Abstract
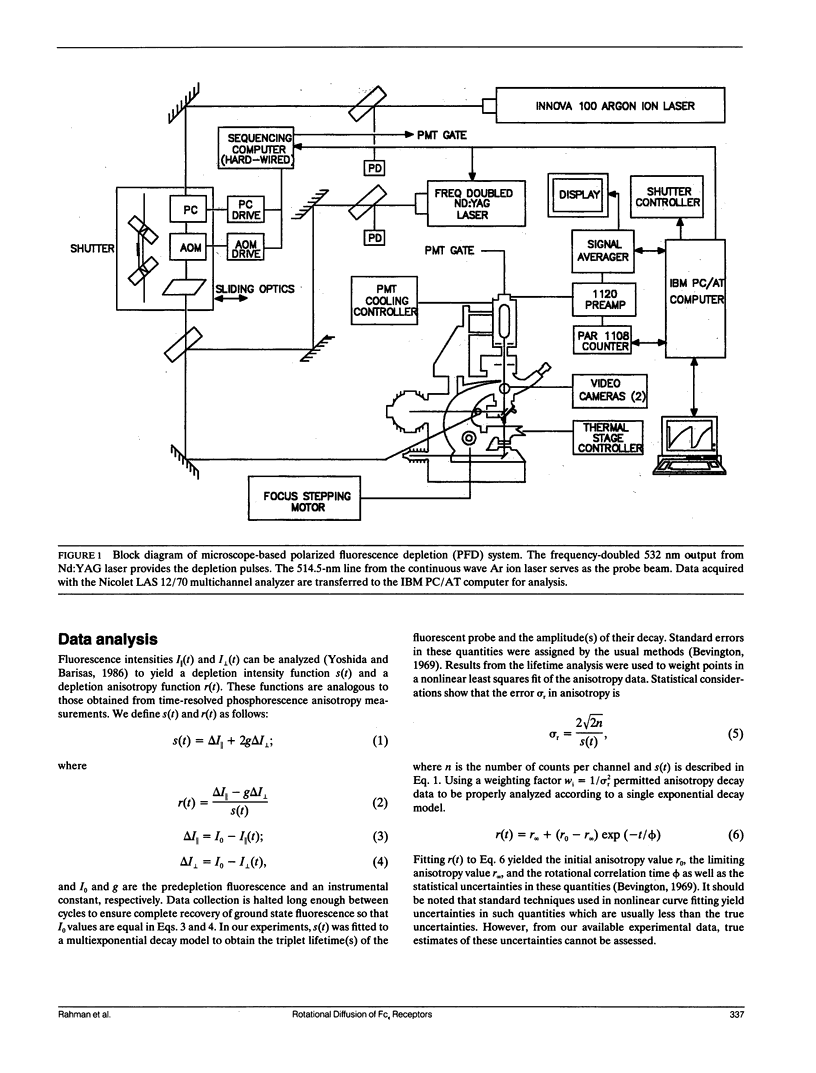
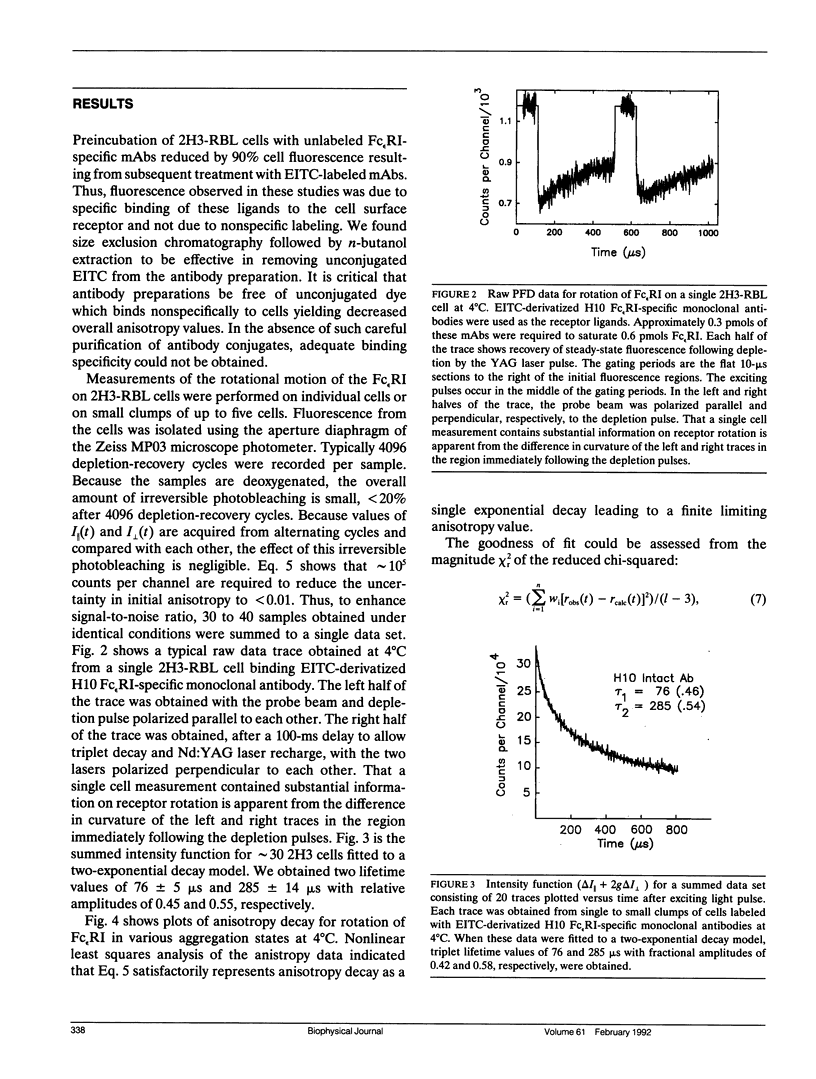
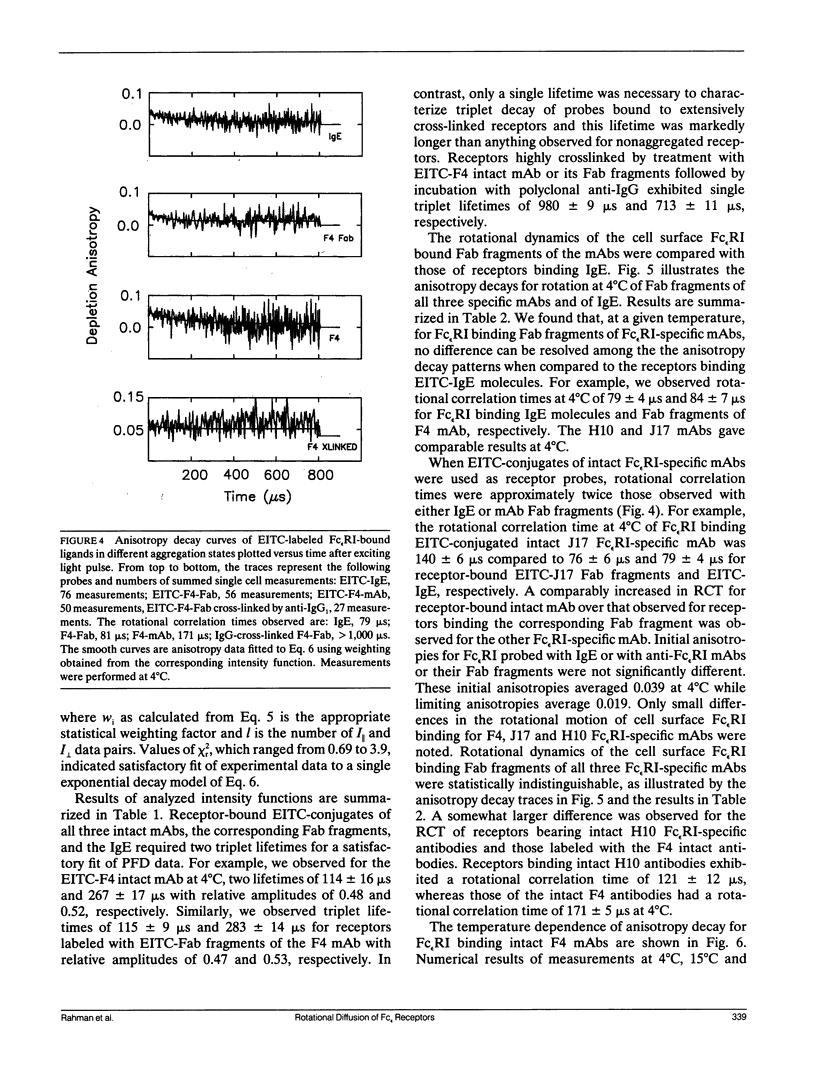
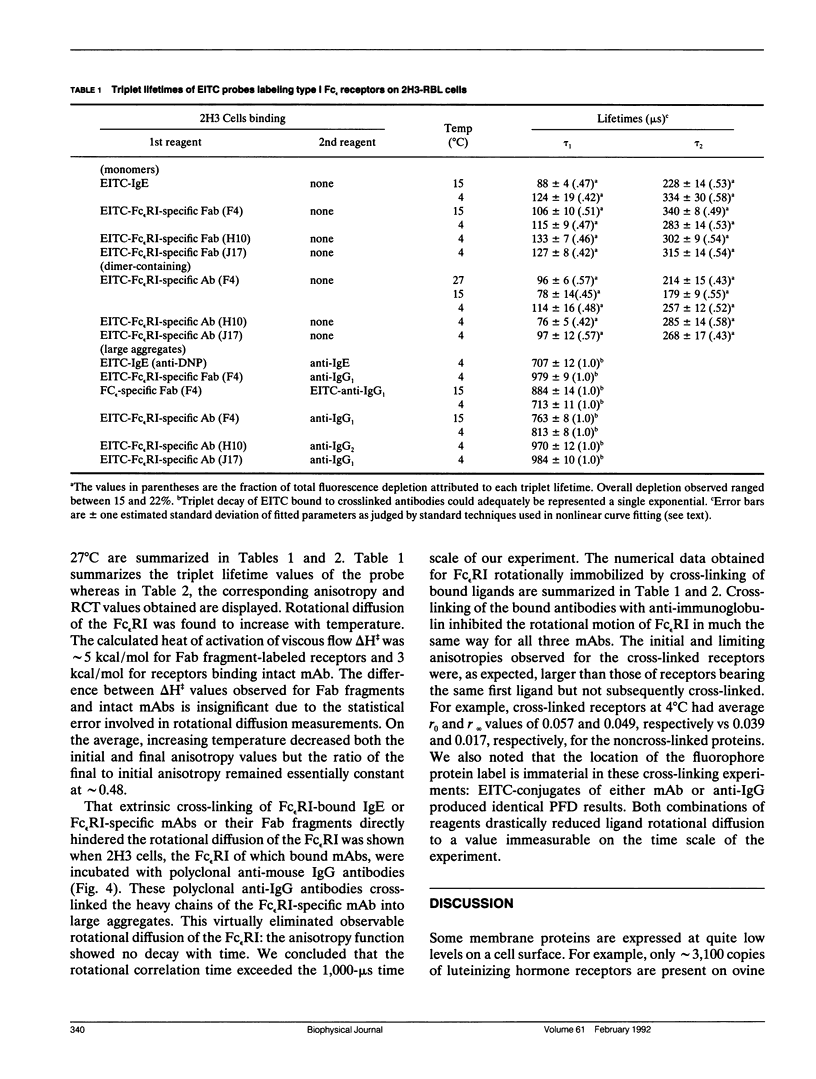
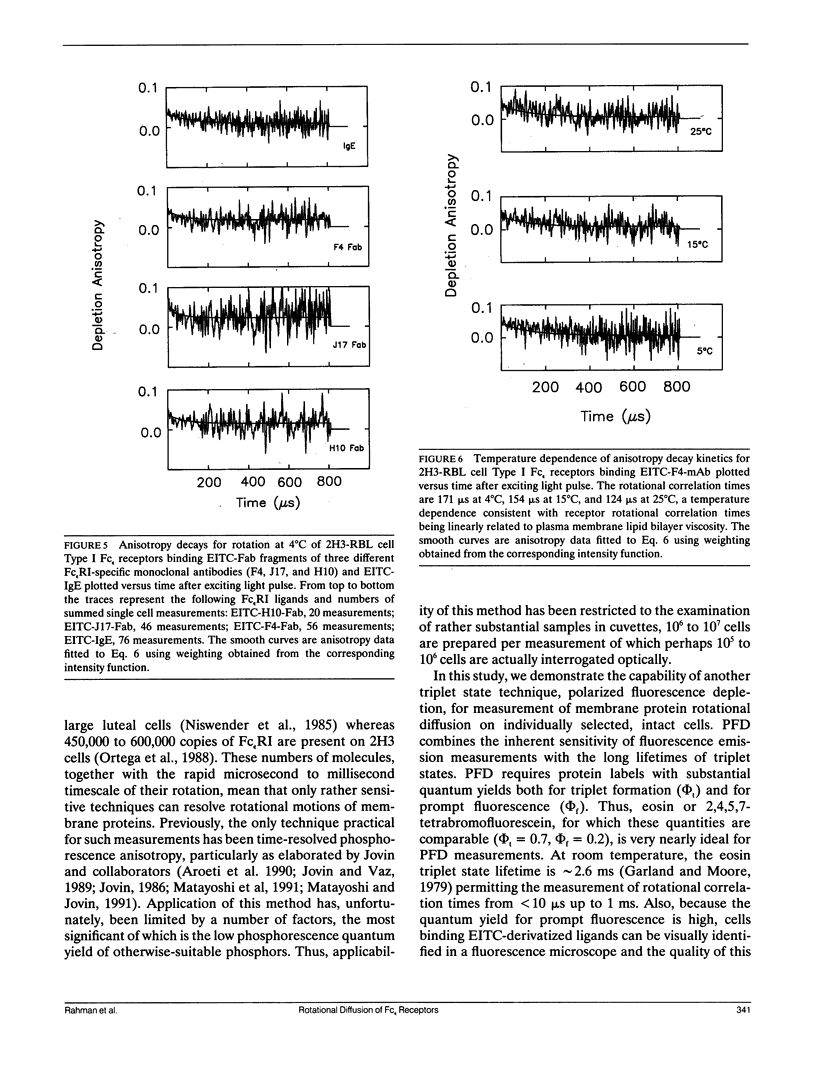
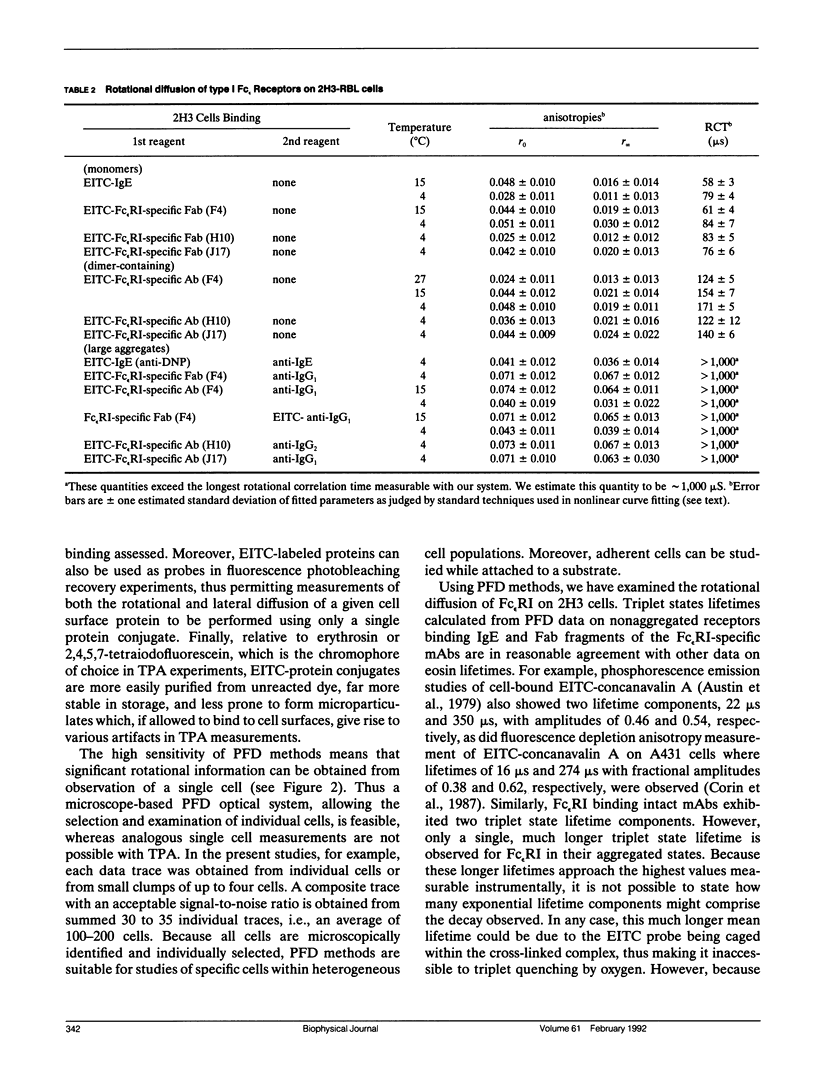
We report the first application of polarized fluorescence depletion (PFD), a technique which combines the sensitivity of fluorescence detection with the long lifetimes of triplet probes, to the measurement of membrane protein rotational diffusion on individually selected, intact mammalian cells. We have examined the rotation of type I Fc epsilon receptors (Fc epsilon RI) on rat mucosal mast cells of the RBL-2H3 line in their resting monomeric and differently oligomerized states using as probes IgE and three monoclonal antibodies (mAbs; H10, J17, and F4) specific for the Fc epsilon RI. PFD experiments using eosin (EITC)-IgE show that individual Fc epsilon RI on cells have a rotational correlation time (RCT) at 4 degrees C of 79 +/- 4 microseconds. Similarly, Fc epsilon RI-bound EITC-Fab fragments of the J17 Fc epsilon RI-specific mAb exhibit an RCT of 76 +/- 6 microseconds. These values agree with previous measurements of Fc epsilon RI-bound IgE rotation by time-resolved phosphorescence anisotropy methods. Receptor-bound EITC-conjugated divalent J17 antibody exhibits an increased RCT of 140 +/- 6 microseconds. This is consistent with the ability of this mAb to form substantial amounts of Fc epsilon RI dimers on these cell surfaces. The ratio of limiting to initial anisotropy in these experiments remains constant at about 0.5 from 5 degrees C through 25 degrees C for IgE, Fab, and intact mAb receptor ligands. Extensive cross-linking by second antibody of cell-bound IgE, of intact Fc epsilon RI-specific mAbs or of their Fab fragments, however, produced large fixed anisotropies demonstrating, under these conditions, receptor immobilization in large aggregates. PFD using the mAbs H10 and F4 as receptor