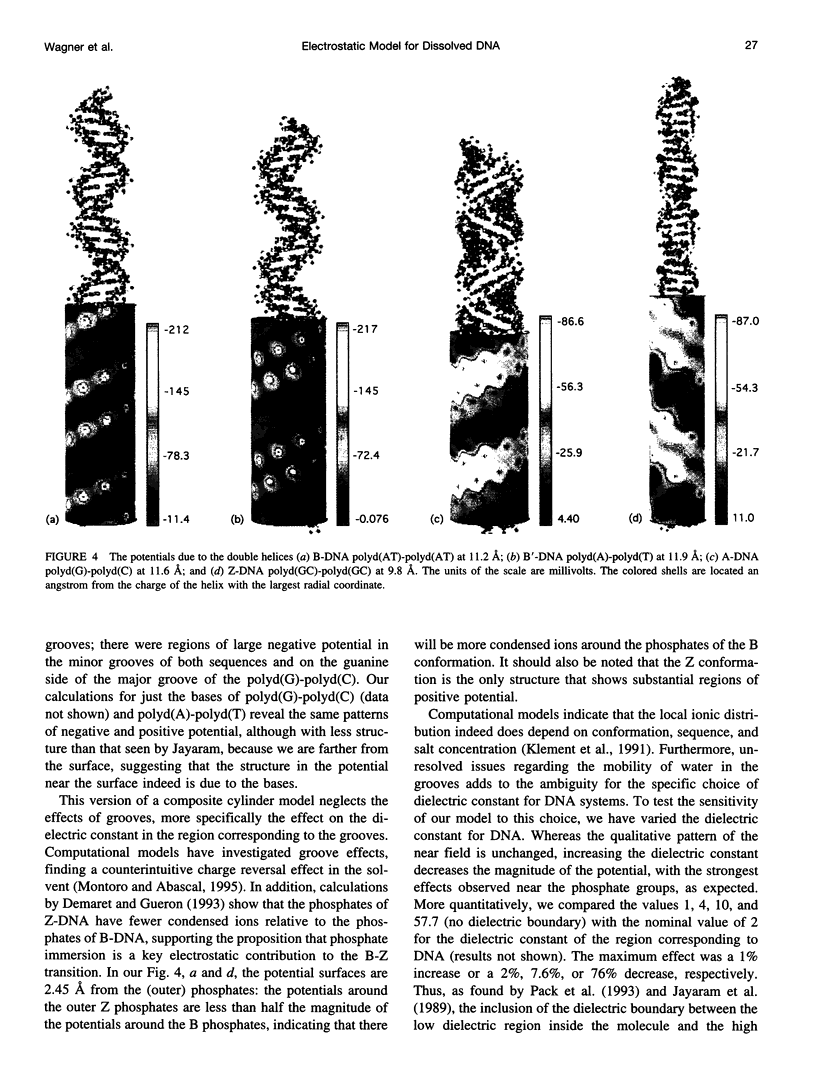
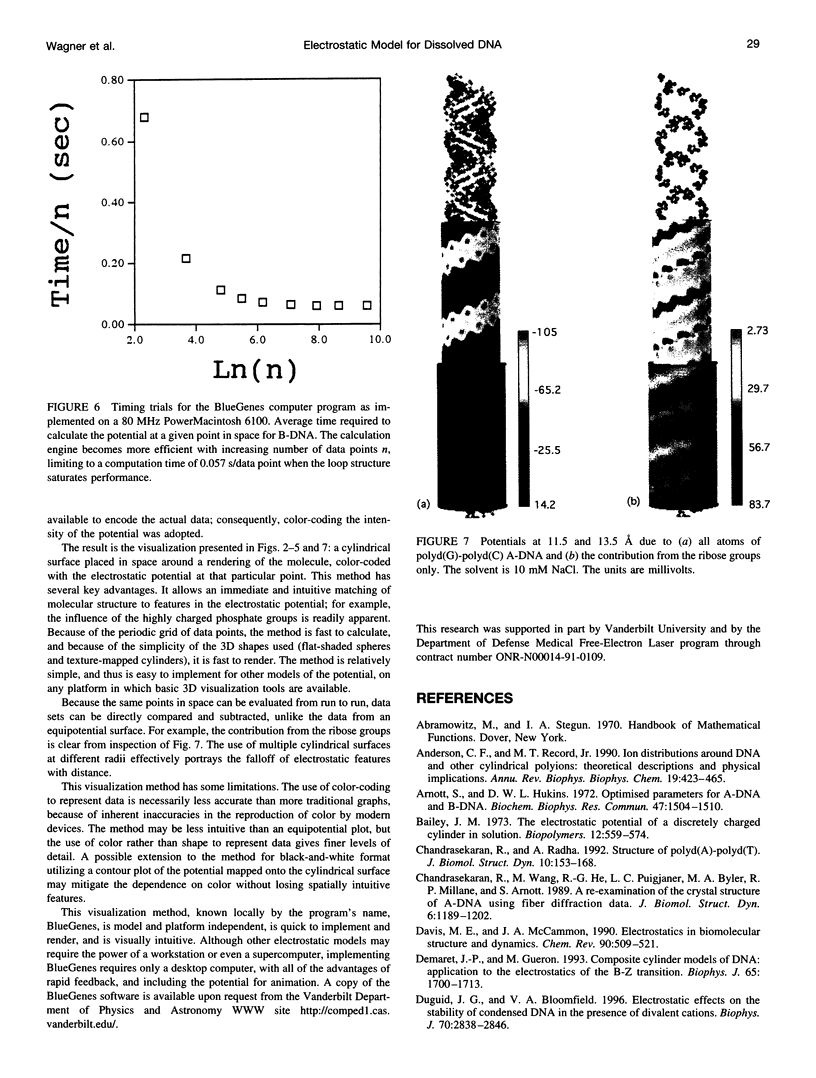
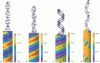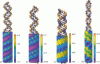Abstract
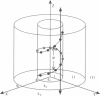
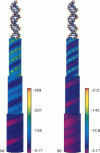
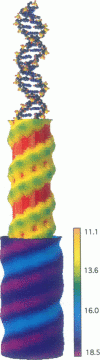
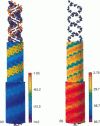
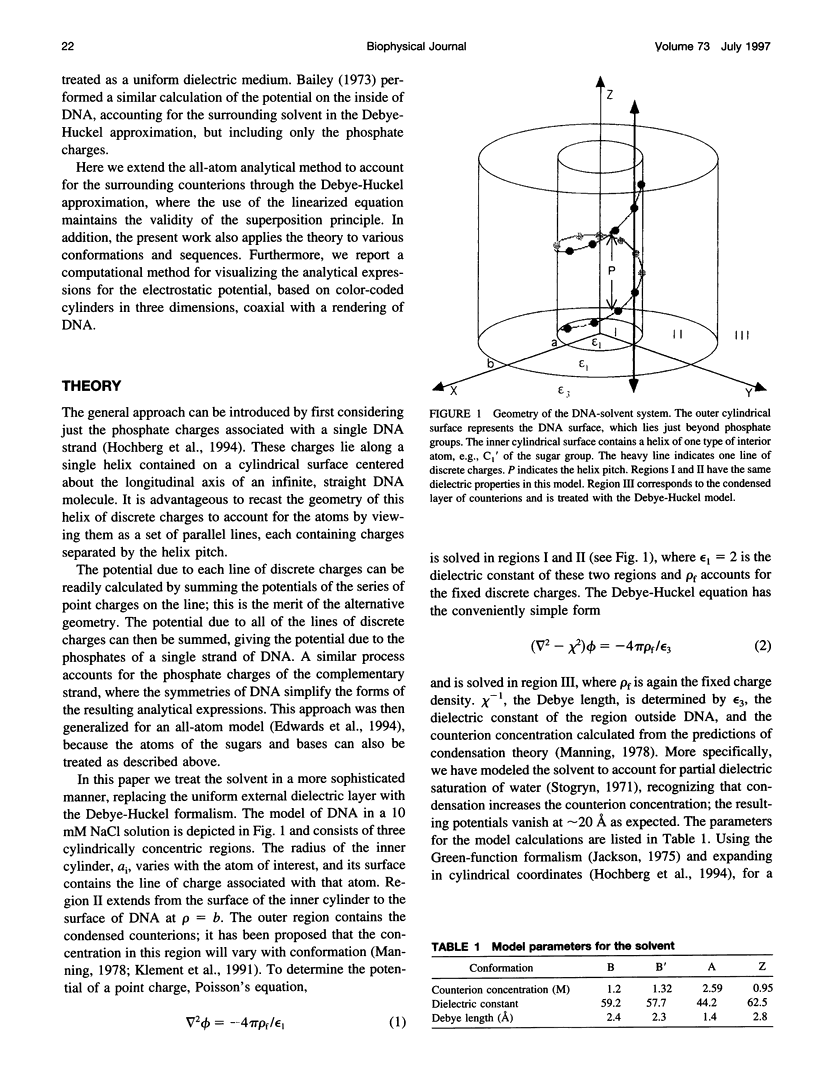
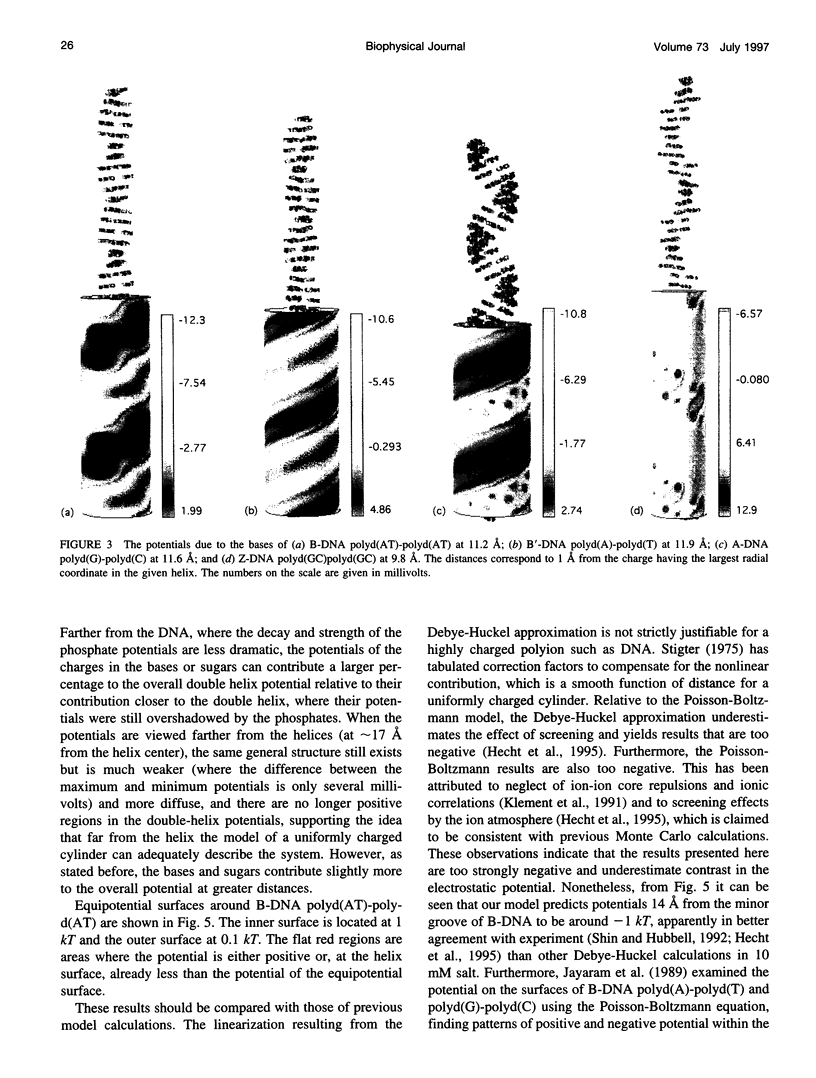
We present an analytical, Green-function-based model for the electric potential of DNA in solution, treating the surrounding solvent with the Debye-Huckel approximation. The partial charge of each atom is accounted for by modeling DNA as linear distributions of atoms on concentric cylindrical surfaces. The condensed ions of the solvent are treated with the Debye-Huckel approximation. The resultant leading term of the potential is that of a continuous shielded line charge, and the higher order terms account for the helical structure. Within several angstroms of the surface there is sufficient information in the electric potential to distinguish features and symmetries of DNA. Plots of the potential and equipotential surfaces, dominated by the phosphate charges, reflect the structural differences between the A, B, and Z conformations and, to a smaller extent, the difference between base sequences. As the distances from the helices increase, the magnitudes of the potentials decrease. However, the bases and sugars account for a larger fraction of the double helix potential with increasing distance. We have found that when the solvent is treated with the Debye-Huckel approximation, the potential decays more rapidly in every direction from the surface than it did in the concentric dielectric cylinder approximation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Ion distributions around DNA and other cylindrical polyions: theoretical descriptions and physical implications. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:423–465. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.002231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Optimised parameters for A-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1504–1509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran R., Radha A. Structure of poly d(A).poly d(T). J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1992 Aug;10(1):153–168. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1992.10508635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran R., Wang M., He R. G., Puigjaner L. C., Byler M. A., Millane R. P., Arnott S. A re-examination of the crystal structure of A-DNA using fiber diffraction data. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1989 Jun;6(6):1189–1202. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1989.10506544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaret J. P., Guéron M. Composite cylinder models of DNA: application to the electrostatics of the B-Z transition. Biophys J. 1993 Oct;65(4):1700–1713. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81213-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. G., Bloomfield V. A. Electrostatic effects on the stability of condensed DNA in the presence of divalent cations. Biophys J. 1996 Jun;70(6):2838–2846. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79853-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G, Hochberg D, Kephart TW. Structure in the electric potential emanating from DNA. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1994 Aug;50(2):R698–R701. doi: 10.1103/physreve.50.r698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenley M. O., Manning G. S., Olson W. K. Approach to the limit of counterion condensation. Biopolymers. 1990;30(13-14):1191–1203. doi: 10.1002/bip.360301305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL T. L. Approximate calculation of the electrostatic free energy of nucleic acids and other cylindrical macromolecules. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Jul;57(1):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg D, Kephart TW, Edwards G. Structural information in the local electric field of dissolved B-DNA. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1994 Jan;49(1):851–867. doi: 10.1103/physreve.49.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Nicholls A. Classical electrostatics in biology and chemistry. Science. 1995 May 26;268(5214):1144–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.7761829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaram B., Sharp K. A., Honig B. The electrostatic potential of B-DNA. Biopolymers. 1989 May;28(5):975–993. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B. J., Pack G. R. Calculations of the spatial distribution of charge density in the environment of DNA. Biopolymers. 