Abstract
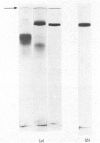
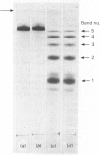
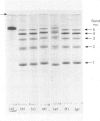
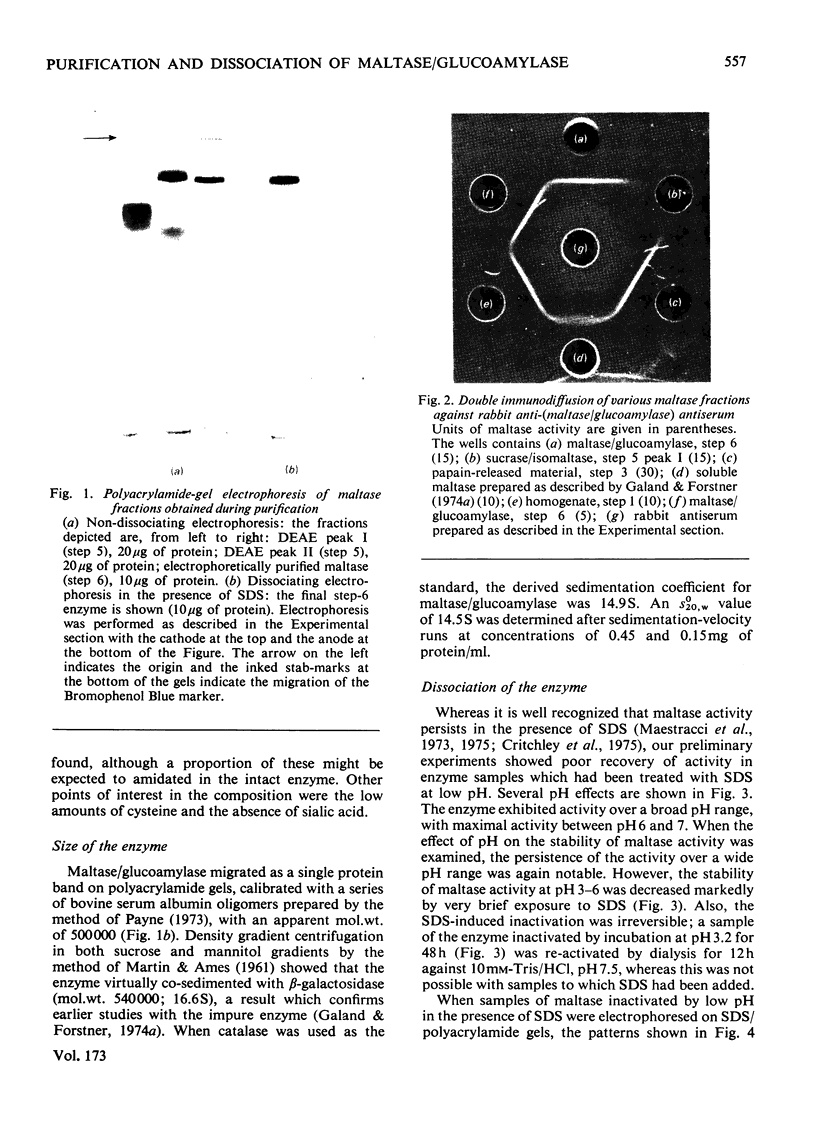
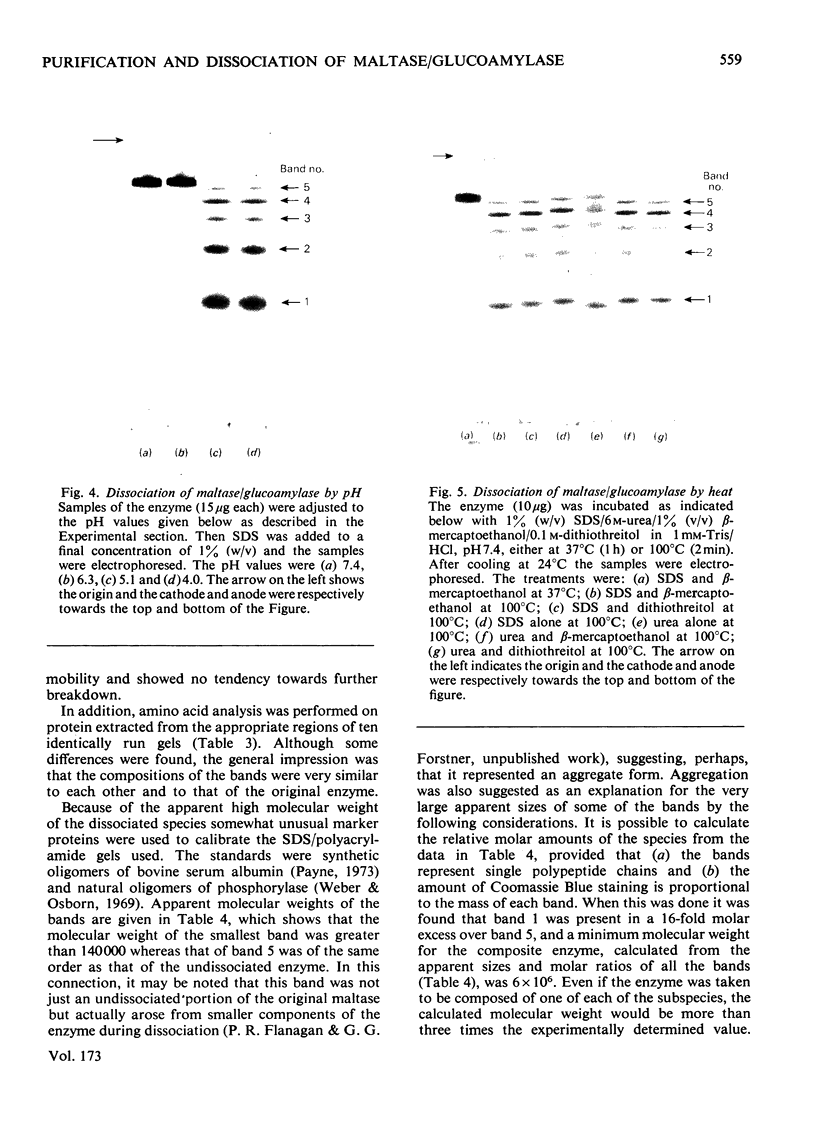
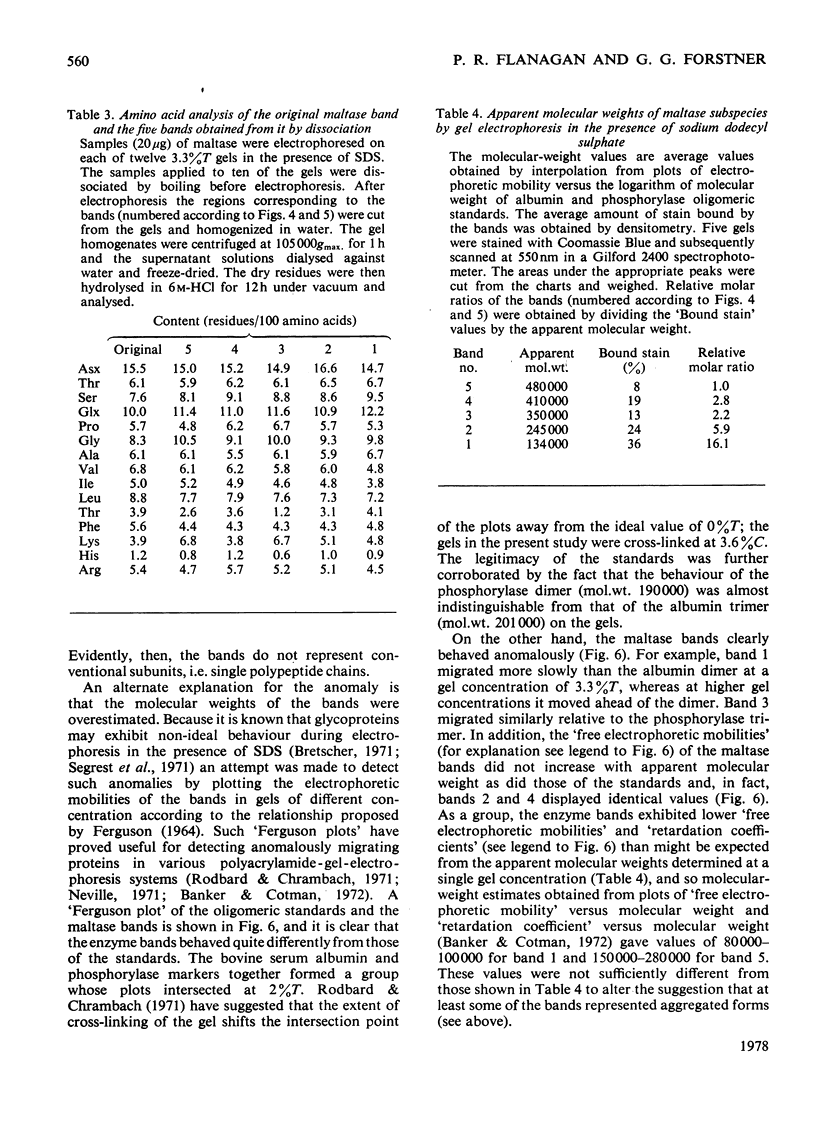
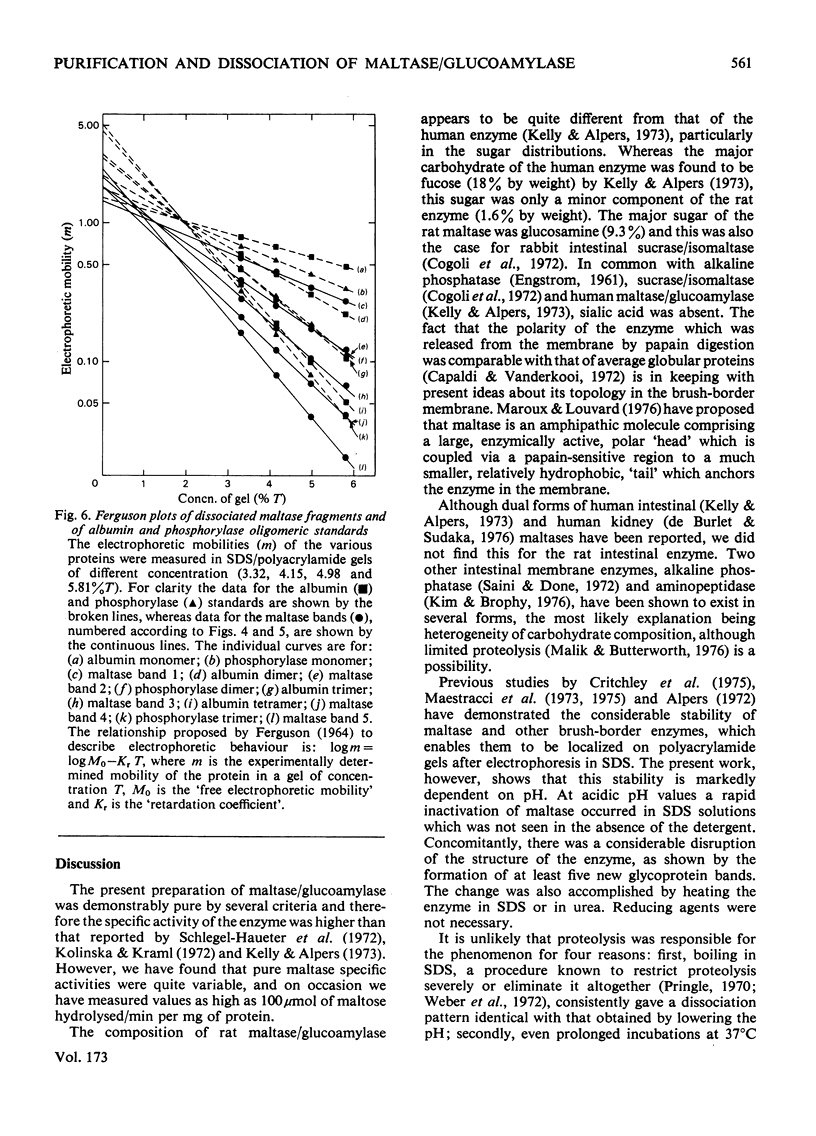
Maltase-glucoamylase, a microvillous membrane ectoenzyme, was solubilized from rat intestinal mucosa by digestion with papain and subsequently purified to homogeneity with an overall yield of 10--20%. An antibody to the purified enzyme formed a single precipitin line in immunodiffusion experiments with an intestinal homogenate. The enzyme was shown to be an acidic glycoprotein (20% sugar by weight) which contained low amounts of cysteine and no sialic acid. At pH3--6, maltase activity was slowly lost, but the enzyme was re-activated by re-adjustment of the pH to neutrality. However, in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate, acid pH values inactivated maltase irreversibly, and at the same time converted the enzyme (mol.wt. 500000 approx.) into five new species with apparent molecular weights ranging from 134000 to 480000 as judged by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. The same five fragments were also formed by boiling the enzyme for brief periods in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate or urea either with or without reducing agents. The dissociated species were stable on re-electrophoresis, and amino acid analysis showed them to be very similar to each other and to the original enzyme. The bands migrated anomalously on polyacrylamide gels of different concentration, thereby preventing the assignment of precise molecular weights. It is possible that the five species may represent stable aggregates of a common monomer of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AURICCHIO S., DAHLQVIST A., SEMENZA G. SOLUBILIZATION OF THE HUMAN INTESTINAL DISACCHARIDASES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 6;73:582–587. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90329-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AURICCHIO S., SEMENZA G., RUBINO A. MULTIPLICITY OF HUMAN INTESTINAL DISACCHARIDASES. II. CHARACTERIZATION OF THE INDIVIDUAL MALTASES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 22;96:498–507. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90566-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpers D. H., Solin M. The characterization of rat intestinal amylase. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jun;58(6):833–842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpers D. H. The relation of size to the relative rates of degradation of intestinal brush border proteins. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2621–2630. doi: 10.1172/JCI107080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banker G. A., Cotman C. W. Measurement of free electrophoretic mobility and retardation coefficient of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis. A method to validate molecular weight estimates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5856–5861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlet G. D., Sudaka P. Purification de la maltase neutre rénale humaine. Biochimie. 