probes yielded values for triplet lifetimes, RCT values, and anisotropy parameters essentially indistinguishable from those obtained with the mAb J17 clone. Possible explanations for these observations are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aroeti B., Jovin T. M., Henis Y. I. Rotational mobility of Sendai virus glycoproteins in membranes of fused human erythrocytes and in the envelopes of cell-bound virions. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 2;29(39):9119–9125. doi: 10.1021/bi00491a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin R. H., Chan S. S., Jovin T. M. Rotational diffusion of cell surface components by time-resolved phosphorescence anisotropy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5650–5654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan K., Hsu F. J., Cooper A. D., McConnell H. M. Lipid hapten containing membrane targets can trigger specific immunoglobulin E-dependent degranulation of rat basophil leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6427–6433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsumian E. L., Isersky C., Petrino M. G., Siraganian R. P. IgE-induced histamine release from rat basophilic leukemia cell lines: isolation of releasing and nonreleasing clones. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Apr;11(4):317–323. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Restall C. J. Rotational and lateral movements in biomembranes: the dynamics of biomembrane components. Biochem Soc Symp. 1981;(46):139–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J. Measurement of protein rotational diffusion in membranes by flash photolysis. Methods Enzymol. 1978;54:47–61. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)54007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corin A. F., Blatt E., Jovin T. M. Triplet-state detection of labeled proteins using fluorescence recovery spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2207–2217. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damjanovich S., Trón L., Szöllösi J., Zidovetzki R., Vaz W. L., Regateiro F., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Jovin T. M. Distribution and mobility of murine histocompatibility H-2Kk antigen in the cytoplasmic membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5985–5989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J., Kane P., Goldstein B., Holowka D., Baird B. Cross-linking of IgE-receptor complexes at the cell surface: a fluorescence method for studying the binding of monovalent and bivalent haptens to IgE. Mol Immunol. 1986 Jul;23(7):769–781. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fewtrell C., Metzger H. Larger oligomers of IgE are more effective than dimers in stimulating rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):701–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland P. B., Moore C. H. Phosphorescence of protein-bound eosin and erythrosin. A possible probe for measurements of slow rotational mobility. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):561–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1830561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P., Garland P. B. Depolarization of fluorescence depletion. A microscopic method for measuring rotational diffusion of membrane proteins on the surface of a single cell. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):252–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P., Garland P. B. Fluorescent triplet probes for measuring the rotational diffusion of membrane proteins. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):313–321. doi: 10.1042/bj2030313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., Arndt-Jovin D. J. Luminescence digital imaging microscopy. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:271–308. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.001415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., Bartholdi M., Vaz W. L., Austin R. H. Rotational diffusion of biological macromolecules by time-resolved delayed luminescence (phosphorescence, fluorescence) anisotropy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;366:176–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb20753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M. Rotational diffusion on cell surfaces: contrasting effect of temperature on epidermal growth factor and Fc (immunoglobulin E) receptors. Biochem Soc Trans. 1986 Oct;14(5):817–818. doi: 10.1042/bst0140817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., Vaz W. L. Rotational and translational diffusion in membranes measured by fluorescence and phosphorescence methods. Methods Enzymol. 1989;172:471–513. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)72030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Structural order of lipids and proteins in membranes: evaluation of fluorescence anisotropy data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6361–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagey-Sobotka A., Dembo M., Goldstein B., Metzger H., Lichtenstein L. M. Qualitative characteristics of histamine release from human basophils by covalently cross-linked IgE. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2285–2291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawato S., Kinosita K., Jr Time-dependent absorption anisotropy and rotational diffusion of proteins in membranes. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):277–296. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84728-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Kawato S., Ikegami A. A theory of fluorescence polarization decay in membranes. Biophys J. 1977 Dec;20(3):289–305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85550-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipari G., Szabo A. Effect of librational motion on fluorescence depolarization and nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation in macromolecules and membranes. Biophys J. 1980 Jun;30(3):489–506. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85109-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Bohn J. W., Ferry E. L., Yamamoto H., Molinaro C. A., Sherman L. A., Klinman N. R., Katz D. H. Monoclonal dinitrophenyl-specific murine IgE antibody: preparation, isolation, and characterization. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2728–2737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matayoshi E. D., Jovin T. M. Rotational diffusion of band 3 in erythrocyte membranes. 1. Comparison of ghosts and intact cells. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3527–3538. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matayoshi E. D., Sawyer W. H., Jovin T. M. Rotational diffusion of band 3 in erythrocyte membranes. 2. Binding of cytoplasmic enzymes. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3538–3543. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey M. A., Liu Z. Y., Poo M. M. Lateral electromigration and diffusion of Fc epsilon receptors on rat basophilic leukemia cells: effects of IgE binding. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):778–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niswender G. D., Schwall R. H., Fitz T. A., Farin C. E., Sawyer H. R. Regulation of luteal function in domestic ruminants: new concepts. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1985;41:101–151. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571141-8.50007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortega E., Schweitzer-Stenner R., Pecht I. Possible orientational constraints determine secretory signals induced by aggregation of IgE receptors on mast cells. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4101–4109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03304.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecht I., Ortega E., Jovin T. M. Rotational dynamics of the Fc epsilon receptor on mast cells monitored by specific monoclonal antibodies and IgE. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3450–3458. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razi Naqvi K., Gonzalez-Rodriguez J., Cherry R. J., Chapman D. Spectroscopic technique for studying protein rotation in membranes. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 24;245(147):249–251. doi: 10.1038/newbio245249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigler R., Ehrenberg M. Molecular interactions and structure as analysed by fluorescence relaxation spectroscopy. Q Rev Biophys. 1973 May;6(2):139–199. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000113x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D., Holowka D., Baird B. Cross-linking of immunoglobulin E-receptor complexes induces their interaction with the cytoskeleton of rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4565–4572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Webb W. W., Elson E. L., Metzger H. Lateral motion and valence of Fc receptors on rat peritoneal mast cells. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):550–552. doi: 10.1038/264550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Taurog J. D., Metzger H. Dimeric immunoglobulin E serves as a unit signal for mast cell degranulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2993–2997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T. M., Barisas B. G. Protein rotational motion in solution measured by polarized fluorescence depletion. Biophys J. 1986 Jul;50(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83437-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zidovetzki R., Bartholdi M., Arndt-Jovin D., Jovin T. M. Rotational dynamics of the Fc receptor for immunoglobulin E on histamine-releasing rat basophilic leukemia cells. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4397–4401. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


