Abstract
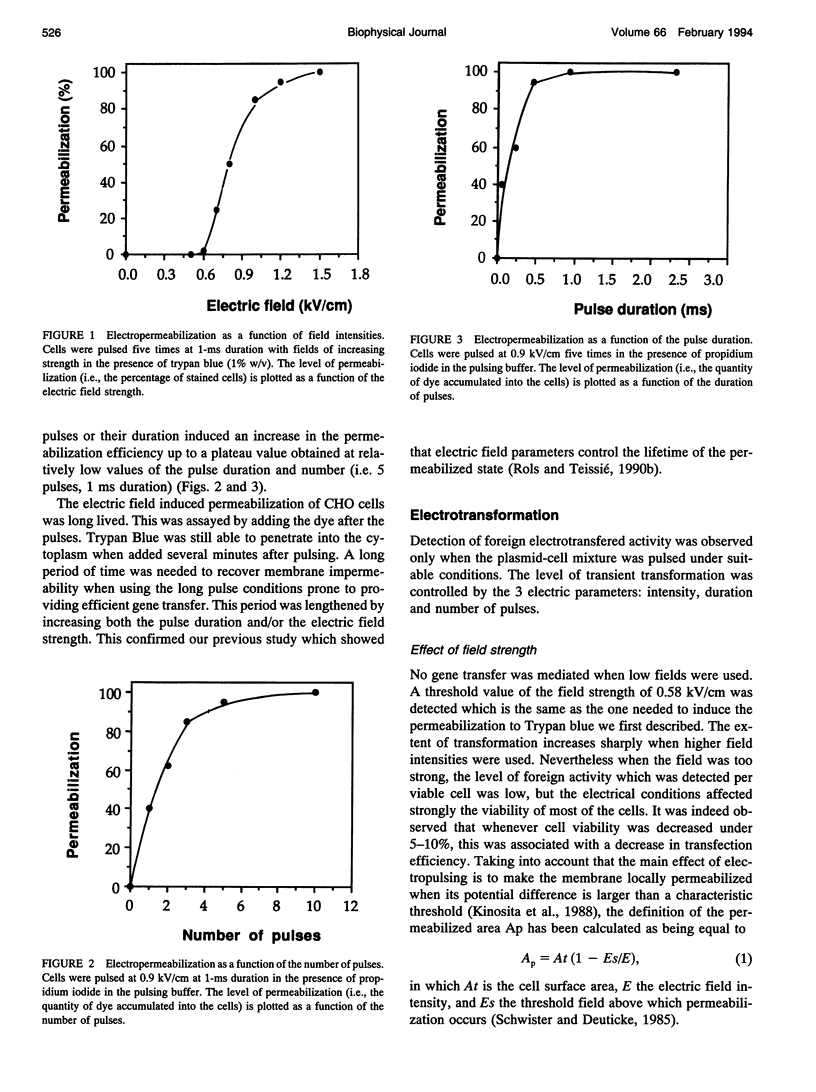
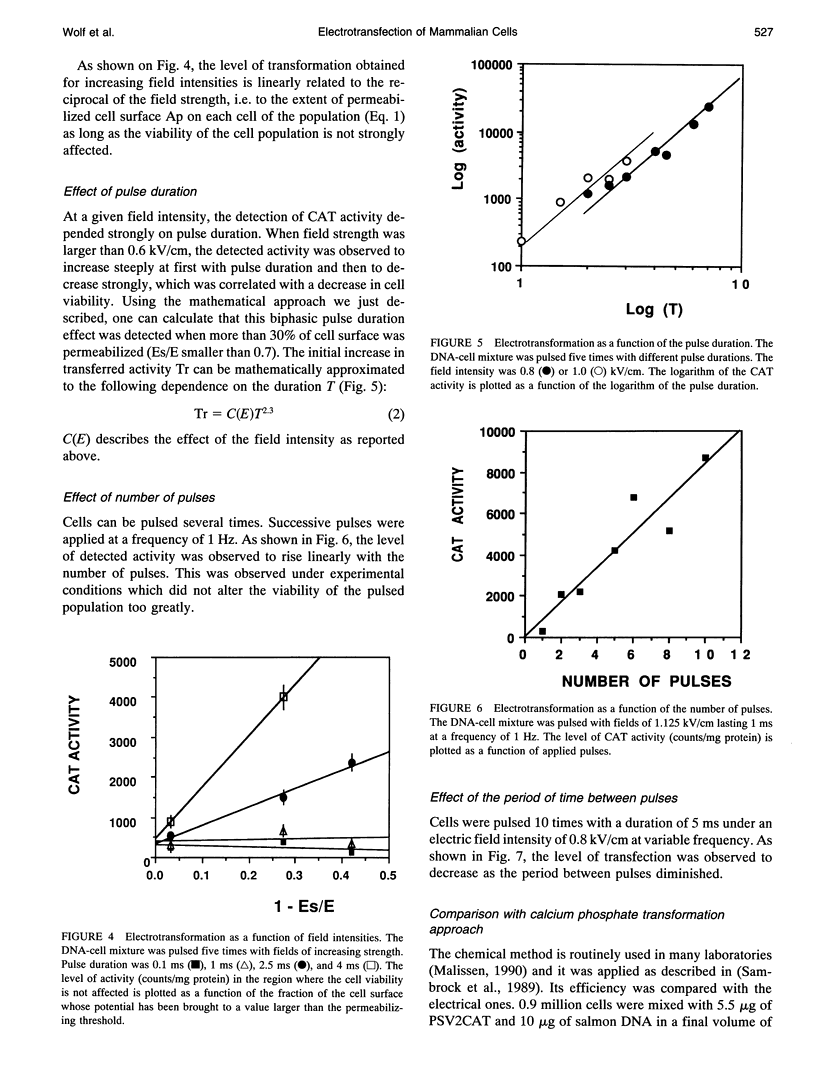
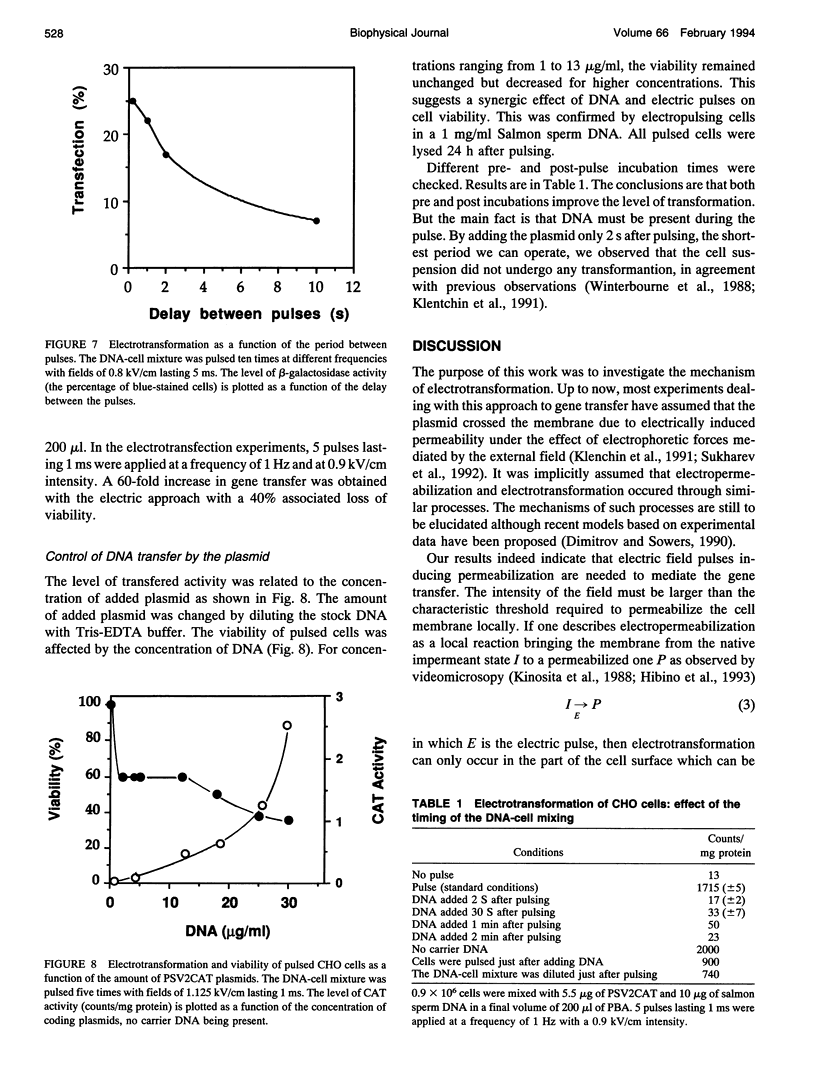
Electric field-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells (electrotransformation) depends on the pulsing conditions (field intensity, pulse duration, number of pulses). The effect of these parameters was systematically investigated using the transient expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase and the beta-galactosidase activities in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Pulsing conditions inducing reversible permeabilization of the cell plasma membrane are not sufficient to induce gene transfer. The plasmid must be present during the electric pulse if it is to be transferred across the membrane into the cytoplasm. Only the localized part of the cell membrane brought to the permeabilized state by the external field is competent. Pulse duration plays a key role in the magnitude of the transfer. The field induces a complex reaction between the membrane and the plasmid that is accumulated at the cell interface by electrophoretic forces. This leads to an insertion of the plasmid, which can then cross the membrane.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreason G. L., Evans G. A. Optimization of electroporation for transfection of mammalian cell lines. Anal Biochem. 1989 Aug 1;180(2):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. C. Cell poration and cell fusion using an oscillating electric field. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):641–652. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82711-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. C., Gao P. Q., Maxwell B. L. High efficiency gene transfection by electroporation using a radio-frequency electric field. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 17;1092(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90149-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. C., Reese T. S. Changes in membrane structure induced by electroporation as revealed by rapid-freezing electron microscopy. Biophys J. 1990 Jul;58(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82348-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley J. M. Electrical breakdown of bimolecular lipid membranes as an electromechanical instability. Biophys J. 1973 Jul;13(7):711–724. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)86017-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruzeiro-Hansson L., Mouritsen O. G. Passive ion permeability of lipid membranes modelled via lipid-domain interfacial area. