Abstract
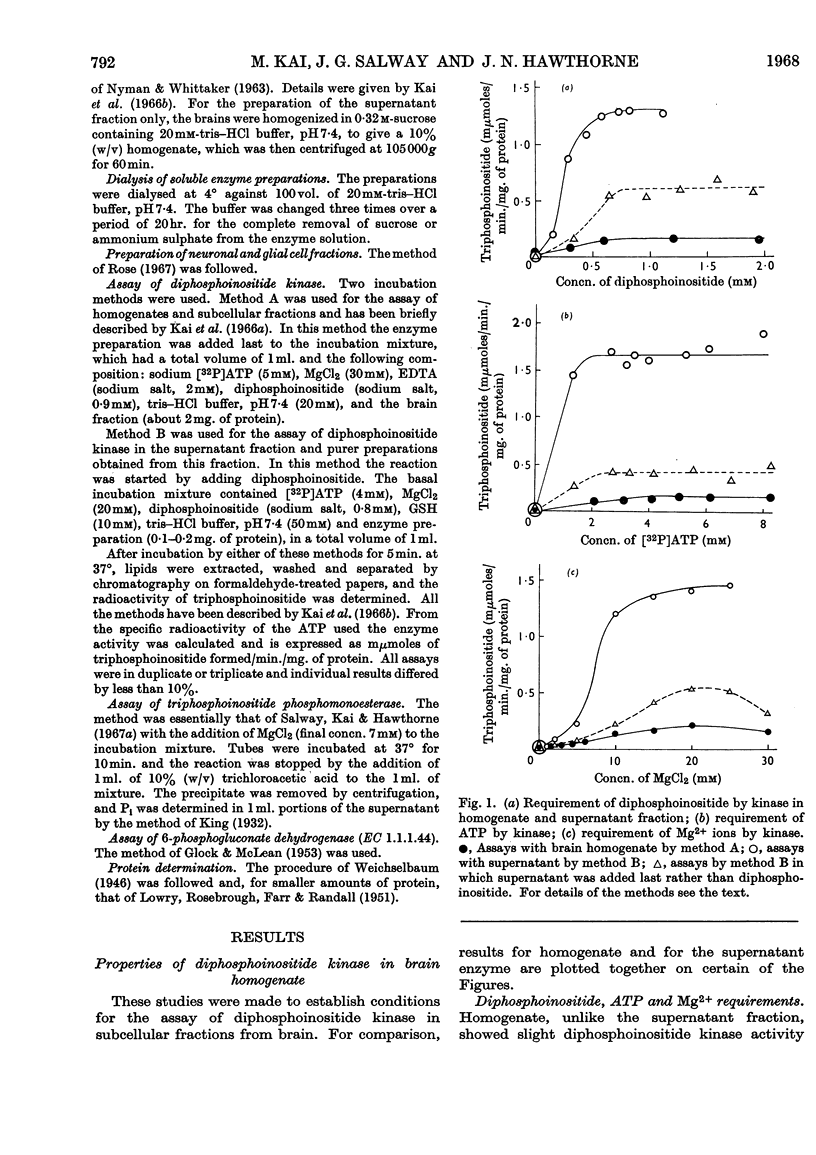
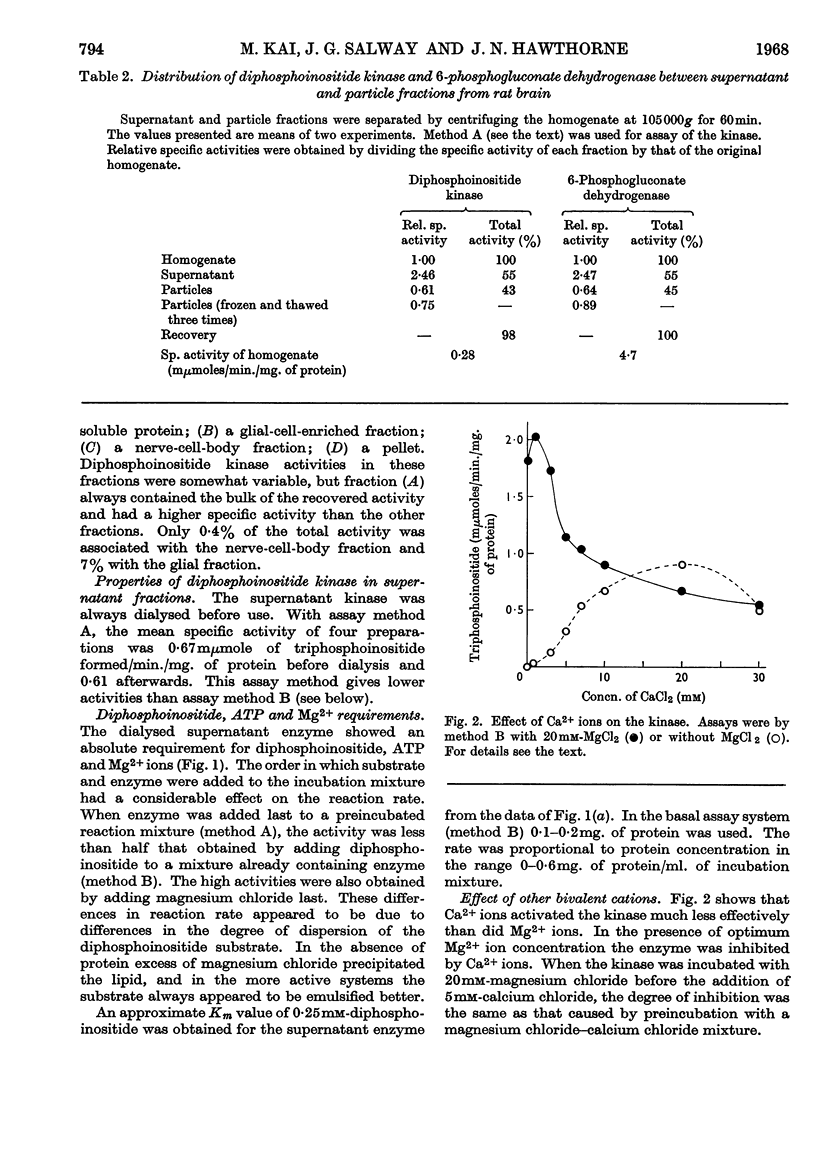
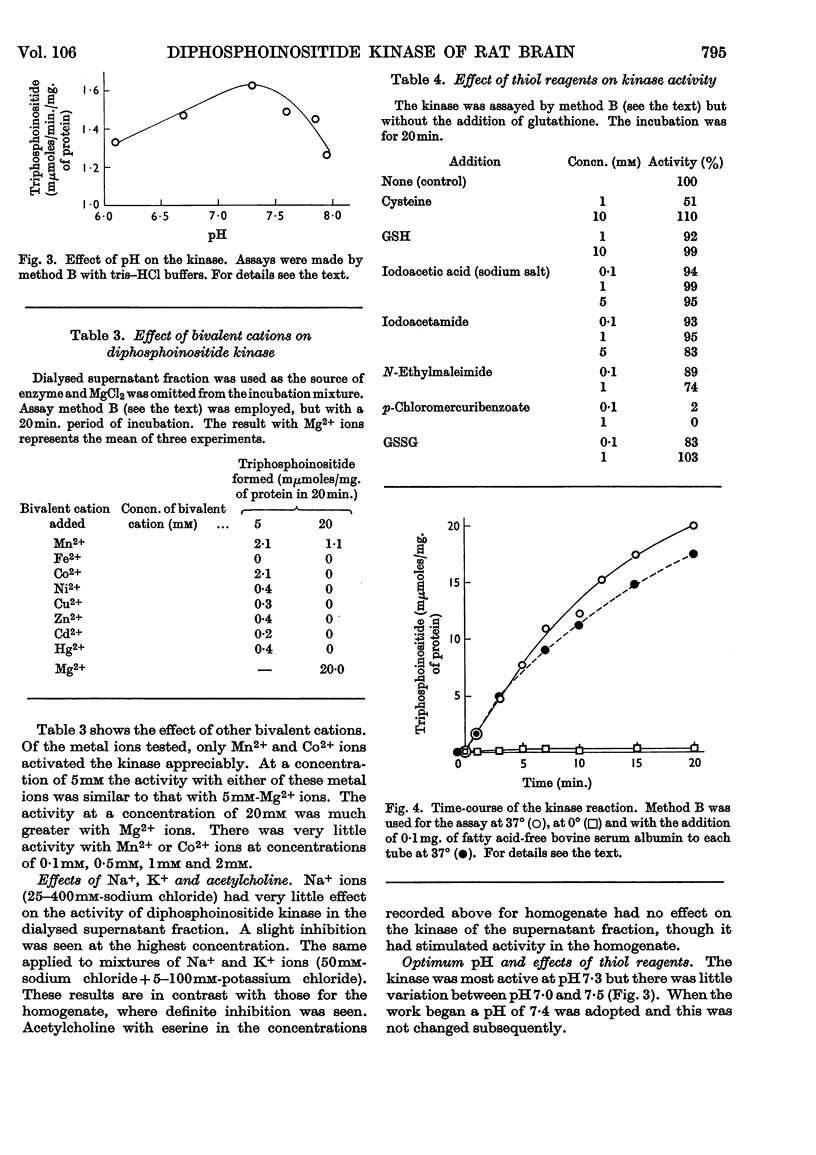
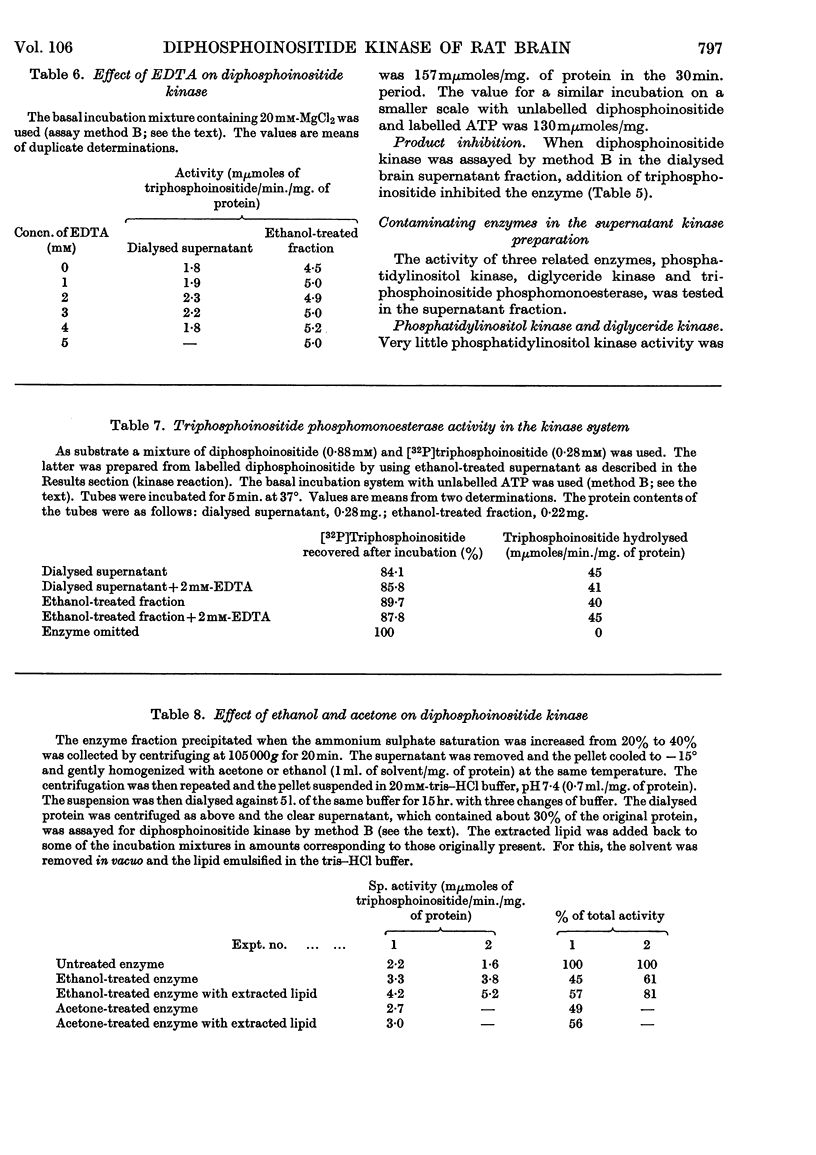
1. The supernatant fraction of adult rat brain contains a diphosphoinositide kinase. 2. Formation of triphosphoinositide by the enzyme in the presence of ATP and Mg2+ ions was shown with labelled ATP or labelled diphosphoinositide. 3. The kinase was also activated by Ca2+, Mn2+ and Co2+ ions, but to a smaller extent than by Mg2+ ions. 4. In the presence of optimum Mg2+ ion concentration the enzyme was inhibited by Ca2+ ions. 5. Activity did not depend on thiol groups and the pH optimum was 7·3. 6. The dialysed supernatant fraction had no diglyceride kinase activity and negligible phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. 7. Triphosphoinositide phosphomonoesterase was present but showed little activity under the conditions used to assay the kinase. 8. Diphosphoinositide kinase was purified by ammonium sulphate fractionation, ethanol treatment and chromatography on Sephadex G-200. 9. This purification removed much of the triphosphoinositide phosphomonoesterase.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colodzin M., Kennedy E. P. Biosynthesis of diphosphoinositide in brain. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3771–3780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M. 'Phosphatido-peptide'-like complexes formed by the interaction of calcium triphosphoinositide with protein. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):134–138. doi: 10.1042/bj0970134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Thompson W. The triphosphoinositide phosphomonoesterase of brain tissue. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):244–250. doi: 10.1042/bj0910244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durell J., Sodd M. A. Studies on the acetylcholine-stimulated incorporation of radioactive inorganic orthophosphate into the phospholipid of brain particulate preparations. II. Subcellular distribution of enzymic activity. J Neurochem. 1966 Jun;13(6):487–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J., Dawson R. M. Polyphosphoinositides in myelin. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):644–650. doi: 10.1042/bj0960644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOCK G. E., McLEAN P. Further studies on the properties and assay of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase of rat liver. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):400–408. doi: 10.1042/bj0550400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S. Preparation of human serum albumin free of long-chain fatty acids. Science. 1957 Jun 28;125(3261):1296–1297. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3261.1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDRICKSON H. S., BALLOU C. E. ION EXCHANGE CHROMATOGRAPHY OF INTACT BRAIN PHOSPHOINOSITIDES ON DIETHYLAMINOETHYL CELLULOSE BY GRADIENT SALT ELUTION IN A MIXED SOLVENT SYSTEM. J Biol Chem. 1964 May;239:1369–1373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN M. R., HOKIN L. E. The synthesis of phosphatidic acid from diglyceride and adenosine triphosphate in extracts of brain microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1381–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai M., White G. L., Hawthorne J. N. The phosphatidylinositol kinase of rat brain. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):328–337. doi: 10.1042/bj1010328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King E. J. The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1932;26(2):292–297. doi: 10.1042/bj0260292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Hawthorne J. N. The site of diphosphoinositide synthesis in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYMAN M., WHITTAKER V. P. The distribution of adenosine triphosphate in subcellular fractions of brain tissue. Biochem J. 1963 May;87:248–255. doi: 10.1042/bj0870248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prottey C., Hawthorne J. N. The lipids of mammalian pancreas. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):191–196. doi: 10.1042/bj1010191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose S. P. Preparation of enriched fractions from cerebral cortex containing isolated, metabolically active neuronal and glial cells. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):33–43. doi: 10.1042/bj1020033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salway J. G., Kai M., Hawthorne J. N. Triphosphoinositide phosphomonoesterase activity in nerve cellbodies, neuroglia and subcellular fractions from whole rat brain. J Neurochem. 1967 Oct;14(10):1013–1024. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheltawy A., Dawson R. M. The polyphosphoinositides and other lipids of peripheral nerves. Biochem J. 1966 Jul;100(1):12–18. doi: 10.1042/bj1000012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


