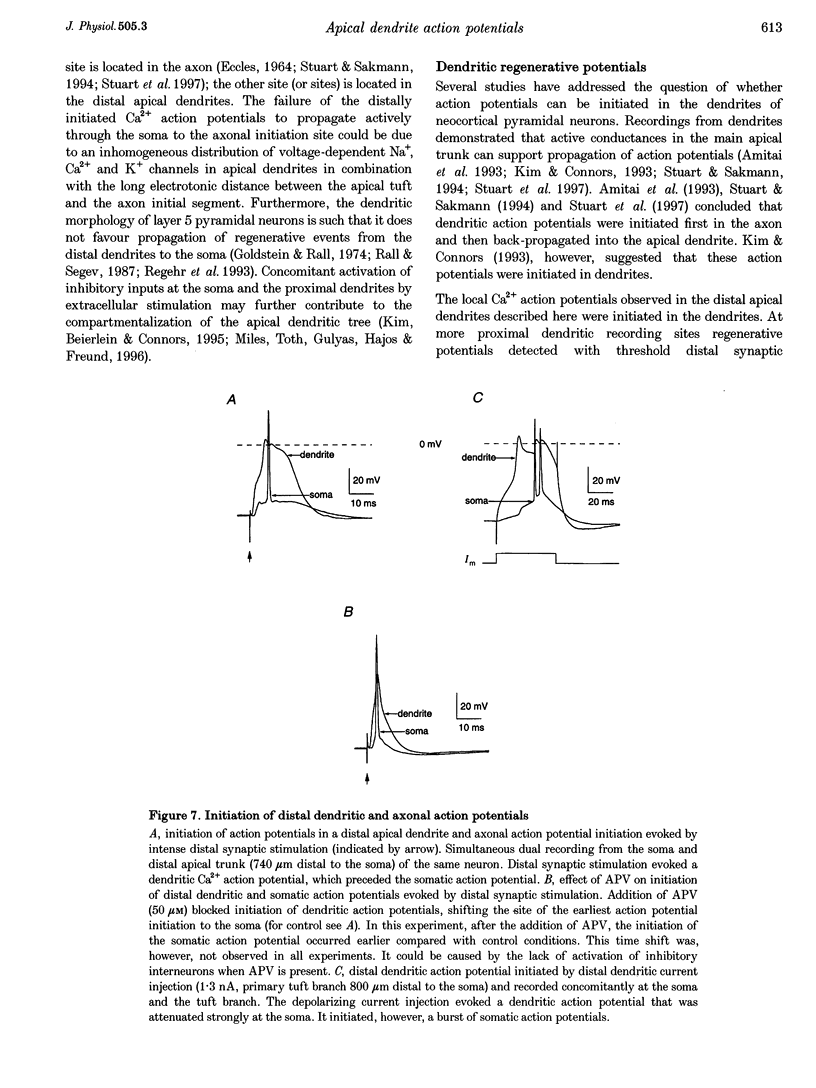
1. Simultaneous whole-cell voltage and Ca2+ fluorescence measurements were made from the distal apical dendrites and the soma of thick tufted pyramidal neurons in layer 5 of 4-week-old (P28-32) rat neocortex slices to investigate whether activation of distal synaptic inputs can initiate regenerative responses in dendrites. 2. Dual whole-cell voltage recordings from the distal apical trunk and primary tuft branches (540-940 microns distal to the soma) showed that distal synaptic stimulation (upper layer 2) evoking a subthreshold depolarization at the soma could initiate regenerative potentials in distal branches of the apical tuft which were either graded or all-or-none. These regenerative potentials did not propagate actively to the soma and axon. 3. Calcium fluorescence measurements along the apical dendrites indicated that the regenerative potentials were associated with a transient increase in the concentration of intracellular free calcium ([Ca2+]i) restricted to distal dendrites. 4. Cadmium added to the bath solution blocked both the all-or-more dendritic regenerative potentials and local dendritic [Ca2+]i transients evoked by distal dendritic current injection. Thus, the regenerative potentials in distal dendrites represent local Ca2+ action potentials. 5. Initiation of distal Ca2+ action potentials by a synaptic stimulus required coactivation of AMPA- and NMDA-type glutamate receptor channels. 6. It is concluded that in neocortical layer 5 pyramidal neurons of P28-32 animals glutamatergic synaptic inputs to the distal apical dendrites can be amplified via local Ca2+ action potentials which do not reach threshold for axonal AP initiation. As amplification of distal excitatory synaptic input is associated with a localized increase in [Ca2+]i these Ca2+ action potentials could control the synaptic efficacy of the distal cortico-cortical inputs to layer 5 pyramidal neurons.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amitai Y., Friedman A., Connors B. W., Gutnick M. J. Regenerative activity in apical dendrites of pyramidal cells in neocortex. Cereb Cortex. 1993 Jan-Feb;3(1):26–38. doi: 10.1093/cercor/3.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen M., Lambert J. D. Regenerative properties of pyramidal cell dendrites in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1995 Mar 1;483(Pt 2):421–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Collingridge G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):31–39. doi: 10.1038/361031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauller L. J., Connors B. W. Synaptic physiology of horizontal afferents to layer I in slices of rat SI neocortex. J Neurosci. 1994 Feb;14(2):751–762. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-02-00751.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers J., Augustine G. J., Konnerth A. Subthreshold synaptic Ca2+ signalling in fine dendrites and spines of cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):155–158. doi: 10.1038/373155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. S., Rall W. Changes of action potential shape and velocity for changing core conductor geometry. Biophys J. 1974 Oct;14(10):731–757. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85947-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J. A., Alonso J. M., Reid R. C. Visually evoked calcium action potentials in cat striate cortex. Nature. 1995 Dec 7;378(6557):612–616. doi: 10.1038/378612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Magee J. C., Colbert C. M., Cristie B. R. Active properties of neuronal dendrites. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1996;19:165–186. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.19.030196.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. G., Beierlein M., Connors B. W. Inhibitory control of excitable dendrites in neocortex. J Neurophysiol. 1995 Oct;74(4):1810–1814. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.74.4.1810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. G., Connors B. W. Apical dendrites of the neocortex: correlation between sodium- and calcium-dependent spiking and pyramidal cell morphology. J Neurosci. 1993 Dec;13(12):5301–5311. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-12-05301.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev-Ram V., Miyakawa H., Lasser-Ross N., Ross W. N. Calcium transients in cerebellar Purkinje neurons evoked by intracellular stimulation. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Oct;68(4):1167–1177. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.4.1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M. Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell somata in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:171–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee J. C., Johnston D. Synaptic activation of voltage-gated channels in the dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):301–304. doi: 10.1126/science.7716525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markram H., Lübke J., Frotscher M., Roth A., Sakmann B. Physiology and anatomy of synaptic connections between thick tufted pyramidal neurones in the developing rat neocortex. J Physiol. 1997 Apr 15;500(Pt 2):409–440. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp022031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Tóth K., Gulyás A. I., Hájos N., Freund T. F. Differences between somatic and dendritic inhibition in the hippocampus. Neuron. 1996 Apr;16(4):815–823. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regehr W., Kehoe J. S., Ascher P., Armstrong C. Synaptically triggered action potentials in dendrites. Neuron. 1993 Jul;11(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90278-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuveni I., Friedman A., Amitai Y., Gutnick M. J. Stepwise repolarization from Ca2+ plateaus in neocortical pyramidal cells: evidence for nonhomogeneous distribution of HVA Ca2+ channels in dendrites. J Neurosci. 1993 Nov;13(11):4609–4621. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-11-04609.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J., Helmchen F., Sakmann B. Spatial profile of dendritic calcium transients evoked by action potentials in rat neocortical pyramidal neurones. J Physiol. 1995 Sep 15;487(Pt 3):583–600. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd G. M., Brayton R. K. Logic operations are properties of computer-simulated interactions between excitable dendritic spines. Neuroscience. 1987 Apr;21(1):151–165. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90329-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruston N., Schiller Y., Stuart G., Sakmann B. Activity-dependent action potential invasion and calcium influx into hippocampal CA1 dendrites. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):297–300. doi: 10.1126/science.7716524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. J., Dodt H. U., Sakmann B. Patch-clamp recordings from the soma and dendrites of neurons in brain slices using infrared video microscopy. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Jun;423(5-6):511–518. doi: 10.1007/BF00374949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. J., Sakmann B. Active propagation of somatic action potentials into neocortical pyramidal cell dendrites. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):69–72. doi: 10.1038/367069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G., Sakmann B. Amplification of EPSPs by axosomatic sodium channels in neocortical pyramidal neurons. Neuron. 1995 Nov;15(5):1065–1076. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G., Schiller J., Sakmann B. Action potential initiation and propagation in rat neocortical pyramidal neurons. J Physiol. 1997 Dec 15;505(Pt 3):617–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.617ba.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda K., Denk W., Kleinfeld D., Tank D. W. In vivo dendritic calcium dynamics in neocortical pyramidal neurons. Nature. 1997 Jan 9;385(6612):161–165. doi: 10.1038/385161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tank D. W., Sugimori M., Connor J. A., Llinás R. R. Spatially resolved calcium dynamics of mammalian Purkinje cells in cerebellar slice. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):773–777. doi: 10.1126/science.2847315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. W., Meyers D. E., Richardson T. L., Barker J. L. The site for initiation of action potential discharge over the somatodendritic axis of rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 1991 Jul;11(7):2270–2280. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-07-02270.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A., Basbaum A. I. Intradendritic recordings from hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):986–990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuste R., Gutnick M. J., Saar D., Delaney K. R., Tank D. W. Ca2+ accumulations in dendrites of neocortical pyramidal neurons: an apical band and evidence for two functional compartments. Neuron. 1994 Jul;13(1):23–43. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90457-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeki S., Shipp S. The functional logic of cortical connections. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):311–317. doi: 10.1038/335311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]