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 15;944(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. S., Sowers A. E. Membrane electroporation--fast molecular exchange by electroosmosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Mar;1022(3):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90289-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escande-Géraud M. L., Rols M. P., Dupont M. A., Gas N., Teissié J. Reversible plasma membrane ultrastructural changes correlated with electropermeabilization in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 7;939(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eynard N., Sixou S., Duran N., Teissie J. Fast kinetics studies of Escherichia coli electrotransformation. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 1;209(1):431–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gass G. V., Chernomordik L. V. Reversible large-scale deformations in the membranes of electrically-treated cells: electroinduced bleb formation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Mar 30;1023(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibino M., Itoh H., Kinosita K., Jr Time courses of cell electroporation as revealed by submicrosecond imaging of transmembrane potential. Biophys J. 1993 Jun;64(6):1789–1800. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81550-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Ashikawa I., Saita N., Yoshimura H., Itoh H., Nagayama K., Ikegami A. Electroporation of cell membrane visualized under a pulsed-laser fluorescence microscope. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):1015–1019. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83181-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Tsong T. Y. Voltage-induced conductance in human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):479–497. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenchin V. A., Sukharev S. I., Serov S. M., Chernomordik L. V., Chizmadzhev YuA Electrically induced DNA uptake by cells is a fast process involving DNA electrophoresis. Biophys J. 1991 Oct;60(4):804–811. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82115-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubiniec R. T., Liang H., Hui S. W. Effects of pulse length and pulse strength on transfection by electroporation. Biotechniques. 1990 Jan;8(1):16–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A., Rols M. P., Teissie J. 31P NMR analysis of membrane phospholipid organization in viable, reversibly electropermeabilized Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 23;27(4):1222–1228. doi: 10.1021/bi00404a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann E., Schaefer-Ridder M., Wang Y., Hofschneider P. H. Gene transfer into mouse lyoma cells by electroporation in high electric fields. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):841–845. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porschke D., Meier H. J., Ronnenberg J. Interactions of nucleic acid double helices induced by electric field pulses. Biophys Chem. 1984 Oct;20(3):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(84)87027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rols M. P., Coulet D., Teissié J. Highly efficient transfection of mammalian cells by electric field pulses. Application to large volumes of cell culture by using a flow system. Eur J Biochem. 1992 May 15;206(1):115–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rols M. P., Teissie J. Ionic-strength modulation of electrically induced permeabilization and associated fusion of mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):109–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rols M. P., Teissié J. Electropermeabilization of mammalian cells. Quantitative analysis of the phenomenon. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1089–1098. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82451-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rols M. P., Teissié J. Modulation of electrically induced permeabilization and fusion of Chinese hamster ovary cells by osmotic pressure. Biochemistry. 1990 May 15;29(19):4561–4567. doi: 10.1021/bi00471a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwister K., Deuticke B. Formation and properties of aqueous leaks induced in human erythrocytes by electrical breakdown. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 27;816(2):332–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90501-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J. A nonchromatographic assay for expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in eucaryotic cells. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers A. E. A long-lived fusogenic state is induced in erythrocyte ghosts by electric pulses. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1358–1362. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenger D. A., Hui S. W. Kinetics of ultrastructural changes during electrically induced fusion of human erythrocytes. J Membr Biol. 1986;93(1):43–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01871017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugar I. P., Förster W., Neumann E. Model of cell electrofusion. Membrane electroporation, pore coalescence and percolation. Biophys Chem. 1987 May 9;26(2-3):321–335. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(87)80033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukharev S. I., Klenchin V. A., Serov S. M., Chernomordik L. V., Chizmadzhev YuA Electroporation and electrophoretic DNA transfer into cells. The effect of DNA interaction with electropores. Biophys J. 1992 Nov;63(5):1320–1327. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81709-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teissie J., Rols M. P. Fusion of mammalian cells in culture is obtained by creating the contact between cells after their electropermeabilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 15;140(1):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tekle E., Astumian R. D., Chock P. B. Electroporation by using bipolar oscillating electric field: an improved method for DNA transfection of NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4230–4234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourne D. J., Thomas S., Hermon-Taylor J., Hussain I., Johnstone A. P. Electric shock-mediated transfection of cells. Characterization and optimization of electrical parameters. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 15;251(2):427–434. doi: 10.1042/bj2510427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie T. D., Sun L., Tsong T. Y. Study of mechanisms of electric field-induced DNA transfection. I. DNA entry by surface binding and diffusion through membrane pores. Biophys J. 1990 Jul;58(1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82349-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie T. D., Sun L., Zhao H. G., Fuchs J. A., Tsong T. Y. Study of mechanisms of electric field-induced DNA transfection. IV. Effects of DNA topology on cell uptake and transfection efficiency. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):1026–1031. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81675-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie T. D., Tsong T. Y. Study of mechanisms of electric field-induced DNA transfection. II. Transfection by low-amplitude, low-frequency alternating electric fields. Biophys J. 1990 Oct;58(4):897–903. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82434-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie T. D., Tsong T. Y. Study of mechanisms of electric field-induced DNA transfection. III. Electric parameters and other conditions for effective transfection. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):28–34. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81580-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Q. A., Chang D. C. High-efficiency gene transfection by in situ electroporation of cultured cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 17;1088(1):104–110. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90158-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


