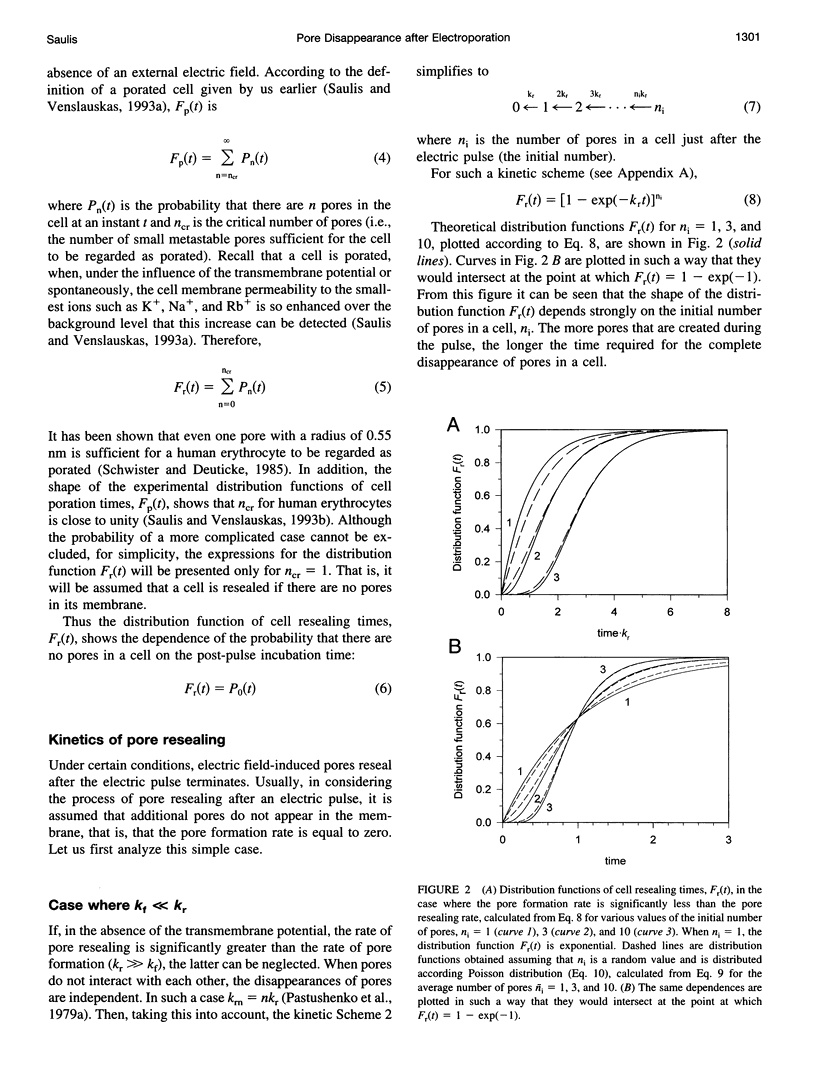
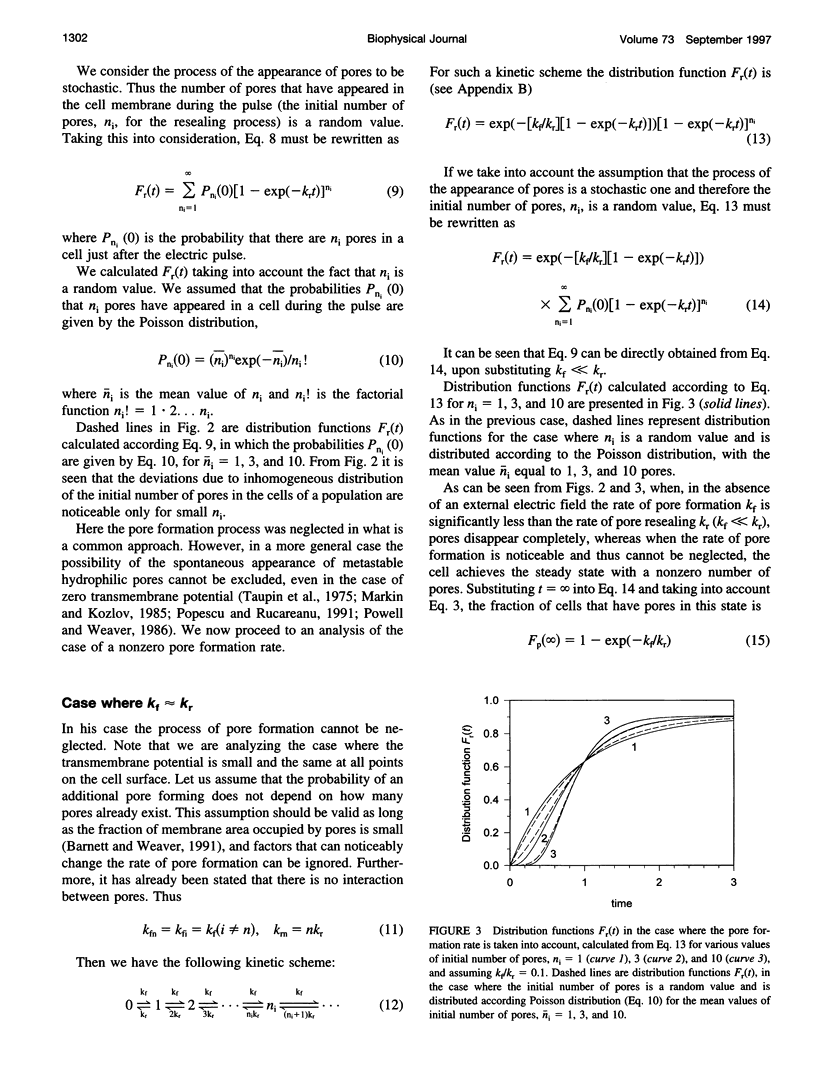
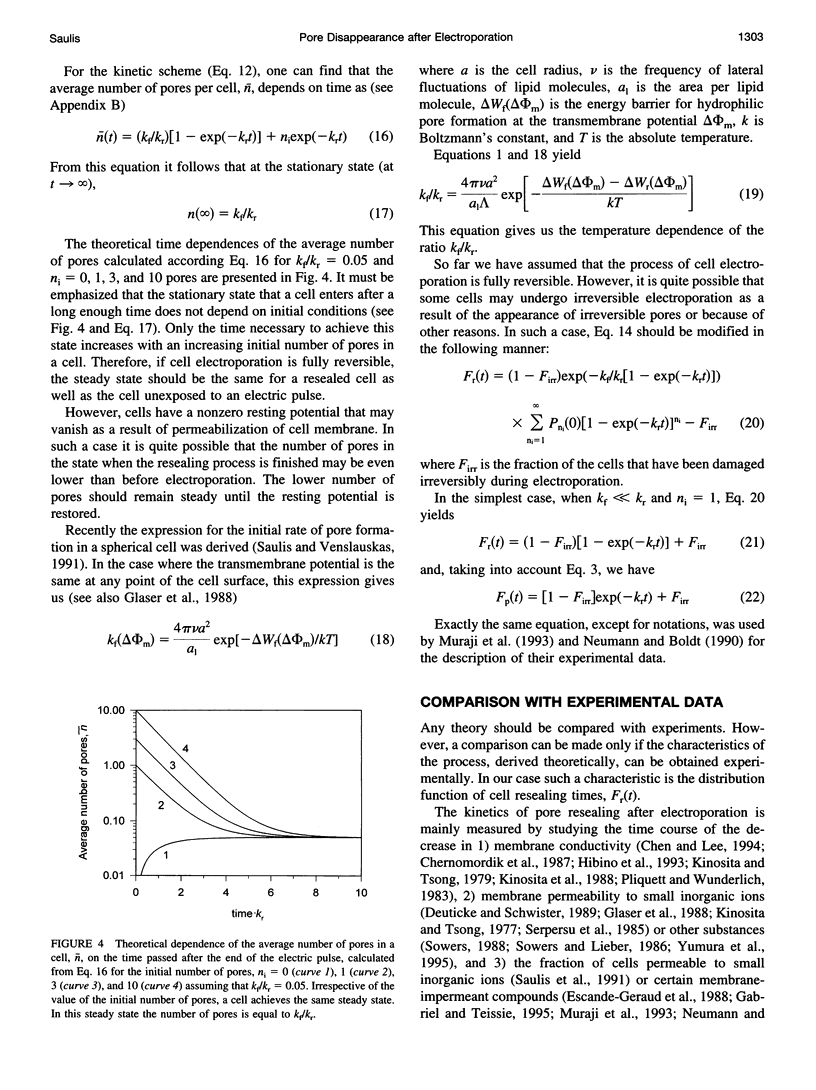
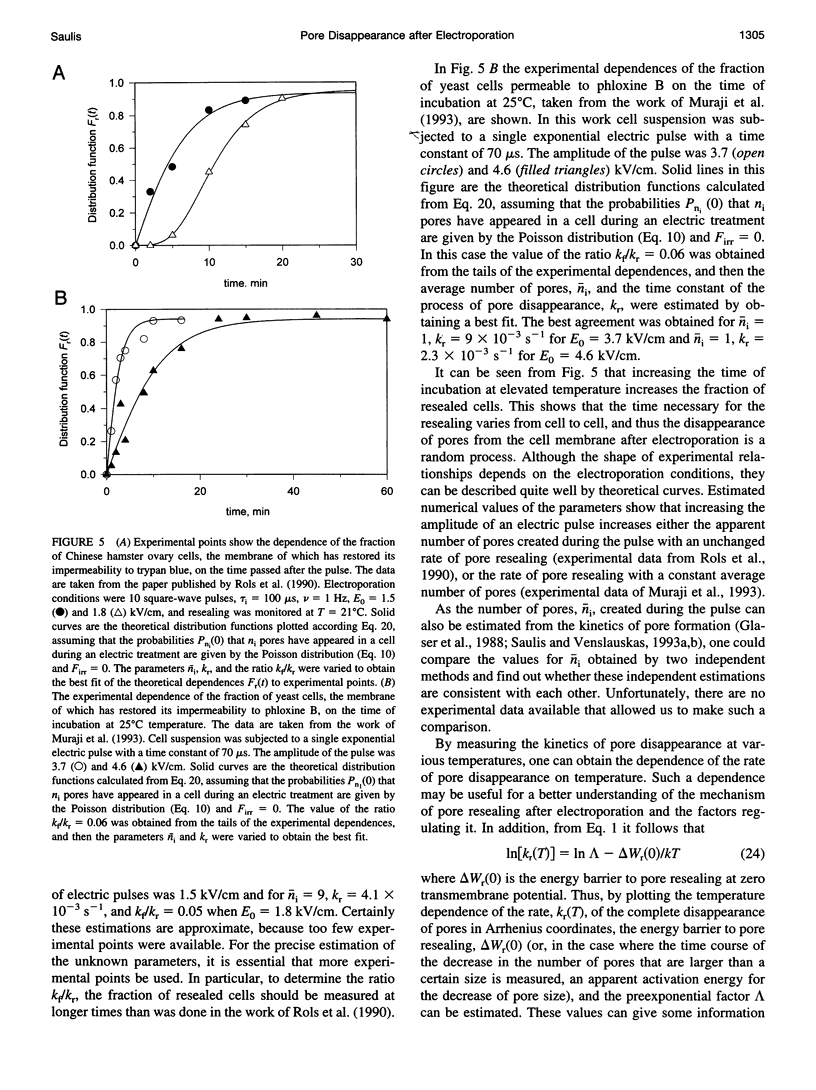
Abstract
The process of pore disappearance after cell electroporation is analyzed theoretically. On the basis of the kinetic model, in which the formation and annihilation of a metastable hydrophilic pore are considered as random one-step processes, a distribution function of cell resealing times, Fr(t), is derived. Two cases are studied: 1) the rate of pore resealing, k(r), is significantly greater than the rate of pore formation, k(f); and 2) the rate of pore formation, k(f), is comparable with k(r). It is determined that the shape of the distribution function depends on the initial number of pores in a cell, n(i). If in the absence of an external electric field the rate of pore formation, k(f), is significantly less than the rate of pore resealing, k(r) (case 1), pores disappear completely, whereas when k(f) approximately k(r) (case 2), the cell achieves a steady state in which the number of pores is equal to k(f)/k(r). In case 1, when n(i) = 1, the distribution function Fr(t) is exponential. The developed theory is compared with experimental data available in the literature. Increasing the time of incubation at elevated temperature increases the fraction of resealed cells. This indicates that the time necessary for the resealing varies from cell to cell. Although the shape of experimental relationships depends on the electroporation conditions they can be described by theoretical curves quite well. Thus it can be concluded that the disappearance of pores in the cell membrane after electroporation is a random process. It is shown that from the comparison of presented theory with experiments, the following parameters can be estimated: the average number of pores, n(i), that appeared in a cell during an electric pulse; the rate of pore disappearance, k(r); the ratio k(f)/k(r); and the energy barrier to pore disappearance deltaWr(0). Estimated numerical values of the parameters show that increasing the amplitude of an electric pulse increases either the apparent number of pores created during the pulse (the rate of pore resealing remains the same) or the rate of pore resealing (the average number of pores remains the same).
