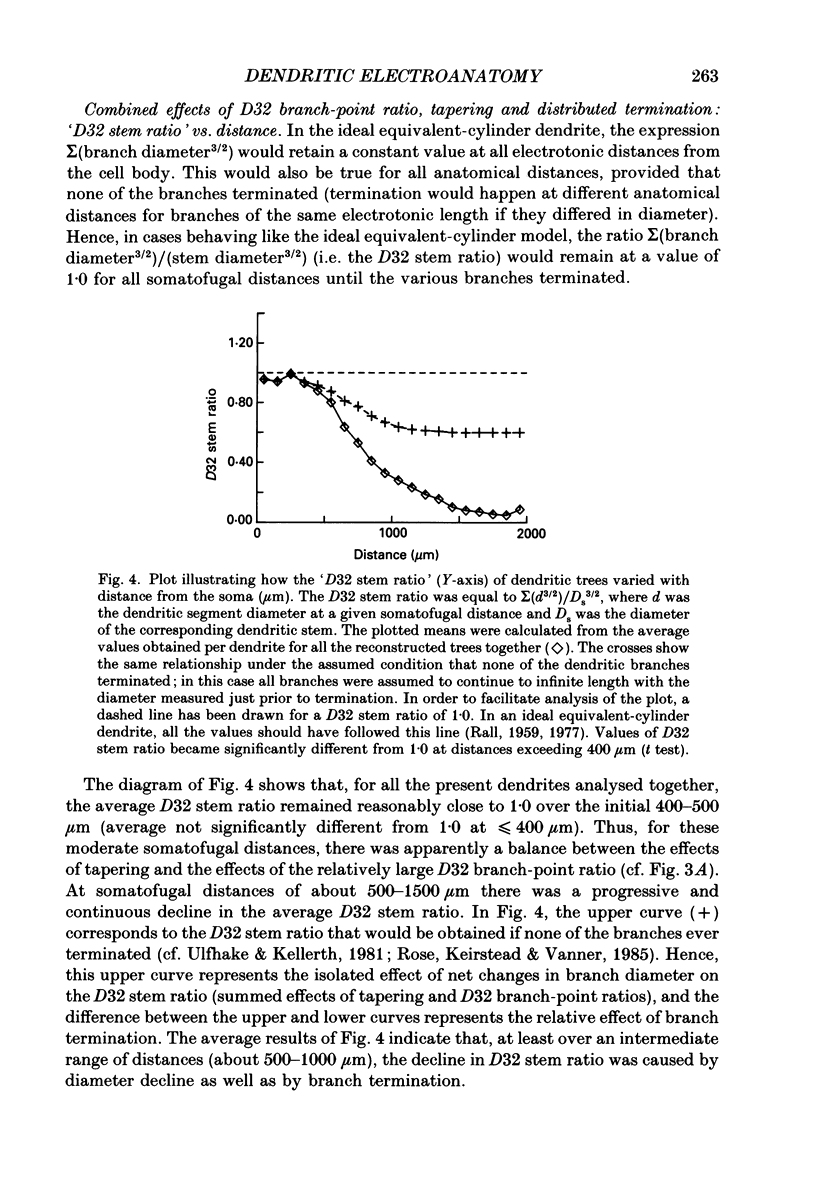
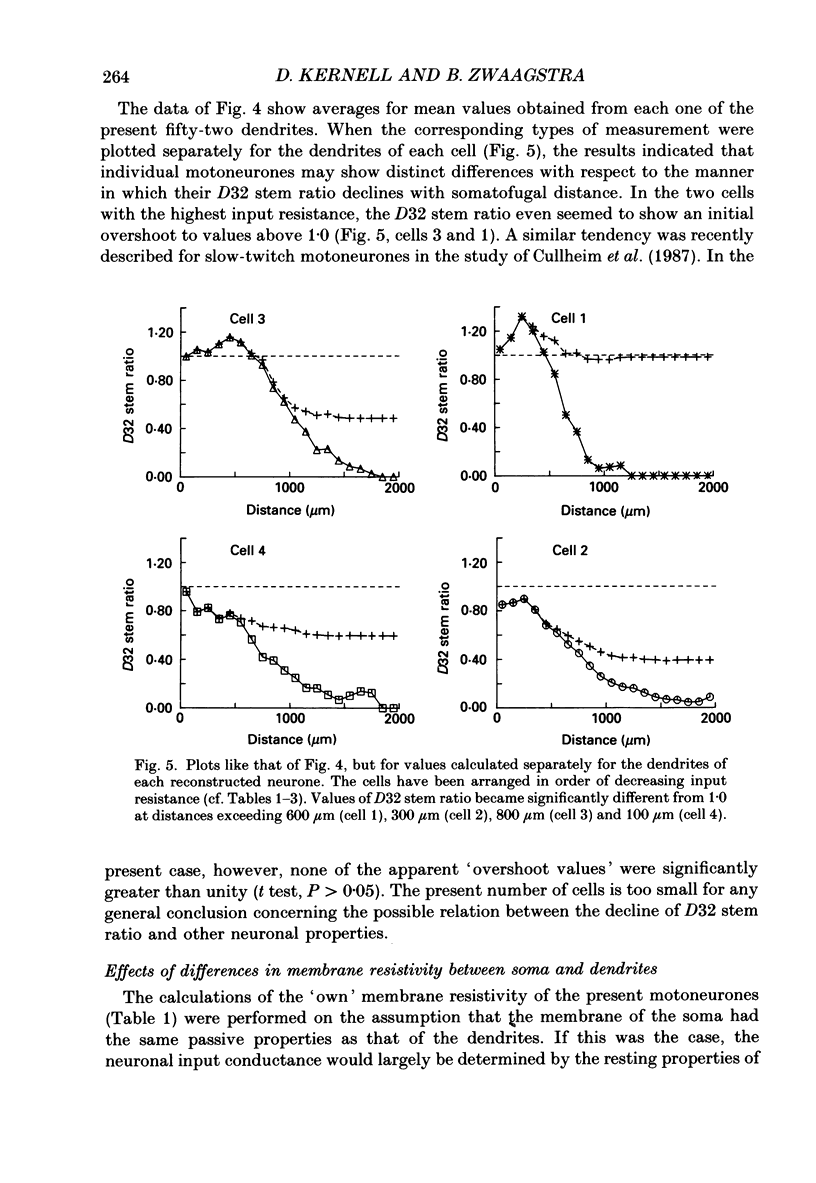
Abstract
1. The electroanatomy of motoneuronal dendrites was analysed using data from fifty-two dendritic trees of four completely reconstructed cat spinal motoneurones that had been labelled with intracellularly injected horseradish peroxidase. The cells belonged to m. triceps surae, and their physiological properties covered much of the known range for this muscle. 2. For each dendritic tree, the input conductance, as seen from the soma, was calculated by the method of Rall (1959), using anatomical measurements of the length and diameter of all branches and different assumed values for dendritic membrane resistivity. 3. There was a strong positive correlation between dendritic stem diameter and the calculated dendritic input conductance. Dendritic input conductance was approximately equal to a constant x (stem diameter)3/2 x (dendritic membrane resistivity)-0.76. 4. The relationship between dendritic stem diameter and computed input conductance was equal to that of Rall's equivalent-cylinder model of a dendritic tree. However, from a number of other points of view, the properties of the reconstructed dendrites differed from those of the model: (a) at branch points, the sum sigma(daughter diameters 3/2) was, on average, 19% greater than the 3/2 power of the parent diameter; (b) dendritic branches often showed a significant amount of tapering, and the mean overall degree of diameter decrease per branch was about 12%; (c) the termination of dendritic branches occurred at widely different distances from the soma within single dendritic trees (true for anatomical as well as for computed electrotonic distances). 5. When used in conjunction with previously published measurements of motoneuronal input resistance and proximal anatomy (Kernell & Zwaagstra, 1981), the present results gave further support to the conclusion that differences in membrane resistivity are of great importance for differences in motoneuronal input resistance. Furthermore, this conclusion was also confirmed by direct observation of the properties of the present four motoneurones: irrespective of the assumed ratio between somatic and dendritic membrane resistivity, there was a statistically significant positive correlation between the measured neuronal input resistance and the required membrane resistivity of soma and dendrites.