1976;58(5):621–623. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(76)80233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. The low polarity of many membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):930–932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers R. E., Clamp J. R. An assessment of methanolysis and other factors used in the analysis of carbohydrate-containing materials. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(4):1009–1018. doi: 10.1042/bj1251009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogoli A., Eberle A., Sigrist H., Joss C., Robinson E., Mosimann H., Semenza G. Subunits of the small-intestinal sucrase-isomaltase complex and separation of its enzymatically active isomaltase moiety. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):40–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogoli A., Mosimann H., Vock C., von Balthazar A. K., Semenza G. A simplified procedure for the isolation of the sucrase-isomaltase complex from rabbit intestine. Its amino-acid and sugar composition. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct 17;30(1):7–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin K. A., Yamashiro K. M., Gray G. M. Human intestinal sucrase-isomaltase. Identification of free sucrase and isomaltase and cleavage of the hybrid into active distinct subunits. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5735–5741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley D. R., Howell K. E., Eichholz A. Solubilization of brush borders of hamster small intestine and fractionation of some of the components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 3;394(3):361–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A., THOMSON D. L. SEPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TWO RAT-INTESTINAL AMYLASES. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:272–277. doi: 10.1042/bj0890272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlqvist A. Assay of intestinal disaccharidases. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jan;22(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGSTROM L. Studies on calf-intestinal alkaline phosphatase. I. Chromatographic purification, microheterogeneity and some other properties of the purified enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 2;52:36–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90901-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggermont E., Hers H. G. The sedimentation properties of the intestinal alpha-glucosidases of normal human subjects and of patients with sucrose intolerance. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jul;9(4):488–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichholz A. Studies on the organization of the brush border in intestinal epithelial cells. V. Subfractionation of enzymatic activities of the microvillus membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug;163(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON K. A. STARCH-GEL ELECTROPHORESIS--APPLICATION TO THE CLASSIFICATION OF PITUITARY PROTEINS AND POLYPEPTIDES. Metabolism. 