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chernomordik L. V., Sukharev S. I., Popov S. V., Pastushenko V. F., Sokirko A. V., Abidor I. G., Chizmadzhev Y. A. The electrical breakdown of cell and lipid membranes: the similarity of phenomenologies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 3;902(3):360–373. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley J. M. Electrical breakdown of bimolecular lipid membranes as an electromechanical instability. Biophys J. 1973 Jul;13(7):711–724. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)86017-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. S. Electric field-induced breakdown of lipid bilayers and cell membranes: a thin viscoelastic film model. J Membr Biol. 1984;78(1):53–60. doi: 10.1007/BF01872532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escande-Géraud M. L., Rols M. P., Dupont M. A., Gas N., Teissié J. Reversible plasma membrane ultrastructural changes correlated with electropermeabilization in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 7;939(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman S. A., Wang M. A., Weaver J. C. Theory of electroporation of planar bilayer membranes: predictions of the aqueous area, change in capacitance, and pore-pore separation. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):42–56. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80453-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel B., Teissié J. Control by electrical parameters of short- and long-term cell death resulting from electropermeabilization of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Apr 28;1266(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(95)00021-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R. W., Leikin S. L., Chernomordik L. V., Pastushenko V. F., Sokirko A. I. Reversible electrical breakdown of lipid bilayers: formation and evolution of pores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 24;940(2):275–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90202-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibino M., Itoh H., Kinosita K., Jr Time courses of cell electroporation as revealed by submicrosecond imaging of transmembrane potential. Biophys J. 1993 Jun;64(6):1789–1800. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81550-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Ashikawa I., Saita N., Yoshimura H., Itoh H., Nagayama K., Ikegami A. Electroporation of cell membrane visualized under a pulsed-laser fluorescence microscope. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):1015–1019. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83181-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Tsong T. Y. Formation and resealing of pores of controlled sizes in human erythrocyte membrane. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):438–441. doi: 10.1038/268438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Tsong T. Y. Voltage-induced conductance in human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):479–497. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marszalek P., Liu D. S., Tsong T. Y. Schwan equation and transmembrane potential induced by alternating electric field. Biophys J. 1990 Oct;58(4):1053–1058. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82447-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann E., Boldt E. Membrane electroporation: the dye method to determine the cell membrane conductivity. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;343:69–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski S., Mir L. M. Cell electropermeabilization: a new tool for biochemical and pharmacological studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 8;1154(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(93)90016-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rols M. P., Dahhou F., Mishra K. P., Teissié J. Control of electric field induced cell membrane permeabilization by membrane order. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 27;29(12):2960–2966. doi: 10.1021/bi00464a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rols M. P., Teissie J. Ionic-strength modulation of electrically induced permeabilization and associated fusion of mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):109–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwister K., Deuticke B. Formation and properties of aqueous leaks induced in human erythrocytes by electrical breakdown. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 27;816(2):332–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90501-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serpersu E. H., Kinosita K., Jr, Tsong T. Y. Reversible and irreversible modification of erythrocyte membrane permeability by electric field. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 14;812(3):779–785. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90272-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers A. E. Fusion events and nonfusion contents mixing events induced in erythrocyte ghosts by an electric pulse. Biophys J. 1988 Oct;54(4):619–626. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82997-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers A. E., Lieber M. R. Electropore diameters, lifetimes, numbers, and locations in individual erythrocyte ghosts. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 15;205(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80893-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugar I. P., Neumann E. Stochastic model for electric field-induced membrane pores. Electroporation. Biophys Chem. 1984 May;19(3):211–225. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(84)87003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taupin C., Dvolaitzky M., Sauterey C. Osmotic pressure induced pores in phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4771–4775. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y. Voltage modulation of membrane permeability and energy utilization in cells. Biosci Rep. 1983 Jun;3(6):487–505. doi: 10.1007/BF01120693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver J. C. Electroporation: a general phenomenon for manipulating cells and tissues. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Apr;51(4):426–435. doi: 10.1002/jcb.2400510407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver J. C. Molecular basis for cell membrane electroporation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994 May 31;720:141–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb30442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yumura S., Matsuzaki R., Kitanishi-Yumura T. Introduction of macromolecules into living Dictyostelium cells by electroporation. Cell Struct Funct. 1995 Jun;20(3):185–190. doi: 10.1247/csf.20.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


