Abstract
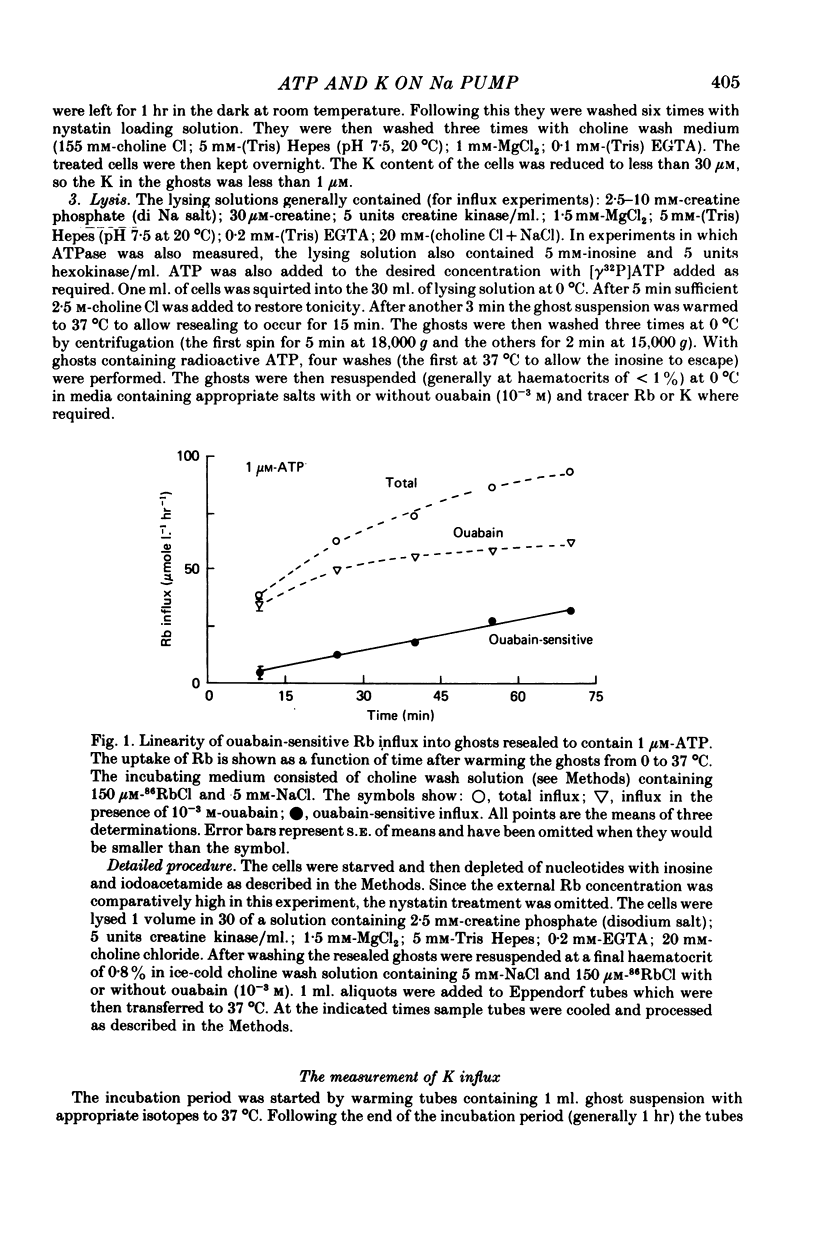
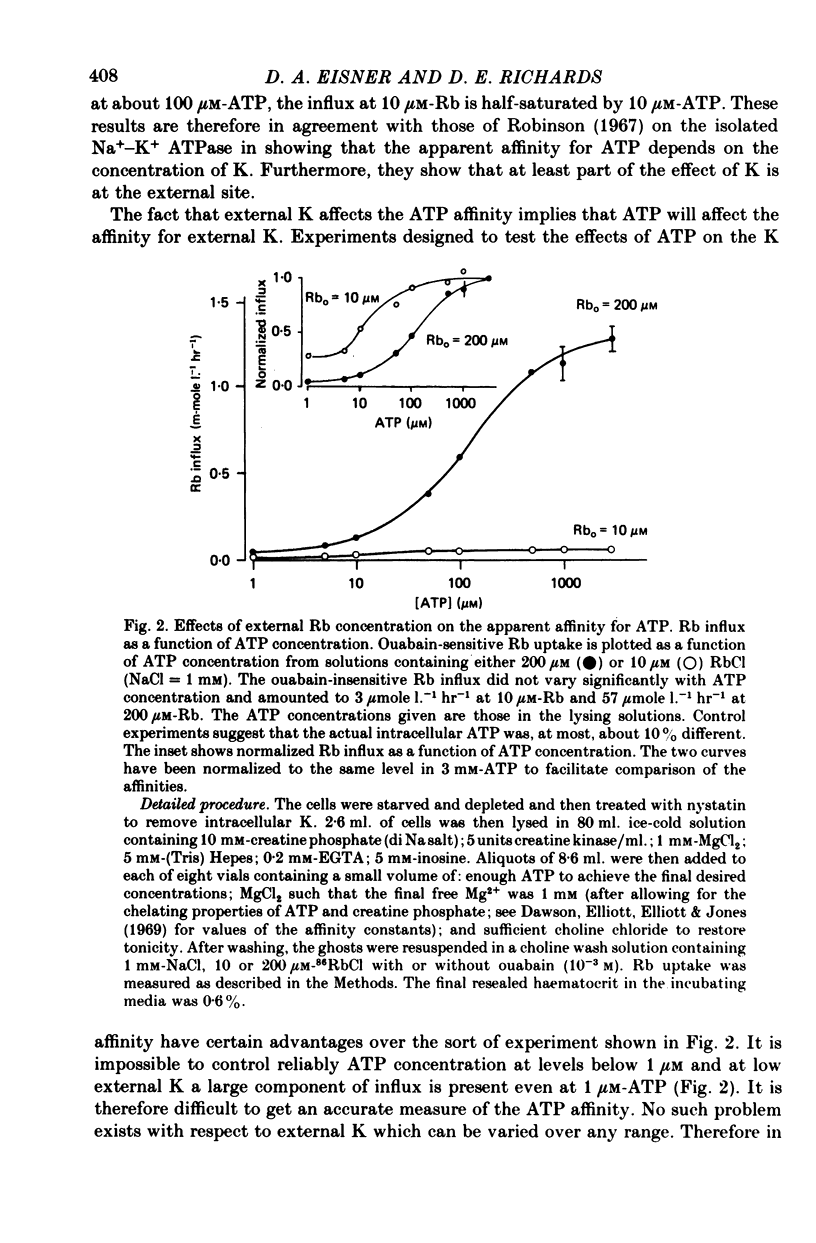
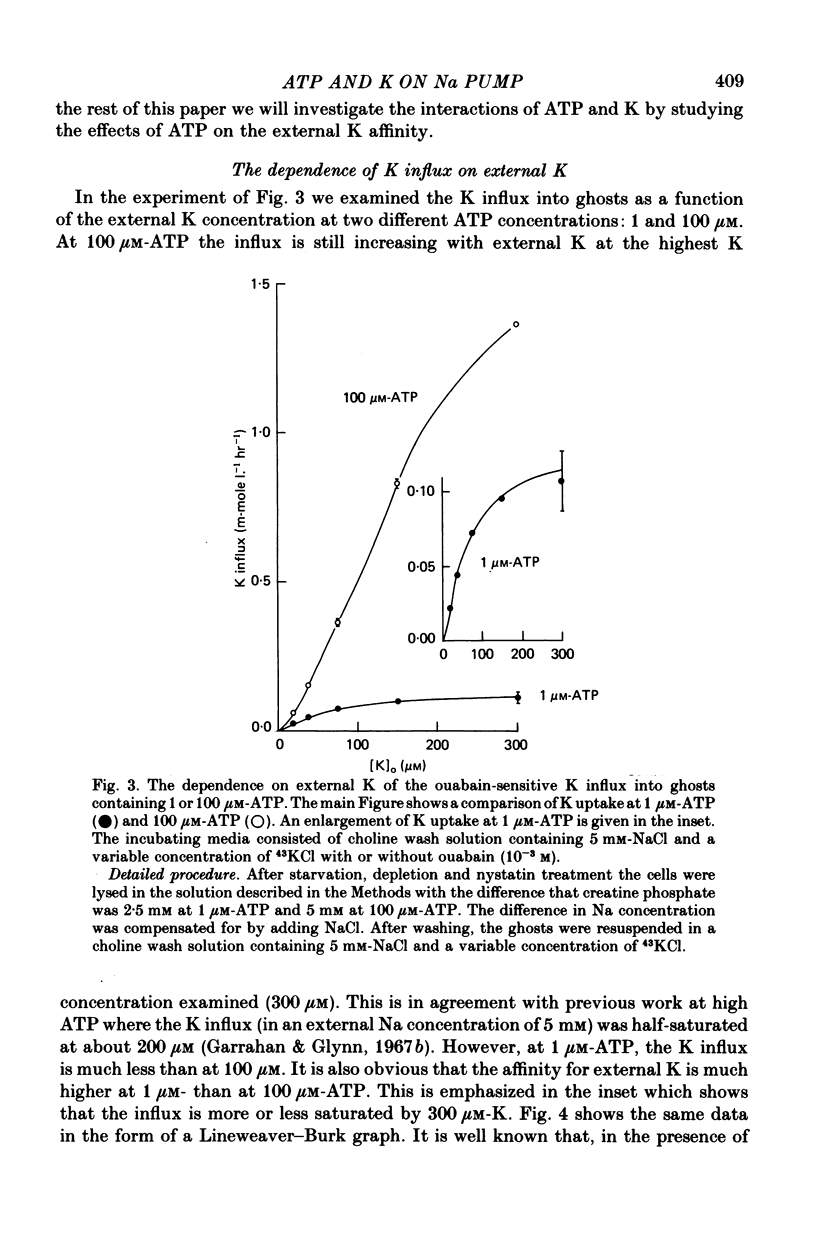
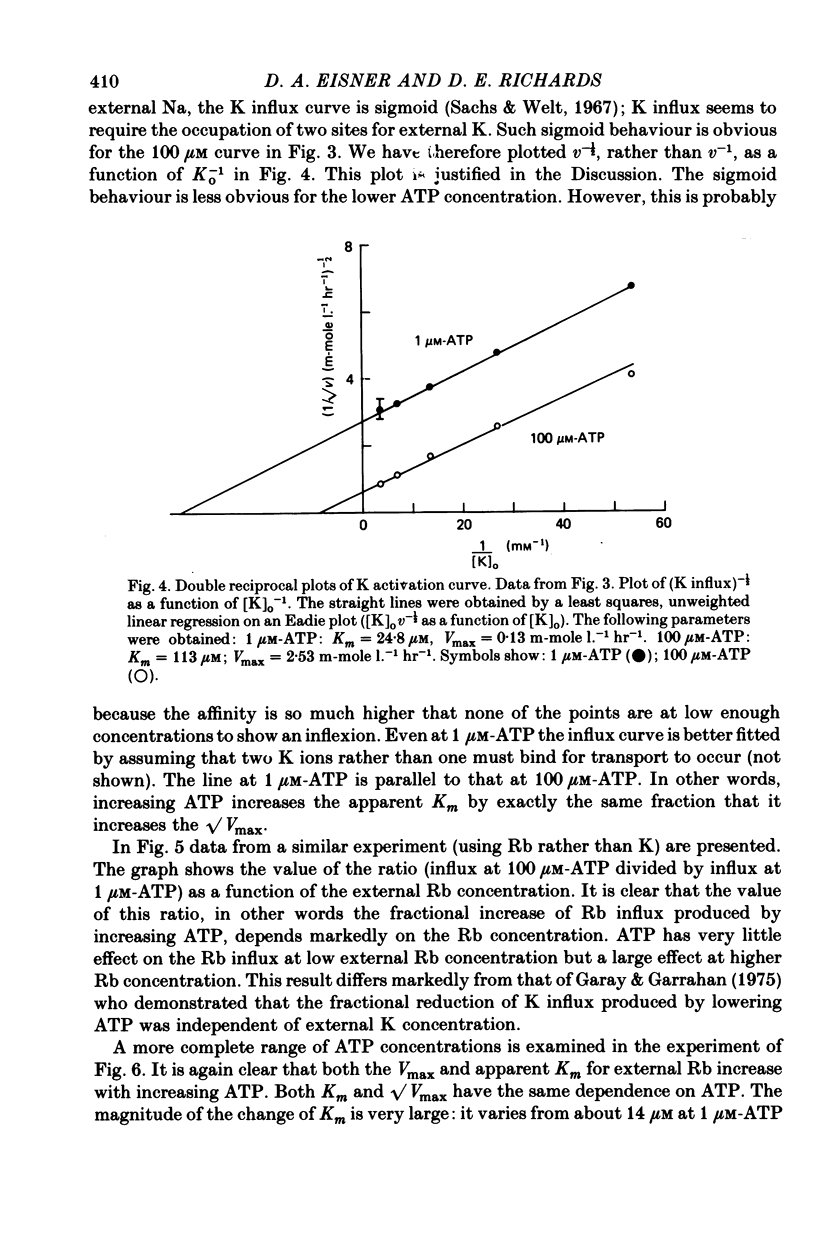
1. Ouabain-sensitive K or Rb influx was measure into ghosts resealed to contain ATP concentrations of 1 micrometers-3 mM and no K. 2. Increasing ATP from 1 to 100 micro M, at saturation external K, increased K influx about twentyfold while have no effect on the ratio of ouabain-sensitive K influx to ouabain-sensitive ATPase activity. 3. Increasing external K decreased the apparent affinity for ATP. Similarly increasing ATP decreased the apparent affinity for external K. 4. The K influx can be empirically described as: influx = VmaxK2/(K + Kapp)2. Increasing ATP increased Vmax and (Kapp)2 by the same amount. 5. These results are consistent with a consecutive model for the Na pump in which an ATP-dependent reaction follows a K-activated dephosphorylation.
Full text
PDF



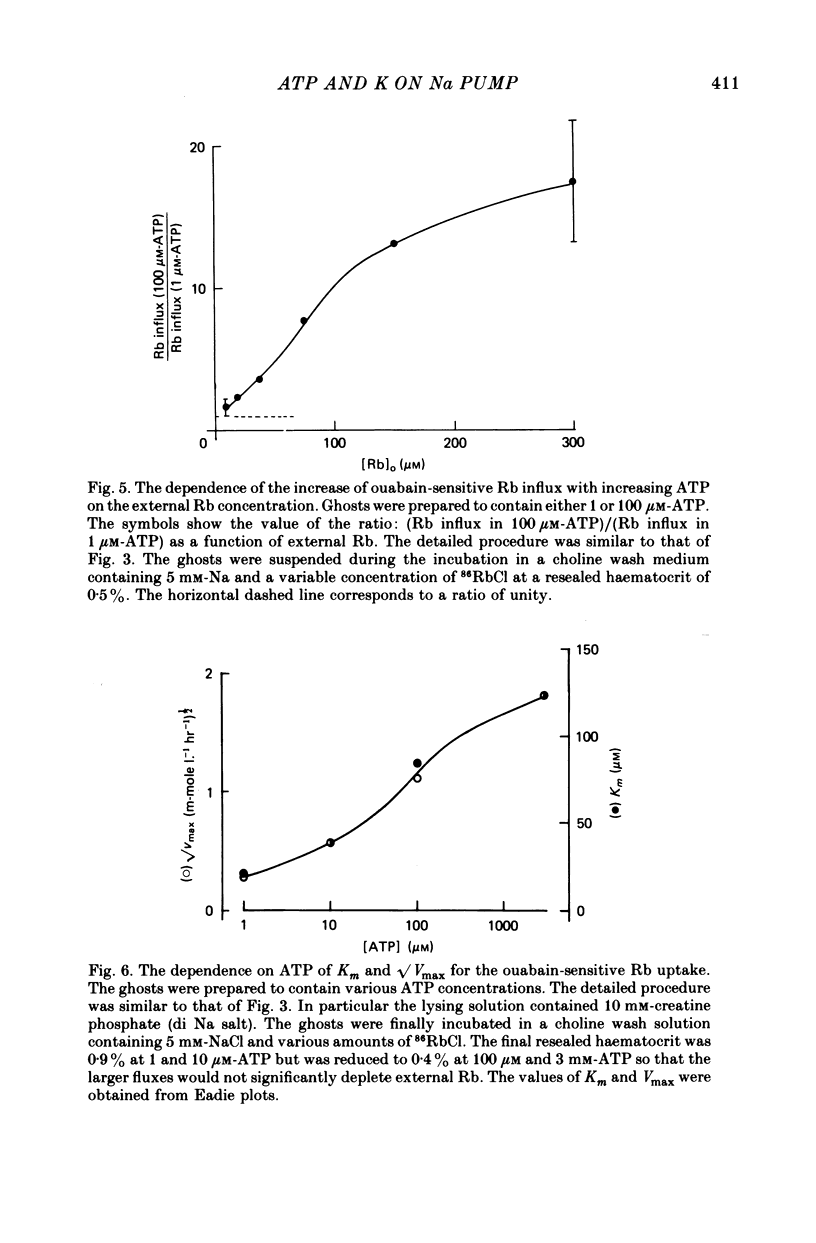
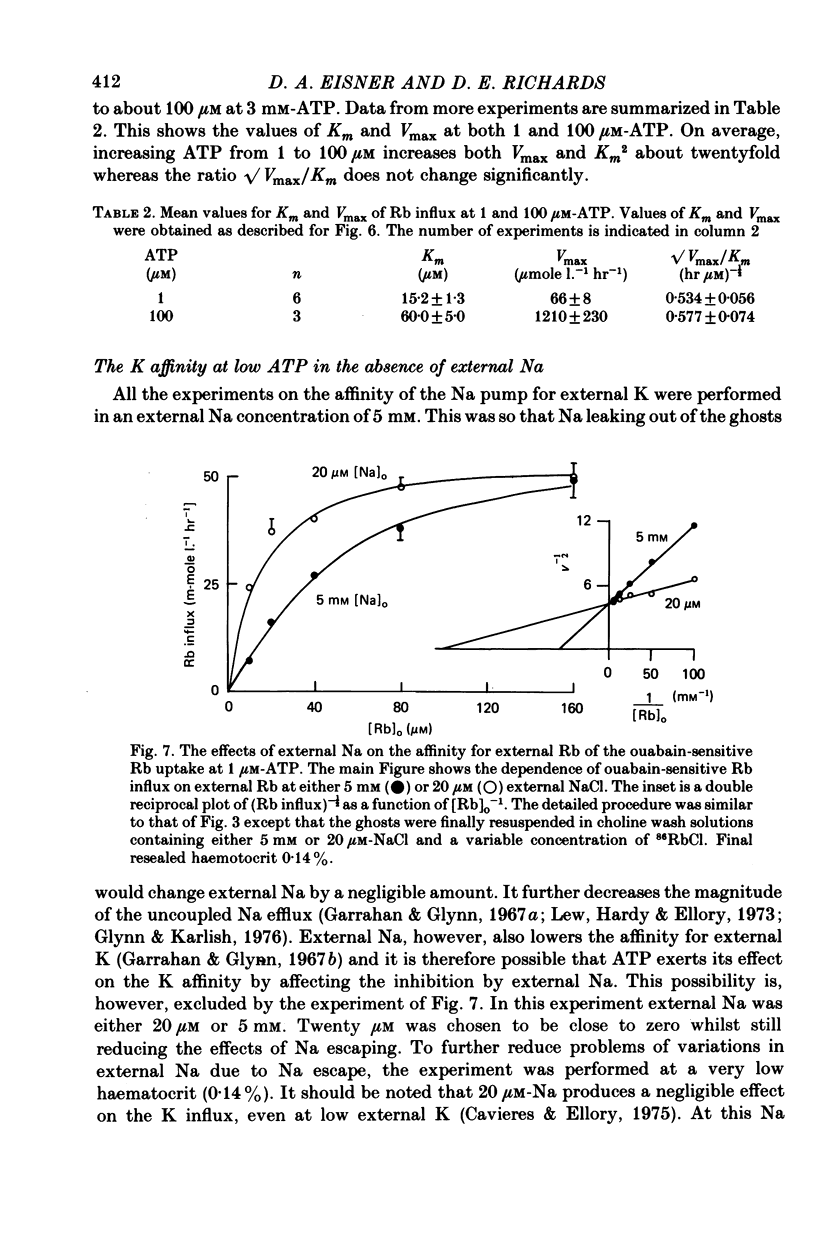






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaugé L. A., Del Campillo E. The ATP dependence of a ouabain-sensitive sodium efflux activated by external sodium, potassium and lithium in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):547–554. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., DiPolo R. Sidedness of the ATP-Na+-K+ interactions with the Na+ pump in squid axons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 2;553(3):495–500. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., Glynn I. M. Occlusion of K ions in the unphosphorylated sodium pump. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):510–512. doi: 10.1038/280510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cass A., Dalmark M. Equilibrium dialysis of ions in nystatin-treated red cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 11;244(132):47–49. doi: 10.1038/newbio244047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavieres J. D., Ellory J. C. Allosteric inhibition of the sodium pump by external sodium. Nature. 1975 May 22;255(5506):338–340. doi: 10.1038/255338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. Sodium and potassium movements in human red cells. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):278–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Garrahan P. J. The interaction of adenosinetriphosphate and inorganic phosphate with the sodium pump in red cells. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(1):51–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The behaviour of the sodium pump in red cells in the absence of external potassium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):159–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The sensitivity of the sodium pump to external sodium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):175–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Hoffman J. F. Nucleotide requirements for sodium-sodium exchange catalysed by the sodium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):239–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Karlish S. J. ATP hydrolysis associated with an uncoupled sodium flux through the sodium pump: evidence for allosteric effects of intracellular ATP and extracellular sodium. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(2):465–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Lew V. L. Affinities or apparent affinities of the transport adenosine triphosphatase system. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Jul 1;54(1):289–305. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.1.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Lew V. L., Lüthi U. Reversal of the potassium entry mechanism in red cells, with and without reversal of the entire pump cycle. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):371–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMAN J. F. The active transport of sodium by ghosts of human red blood cells. J Gen Physiol. 1962 May;45:837–859. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.5.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hexum T., Samson F. E., Jr, Himes R. H. Kinetic studies of membrane (Na+-K+-Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 15;212(2):322–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Yates D. W., Glynn I. M. Conformational transitions between Na+-bound and K+-bound forms of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase, studied with formycin nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 7;525(1):252–264. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Yates D. W. Tryptophan fluorescence of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase as a tool for study of the enzyme mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 10;527(1):115–130. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Hardy M. A., Jr, Ellory J. C. The uncoupled extrusion of Na+ through the Na+ pump. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 11;323(2):251–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L. On the ATP dependence of the Ca 2+ -induced increase in K + permeability observed in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 1;233(3):827–830. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J., Brinley F. J., Jr Potassium fluxes in dialyzed squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Jun;53(6):704–740. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.6.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh S., Zetterqvist O. Phosphorylation of bovine brain Na + , K + -stimulated ATP phosphohydrolase by adenosine ( 32 P)triphosphate studied by a rapid-mixing technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter H. W., Wolf H. U. Kinetics of (Na + ,K + )-ATPase of human erythrocyte membranes. I. Activation by Na + and K + . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 1;290(1):300–309. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. L., Hegyvary C., Kume S. Activation by adenosine triphosphate in the phosphorylation kinetics of sodium and potassium ion transport adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6530–6540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. L., Toda G., Rogers F. N. Phosphorylation by inorganic phosphate of sodium plus potassium ion transport adenosine triphosphatase. Four reactive states. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):691–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. D. Kinetic studies on a brain microsomal adenosine triphosphatase. Evidence suggesting conformational changes. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3250–3258. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R., Welt L. G. The concentration dependence of active potassium transport in the human red blood cell. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):65–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI105512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons T. J. Potassium: potassium exchange catalysed by the sodium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;237(1):123–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skou J. C. Effect of ATP on the intermediary steps of the reaction of the (Na+ plusK+)-dependent enzyme system. II. Effect of a variation in the ATP-Mg2+ ratio. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 15;339(2):246–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90322-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


