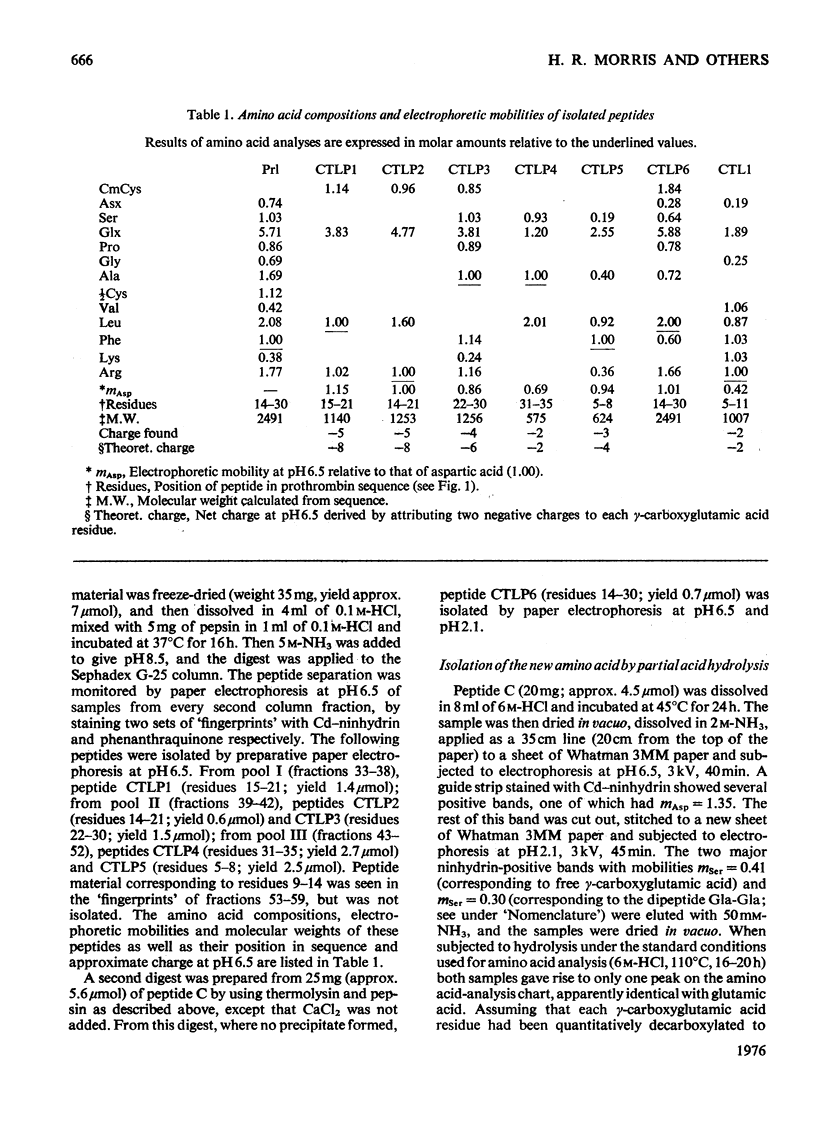
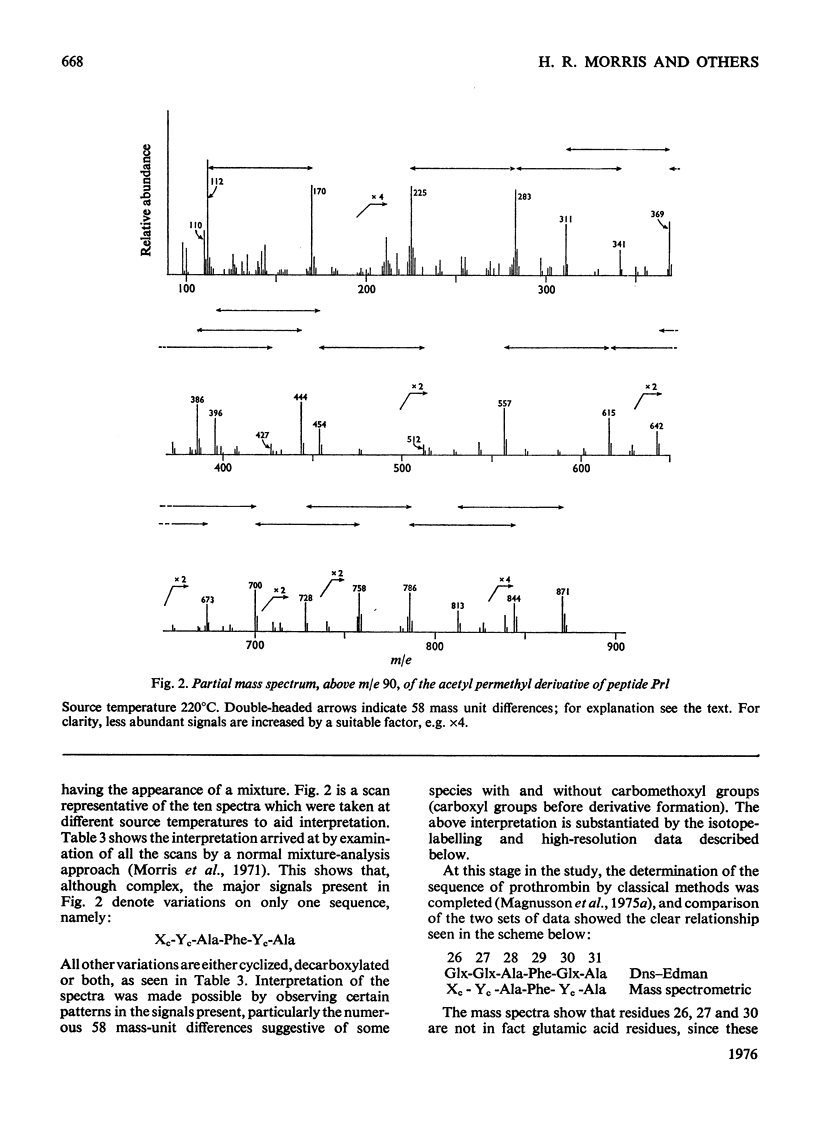
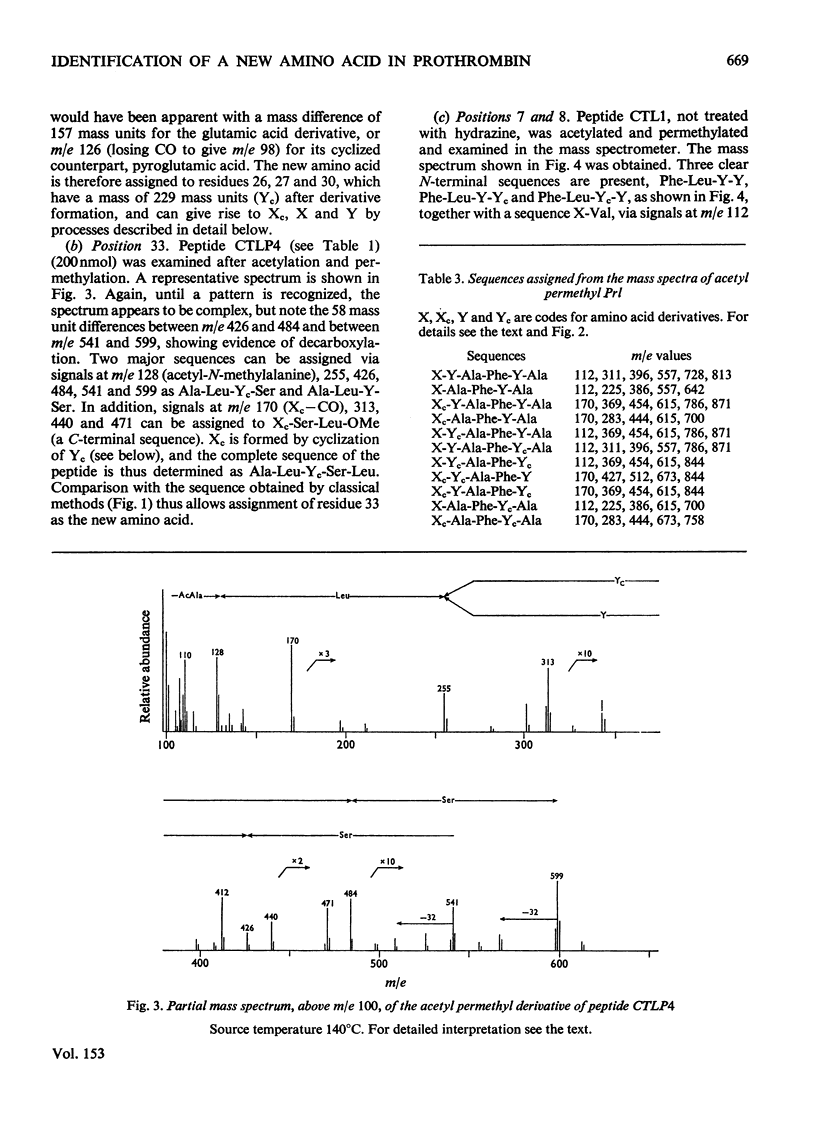
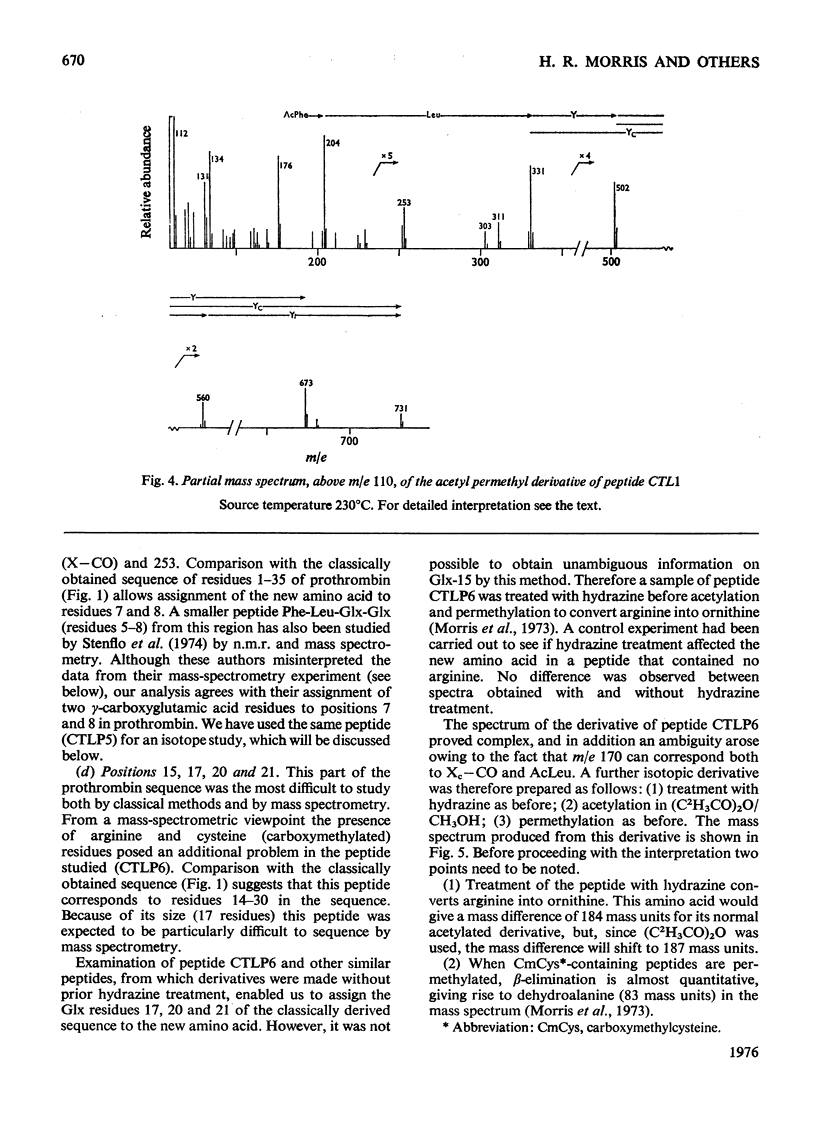
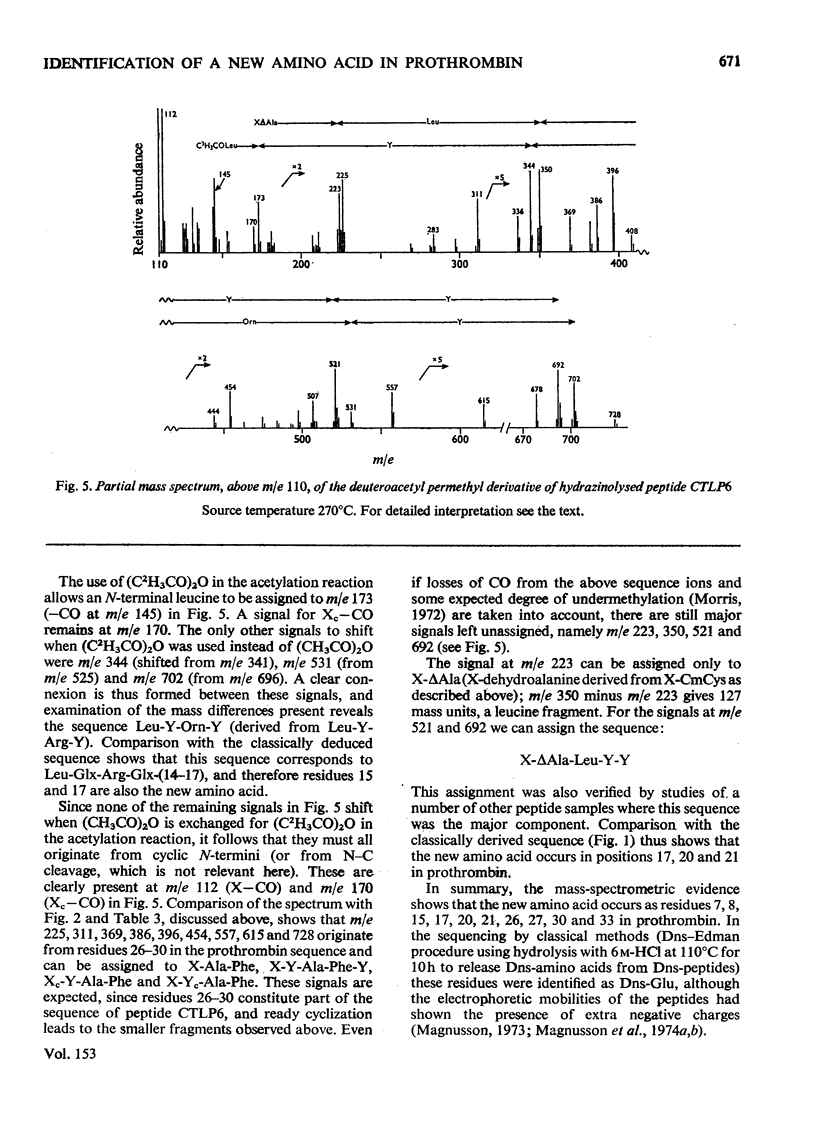
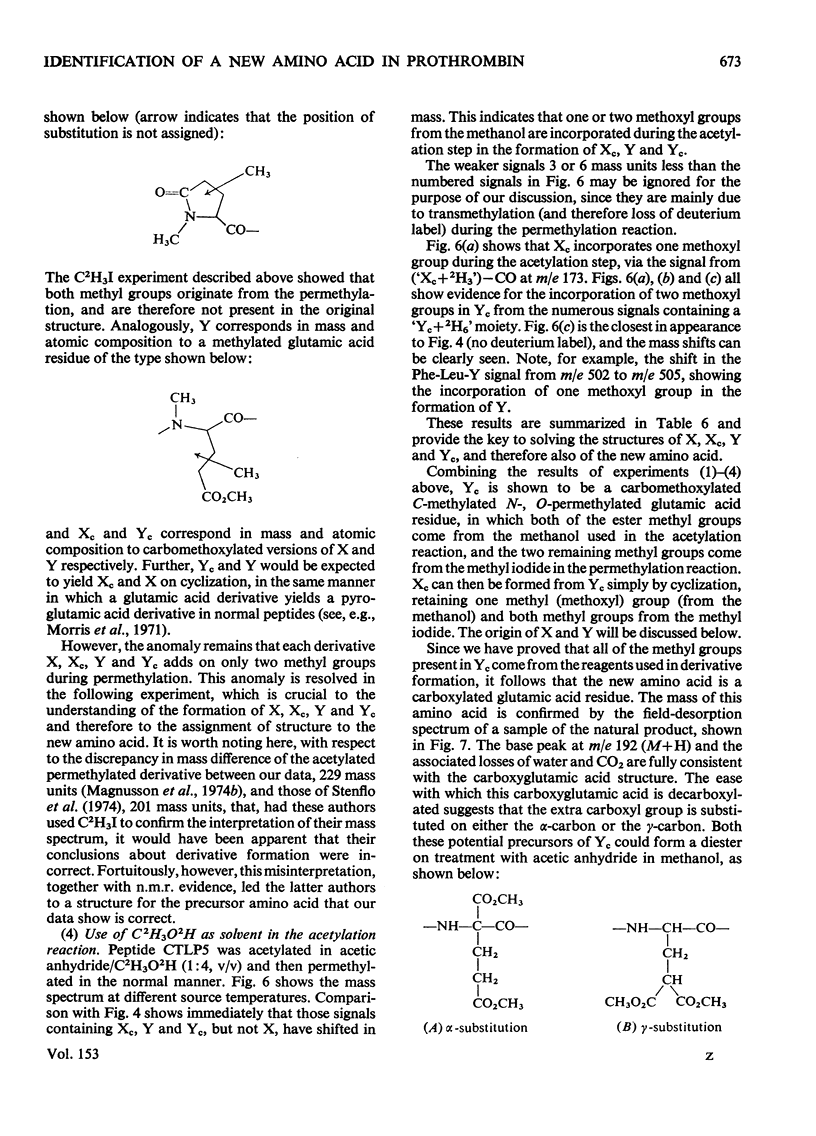
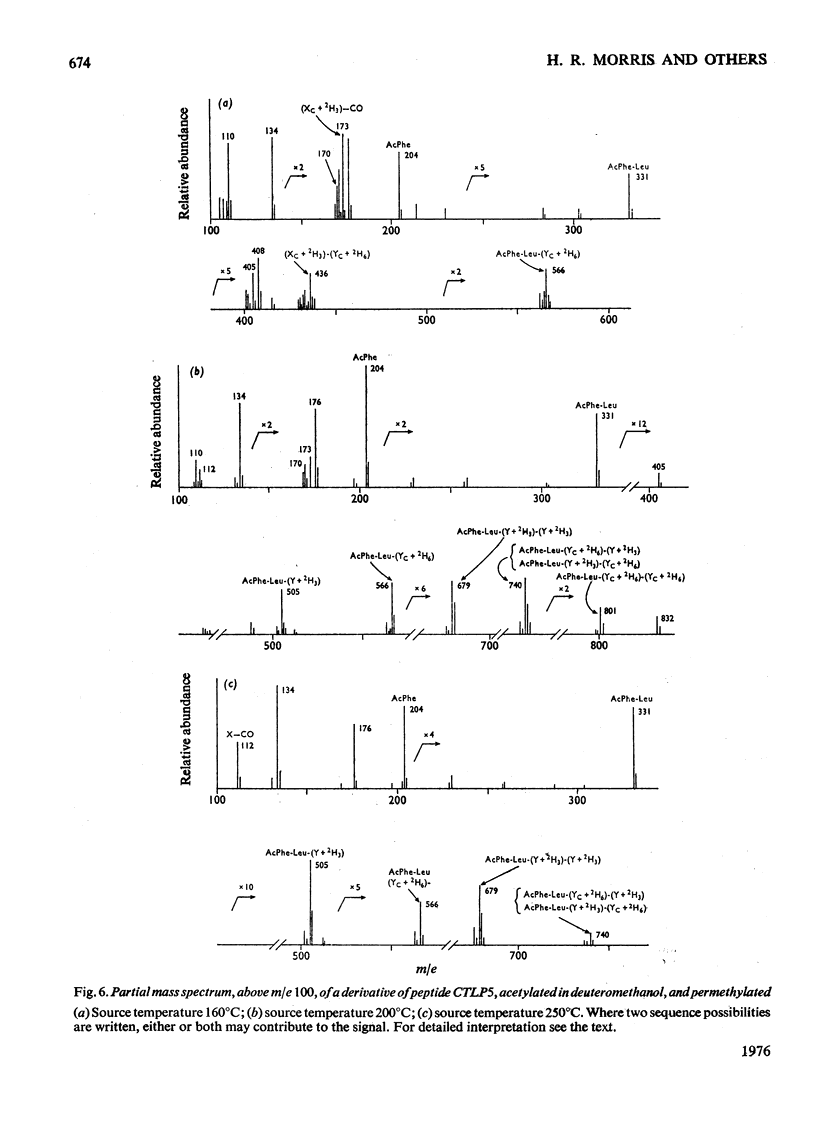
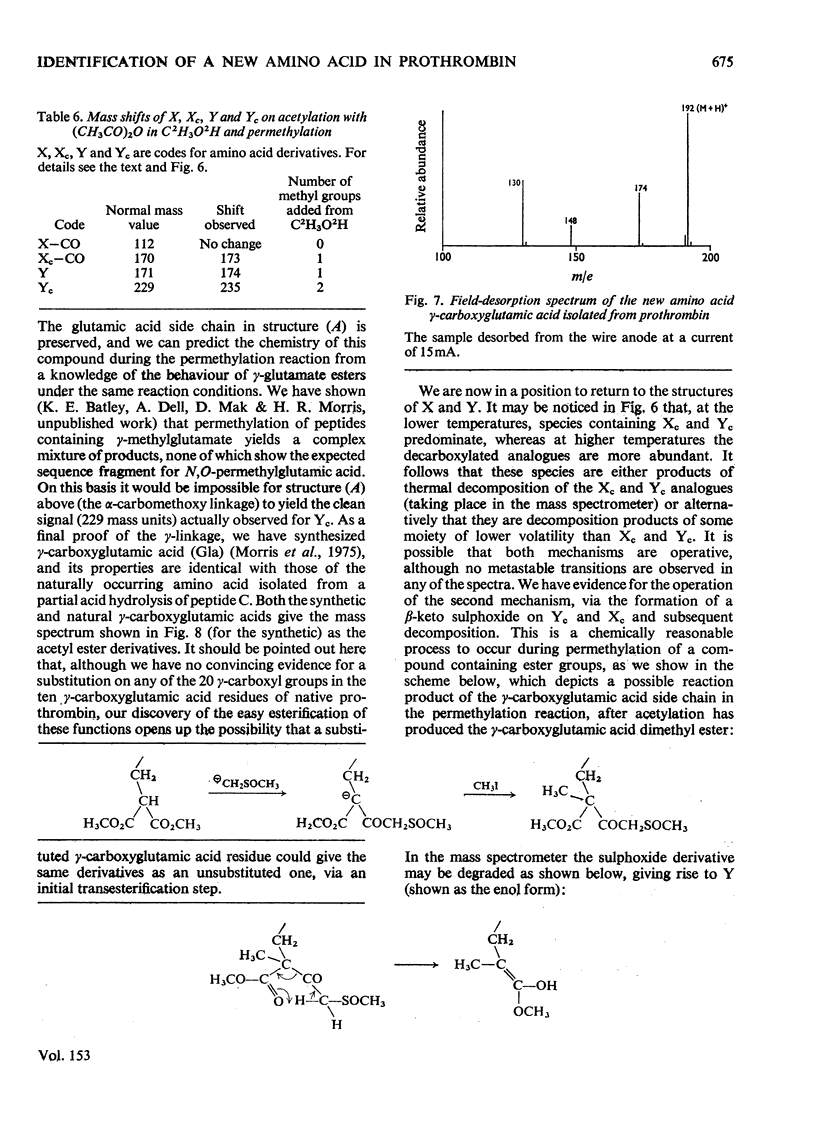
Abstract
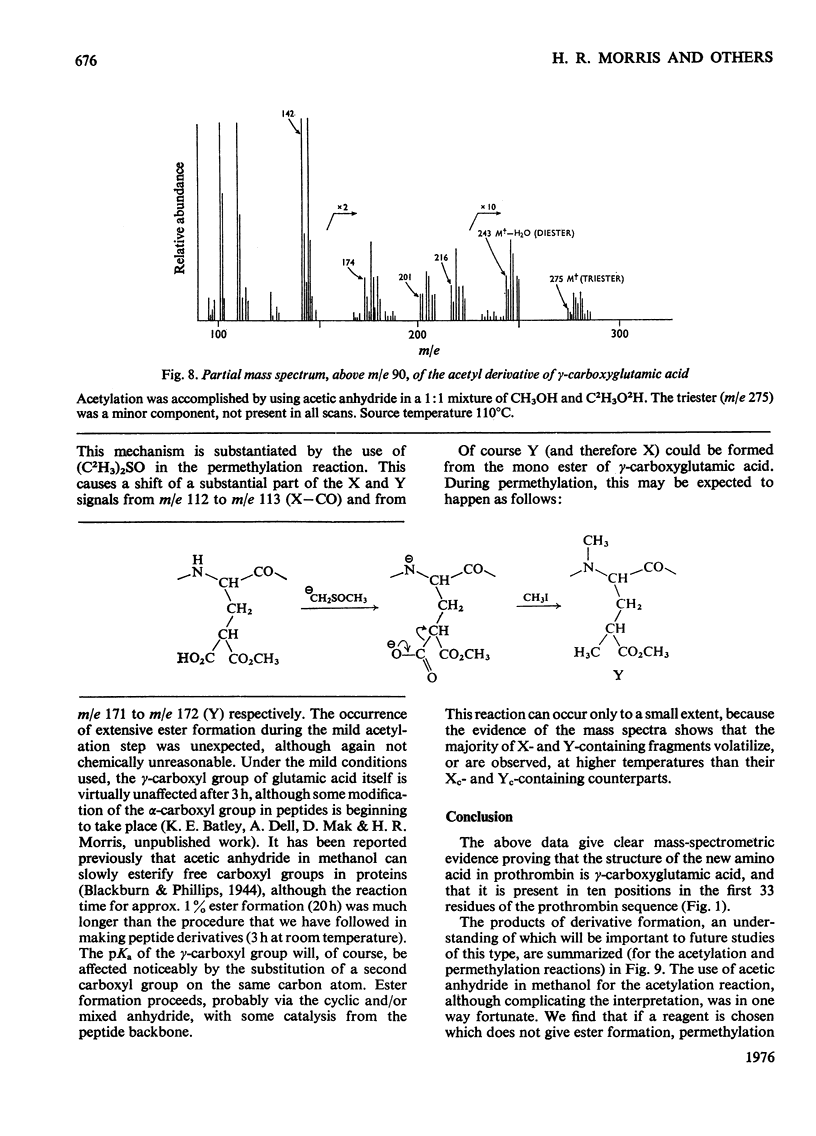
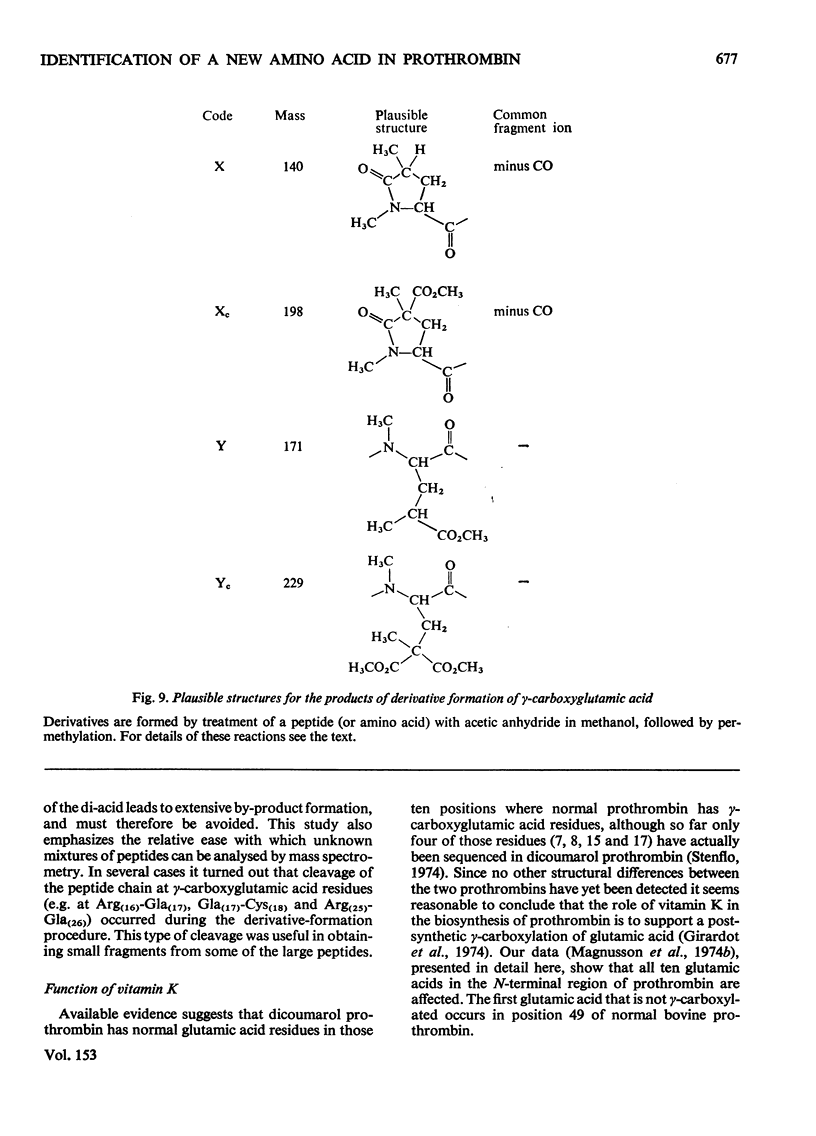
The detailed mass-spectrometric evidence for our original findings [Magnusson et al. (1974) FEBS Lett. 44, 189-193] of ten gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues in the N-terminal calcium-binding polypeptide of prothrombin is presented. The identification and sequence location of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid was made by electron-impact and field-desorption studies on acetyl permethyl peptide derivatives, and on the free amino acid. Details of the derivatives formed, and how this new amino acid may be easily recognized and sequenced from the mass spectrum, are given as a basis for future work.