Full text
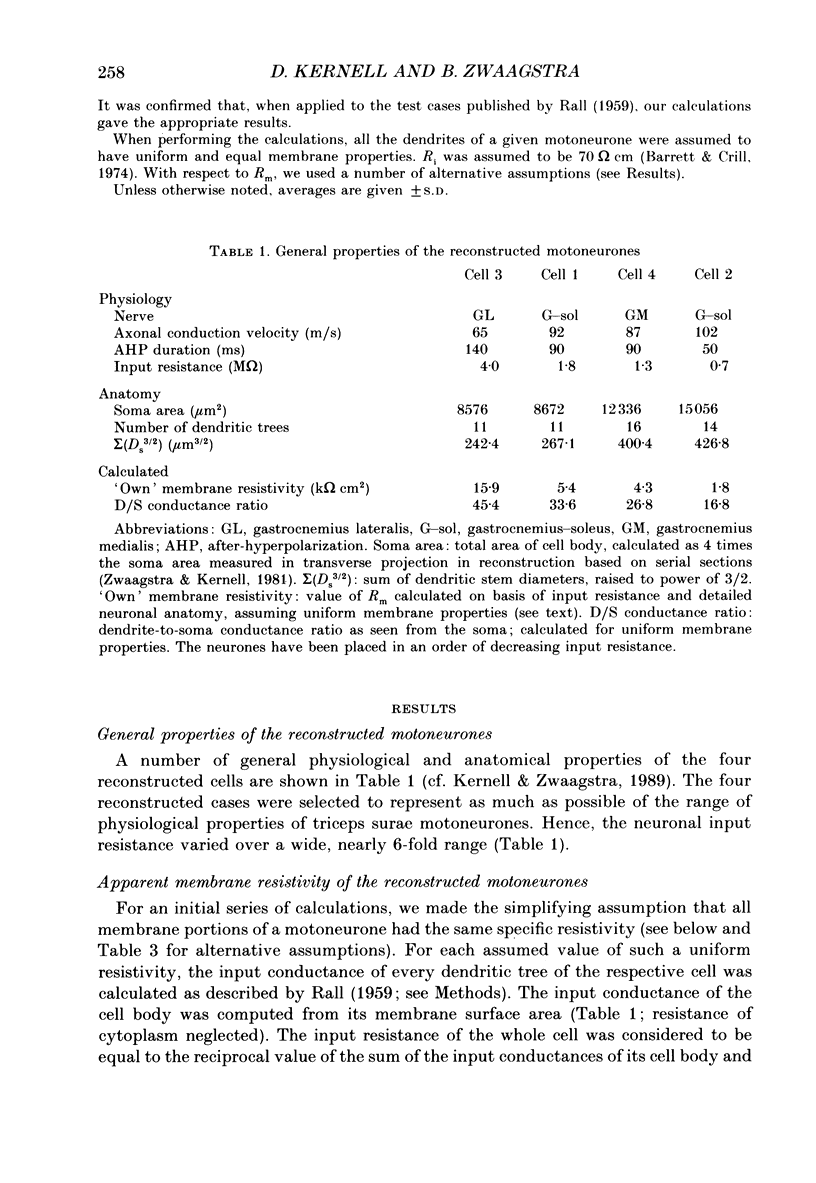
PDF


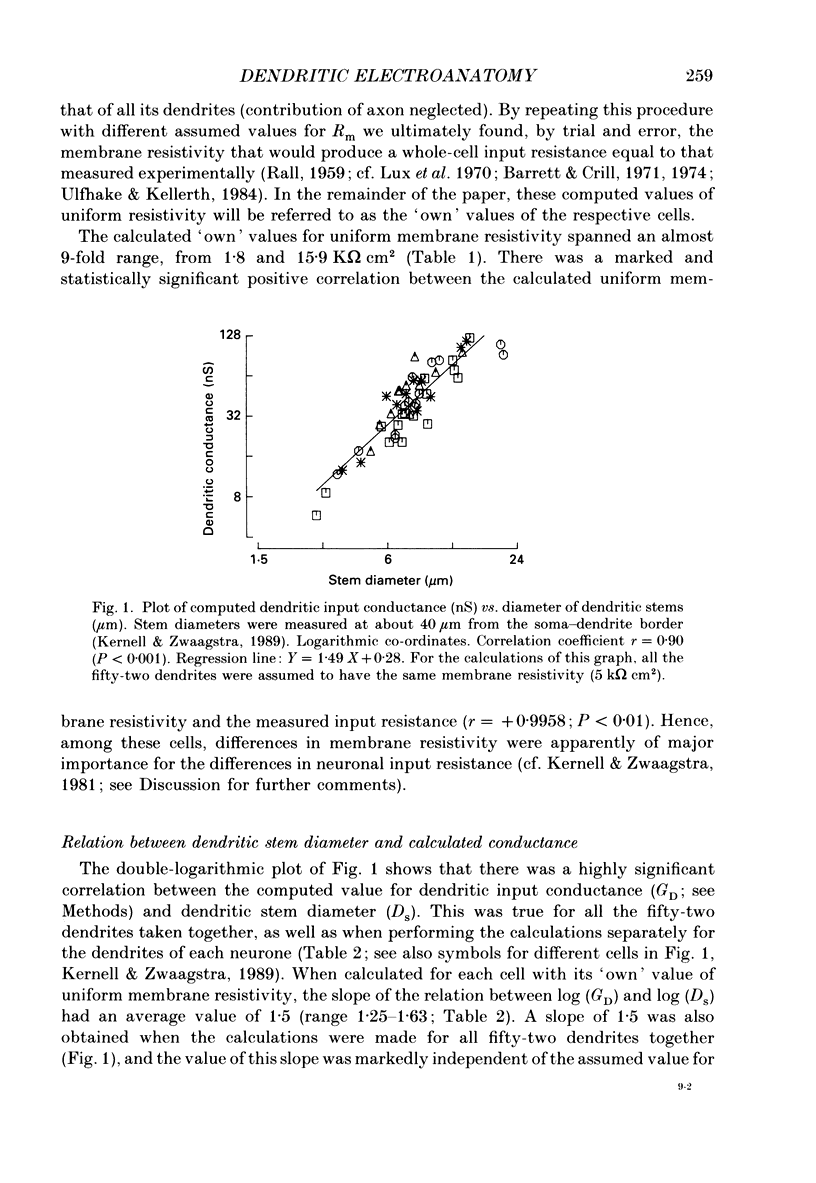
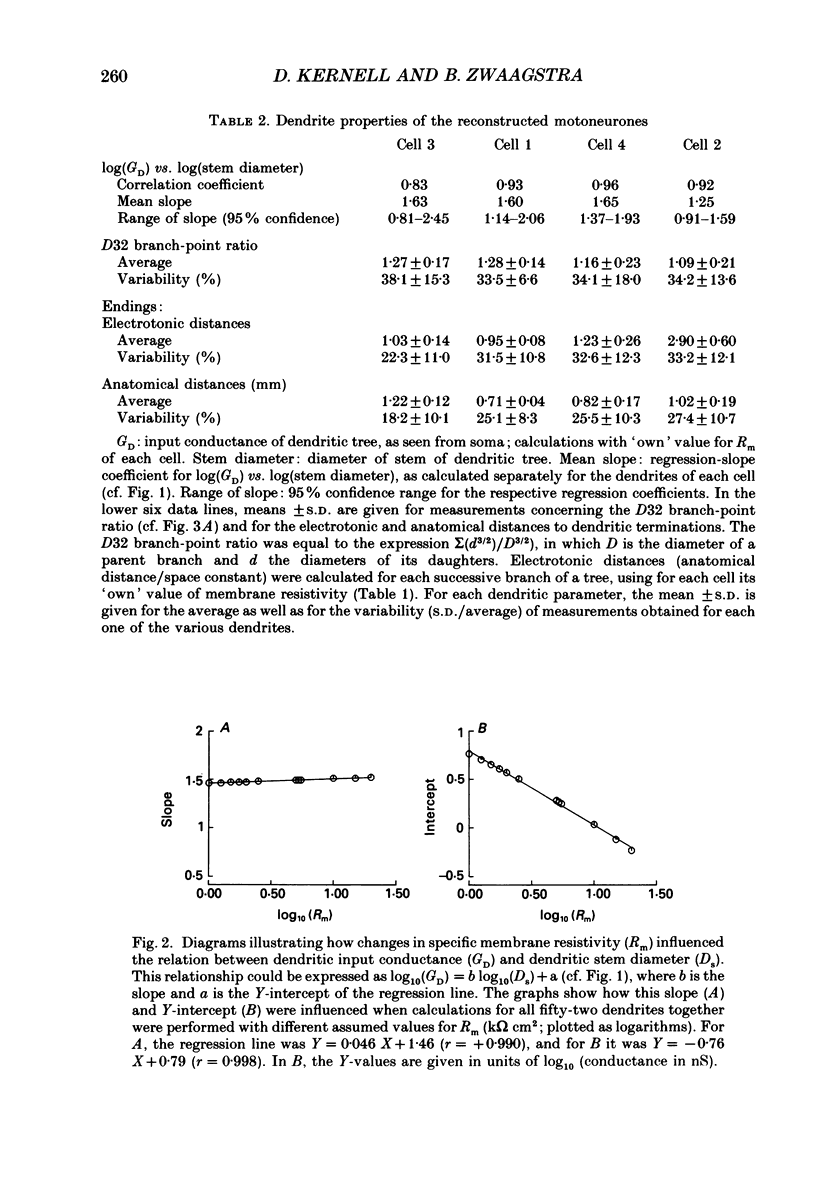

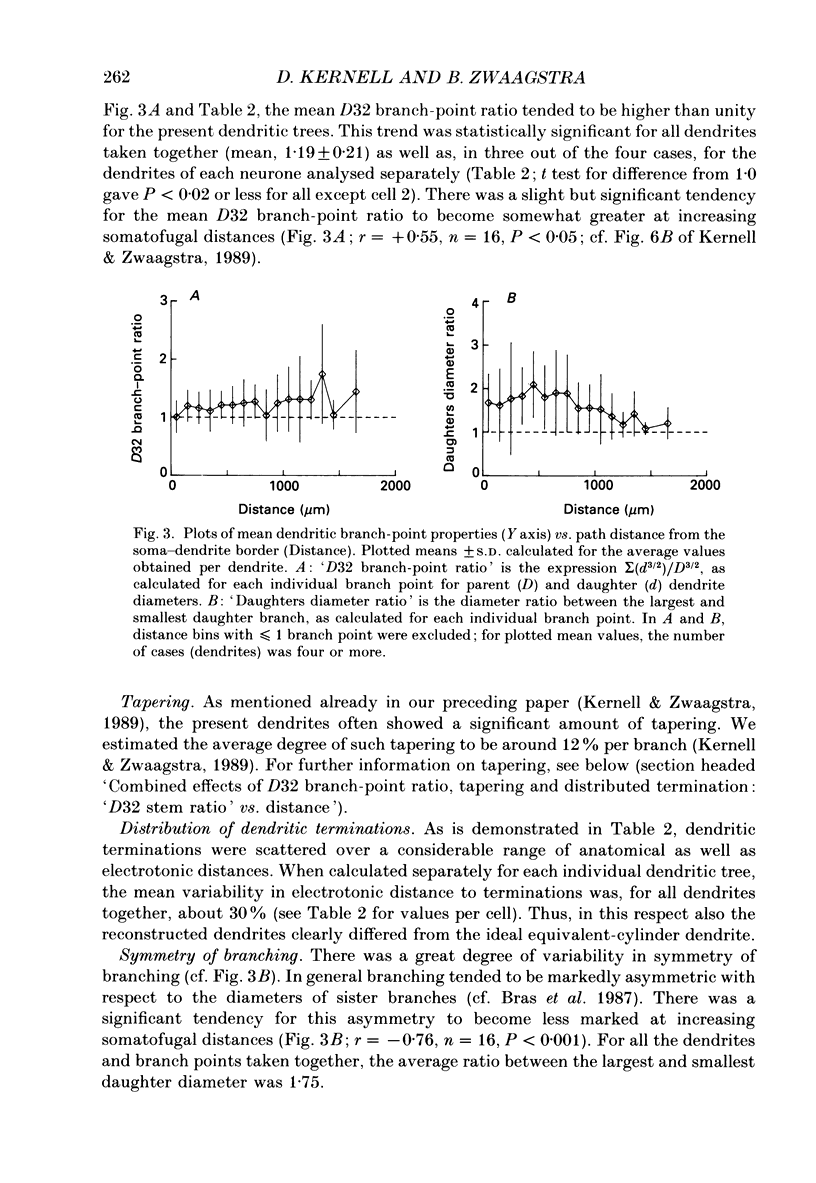





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett J. N., Crill W. E. Specific membrane properties of cat motoneurones. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):301–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Crill W. E. Specific membrane resistivity of dye-injected cat motoneurons. Brain Res. 1971 May 21;28(3):556–561. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bras H., Gogan P., Tyc-Dumont S. The dendrites of single brain-stem motoneurons intracellularly labelled with horseradish peroxidase in the cat. Morphological and electrical differences. Neuroscience. 1987 Sep;22(3):947–970. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)92972-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Fyffe R. E. Direct observations on the contacts made between Ia afferent fibres and alpha-motoneurones in the cat's lumbosacral spinal cord. J Physiol. 1981;313:121–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Dum R. P., Fleshman J. W., Glenn L. L., Lev-Tov A., O'Donovan M. J., Pinter M. J. A HRP study of the relation between cell size and motor unit type in cat ankle extensor motoneurons. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Jul 20;209(1):17–28. doi: 10.1002/cne.902090103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullheim S., Fleshman J. W., Glenn L. L., Burke R. E. Membrane area and dendritic structure in type-identified triceps surae alpha motoneurons. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jan 1;255(1):68–81. doi: 10.1002/cne.902550106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egger M. D., Egger L. D. Quantitative morphological analysis of spinal motoneurons. Brain Res. 1982 Dec 16;253(1-2):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90669-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G. Stimulation of spinal motoneurones with intracellular electrodes. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn L. L., Samojla B. G., Whitney J. F. Electrotonic parameters of cat spinal alpha-motoneurons evaluated with an equivalent cylinder model that incorporates non-uniform membrane resistivity. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 1;435(1-2):398–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91633-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Pinter M. J. Relations among passive electrical properties of lumbar alpha-motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:401–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iansek R., Redman S. J. An analysis of the cable properties of spinal motoneurones using a brief intracellular current pulse. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):613–636. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Miller S., Porter R., Redman S. J. The time course of minimal excitory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurones by group Ia afferent fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):353–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D. Input resistance, electrical excitability, and size of ventral horn cells in cat spinal cord. Science. 1966 Jun 17;152(3729):1637–1640. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3729.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D., Zwaagstra B. Input conductance axonal conduction velocity and cell size among hindlimb motoneurones of the cat. Brain Res. 1981 Jan 12;204(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90591-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D., Zwaagstra B. Size and remoteness: two relatively independent parameters of dendrites, as studied for spinal motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1989 Jun;413:233–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Lux H. D. Some electrical measurements of motoneuron parameters. Biophys J. 1970 Jan;10(1):55–73. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86285-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. Branching dendritic trees and motoneuron membrane resistivity. Exp Neurol. 1959 Nov;1:491–527. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(59)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose P. K., Keirstead S. A., Vanner S. J. A quantitative analysis of the geometry of cat motoneurons innervating neck and shoulder muscles. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Sep 1;239(1):89–107. doi: 10.1002/cne.902390108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfhake B., Kellerth J. O. A quantitative light microscopic study of the dendrites of cat spinal alpha-motoneurons after intracellular staining with horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Nov 10;202(4):571–583. doi: 10.1002/cne.902020409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfhake B., Kellerth J. O. A quantitative morphological study of HRP-labelled cat alpha-motoneurones supplying different hindlimb muscles. Brain Res. 1983 Mar 28;264(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfhake B., Kellerth J. O. Electrophysiological and morphological measurements in cat gastrocnemius and soleus alpha-motoneurones. Brain Res. 1984 Jul 30;307(1-2):167–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. E., Reid S. A., Sypert G. W., Munson J. B. Membrane electrical properties and prediction of motor-unit type of medial gastrocnemius motoneurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1985 May;53(5):1323–1344. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.5.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaagstra B., Kernell D. Sizes of soma and stem dendrites in intracellularly labelled alpha-motoneurones of the cat. Brain Res. 1981 Jan 12;204(2):295–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90590-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jongh H. R., Kernell D. Limits of usefulness of electrophysiological methods for estimating dendritic length in neurones. J Neurosci Methods. 1982 Jul;6(1-2):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(82)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