1983 Nov;22(11):2331–2352. doi: 10.1002/bip.360221103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klement R., Soumpasis D. M., Jovin T. M. Computation of ionic distributions around charged biomolecular structures: results for right-handed and left-handed DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. U., Chrisey L. A., Colton R. J. Direct measurement of the forces between complementary strands of DNA. Science. 1994 Nov 4;266(5186):771–773. doi: 10.1126/science.7973628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin-Chung PJ, Rajagopal AK. Helical coordinate system and electrostatic fields of double-helix charge distributions. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1995 Jul;52(1):901–906. doi: 10.1103/physreve.52.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyubchenko Y. L., Gall A. A., Shlyakhtenko L. S., Harrington R. E., Jacobs B. L., Oden P. I., Lindsay S. M. Atomic force microscopy imaging of double stranded DNA and RNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1992 Dec;10(3):589–606. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1992.10508670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyubchenko Y., Shlyakhtenko L., Harrington R., Oden P., Lindsay S. Atomic force microscopy of long DNA: imaging in air and under water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2137–2140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V. K., Hecht J. L., Sharp K. A., Friedman R. A., Honig B. Salt effects on protein-DNA interactions. The lambda cI repressor and EcoRI endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 29;238(2):264–280. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V. K., Sharp K. A., Friedman R. A., Honig B. Salt effects on ligand-DNA binding. Minor groove binding antibiotics. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 29;238(2):245–263. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pack G. R., Garrett G. A., Wong L., Lamm G. The effect of a variable dielectric coefficient and finite ion size on Poisson-Boltzmann calculations of DNA-electrolyte systems. Biophys J. 1993 Oct;65(4):1363–1370. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81187-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pack G. R., Klein B. J. Generalized Poisson-Boltzmann calculation of the distribution of electrolyte ions around the B- and Z-conformers of DNA. Biopolymers. 1984 Dec;23(12):2801–2823. doi: 10.1002/bip.360231208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pack G. R., Wong L., Prasad C. V. Counterion distribution around DNA: variation with conformation and sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1479–1493. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman D. A., Kim S. H. Atomic charges for DNA constituents derived from single-crystal X-ray diffraction data. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 5;211(1):171–187. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90019-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullman A., Pullman B. Molecular electrostatic potential of the nucleic acids. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 Aug;14(3):289–380. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rau D. C., Parsegian V. A. Direct measurement of the intermolecular forces between counterion-condensed DNA double helices. Evidence for long range attractive hydration forces. Biophys J. 1992 Jan;61(1):246–259. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81831-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr Electrostatic effects on polynucleotide transitions. I. Behavior at neutral pH. Biopolymers. 1967;5(10):975–992. doi: 10.1002/bip.1967.360051010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellman J. A. Electrical double layer, zeta potential, and electrophoretic charge of double-stranded DNA. Biopolymers. 1977 Jul;16(7):1415–1434. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp K. A., Honig B. Electrostatic interactions in macromolecules: theory and applications. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:301–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin Y. K., Hubbell W. L. Determination of electrostatic potentials at biological interfaces using electron-electron double resonance. Biophys J. 1992 Jun;61(6):1443–1453. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81950-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stigter D. Evaluation of the counterion condensation theory of polyelectrolytes. Biophys J. 1995 Aug;69(2):380–388. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79910-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vologodskii A., Cozzarelli N. Modeling of long-range electrostatic interactions in DNA. Biopolymers. 1995 Mar;35(3):289–296. doi: 10.1002/bip.360350304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. J., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., van der Marel G., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Left-handed double helical DNA: variations in the backbone conformation. Science. 1981 Jan 9;211(4478):171–176. doi: 10.1126/science.7444458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]