Abstract
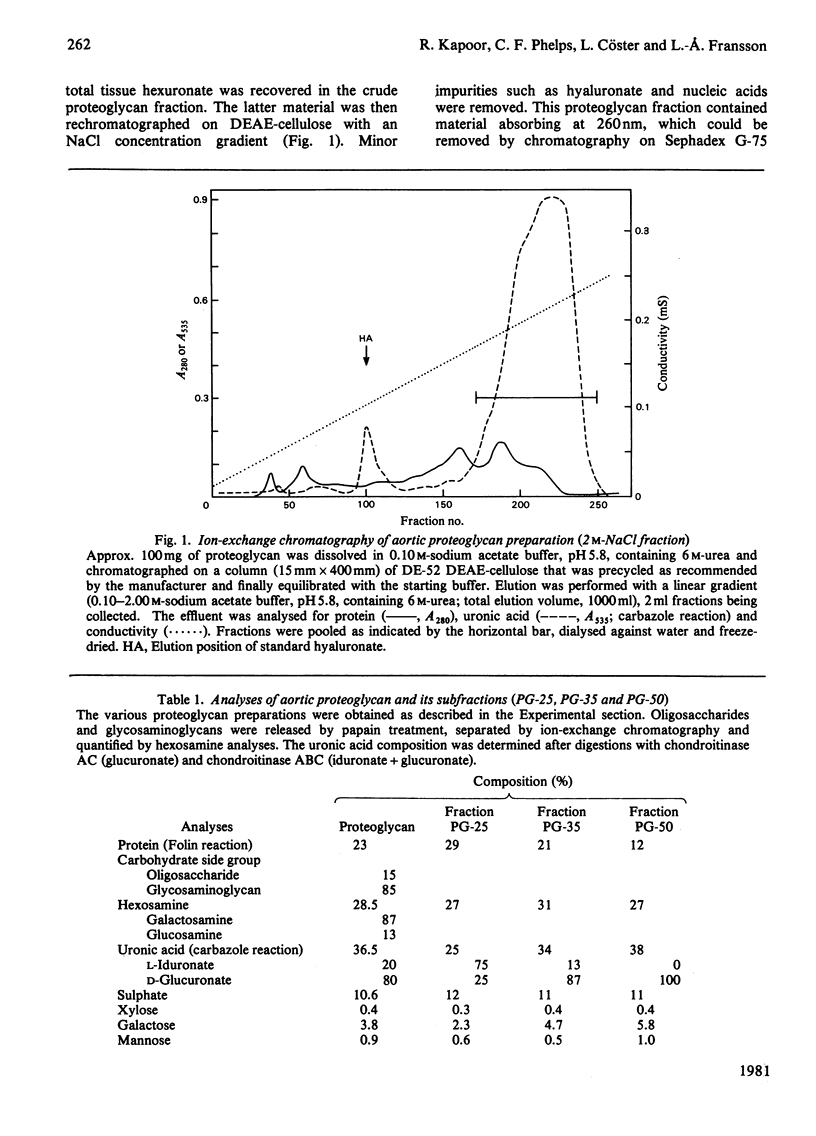
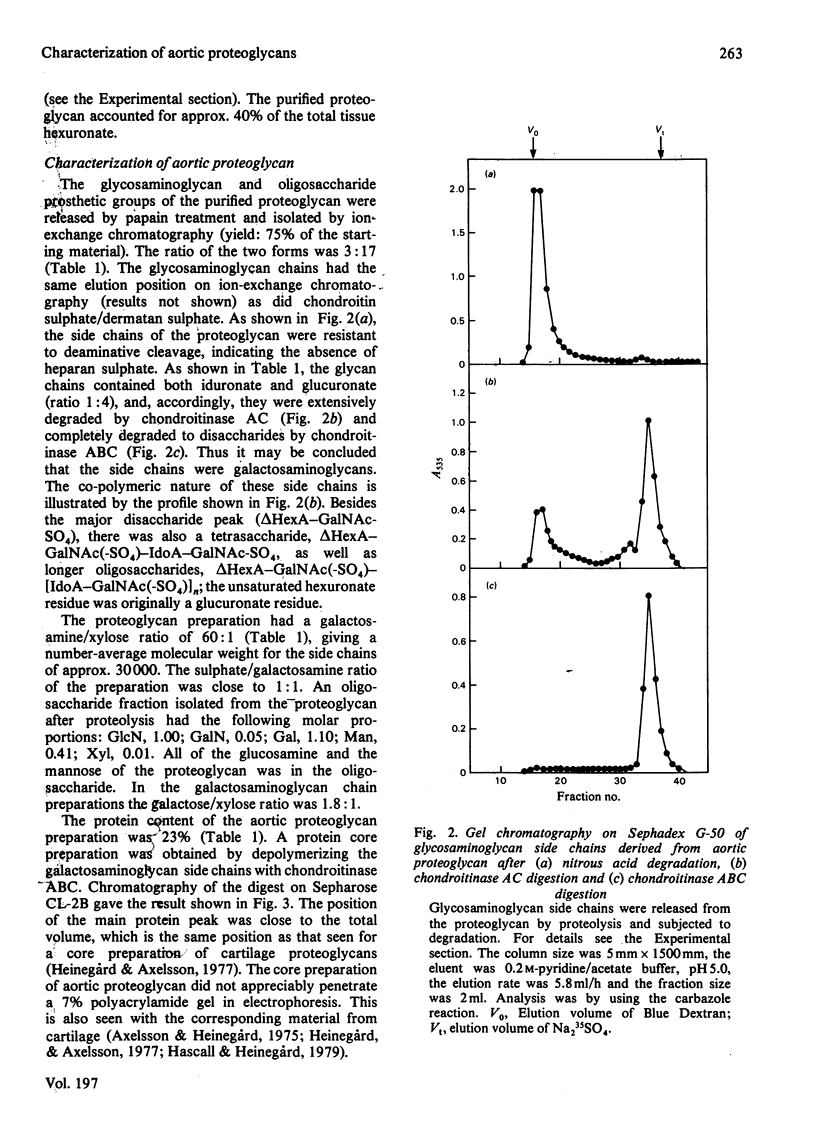
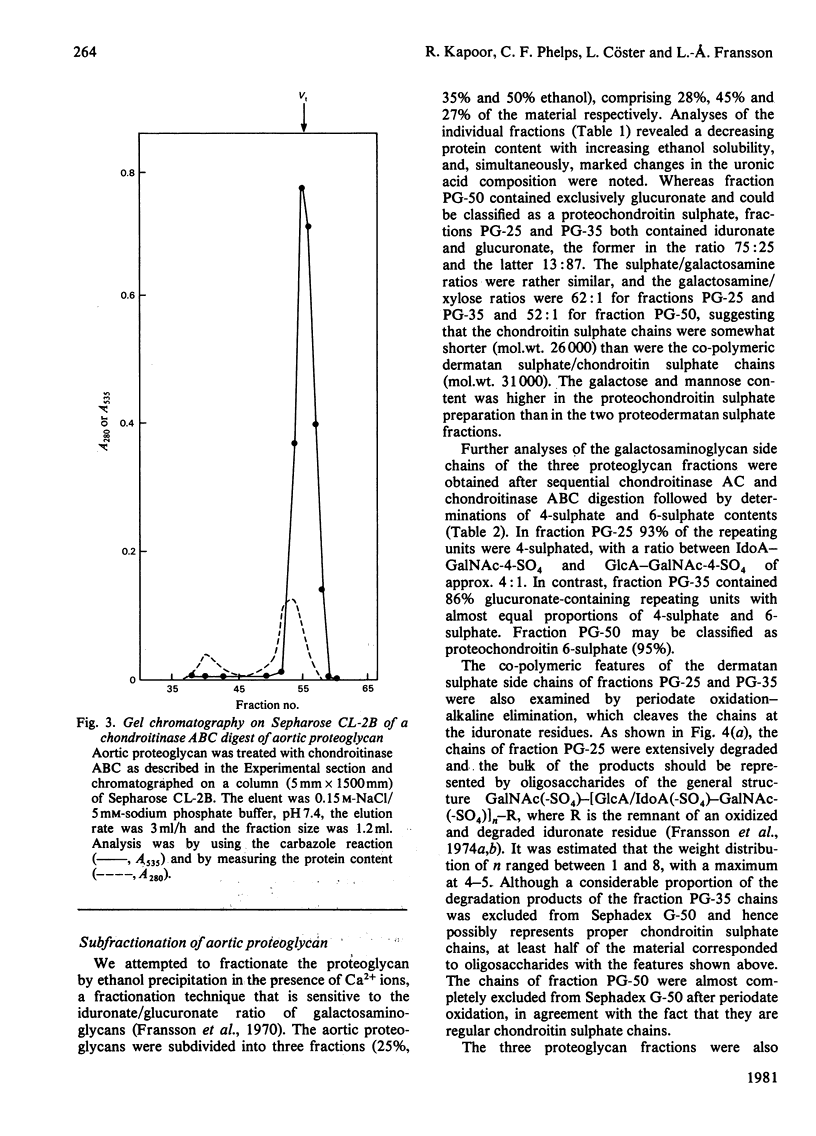
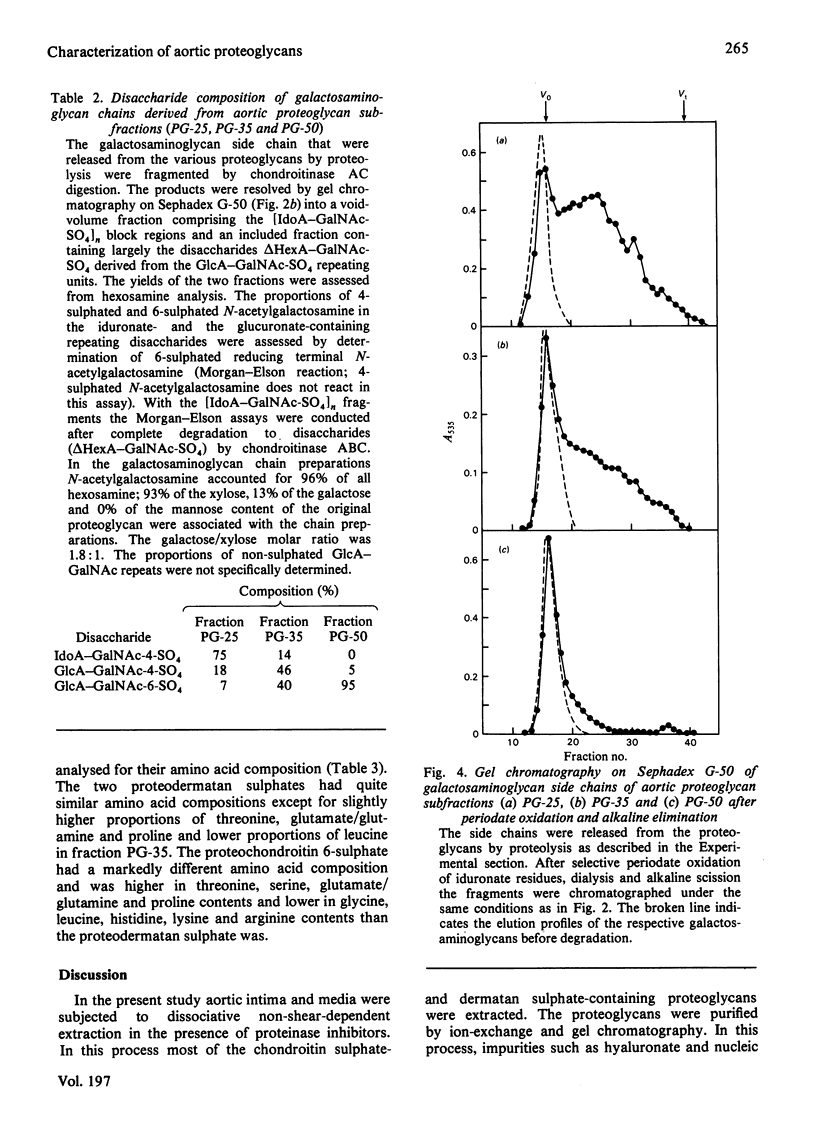
1. Guanidinium chloride (4M) in the presence of proteinase inhibitors extracted 90% of bovine aorta galactosaminoglycans as proteoglycans that were subsequently purified by ion-exchange and gel chromatography. 2. Fractionation of the calcium salts of the purified proteoglycans with increasing concentration of ethanol yielded fractions PG-25 (28%), PG-35 (45%) and PG-50 (37%). 3. Fraction PG-50 contained proteochondroitin 6-sulphate, whereas fractions PG-25 and PG-35 were proteodermatan sulphates of greatly different carbohydrate composition; the molar proportions of L-iduronate-N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulphate, D-glucuronate-N-acetyl-galactosamine 4-sulphate and D-glucuronate-N-acetylgalactosamine 6-sulphate were 75: 18 :7 in fraction PG-25 and 14 :46 :40 in fraction PG-35. 4. The presence of alternating or mixed sequences with L-iduronate- and D-glucuronate-containing repeating disaccharides was indicated by the formation of tetrasaccharides after chondroitinase AC digestion (single L-iduronate residues) and by the release of fragments containing four or five consecutive D-glucuronate-N-acetylgalactosamine repeats after periodate oxidation and alkaline elimination. 5. The amino acid compositions of fractions PG-25 and PG-35 were similar and markedly different from that of fraction PG-50, which also contained more side chains.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelsson I., Heinegård D. Fractionation of proteoglycans from bovine corneal stroma. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):491–500. doi: 10.1042/bj1450491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUDDECKE E., KROEZ W., LANKA E. [Chemical composition and macromolecular structure of chondroitin sulfate proteins]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1963 Mar;331:196–218. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1963.331.1.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti T., Chambers R. E., Clamp J. R. The gas chromatographic properties of biologically important N-acetylglucosamine derivatives, monosaccharides, disaccharides, trisaccharides, tetrasaccharides and pentasaccharides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 24;222(2):339–347. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cöster L., Fransson L. A. Isolation and characterization of dermatan sulphate proteoglycans from bovine sclera. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):143–153. doi: 10.1042/bj1930143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrin P. B. Mechanical properties of arterises. Physiol Rev. 1978 Apr;58(2):397–460. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.2.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich K. C., Radhakrishnamurthy B., Berenson G. S. Isolation of a chondroitin sulfate--dermatan sulfate proteoglycan from bovine aorta. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Nov;171(1):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein R., Larsson S. E., Kuettner K. E., Sorgente N., Hascal V. C. The ground substance of the arterial wall. Part 1. Extractability of glycosaminoglycans and the isolation of a proteoglycan from bovine aorta. Atherosclerosis. 1975 Jul-Aug;22(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(75)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A., Cöster L., Havasmark B., Malmström A., Sjöberg I. The copolymeric structure of pig skin dermatan sulphate. Isolation and characterization of L-idurono-sulphate-containing oligosaccharides from copolymeric chains. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;143(2):379–389. doi: 10.1042/bj1430379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A., Cöster L. Interaction between dermatan sulphate chains. II. Structural studies on aggregating glycan chains and oligosaccharides with affinity for dermatan sulphate-substituted agarose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 4;582(1):132–144. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A., Cöster L., Malmstrom A., Sjöberg I. The copolymeric structure of pig skin dermatan suplhate. Characterization of D-glucuronic acid-containing oligosaccharides isolated after controlled degradation of oxydermatan sulphate. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;143(2):369–378. doi: 10.1042/bj1430369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A., Havsmark B. Structure of dermatan sulfate. VII. The copolymeric structure of dermatan sulfate from horse aorta. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4770–4783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDELL S. Determination of hexosamines. Methods Biochem Anal. 1958;6:289–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardell S., Baker J., Caterson B., Heinegård D., Rodén L. Link protein and a hyaluronic acid-binding region as components of aorta proteoglycan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 29;95(4):1823–1831. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Riolo R. L., Hayward J., Jr, Reynolds C. C. Treatment of bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan with chondroitinases from Flavobacterium heparinum and Proteus vulgaris. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4521–4528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Axelsson I. Distribution of keratan sulfate in cartilage proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1971–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Extraction, fractionation and characterization of proteoglycans from bovine tracheal cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN D., MEYER K. Mucopolysaccharides of aorta at various ages. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Oct;105:78–81. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIMMEL J. R., SMITH E. L. Crystalline papain. I. Preparation, specificity, and activation. J Biol Chem. 1954 Apr;207(2):515–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresse H., Heidel H., Buddecke E. Chemical and metabolic heterogeneity of a bovine aorta chondroitin sulfate-dermatan sulfate proteoglycan. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Oct 26;22(4):557–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Berenson G. S., Ruiz H., Dalferes E. R., Jr, Strong J. P. Acid mucopolysaccharides of human aorta. 1. Variations with maturation. J Atheroscler Res. 1967 Sep-Oct;7(5):573–581. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(67)80035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Bäckström G., Jansson L., Hallén A. Biosynthesis of heparin. II. Formation of sulfamino groups. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7234–7241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander L. S., De Luca S., Nilsson B., Hascall V. C., Caputo C. B., Kimura J. H., Heinegard D. Oligosaccharides on proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6084–6091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhavan M., Chandra K. Acid mucopolysaccharide distribution in normal human aorta in the various anatomic segments. Indian Heart J. 1971 Jul;23(3):202–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurtrey J., Radhakrishnamurthy B., Dalferes E. R., Jr, Berenson G. S., Gregory J. D. Isolation of proteoglycan-hyaluronate complexes from bovine aorta. