Abstract
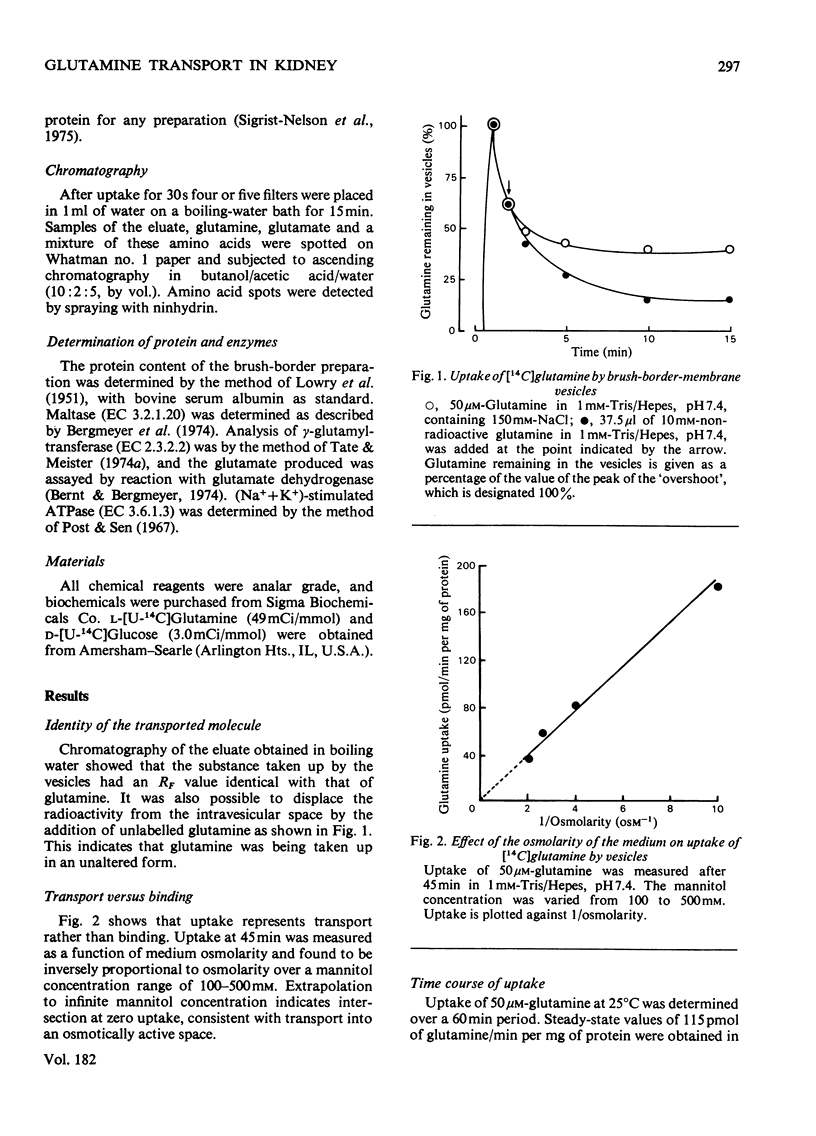
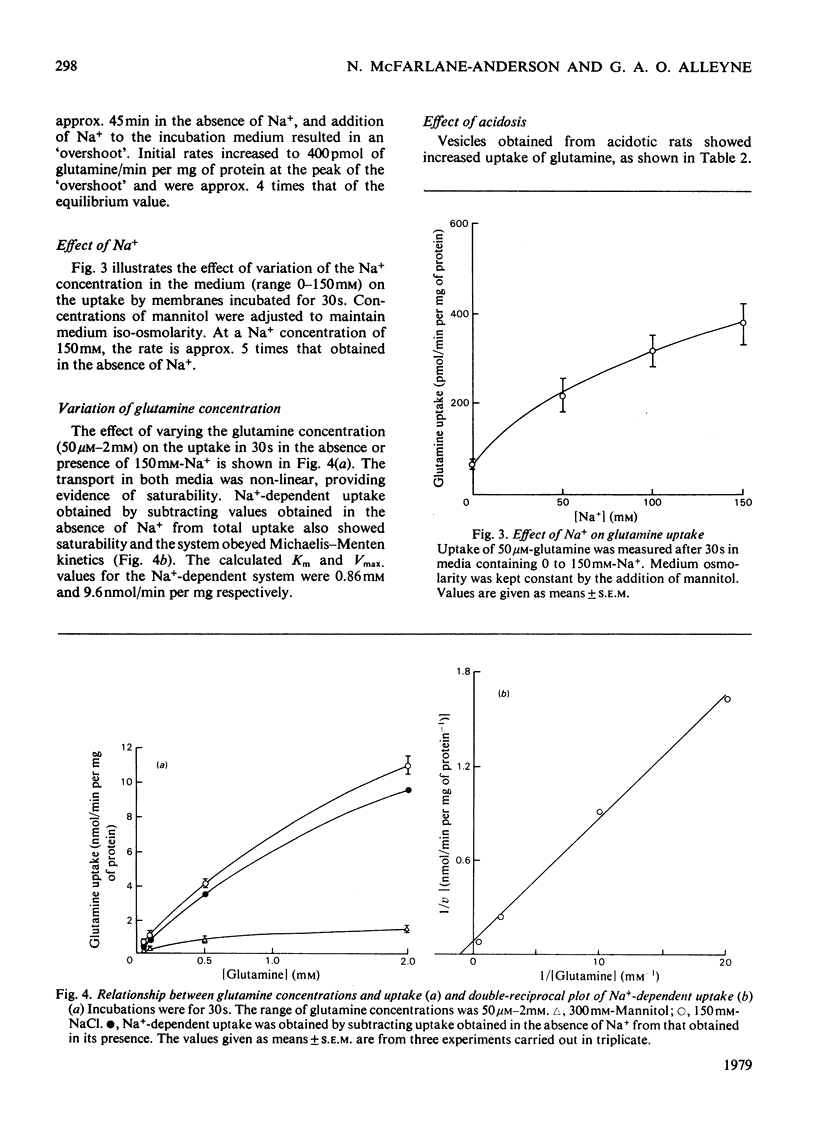
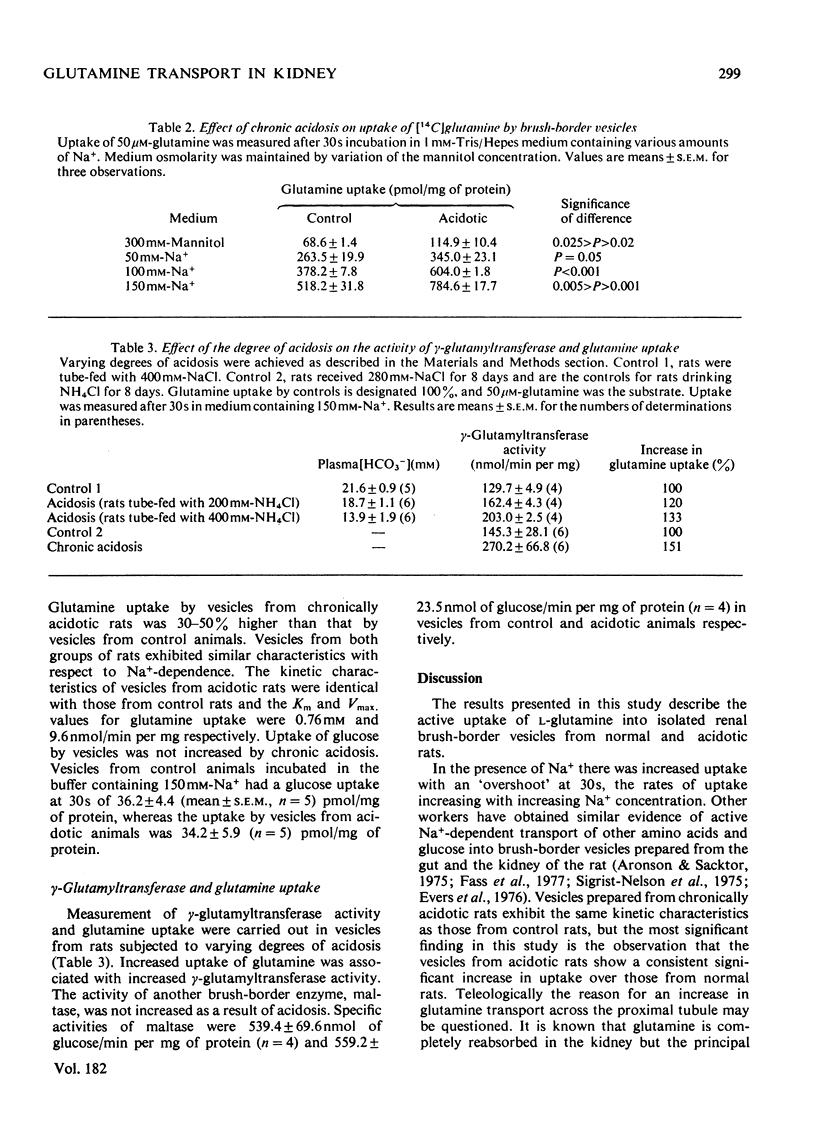
Transport of glutamine by brush-border vesicles prepared from the renal cortex was studied. The transport system had both Na+-dependent and Na+-independent components.The presence of Na+ in the incubation resulted in an 'overshoot' at 30s at which time the rates of transport were approx. 8 times the values obtained in the absence of Na+. Variation of the glutamine concentration showed that the system obeyed Michaelis-Menten kinetics with Km and Vmax. values for the Na+-dependent system of 0.86 mM and 9.6 nmol/min per mg of protein respectively. Vesicles obtained from chronically acidotic rats showed similar kinetic characteristics. The Km and Vmax. values for the Na+-dependent system were 0.76 mM and 9.6 nmol/min per mg of protein respectively. There was increased uptake of glutamine by vesicles from acidotic rats and this increase was associated with increased activity of gamma-glutamyltransferase in these preparations. Vesicles from acidotic rats, however, showed no increase in glucose transport and no increase in the activity of maltase, another brush-border enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alleyne G. A., Roobol A. Regulation of renal cortex ammoniagenesis. I. Stimulation of renal cortex ammoniagenesis in vitro by plasma isolated from acutely acidotic rats. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):117–121. doi: 10.1172/JCI107528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Sacktor B. The Na+ gradient-dependent transport of D-glucose in renal brush border membranes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6032–6039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curthoys N. P., Lowry O. H. The distribution of glutaminase isoenzymes in the various structures of the nephron in normal, acidotic, and alkalotic rat kidney. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):162–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elce J. S., Broxmeyer B. Gamma-glutamyltransferase of rat kidney. Simultaneous assay of the hydrolysis and transfer reactions with (glutamate-14C)glutathione. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):223–232. doi: 10.1042/bj1530223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers J., Murer H., Kinne R. Phenylalanine uptake in isolated renal brush border vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 5;426(4):598–615. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass S. J., Hammerman M. R., Sacktor B. Transport of amino acids in renal brush border membrane vesicles. Uptake of the neutral amino acid L-alanine. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):583–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricke U. Tritosol: a new scintillation cocktail based on Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):555–558. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerman M. R., Sacktor B. Transport of amino acids in renal brush border membrane vesicles. Uptake of L-proline. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):591–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm D. E., Strope G. L. The effects of acidosis and alkalosis on the metabolism of glutamine and glutamate in renal cortex slices. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1251–1263. doi: 10.1172/JCI106920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane Anderson N., Alleyne G. A. The effect of metabolic acidosis on gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase activity in the rat kidney. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):51–53. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A. Function of glutathione in kidney via the gamma-glutamyl cycle. Med Clin North Am. 1975 May;59(3):649–666. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Tate S. S., Meister A. Uptake and utilization of L-glutamine by human lymphoid cells; relationship to gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):222–229. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S., Doak C. W., Kirk G. A novel mechanism for group translocation: substrate-product reutilization by gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in peptide and amino acid transport. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Dec;89(4):853–863. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigrist-Nelson K., Murer H., Hopfer U. Active alanine transport in isolated brush border membranes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5674–5680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Interaction of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase with amino acids, dipeptides, and derivatives and analogs of glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7593–7602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Stimulation of the hydrolytic activity and decrease of the transpeptidase activity of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase by maleate; identity of a rat kidney maleate-stimulated glutaminase and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3329–3333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tietze F. Enzymic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: applications to mammalian blood and other tissues. Anal Biochem. 1969 Mar;27(3):502–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Silverman M. Sugar uptake into brush border vesicles from normal human kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2825–2829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welbourne T. C. Mechanism of renal ammonia production adaptation to chronic acidosis. Med Clin North Am. 1975 May;59(3):629–648. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



