Abstract
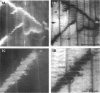
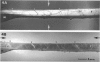
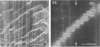
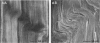
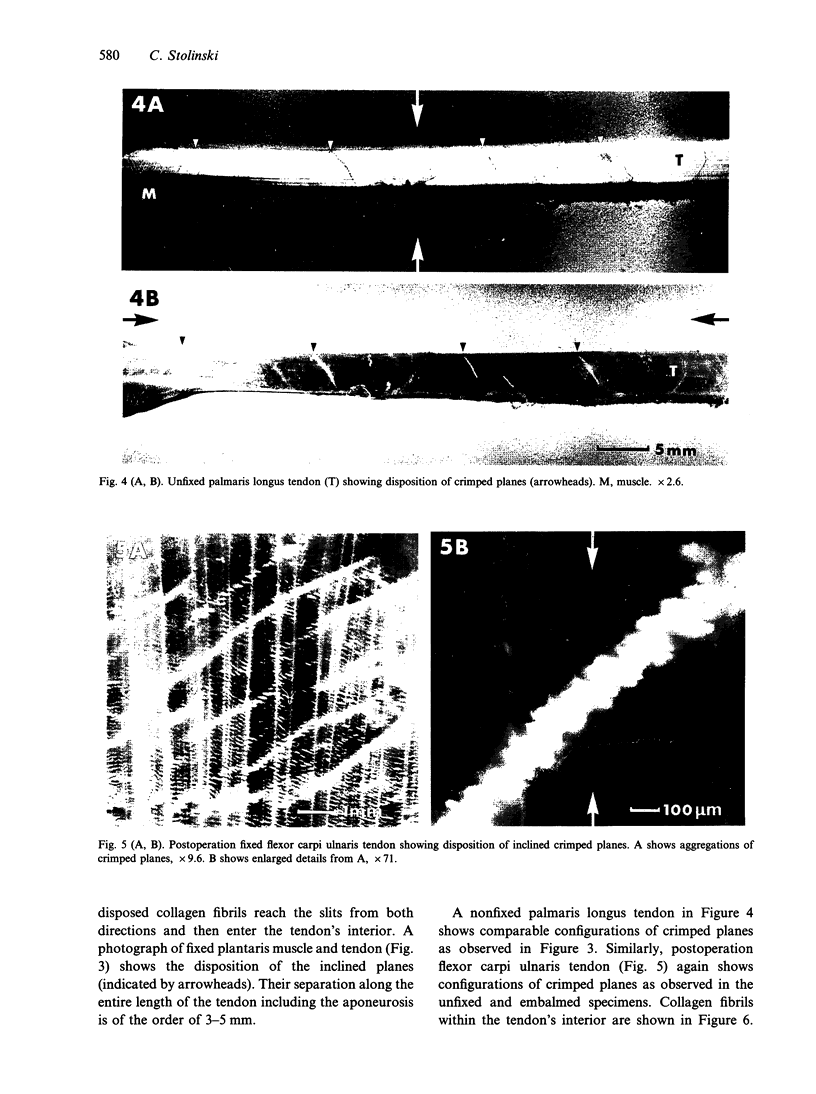
Fixed and unfixed human tendons originating from cadavers and postoperation specimens were examined using inclined parallel beams of light in a reflecting mode. Along the tendon, numerous planes, constantly inclined to the axis, were observed edge-on at the surface and within the interior. Their angle of inclination, with respect to the distal end was very nearly +/- 50 degrees. The planes consisted of individual segments arranged in steps which were on average 190 x 50 microns. Similar configurations were also observed with the scanning electron microscope. Using this technique, the segments were identified with collagen bundles turning at a sharp angle with respect to the axis of the tendon at the level of the inclined plane. Crimped planes were found to be irregularly distributed along the tendons. On longer flatter tendons the average distance between planes was in the range of 1-12 mm. On stretching, the inclined pattern disappeared and was rapidly reestablished in the previously observed position when the strain was released. It is suggested that the observed structure forms a mechanism which is responsible for the appearance of the first part of 'foot' region of the tendon's stress-strain diagram.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benjamin M., Evans E. J., Copp L. The histology of tendon attachments to bone in man. J Anat. 1986 Dec;149:89–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birk D. E., Zycband E. Assembly of the tendon extracellular matrix during development. J Anat. 1994 Jun;184(Pt 3):457–463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant J., Keller A., Baer E., Litt M., Arridge R. G. Collagen; ultrastructure and its relation to mechanical properties as a function of ageing. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1972 Mar 14;180(1060):293–315. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1972.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. A. The blood supply and lymphatic drainage of tendons. J Anat. 1946 Jul;80(Pt 3):147–152.2. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. H., Barbenel J. C. Structural and mechanical properties of tendon related to function. Equine Vet J. 1975 Jan;7(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1975.tb03221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V. The mechanics of voluntary muscle. Lancet. 1951 Nov 24;2(6691):947–951. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)91922-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanak H., Böck P. Die Feinstruktur der Muskel-Sehnenverbindung von Skelett- und Herzmuskel. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Jul;36(1):68–85. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooley C. J., McCrum N. G., Cohen R. E. The viscoelastic deformation of tendon. J Biomech. 1980;13(6):521–528. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(80)90345-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jozsa L., Kannus P., Balint J. B., Reffy A. Three-dimensional ultrastructure of human tendons. Acta Anat (Basel) 1991;142(4):306–312. doi: 10.1159/000147207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastelic J., Galeski A., Baer E. The multicomposite structure of tendon. Connect Tissue Res. 1978;6(1):11–23. doi: 10.3109/03008207809152283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ker R. F. Dynamic tensile properties of the plantaris tendon of sheep (Ovis aries). J Exp Biol. 1981 Aug;93:283–302. doi: 10.1242/jeb.93.1.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN B. F. The tendons of flexor digitorum profundus. J Anat. 1958 Oct;92(4):602–608. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M. Functional anatomy and physiology of tendons. Clin Sports Med. 1992 Jul;11(3):505–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolinski C. Structure and composition of the outer connective tissue sheaths of peripheral nerve. J Anat. 1995 Feb;186(Pt 1):123–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERZAR F., HUBER K. Die Struktur der Sehnen-Faser. Acta Anat (Basel) 1958;33(3):215–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]