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1621–1626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y. The preparation of guanidine hydrochloride. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:43–50. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6151–6159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Eisenstein R. Characterization of bovine aorta proteoglycan extracted with guanidine hydrochloride in the presence of protease inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1312–1318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISSIG J. L., STORMINGER J. L., LELOIR L. F. A modified colorimetric method for the estimation of N-acetylamino sugars. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):959–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnamurthy B., Ruiz H. A., Jr, Berenson G. S. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from bovine aorta. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4831–4841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT J. E. Aliphatic ammonium salts in the assay of acidic polysaccharides from tissues. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:145–197. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIREK O. V., SCHILLER S., DORFMAN A. ACID MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES IN AORTIC TISSUE OF THE DOG. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 7;83:148–151. doi: 10.1016/0926-6526(64)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner D. S., Hokanson D. E., Strandness D. E., Jr Arterial walls before and after endarterectomy. Stress-strain characteristics and collagen-elastin content. Arch Surg. 1969 Nov;99(5):606–611. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1969.01340170058013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terho T. T., Hartiala K. Method for determination of the sulfate content of glycosaminoglycans. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jun;41(2):471–476. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90167-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata T., Saito H., Habuchi O., Suzuki S. Purification and properties of bacterial chondroitinases and chondrosulfatases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1523–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