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMBLER R. P. THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE OF PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:349–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0890349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P. G., Hanahan D. J. Some lipid-protein interactions involved in prothrombin activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 28;187(3):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn S., Phillips H. Experiments on the methylation and acetylation of wool, silk fibroin, collagen and gelatin. Biochem J. 1944;38(2):171–178. doi: 10.1042/bj0380171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull R. K., Jevons S., Barton P. G. Complexes of prothrombin with calcium ions and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2747–2754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dell A., Morris H. R. New observations on the fragmentation properties of peptides under electron impact mass spectrometry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1125–1132. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80400-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enfield D. L., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Titani K. Bovine factor X1 (Stuart factor). Primary structure of the light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):16–19. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G., Jackson C. M. The conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. II. Differentiation between thrombin- and factor Xa-catalyzed proteolyses. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):606–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN R., LE BOLLOC'H A., ALEXANDER B., ZONDERMAN E. Preparation and properties of prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2857–2866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O., Niléhn J. E. Immunochemical determination of human prothrombin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(3):238–244. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O., Niléhn J. E. Plasma prothrombin during treatment with Dicumarol. II. Demonstration of an abnormal prothrombin fraction. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;22(1):23–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardot J. M., Delaney R., Johnson B. C. Carboxylation, the completion step in prothrombin biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 19;59(4):1197–1203. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMANN J., BARROLLIER J., WATZKE E. Beitrag zur Aminosäurebestimmung auf Papierchromatogrammen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1957;309(4-6):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. B., Nelsestuen G. L. Isolation and characterization of vitamin K-dependent region of bovine blood clotting factor X. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1281–1285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josso F., Lavergne J. M., Gouault M., Prou-Wartelle O., Soulier J. P. Différents états moléculaires du facter II (prothrombine). Leur étude à l'aide de la staphylocoagulase et d'anticorps anti-facteur II. I. Le facteur II chez les sujets traités par les antagonistes de la vitamine K. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Nov 15;20(1):88–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS M. L., WARE A. G. A simple procedure for separation of prothrombin and accelerator globulin from citrated human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Dec;84(3):636–640. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson S. On the primary structure of bovine thrombin. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1972;98(4):385–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson S., Sottrup-Jensen L., Petersen T. E., Morris H. R., Dell A. Primary structure of the vitamin K-dependent part of prothrombin. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 25;44(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80723-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Dickinson R. J., Williams D. H. Studies towards the complete sequence determination of proteins by mass spectrometry: derivatisation of methionine, cysteine and arginine containing peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 5;51(1):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R. Studies towards the complete sequence determination of proteins by mass spectrometry; a rapid procedure for the successful permethylation of histidine containing peptides. FEBS Lett. 1972 May 15;22(3):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Thompson M. R., Dell A. Synthesis and proof of structure of the new amino acid in prothrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 17;62(4):856–861. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90401-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Williams D. H., Ambler R. P. Determination of the sequences of protein-derived peptides and peptide mixtures by mass spectrometry. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):189–201. doi: 10.1042/bj1250189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Williams D. H., Midwinter G. G., Hartley B. S. A mass-spectrometric sequence study of the enzyme ribitol dehydrogenase from Klebsiella aerogenes. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):701–713. doi: 10.1042/bj1410701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Suttie J. W. Mode of action of vitamin K. Calcium binding properties of bovine prothrombin. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4961–4964. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Suttie J. W. The mode of action of vitamin K. Isolation of a peptide containing the vitamin K-dependent portion of prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3366–3370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Suttie J. W. The purification and properties of an abnormal prothrombin protein produced by dicumarol-treated cows. A comparison to normal prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8176–8182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Zytkovicz T. H., Howard J. B. The mode of action of vitamin K. Identification of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid as a component of prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6347–6350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegers W. H., Marciniak E., Kipfer R. D., Yasunaga K. Isolation and sme properties of prethrombin and autoprothrombin III. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Aug;121(2):372–383. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Fernlund P., Egan W., Roepstorff P. Vitamin K dependent modifications of glutamic acid residues in prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2730–2733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Ganrot P. O. Binding of Ca 2+ to normal and dicoumarol-induced prothrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 4;50(1):98–104. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. Vitamin K and the biosynthesis of prothrombin. 3. Structural comparison of an NH2-terminal fragment from normal and from dicoumarol-induced bovine prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6325–6332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. Vitamin K and the biosynthesis of prothrombin. II. Structural comparison of normal and dicoumarol-induced bovine prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8167–8175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. Vitamin K and the biosynthesis of prothrombin. IV. Isolation of peptides containing prosthetic groups from normal prothrombin and the corresponding peptides from dicoumarol-induced prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5527–5535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Das B. C., Géro S. D., Lederer E. Mass spectrometry of permethylated peptide derivatives; extension of the technique to peptides containing arginine or methionine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Aug 13;32(3):519–525. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90693-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. R., Wang K. T. Separation of dansyl-amino acids by polyamide layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):369–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Itano H. Phenanthrenequinone as an analytical reagent for arginine and other monosubstituted guanidines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 28;130(2):538–540. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90256-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


