Abstract
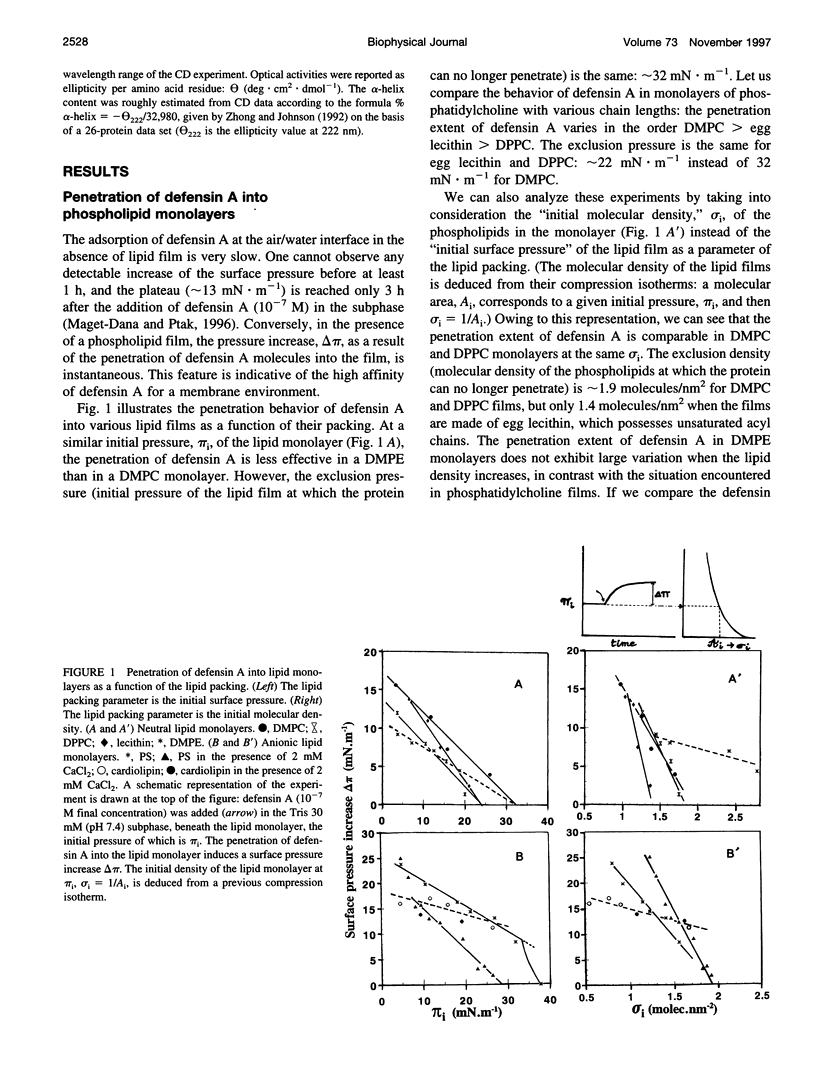
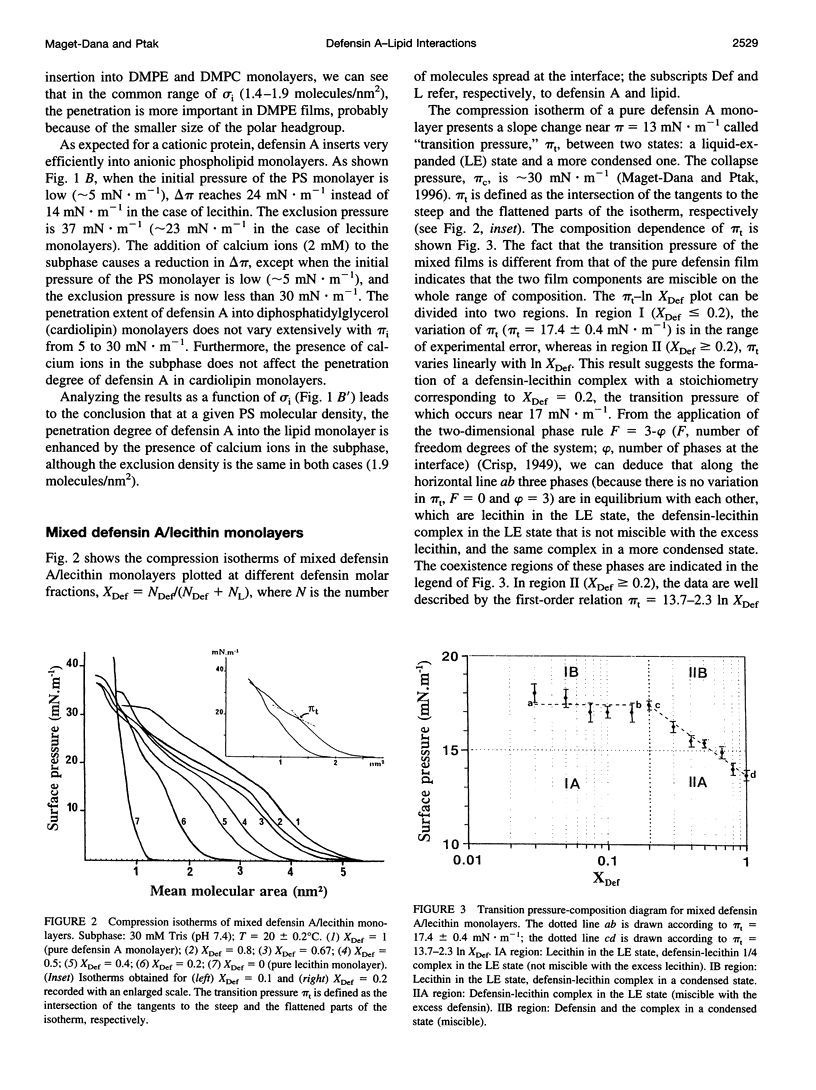
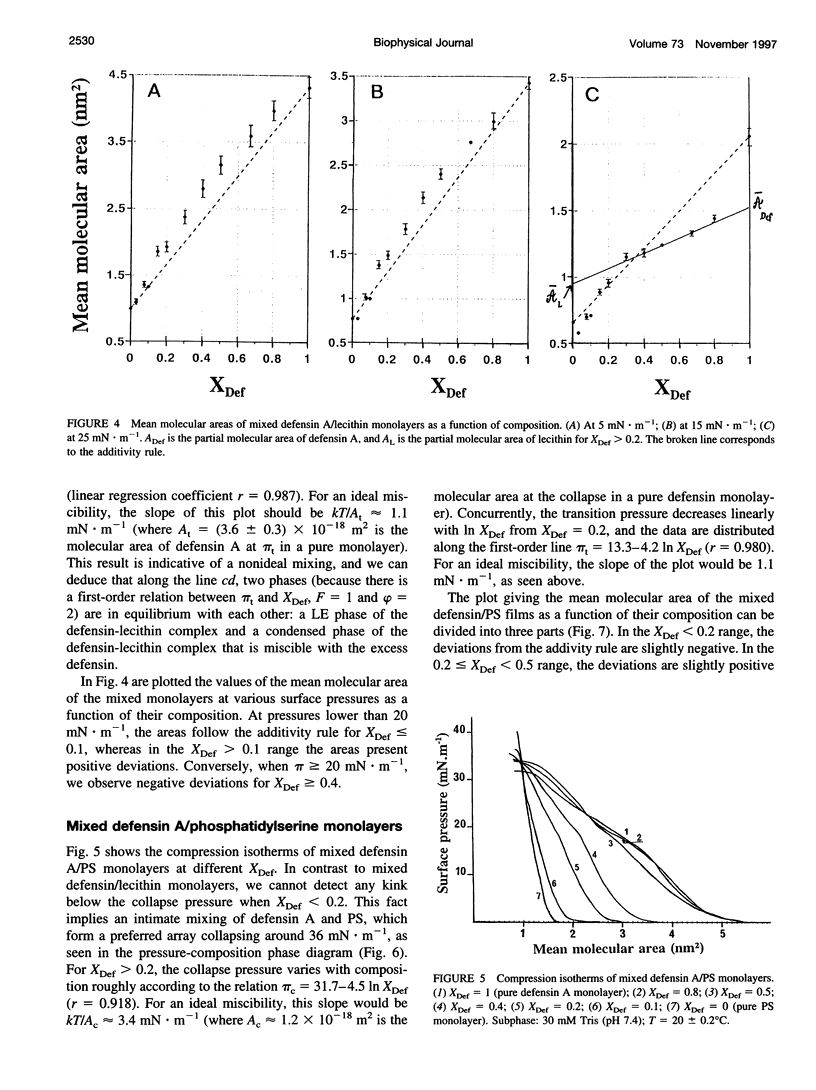
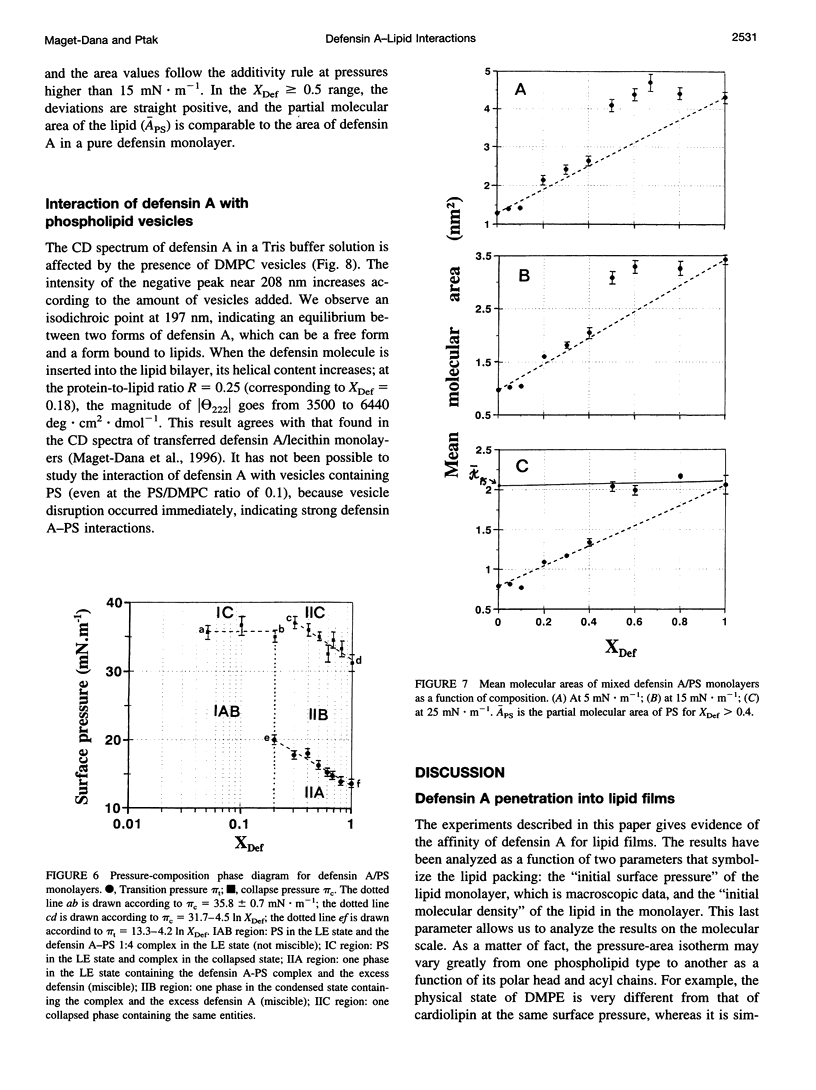
Defensin A is an inducible cationic protein secreted in the hemolymph of fleshfly Phormia terranovae larvae in response to bacterial or septic injuries. Defensin A is known to permeabilize the bacteria cell membranes by forming voltage-dependent channels. The penetration of this small protein into lipid monolayers was studied as a function of the polar head and acyl chain length of phospholipids. The extent of penetration by defensin A is higher in monolayers made of anionic phospholipids than in monolayers made of zwitterionic phospholipids (phosphatidylcholines), because of electrostatic interactions. From the analysis of the compression isotherm parameters of mixed defensin A/phospholipid monolayers, it appears that defensin A interacts with phospholipid by forming 1:4 complexes. These complexes are not miscible in the lipid phase and induce microheterogeneity in the lipid membrane. These clusters might be related to the ion-channel structures responsible for the biological activity of defensin A.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boman H. G., Faye I., Gudmundsson G. H., Lee J. Y., Lidholm D. A. Cell-free immunity in Cecropia. A model system for antibacterial proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Oct 1;201(1):23–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büldt G., Seelig J. Conformation of phosphatidylethanolamine in the gel phase as seen by neutron diffraction. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):6170–6175. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cociancich S., Ghazi A., Hetru C., Hoffmann J. A., Letellier L. Insect defensin, an inducible antibacterial peptide, forms voltage-dependent channels in Micrococcus luteus. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19239–19245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell B. A., Separovic F. Membrane thickness and acyl chain length. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 24;733(1):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornet B., Bonmatin J. M., Hetru C., Hoffmann J. A., Ptak M., Vovelle F. Refined three-dimensional solution structure of insect defensin A. Structure. 1995 May 15;3(5):435–448. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann J. A., Hetru C. Insect defensins: inducible antibacterial peptides. Immunol Today. 1992 Oct;13(10):411–415. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90092-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C., Mason J. T. Geometric packing constraints in egg phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):308–310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer J. M., Esker M. W., Pathmamanoharan C., Wiersema P. H. Vesicles of variable diameter prepared by a modified injection method. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 23;16(17):3932–3935. doi: 10.1021/bi00636a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J., Keppi E., Dimarcq J. L., Wicker C., Reichhart J. M., Dunbar B., Lepage P., Van Dorsselaer A., Hoffmann J., Fothergill J. Insect immunity: isolation from immune blood of the dipteran Phormia terranovae of two insect antibacterial peptides with sequence homology to rabbit lung macrophage bactericidal peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):262–266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maget-Dana R., Bonmatin J. M., Hetru C., Ptak M., Maurizot J. C. The secondary structure of the insect defensin A depends on its environment. A circular dichroism study. Biochimie. 1995;77(4):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(96)88130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maget-Dana R., Ptak M. Interactions of surfactin with membrane models. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1937–1943. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80370-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy W. L., Kari U. P. Structure-activity studies on magainins and other host defense peptides. Biopolymers. 1995;37(2):105–122. doi: 10.1002/bip.360370206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B., Vizioli L. D., Boman H. G. Synthesis of the antibacterial peptide cecropin A (1-33). Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):5020–5031. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J. Interaction of phospholipids with Ca2+ ions. On the role of the phospholipid head groups. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1990 Apr;14(4):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(90)91204-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N. Lipid composition as a guide to the classification of bacteria. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1974;17(0):63–108. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70555-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneva S., Keough K. M. Pulmonary surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C in spread monolayers at the air-water interface: I. Monolayers of pulmonary surfactant protein SP-B and phospholipids. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):1137–1148. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80895-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyäuble H., Teubner M., Woolley P., Eibl H. Electrostatic interactions at charged lipid membranes. I. Effects of pH and univalent cations on membrane structure. Biophys Chem. 1976 Jul;4(4):319–342. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)80013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong L., Johnson W. C., Jr Environment affects amino acid preference for secondary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4462–4465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


