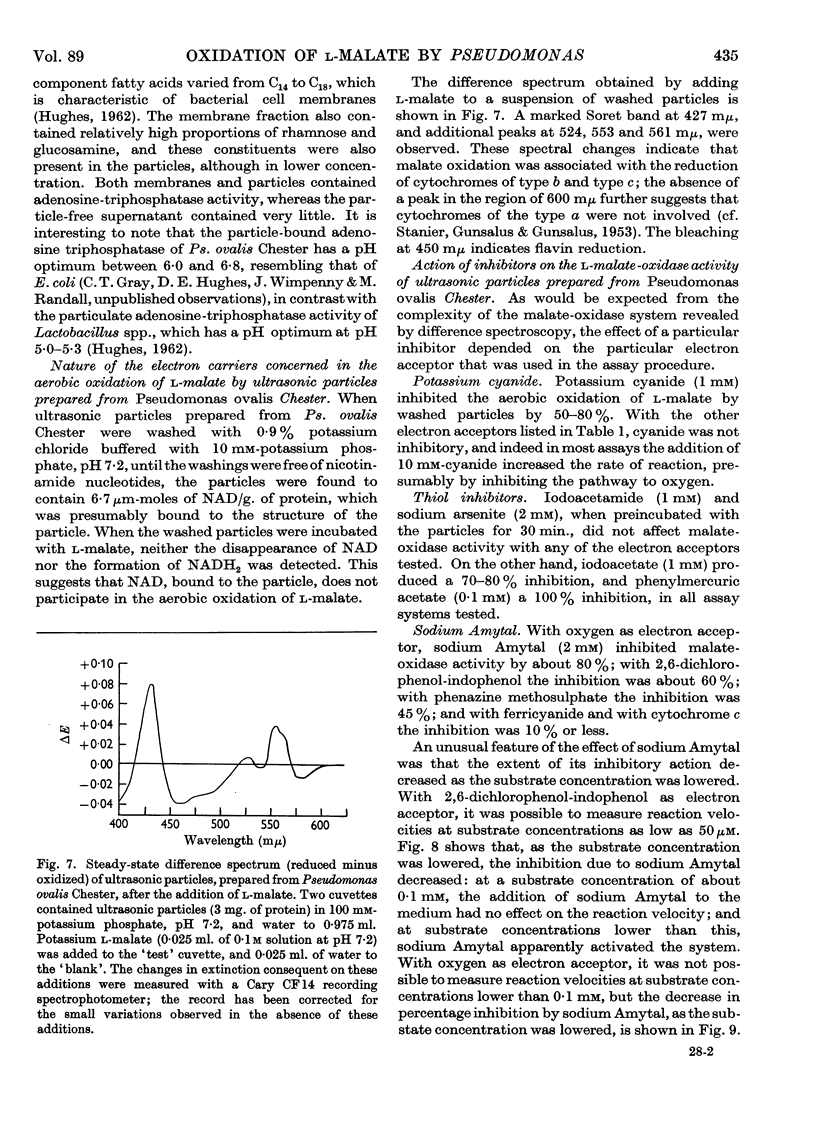
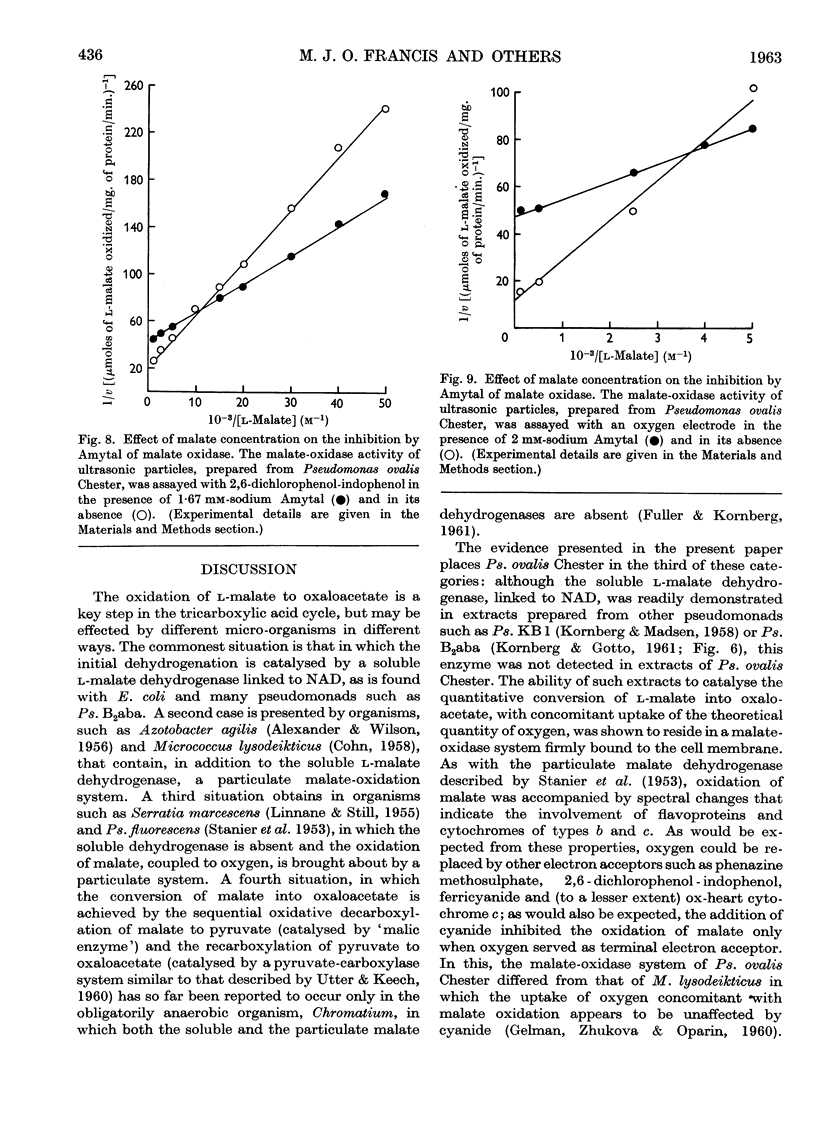
Full text
PDF


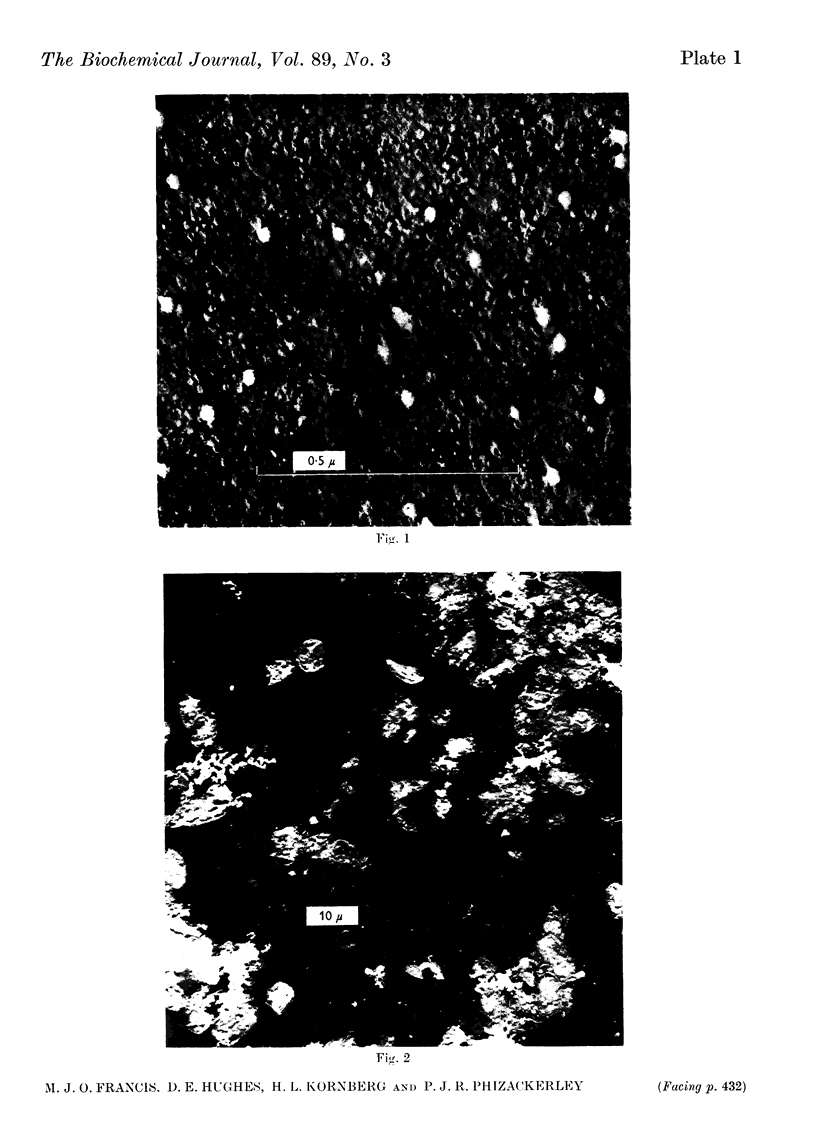
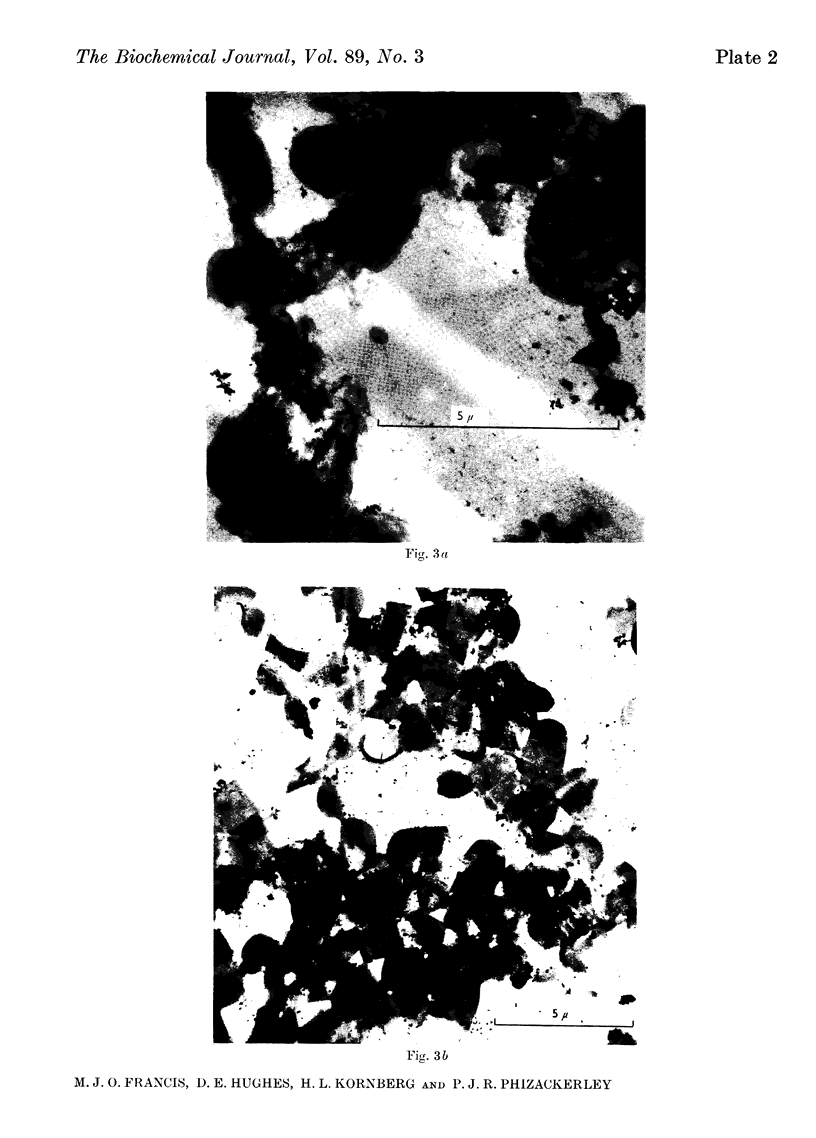
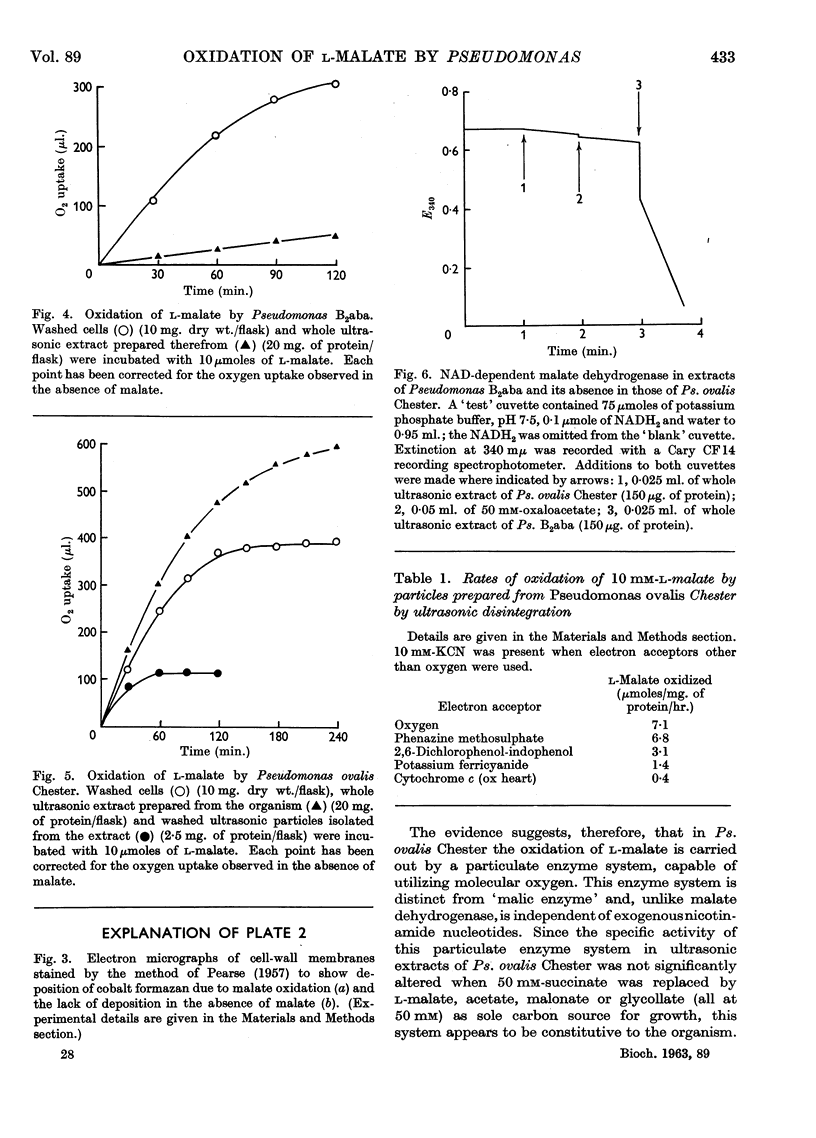



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER M., WILSON P. W. Intracellular distribution of tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1956 Feb;71(2):252–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.2.252-253.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BASSHAM J. A., BIRT L. M., HEMS R., LOENING U. E. Determination of the reduced and oxidized pyridine nucleotides in animal tissues. Biochem J. 1959 Nov;73:491–499. doi: 10.1042/bj0730491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN D. V. The enzymatic formation of oxalacetic acid by nonpyridine nucleotide malic dehydrogenase of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):299–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON G. H., KORNBERG H. L., LUND P. Purification and properties of malate synthetase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 1;41:217–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EL HAWARY M. F. S., THOMPSON R. H. S. Separation and estimation of blood keto acids by paper chromatography. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):340–347. doi: 10.1042/bj0530340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GETZ G. S., BARTLEY W. The intracellular distribution of fatty acids in rat liver. The fatty acids of intracellular compartments. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78:307–312. doi: 10.1042/bj0780307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES D. E. A press for disrupting bacteria and other micro-organisms. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Apr;32(2):97–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES D. E. The bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Sep;29:39–46. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT A. L., RODGERS A., HUGHES D. E. Sub-cellular particles and the nicotinic acid hydroxylase system in extracts of. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Aug;34:354–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOGUT M., PODOSKI E. P. Oxidative pathways in a fluorescent Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1953 Dec;55(5):800–811. doi: 10.1042/bj0550800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., ELSDEN S. R. The metabolism of 2-carbon compounds by microorganisms. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1961;23:401–470. doi: 10.1002/9780470122686.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., GOTTO A. M. The metabolism of C2 compounds in micro-organisms. 6. Synthesis of cell constituents from glycollate by Pseudomonas sp. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:69–82. doi: 10.1042/bj0780069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., MADSEN N. B. The metabolism of C2 compounds in microorganisms. 3. Synthesis of malate from acetate via the glyoxylate cycle. Biochem J. 1958 Mar;68(3):549–557. doi: 10.1042/bj0680549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L. The metabolism of C2 compounds in micro-organisms. I. The incorporation of [2-14C] acetate by Pseudomonas fluorescens, and by a Corynebacterium, grown on ammonium acetate. Biochem J. 1958 Mar;68(3):535–542. doi: 10.1042/bj0680535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINNANE A. W., STILL J. L. The intracellular distribution of enzymes in Serratia marcescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Feb;16(2):305–306. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSE A. G. Intracellular localisation of dehydrogenase systems using monotetrazolium salts and metal chelation of their formazans. J Histochem Cytochem. 1957 Sep;5(5):515–527. doi: 10.1177/5.5.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUMPHREY A. M., REDFEARN E. R. INHIBITION OF SUCCINATE OXIDATION BY BARBITURATES IN TIGHTLY COUPLED MITOCHONDRIA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 13;74:317–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER T. P., KEARNEY E. B. Determination of succinic dehydrogenase activity. Methods Biochem Anal. 1957;4:307–333. doi: 10.1002/9780470110201.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANIER R. Y., GUNSALUS I. C., GUNSALUS C. F. The enzymatic conversion of mandelic acid to benzoic acid. II. Properties of the particulate fractions. J Bacteriol. 1953 Nov;66(5):543–547. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.5.543-547.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLEE C. A. An enzymic method for the assay of pyridine nucleotides in extracts of animal tissues. Biochem J. 1962 Apr;83:191–194. doi: 10.1042/bj0830191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]