Abstract
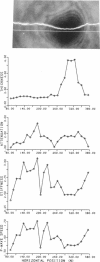
In this paper a new technique is proposed to determine the acoustic properties as well as the thickness (and volume) of biological cells. Variations of thickness, density, acoustic wave velocity, stiffness, and attenuation coefficient of a living or dead cell are obtained by scanning the cell by an acoustic microscope. The distance between the cell and the microscope lens is varied and several voltage curves are thus obtained. These curves are then inverted by simplex optimization technique to obtain the cell parameters. The spatial resolution of the method is limited to the resolution of the scanning acoustic microscope. It allows to take advantage of the full range of frequencies and amplification of the microscope. Characteristic distributions of stiffness are exemplified with an endothelial cell in culture. The main part of the thin, lamellar cytoplasm has high stiffness, which drops close to the lamella/cell body transition region and only slightly increases again through the central part of the cell. Acoustic attenuation seems to be related to two factors, cytoplasm accumulation (in the lamellar parts) and scattering in the central part rich in organelles.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bereiter-Hahn J., Fox C. H., Thorell B. Quantitative reflection contrast microscopy of living cells. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):767–779. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bereiter-Hahn J. Scanning acoustic microscopy visualizes cytomechanical responses to cytochalasin D. J Microsc. 1987 Apr;146(Pt 1):29–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1987.tb01324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson E. L. Cellular mechanics as an indicator of cytoskeletal structure and function. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:397–430. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand J. A., Rugar D., Johnston R. N., Quate C. F. Acoustic microscopy of living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1656–1660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand J. A., Rugar D. Measurement of cellular elastic properties by acoustic microscopy. J Microsc. 1984 Jun;134(Pt 3):245–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1984.tb02518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzard C. S., Lochner L. R. Cell-to-substrate contacts in living fibroblasts: an interference reflexion study with an evaluation of the technique. J Cell Sci. 1976 Jun;21(1):129–159. doi: 10.1242/jcs.21.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. N., Atalar A., Heiserman J., Jipson V., Quate C. F. Acoustic microscopy: resolution of subcellular detail. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3325–3329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litniewski J., Bereiter-Hahn J. Measurements of cells in culture by scanning acoustic microscopy. J Microsc. 1990 Apr;158(Pt 1):95–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1990.tb02981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Schönbein G. W., Sung K. L., Tözeren H., Skalak R., Chien S. Passive mechanical properties of human leukocytes. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):243–256. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84726-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthen G. S., Schwab B., 3rd, Elson E. L., Downey G. P. Mechanics of stimulated neutrophils: cell stiffening induces retention in capillaries. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):183–186. doi: 10.1126/science.2749255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]