1964 Oct;13:SUPPL–SUPPL1002. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(64)80018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan P. R., Zbarsky S. H. Rat intestinal phosphodiesterase II. Properties of the highly purified enzyme and its inactivation by iodoacetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 11;480(1):204–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90334-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G. Release of intestinal surface-membrane glycoproteins associated with enzyme activity by brief digestion with papain. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;121(5):781–789. doi: 10.1042/bj1210781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G., Sabesin S. M., Isselbacher K. J. Rat intestinal microvillus membranes. Purification and biochemical characterization. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):381–390. doi: 10.1042/bj1060381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G., Galand G. The influence of hydrocortisone on the synthesis and turnover of microvillous membrane glycoproteins in suckling rat intestine. Can J Biochem. 1976 Mar;54(3):224–232. doi: 10.1139/o76-035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner J., Taichman N., Kalnins V., Forstner G. Intestinal goblet cell mucus: isolation and identification by immunofluorescence of a goblet cell glycoprotein. J Cell Sci. 1973 Mar;12(2):585–602. doi: 10.1242/jcs.12.2.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- France: at the crossroads. Nature. 1971 May 28;231(5300):229–230. doi: 10.1038/231229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galand G., Forstner G. G. Isolation of microvillus plasma membranes from suckling-rat intestine. The influence of premature induction of digestive enzymes by injection of cortisol acetate. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;144(2):293–302. doi: 10.1042/bj1440293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galand G., Forstner G. G. Soluble neutral and acid maltases in the suckling-rat intestine. The effect of cortisol and development. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;144(2):281–292. doi: 10.1042/bj1440281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grefrath S. P., Reynolds J. A. The molecular weight of the major glycoprotein from the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3913–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S. "Molecular sieve" chromatography on polyacrylamide gels, prepared according to a simplified method. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabbal I., Kells D. I., Forstner G., Forstner J. Human intestinal goblet cell mucin. Can J Biochem. 1976 Aug;54(8):707–716. doi: 10.1139/o76-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaid J. I., Winzler R. J. Association of glycoproteins with the membranes. I. Isolation and molecular weight of the monomeric unit of the major glycoprotein from human erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3635–3638. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. J., Alpers D. H. Properties of human intestinal glucoamylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 5;315(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. S., Brophy E. J. Rat intestinal brush border membrane peptidases. I. Solubilization, purification, and physicochemical properties of two different forms of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3199–3205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobylka D., Khettry A., Shin B. C., Carraway K. L. Proteins and glycoproteins of the erythrocyte membrane. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Feb;148(2):475–487. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolínská J., Kraml J. Separation and characterization of sucrose-isomaltase and of glucoamylase of rat intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 19;284(1):235–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER D., CRANE R. K. The digestive function of the epithelium of the small intestine. II. Localization of disaccharide hydrolysis in the isolated brush border portion of intestinal epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 16;52:293–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90678-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maestracci D., Preiser H., Hedges T., Schmitz J., Crane R. K. Enzymes of the human intestinal brush border membrane. Identification after gel electrophoretic separation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 13;382(2):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maestracci D., Schmitz J., Preiser H., Crane R. K. Proteins and glycoproteins of the human intestinal brush border membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90435-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroux S., Louvard D., Baratti J. The aminopeptidase from hog intestinal brush border. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 15;321(1):282–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroux S., Louvard D. On the hydrophobic part of aminopeptidase and maltases which bind the enzyme to the intestinal brush border membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 21;419(2):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marton L. S., Garvin L. E. Subunit structure of the major human erythrocytes glycoprotein: depolymerization by heating ghosts with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 19;52(4):1457–1462. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90664-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosimann H., Semenza G., Sund H. Hydrodynamic properties of the sucrase-isomaltase complex from rabbit small intestine. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 16;36(2):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oho M., Riquetti P., Hudson B. G. Bovine renal glomerular basement membrane. Isolation and characterization of a glycoprotein component. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7780–7787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. W. Polymerization of proteins with glutaraldehyde. Soluble molecular-weight markers. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):867–873. doi: 10.1042/bj1350867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt-Rivers R., Impiombato F. S. The binding of sodium dodecyl sulphate to various proteins. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):825–830. doi: 10.1042/bj1090825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potempa L. A., Garvin J. E. A third form for the major glycoprotein of the human erythrocyte membrane in sodium dodecyl sulfate: electrophoresis as band PAS-4 at high ionic strength. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 4;72(3):1049–1055. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R. The molecular weight of the undegraded polypeptide chain of yeast hexokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Apr 8;39(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90755-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Estimation of molecular radius, free mobility, and valence using polyacylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Mar;40(1):95–134. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saini P. K., Done J. The diversity of alkaline phosphatase from rat intestine. Isolation and purification of the enzyme (s). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 20;258(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90974-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel-Haueter S., Hore P., Kerry K. R., Semenza G. The preparation of lactase and glucoamylase of rat small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):506–519. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seetharam B., Swaminathan N., Radhakrishnan A. N. Studies on mammalian glucoamylases with special reference to monkey intestinal glucoamylase. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):939–946. doi: 10.1042/bj1170939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Jackson R. L., Andrews E. P., Marchesi V. T. Human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein: a re-evaluation of the molecular weight as determined by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivakami S., Radhakrishnan A. N. Kinetic studies on glucoamylase of rabbit small intestine. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):321–327. doi: 10.1042/bj1530321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivakami S., Radhakrishnan A. N. Purification of rabbit intestinal glucoamylase by affinity chromatography on Sephadex G-200. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1973 Dec;10(4):283–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutzky G. M., Ji T. H. The dissimilar nature of two forms of the major human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 24;373(3):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Yu J. Selective solubilization of proteins from red blood cell membranes by protein perturbants. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):220–232. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuech J. K., Morrison M. Human erythrocyte membrane sialoglycoproteins: a study of interconversion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 10;59(1):352–360. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Steck T. L. Isolation and characterization of band 3, the predominant polypeptide of the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9170–9175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]