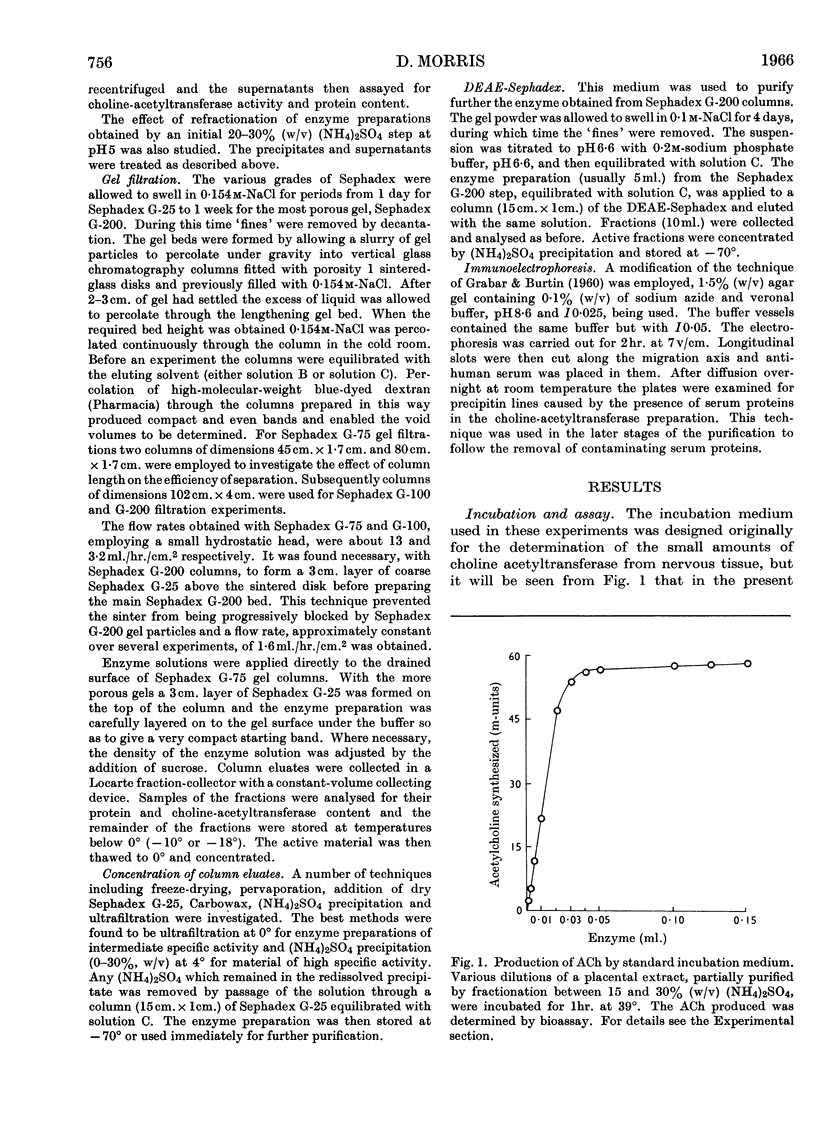
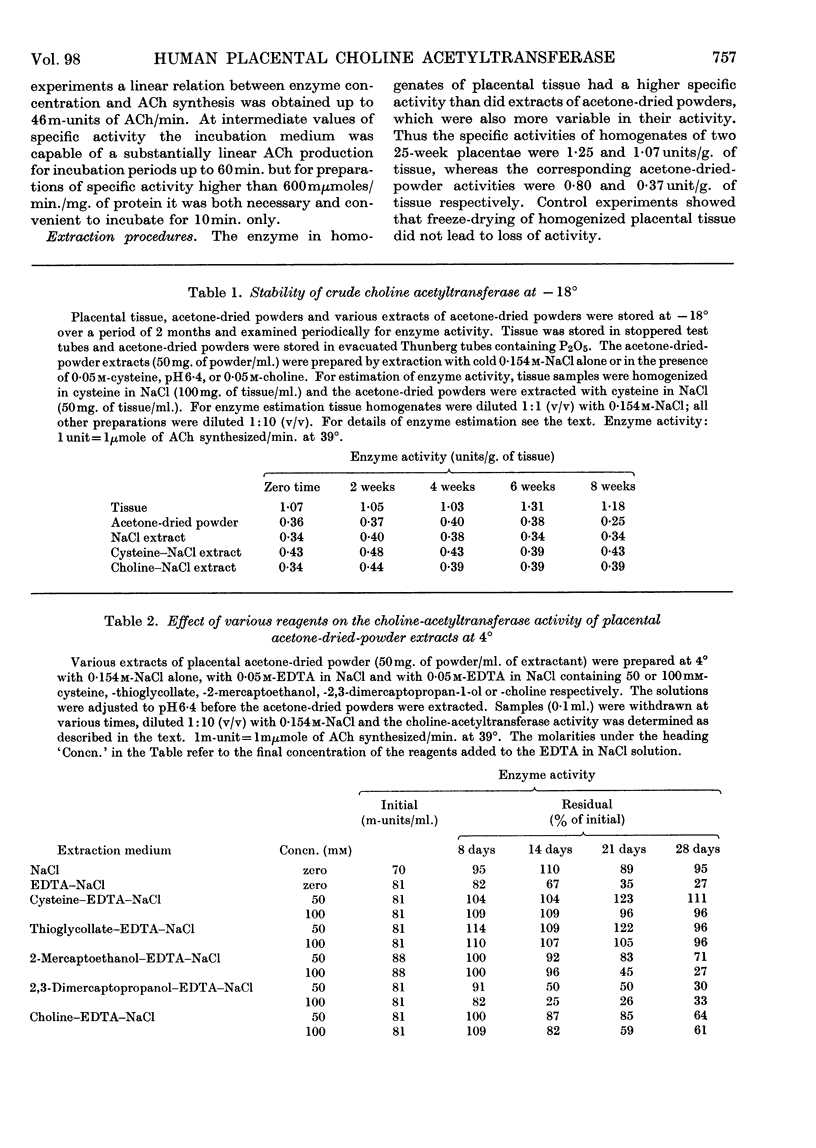
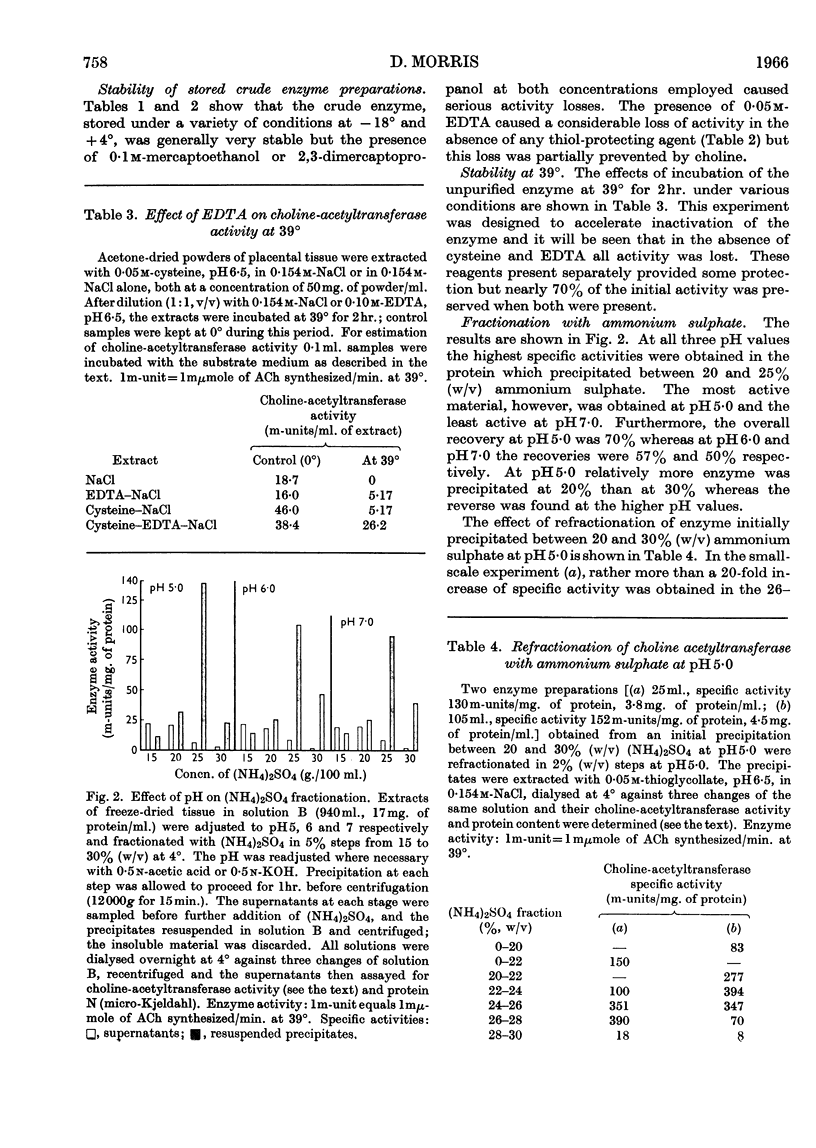
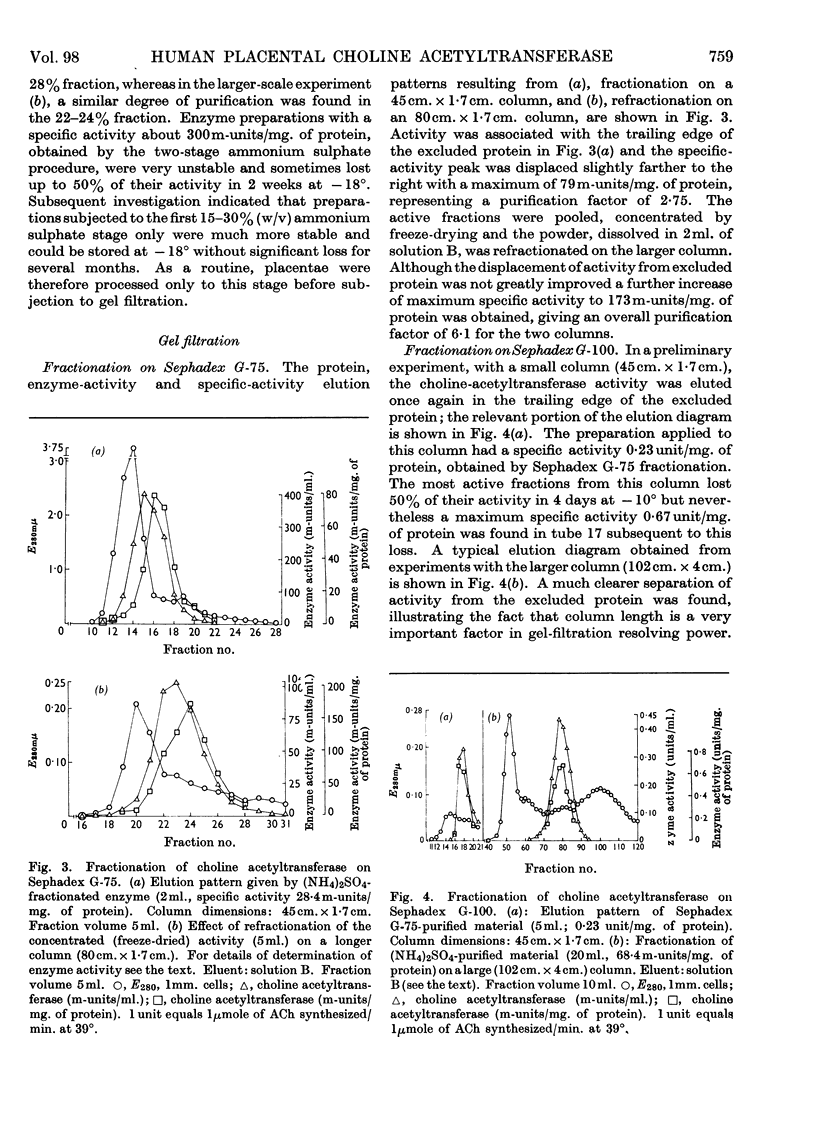
Abstract
1. Various methods for the extraction of choline acetyltransferase (acetyl-CoA–choline O-acetyltransferase, EC 2.3.1.6) from immature human placenta (18–28 weeks of gestation) are described. 2. The crude enzyme was found to be stable at −18° and +4° under a variety of conditions. 3. Purification methods, including ammonium sulphate fractionation, gel filtration on various grades of Sephadex and DEAE-Sephadex fractionation, have yielded a preparation of high specific activity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BULL G., FEINSTEIN A., MORRIS D. SEDIMENTATION BEHAVIOR AND MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF CHOLINE ACETYLTRANSFERASE. Nature. 1964 Mar 28;201:1326–1326. doi: 10.1038/2011326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGEN A. S., BURKE G., DESBARATSSCHONBAUM M. L. The specificity of brain choline acetylase. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1956 Sep;11(3):308–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb01071.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. C., Gaddum J. H. Choline esters in tissue extracts. J Physiol. 1933 Oct 6;79(3):255–285. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1933.sp003049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEBB C. O. Biochemical evidence for the neural function of acetylcholine. Physiol Rev. 1957 Apr;37(2):196–220. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1957.37.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEBB C. O., KRNJEVIC K., SILVER A. ACETYLCHOLINE AND CHOLINE ACETYLTRANSFERASE IN THE DIAPHRAGM OF THE RAT. J Physiol. 1964 Jun;171:504–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEMSWORTH B. A., MORRIS D. A COMPARISON OF THE N-ALKYL GROUP SPECIFICITY OF CHOLINE ACETYLTRANSFERASE FROM DIFFERENT SPECIES. J Neurochem. 1964 Nov;11:793–803. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb06728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebb C. O., Ratković D. Choline acetylase in the placenta of man and other species. J Physiol. 1962 Sep;163(2):307–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUMAGAI H., EBASHI S. Highly purified choline acetylase. Nature. 1954 May 8;173(4410):871–872. doi: 10.1038/173871a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDENFELT I. Choline acetylase in normal and denervated salivary glands. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1963 Jan;48:67–79. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1963.sp001639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISBERG R. B. Properties and biological significance of choline acetylase. Yale J Biol Med. 1957 Feb;29(4):403–435. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGEL L. M., MONTY K. J. DETERMINATION OF MOLECULAR WEIGHTS AND FRICTIONAL RATIOS OF MACROMOLECULES IN IMPURE SYSTEMS: AGGREGATION OF UREASE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 3;19:494–499. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMALLMAN B. N. Mechanisms of acetylcholine synthesis in the blowfly. J Physiol. 1956 May 28;132(2):343–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


