Abstract
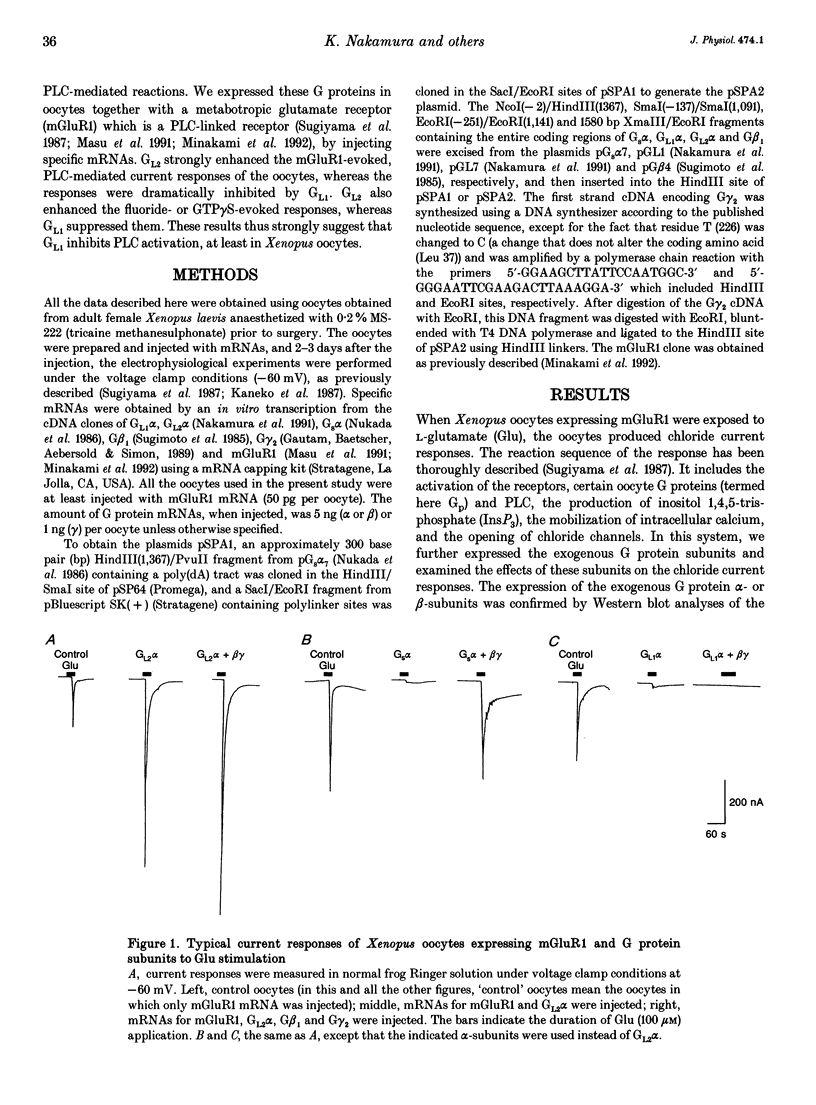
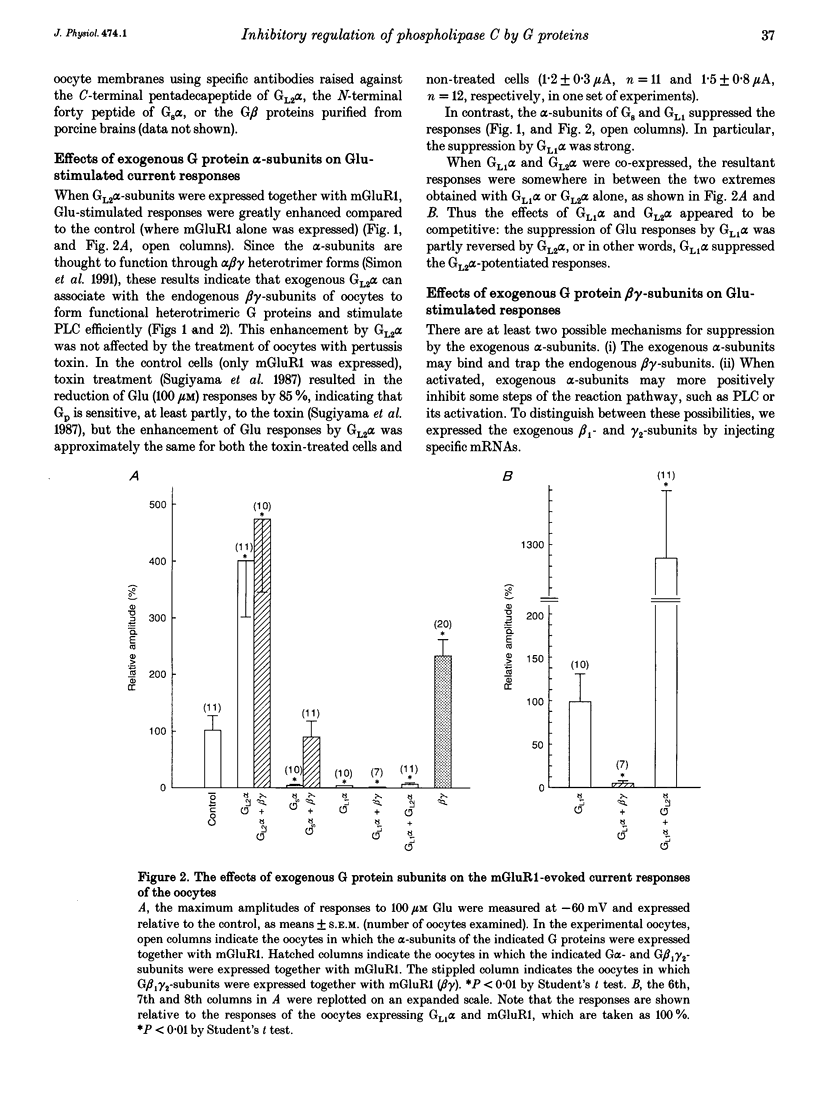
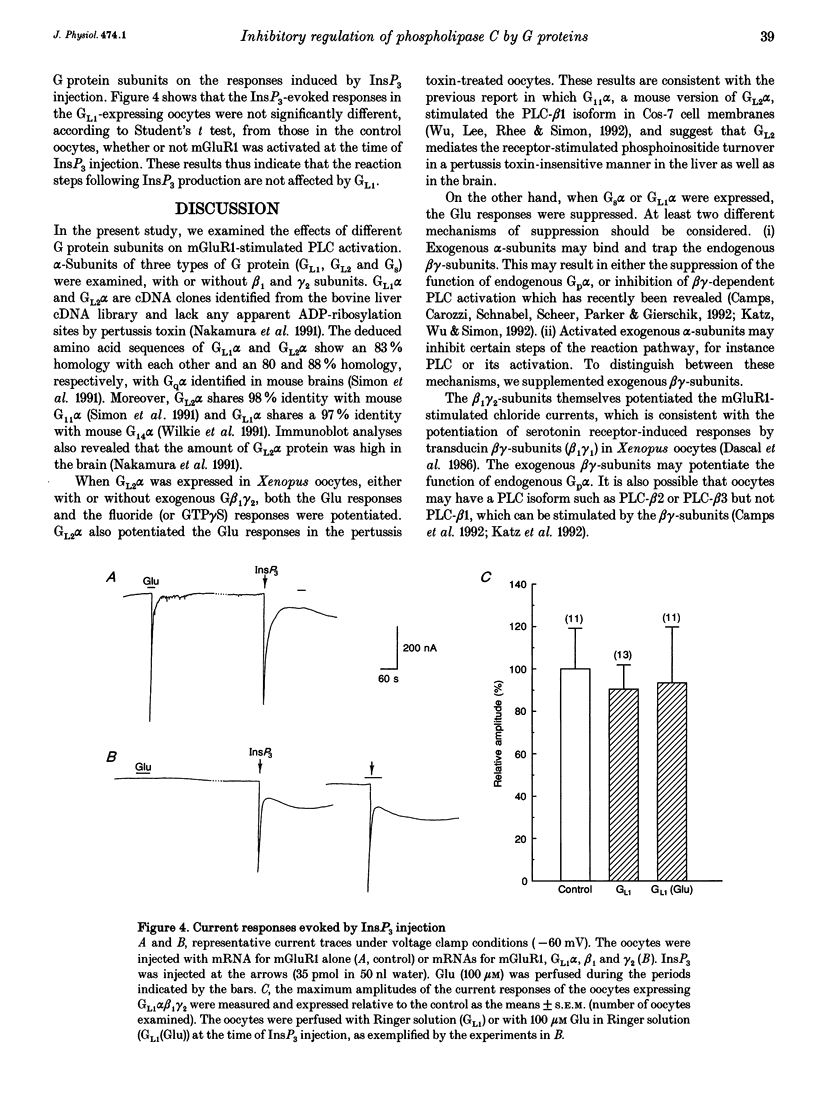
1. Metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 1 (mGluR1), when expressed in Xenopus oocytes, activates phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PLC) in a G protein-dependent manner. This reaction results in the activation of chloride channels in the oocytes, and can be monitored electrophysiologically. We expressed different G protein alpha-subunits together with mGluR1 in oocytes, and examined the effects of these G protein subunits on the PLC-mediated reaction. 2. The expression of the alpha-subunit of GL2, a bovine version of G11, which is a member of the Gq subgroup, potentiated the mGluR1-evoked reaction, whereas the alpha-subunit of GL1, a bovine G14, which is also a member of the Gq subgroup, strongly suppressed it. The expression of Gs alpha also suppressed this reaction. 3. We then expressed G beta 1 gamma 2-subunits in addition to the G alpha-subunits, and examined the mGluR1-evoked reactions. Both the potentiation and suppression by GL2 alpha and GL1 alpha, respectively, were more pronounced in the presence of the G beta 1 gamma 2-subunits. In contrast, the suppression by Gs alpha was completely reversed by G beta 1 gamma 2. 4. The direct activation of G proteins by the intracellular injection of either fluoride ions or guanosine-5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) (GTP gamma S) causes similar PLC-mediated reactions. The expression of GL2 alpha, GL1 alpha or Gs alpha caused potentiation, suppression and no change, respectively, on the fluoride- (or GTP gamma S-) evoked reactions.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
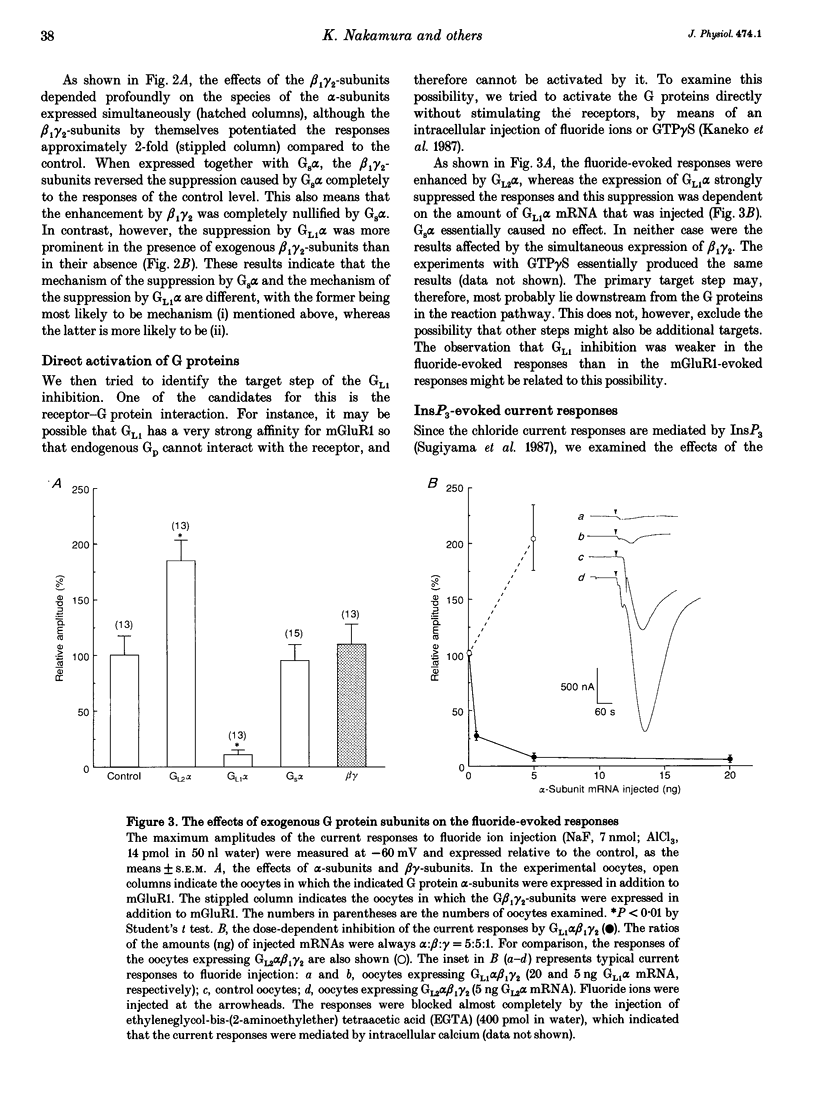


