Abstract
We present here a maximal likelihood algorithm for estimating single-channel kinetic parameters from idealized patch-clamp data. The algorithm takes into account missed events caused by limited time resolution of the recording system. Assuming a fixed dead time, we derive an explicit expression for the corrected transition rate matrix by generalizing the theory of Roux and Sauve (1985, Biophys. J. 48:149-158) to the case of multiple conductance levels. We use a variable metric optimizer with analytical derivatives for rapidly maximizing the likelihood. The algorithm is applicable to data containing substates and multiple identical or nonidentical channels. It allows multiple data sets obtained under different experimental conditions, e.g., concentration, voltage, and force, to be fit simultaneously. It also permits a variety of constraints on rate constants and provides standard errors for all estimates of model parameters. The algorithm has been tested extensively on a variety of kinetic models with both simulated and experimental data. It is very efficient and robust; rate constants for a multistate model can often be extracted in a processing time of approximately 1 min, largely independent of the starting values.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertsen A., Hansen U. P. Estimation of kinetic rate constants from multi-channel recordings by a direct fit of the time series. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1393–1403. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80613-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A. A statistical analysis of acetylcholine receptor activation in Xenopus myocytes: stepwise versus concerted models of gating. J Physiol. 1993 Feb;461:339–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball F. G., Sansom M. S. Ion-channel gating mechanisms: model identification and parameter estimation from single channel recordings. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1989 May 22;236(1285):385–416. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1989.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Correcting single channel data for missed events. Biophys J. 1986 May;49(5):967–980. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83725-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
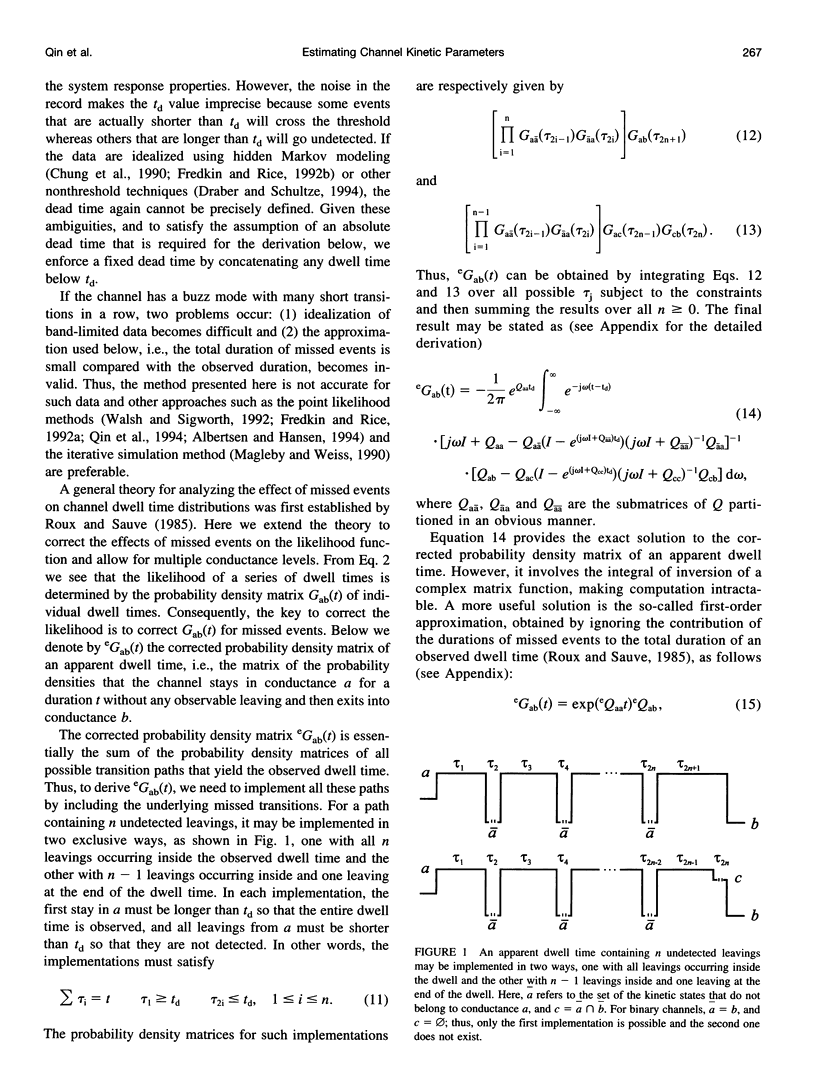
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Quantitative description of three modes of activity of fast chloride channels from rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:141–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R. Kinetic modeling for the channel gating process from single channel patch clamp data. J Theor Biol. 1988 Jun 22;132(4):449–468. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(88)80084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. H., Moore J. B., Xia L. G., Premkumar L. S., Gage P. W. Characterization of single channel currents using digital signal processing techniques based on Hidden Markov Models. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Sep 29;329(1254):265–285. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1990.0170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of single ion channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Mar 6;211(1183):205–235. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Relaxation and fluctuations of membrane currents that flow through drug-operated channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):231–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouzy S. C., Sigworth F. J. Yet another approach to the dwell-time omission problem of single-channel analysis. Biophys J. 1990 Sep;58(3):731–743. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82416-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draber S., Schultze R. Detection of jumps in single-channel data containing subconductance levels. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1404–1413. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80614-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredkin D. R., Rice J. A. Bayesian restoration of single-channel patch clamp recordings. Biometrics. 1992 Jun;48(2):427–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes A. G., Jalali A., Colquhoun D. Asymptotic distributions of apparent open times and shut times in a single channel record allowing for the omission of brief events. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1992 Sep 29;337(1282):383–404. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1992.0116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Lange K. Estimating kinetic constants from single channel data. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):207–223. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84341-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Moran N., Ehrenstein G. Gating kinetics of batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels in neuroblastoma cells determined from single-channel measurements. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):313–322. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84157-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Internal motions in proteins and gating kinetics of ionic channels. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):877–884. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83168-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Calcium dependence of open and shut interval distributions from calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:585–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Weiss D. S. Estimating kinetic parameters for single channels with simulation. A general method that resolves the missed event problem and accounts for noise. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1411–1426. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82487-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus O. B., Magleby K. L. Accounting for the Ca(2+)-dependent kinetics of single large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1991 Nov;443:739–777. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne R. K., Yeo G. F., Edeson R. O., Madsen B. W. Stochastic modelling of a single ion channel: an alternating renewal approach with application to limited time resolution. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Apr 22;233(1272):247–292. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux B., Sauvé R. A general solution to the time interval omission problem applied to single channel analysis. Biophys J. 1985 Jul;48(1):149–158. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83768-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs F., Neil J., Barkakati N. The automated analysis of data from single ionic channels. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Dec;395(4):331–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00580798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberg C. A., Bezanilla F. A sodium channel gating model based on single channel, macroscopic ionic, and gating currents in the squid giant axon. Biophys J. 1991 Dec;60(6):1511–1533. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82186-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss D. S., Magleby K. L. Voltage-dependent gating mechanism for single fast chloride channels from rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1992;453:279–306. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]