Abstract
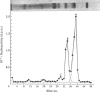
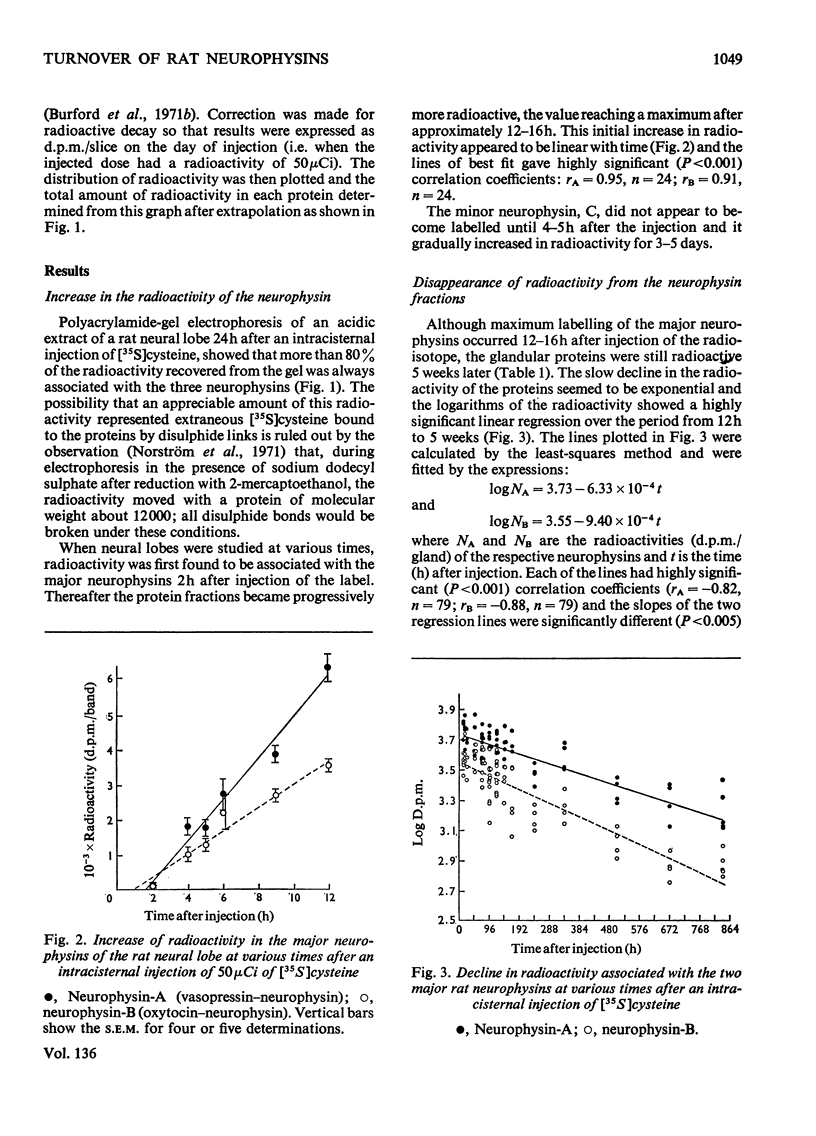
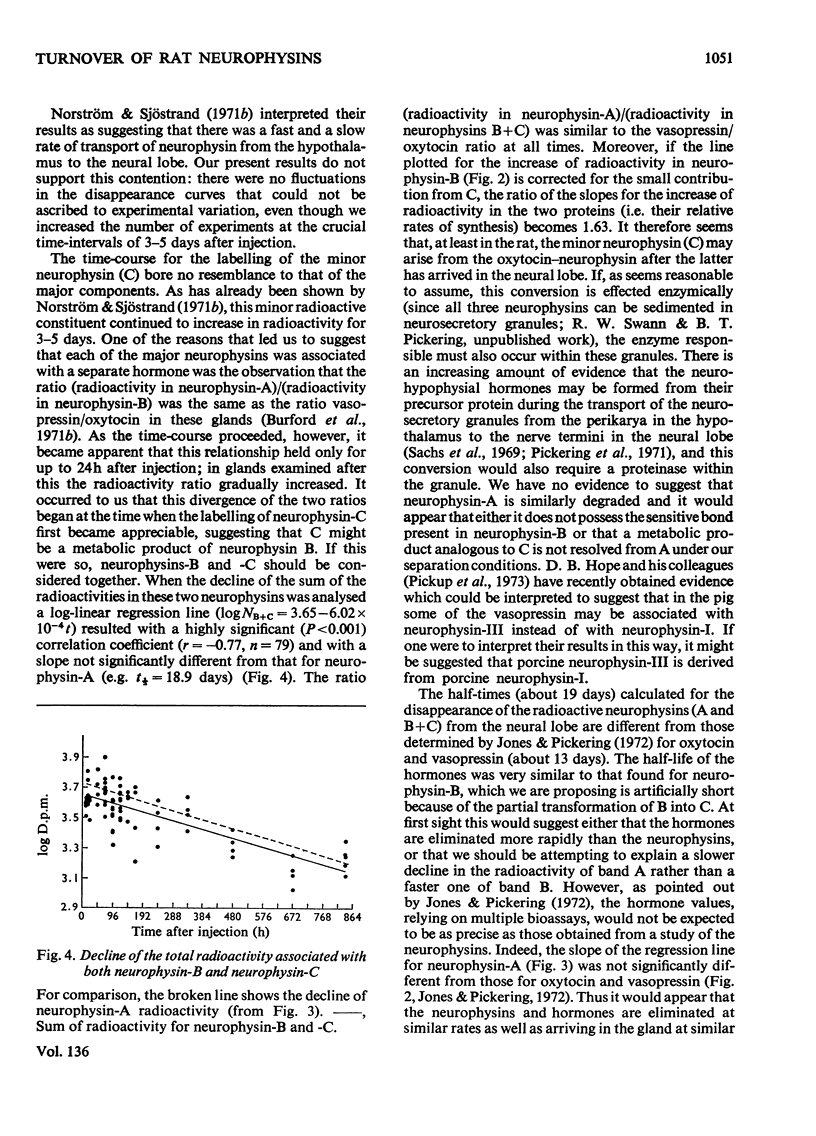
1. Radioactivity associated with the three neurophysins in the neural lobe of the rat was determined at intervals up to 5 weeks after an intracisternal injection of [35S]cysteine. 2. The radioactivity associated with the two major neurophysins (one supposedly associated with vasopressin and the other with oxytocin) increased linearly for 12h after the injection and the ratio of the rates of increase in the two proteins was very similar to the ratio of vasopressin to oxytocin in the gland. 3. From 12h onwards the radioactivity associated with each major neurophysin declined exponentially but the half-life of the supposed oxytocin–neurophysin (13.3 days) was shorter than that for the supposed vasopressin–neurophysin (19.8 days). 4. The kinetics of labelling of the minor neurophysin was quite different from that of the two major ones. It became slowly labelled during 3–5 days after injection and the radioactivity hardly decreased during the following 4 weeks. 5. The data could support the hypothesis that the minor neurophysin is a metabolic product of oxytocin–neurophysin. The exponential rate of disappearance of radioactivity from oxytocin–neurophysin and the minor component taken together has a rate constant similar to that for vasopressin–neurophysin (e.g. half-life=18.9 days).
Full text
PDF
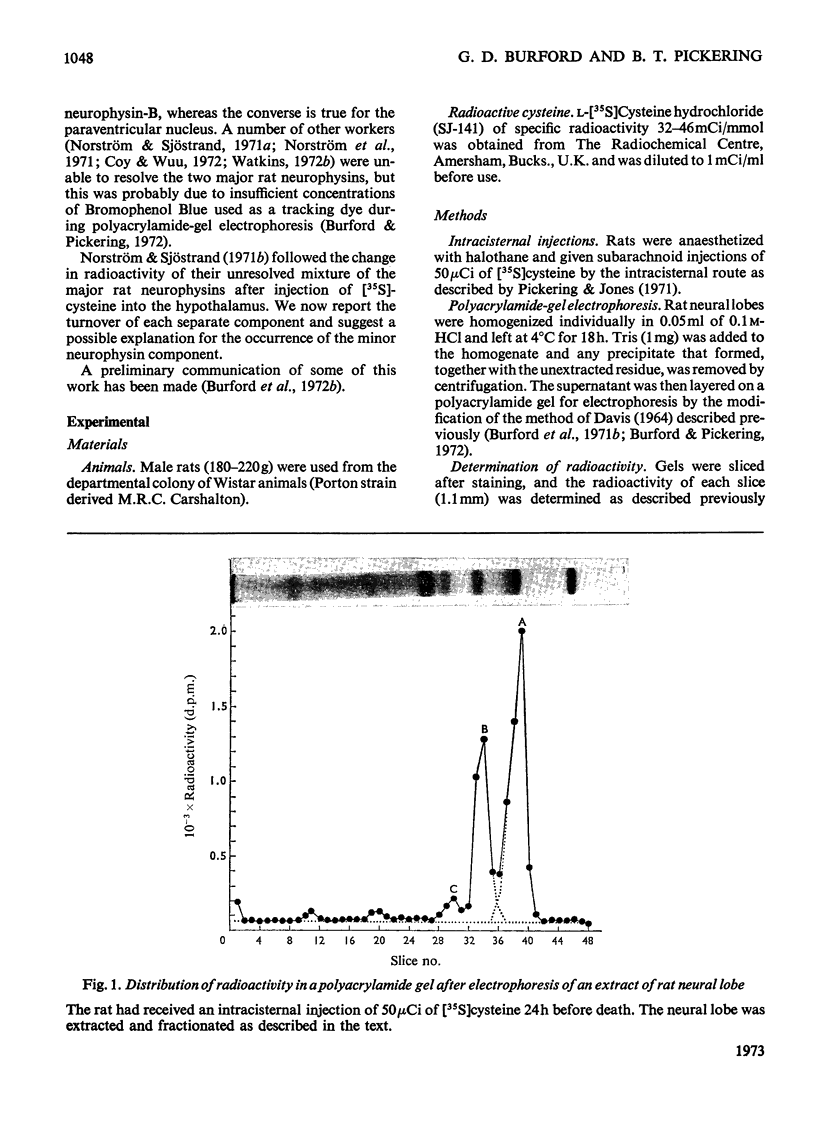
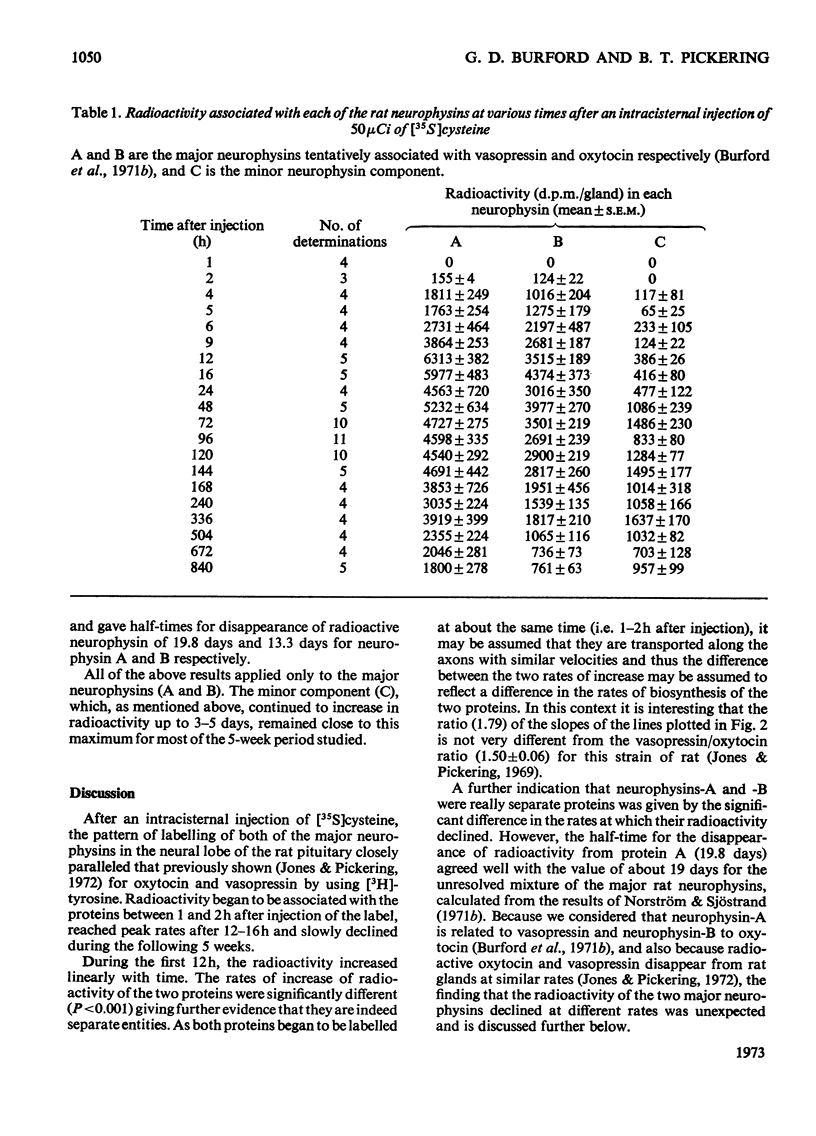

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACHER R., MANOUSSOS G., OLIVRY G. Sur les relations entre l'ocytocine et la vasopressine d'une part et la protéine de Van Dyke d'autre part. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Jan;16(1):155–156. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90193-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burford G. D., Ginsburg M., Thomas P. J. The effect of denaturants and Ca2+ on the molecular weight and polymerisation of neurophysin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 23;229(3):730–738. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90291-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burford G. D., Jones C. W., Pickering B. T. Tentative identification of a vasopressin-neurophysin and an oxytocin-neurophysin in the rat. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(4):809–813. doi: 10.1042/bj1240809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burford G. D., Pickering B. T. The number of neurophysins in the rat. Influence of the concentration of Bromophenol Blue, used as a tracking dye, on the resolution of proteins by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(4):941–944. doi: 10.1042/bj1280941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. W., Friesen H. G. The isolation and characterization of human neurophysin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jan;34(1):165–176. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coy D. H., Wuu T. C. Convenient apparatus for preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and its use in purification of three porcine neurophysins. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):174–181. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90358-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coy D. H., Wuu T. C. Purification and amino acid composition of constituents of rat neurophysin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 15;263(1):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett C. P., Powell A. E., Sachs H. Biosynthesis and release of neurophysin. Endocrinology. 1968 Dec;83(6):1299–1310. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-6-1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. W., Pickering B. T. Comparison of the effects of water deprivation and sodium chloride imbibition on the hormone content of the neurohypophysis of the rat. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):449–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. W., Pickering B. T. Intra-axonal transport and turnover of neurohypophysial hormones in the rat. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):553–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeilly A. S., Legros J. J., Forsling M. L. Release of oxytocin, vasopressin and neurophysin in the goat. J Endocrinol. 1972 Jan;52(1):209–210. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0520209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norström A., Sjöstrand J., Livett B. G., Uttenthal L. O., Hope D. B. Electrophoretic and immunological characterization of rat neurophysin. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(5):671–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1220671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering B. T., Jones C. W. Isolation of radioactive oxytocin and vasopressin from the posterior pituitary gland of the rat after the injection of labelled tyrosine into the cerebrospinal fluid. J Endocrinol. 1971 Jan;49(1):93–103. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0490093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickup J. C., Johnston C. I., Nakamura S., Uttenthal L. O., Hope D. B. Subcellular organization of neurophysins, oxytocin, (8-lysine)-vasopressin and adenosine triphosphatase in porcine posterior pituitary lobes. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):361–371. doi: 10.1042/bj1320361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch R., Hollenberg M. D., Hope D. B. Isolation of a third bovine neurophysin. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):473–479. doi: 10.1042/bj1150473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. G., Zimmerman E. A., Frantz A. G. Physiologic investigation of posterior pituitary binding proteins neurophysin I and neurophysin II. Metabolism. 1971 Dec;20(12):1148–1155. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACHS H., TAKABATAKE Y. EVIDENCE FOR A PRECURSOR IN VASOPRESSIN BIOSYNTHESIS. Endocrinology. 1964 Dec;75:943–948. doi: 10.1210/endo-75-6-943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs H., Fawcett P., Takabatake Y., Portanova R. Biosynthesis and release of vasopressin and neurophysin. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:447–491. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttenthal L. O., Hope D. B. The isolation of three neurophysins from porcine posterior pituitary lobes. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;116(5):899–909. doi: 10.1042/bj1160899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttenthal L. O., Livett B. G., Hope D. B. Release of neurophysin together with vasopressin by a Ca 2 dependent mechanism. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Jun 17;261(839):379–380. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1971.0068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins W. B. Neurophysins of the human pituitary gland. J Endocrinol. 1971 Nov;51(3):595–596. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0510595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins W. B. Neurophysins of the sheep. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):759–760. doi: 10.1042/bj1260759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins W. B. The tentative identification of three neurophysins from the rat posterior pituitary gland. J Endocrinol. 1972 Dec;55(3):577–589. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0550577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]