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Camps M., Carozzi A., Schnabel P., Scheer A., Parker P. J., Gierschik P. Isozyme-selective stimulation of phospholipase C-beta 2 by G protein beta gamma-subunits. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):684–686. doi: 10.1038/360684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascal N., Ifune C., Hopkins R., Snutch T. P., Lübbert H., Davidson N., Simon M. I., Lester H. A. Involvement of a GTP-binding protein in mediation of serotonin and acetylcholine responses in Xenopus oocytes injected with rat brain messenger RNA. Brain Res. 1986 Dec;387(3):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enjalbert A., Guillon G., Mouillac B., Audinot V., Rasolonjanahary R., Kordon C., Bockaert J. Dual mechanisms of inhibition by dopamine of basal and thyrotropin-releasing hormone-stimulated inositol phosphate production in anterior pituitary cells. Evidence for an inhibition not mediated by voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18816–18822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautam N., Baetscher M., Aebersold R., Simon M. I. A G protein gamma subunit shares homology with ras proteins. Science. 1989 May 26;244(4907):971–974. doi: 10.1126/science.2499046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito I., Hirono C., Yamagishi S., Nomura Y., Kaneko S., Sugiyama H. Roles of protein kinases in neurotransmitter responses in Xenopus oocytes injected with rat brain mRNA. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Jan;134(1):155–160. