Abstract
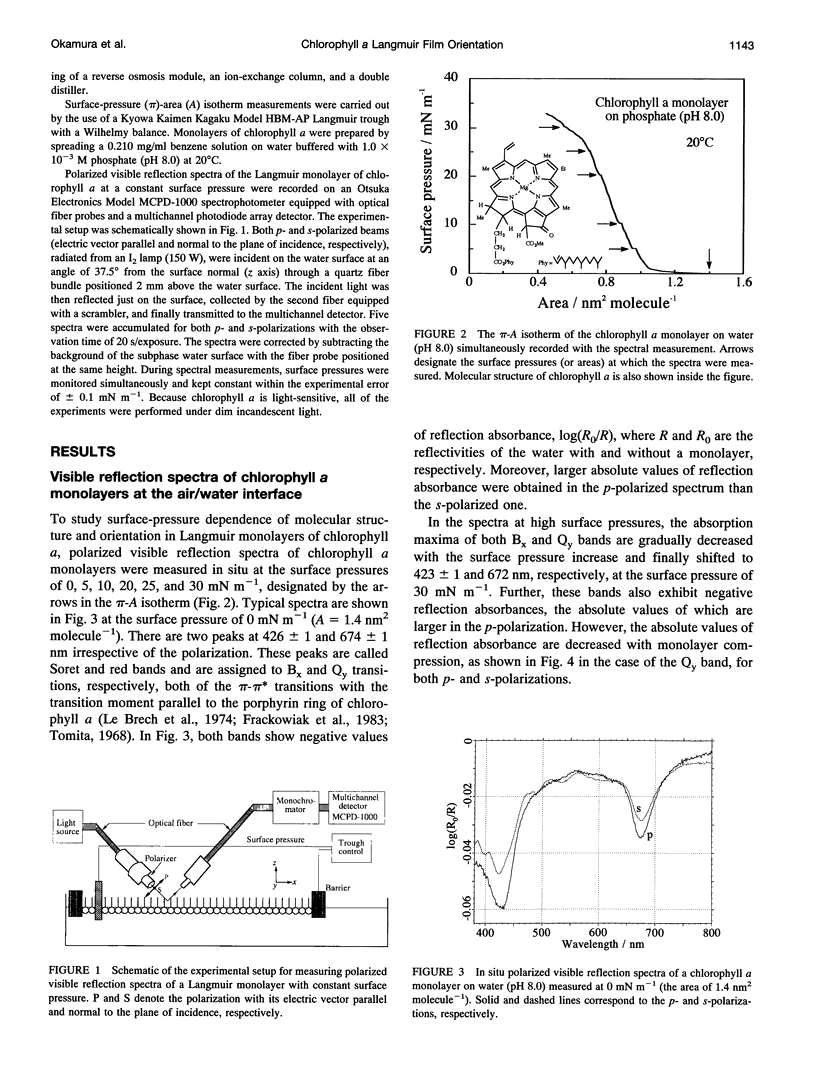
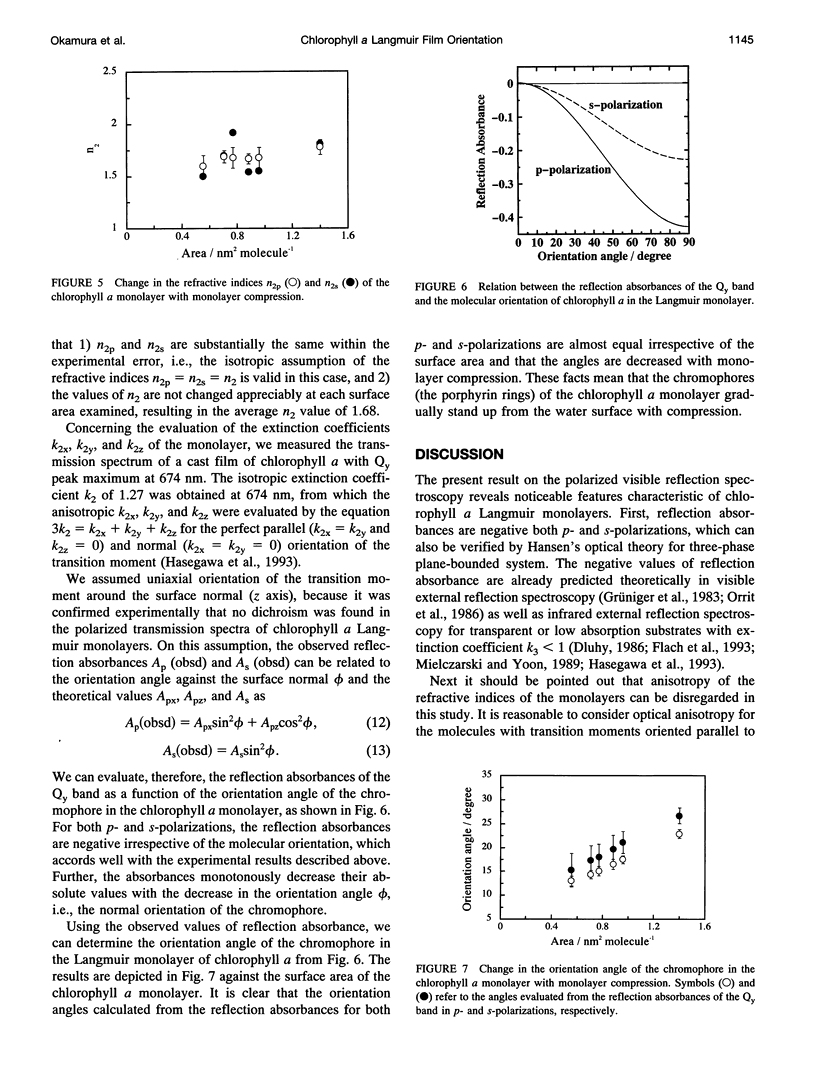
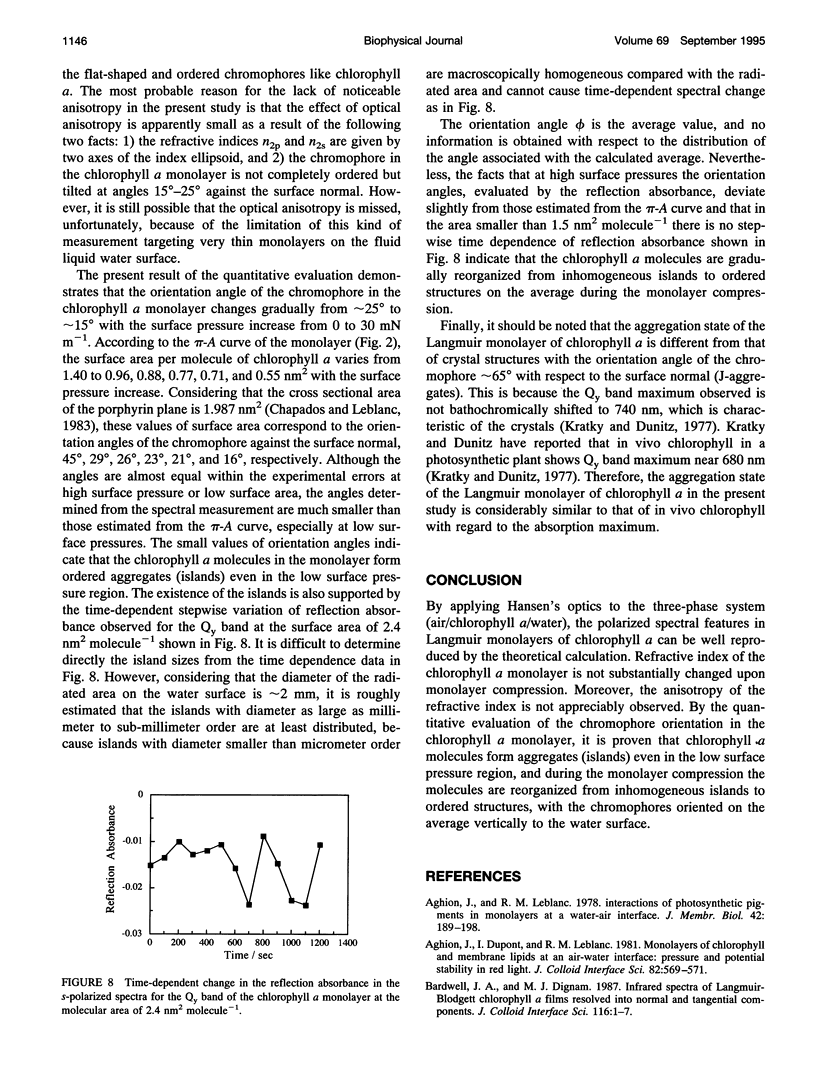
Polarized visible reflection spectra of a chlorophyll a (Chl.a) Langmuir monolayer have been measured in situ at various surface pressures. By applying Hansen's optics to the three-phase plane-bounded system (air/Chl.a monolayer/water), the negative reflection absorbances observed were reproduced satisfactorily by the theoretical calculation. Molecular orientation of Chl.a in the monolayer was evaluated quantitatively as a function of surface pressure, from the reflection absorbance of p- and s-polarized spectra of the red (Qy) band. It has been proven that Chl.a molecules in the monolayer form aggregates (islands) even in the low surface pressure region and that during the monolayer compression the molecules are gradually reorganized from inhomogeneous islands to ordered structures, with the chromophores oriented on the average vertically to the water surface.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chapados C., Germain D., Leblanc R. M. Aggregation of chlorophylls in monolayers. Part IV. The reorganisation of chlorophyll a in multilayer array. Biophys Chem. 1980 Oct;12(2):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(80)80051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapados C., Leblanc R. M. Aggregation of chlorophylls in monolayers. V. The effect of water on chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b in mono and multilayer arrays. Biophys Chem. 1983 Apr;17(3):211–244. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(83)87006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flach C. R., Brauner J. W., Mendelsohn R. Calcium ion interactions with insoluble phospholipid monolayer films at the A/W interface. External reflection-absorption IR studies. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):1994–2001. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81276-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyot-Sionnest P, Hunt JH, Shen YR. Sum-frequency vibrational spectroscopy of a Langmuir film: Study of molecular orientation of a two-dimensional system. Phys Rev Lett. 1987 Oct 5;59(14):1597–1600. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.59.1597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratky C., Dunitz J. D. Ordered aggregation states of chlorophyll a and some derivatives. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 25;113(2):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutz W. On the state of chlorophyll in vivo. Z Naturforsch B. 1968 Apr;23(4):520–527. doi: 10.1515/znb-1968-0419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamarche F., Picard G., Téchy F., Aghion J., Leblanc R. M. Complex formation between chlorophyll a and cytochrome c: surface properties at the air-water interface. Absorbance, fluorescence and fluorescence-lifetime in Langmuir-Blodgett films. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 23;197(2):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhwald H. Phospholipid and phospholipid-protein monolayers at the air/water interface. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1990;41:441–476. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.41.100190.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita G. Dimer and polymers in solutions of chlorophyll a. Biophysik. 1968 May 15;4(4):296–301. doi: 10.1007/BF01195040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaknin D., Kjaer K., Als-Nielsen J., Lösche M. Structural properties of phosphatidylcholine in a monolayer at the air/water interface: Neutron reflection study and reexamination of x-ray reflection measurements. Biophys J. 1991 Jun;59(6):1325–1332. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82347-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