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041340120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Kato K., Yamagishi S., Sugiyama H., Nomura Y. GTP-binding proteins Gi and Go transplanted onto Xenopus oocyte by rat brain messenger RNA. Brain Res. 1987 Dec;427(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(87)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Kaneko S., Nomura Y. Phorbol ester inhibition of current responses and simultaneous protein phosphorylation in Xenopus oocyte injected with brain mRNA. J Neurochem. 1988 Mar;50(3):766–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Wu D., Simon M. I. Subunits beta gamma of heterotrimeric G protein activate beta 2 isoform of phospholipase C. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):686–689. doi: 10.1038/360686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Park D., Wu D., Rhee S. G., Simon M. I. Members of the Gq alpha subunit gene family activate phospholipase C beta isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16044–16047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden J., Delahunty T. M. Receptors that inhibit phosphoinositide breakdown. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Mar;10(3):114–120. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masu M., Tanabe Y., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S. Sequence and expression of a metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):760–765. doi: 10.1038/349760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minakami R., Hirose E., Yoshioka K., Yoshimura R., Misumi Y., Sakaki Y., Tohyama M., Kiyama H., Sugiyama H. Postnatal development of mRNA specific for a metabotropic glutamate receptor in the rat brain. Neurosci Res. 1992 Oct;15(1-2):58–63. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(92)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura F., Ogata K., Shiozaki K., Kameyama K., Ohara K., Haga T., Nukada T. Identification of two novel GTP-binding protein alpha-subunits that lack apparent ADP-ribosylation sites for pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12676–12681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukada T., Tanabe T., Takahashi H., Noda M., Hirose T., Inayama S., Numa S. Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of bovine adenylate cyclase-stimulating G-protein deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):220–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrcka A. V., Hepler J. R., Brown K. O., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activity by purified Gq. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):804–807. doi: 10.1126/science.1846707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Nukada T., Tanabe T., Takahashi H., Noda M., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Inayama S. Primary structure of the beta-subunit of bovine transducin deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Ito I., Hirono C. A new type of glutamate receptor linked to inositol phospholipid metabolism. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):531–533. doi: 10.1038/325531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie T. M., Scherle P. A., Strathmann M. P., Slepak V. Z., Simon M. I. Characterization of G-protein alpha subunits in the Gq class: expression in murine tissues and in stromal and hematopoietic cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10049–10053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D. Q., Lee C. H., Rhee S. G., Simon M. I. Activation of phospholipase C by the alpha subunits of the Gq and G11 proteins in transfected Cos-7 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1811–1817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


