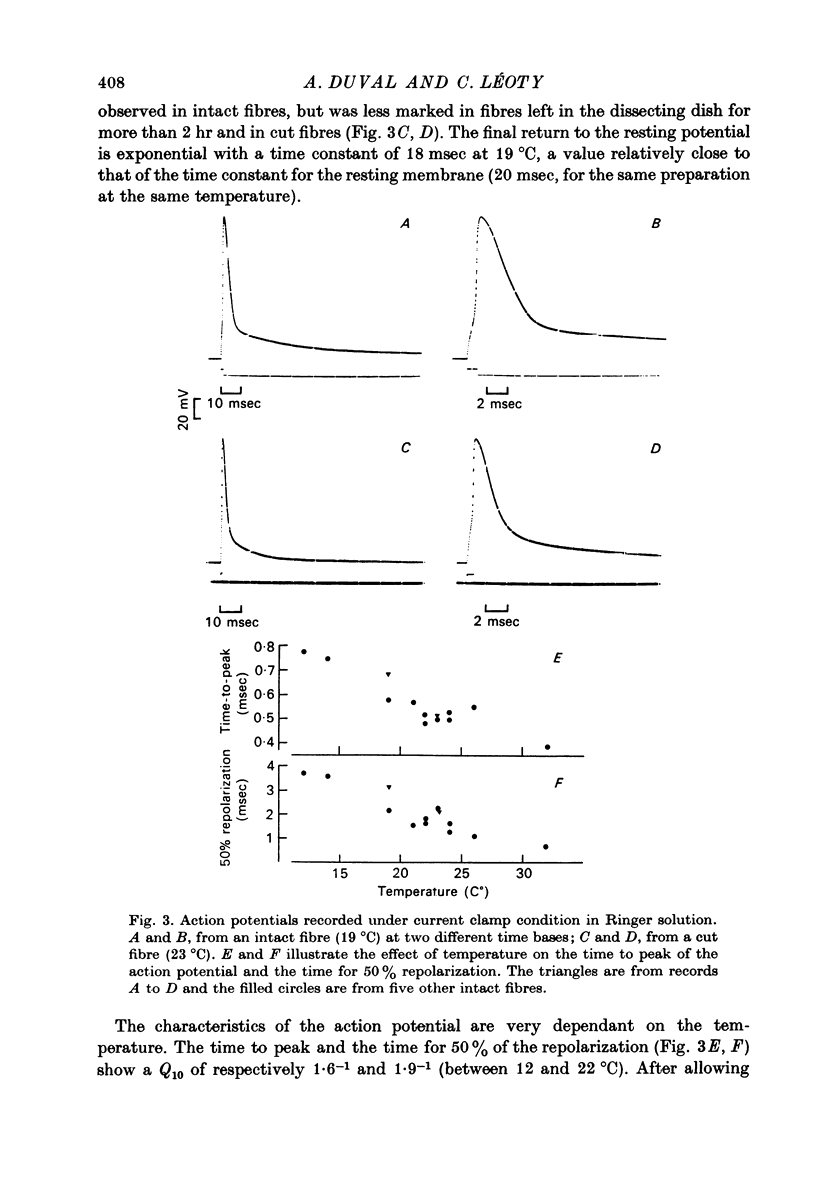
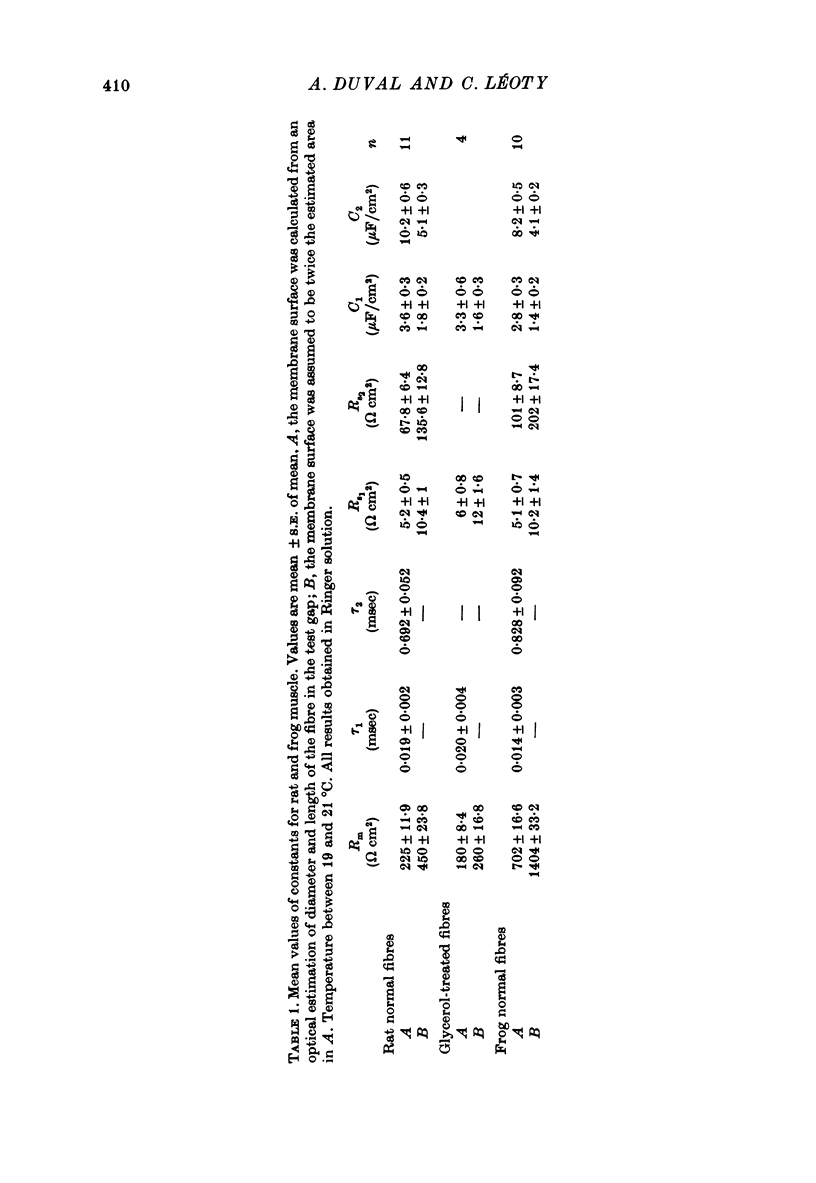
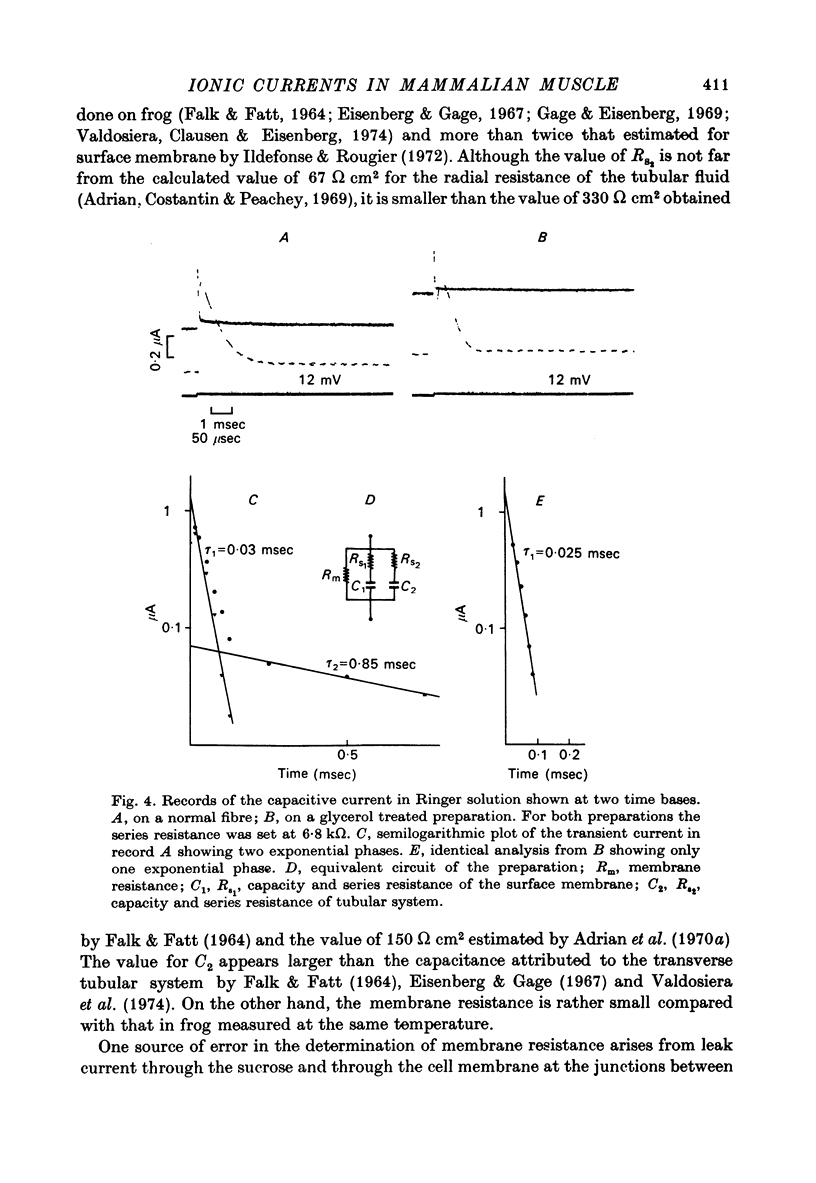
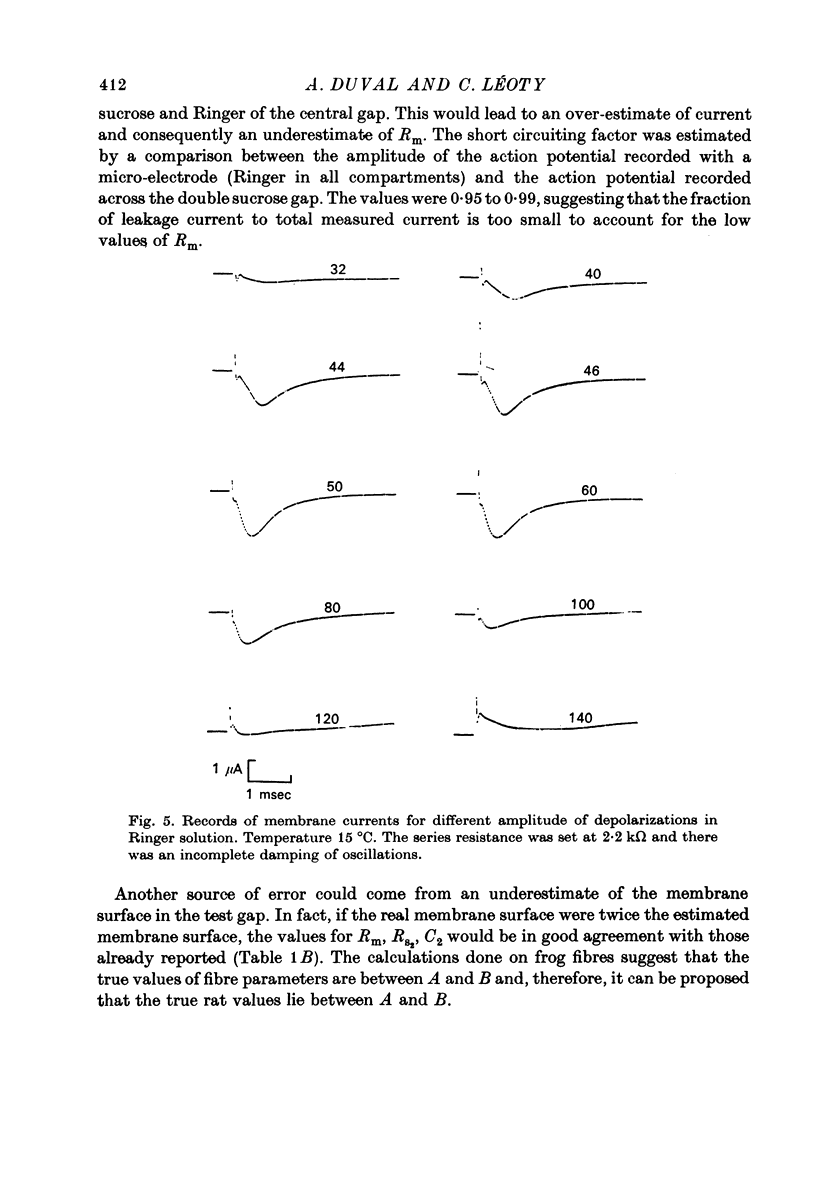
Abstract
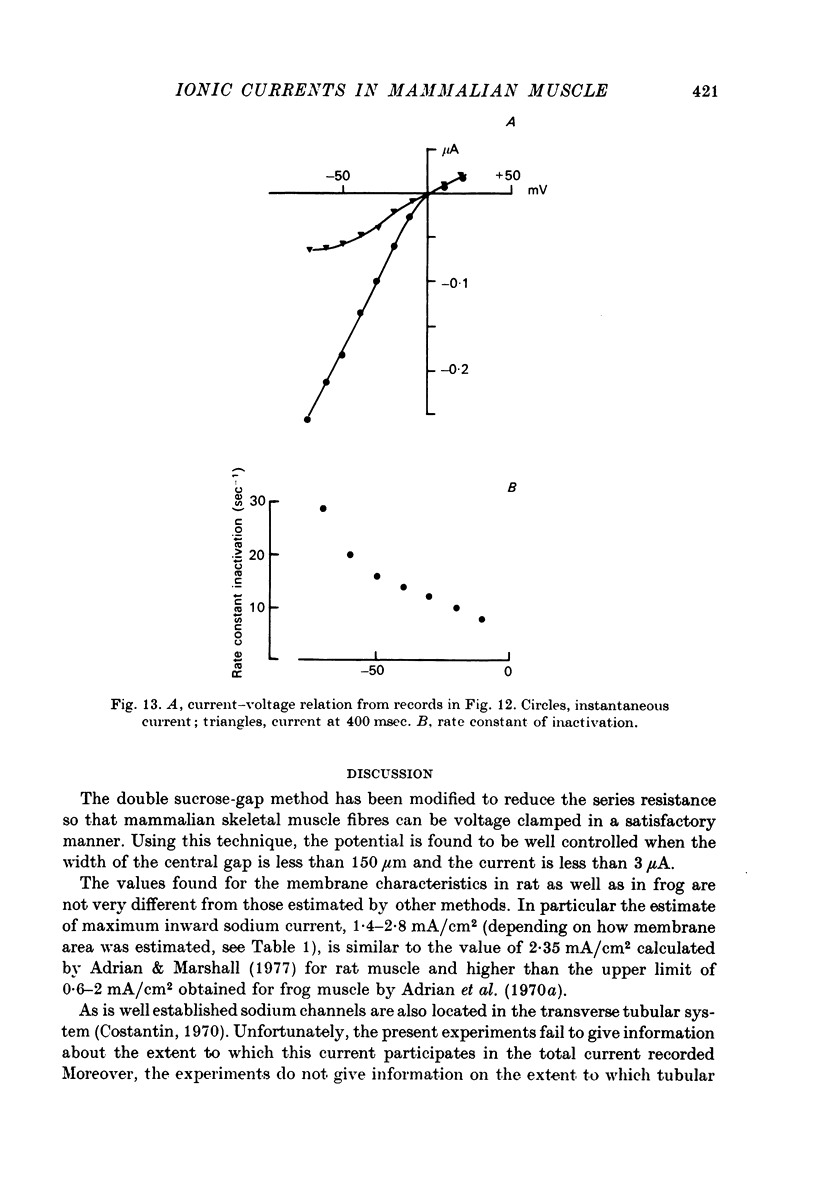
1. The double sucrose-gap technique has been applied to rat skeletal muscle fibres to study the ionic currents under voltage-clamp conditions. 2. The iliacus muscle was found to be of 'fast' type according to the characteristics of the twitch generated by an action potential. 3. Micro-electrode measurements have shown that the intracellular potential is under good control even when an inward current develops. 4. The components of an equivalent circuit with two time constants have been estimated from the records of the capacitive current. 5. In rat muscle, between 15 and 21 degrees C, inward and outward currents are similar to sodium and potassium currents found in frog muscle at lower temperature (1--3 degrees C). 6. The inward current which depends on [Na]o and is abolished by tetrodotoxin is carried by sodium ions. Related to the mean value for the holding potential (-90.5 mV) this current reaches its maximum amplitude a +40 and +50 mV, reverses between +130 and +150 mV and its half inactivation occurs between +14 and +22 mV. The effect of low doses of tetrodotoxin suggests that two components participate in the sodium current. 7. The delayed outward current which shows inactivation is divided in two components: (i) the fast has a linear instantaneous current-voltage relation and differs from the fast component of frog muscle in that its equilibrium potential is more negative than the resting potential; (ii) the slow has a linear instantaneous current-voltage relation and the mean value for its equilibrium potential is 26 mV less negative than the resting potential. 8. Inward-going rectification is present in rat muscle.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
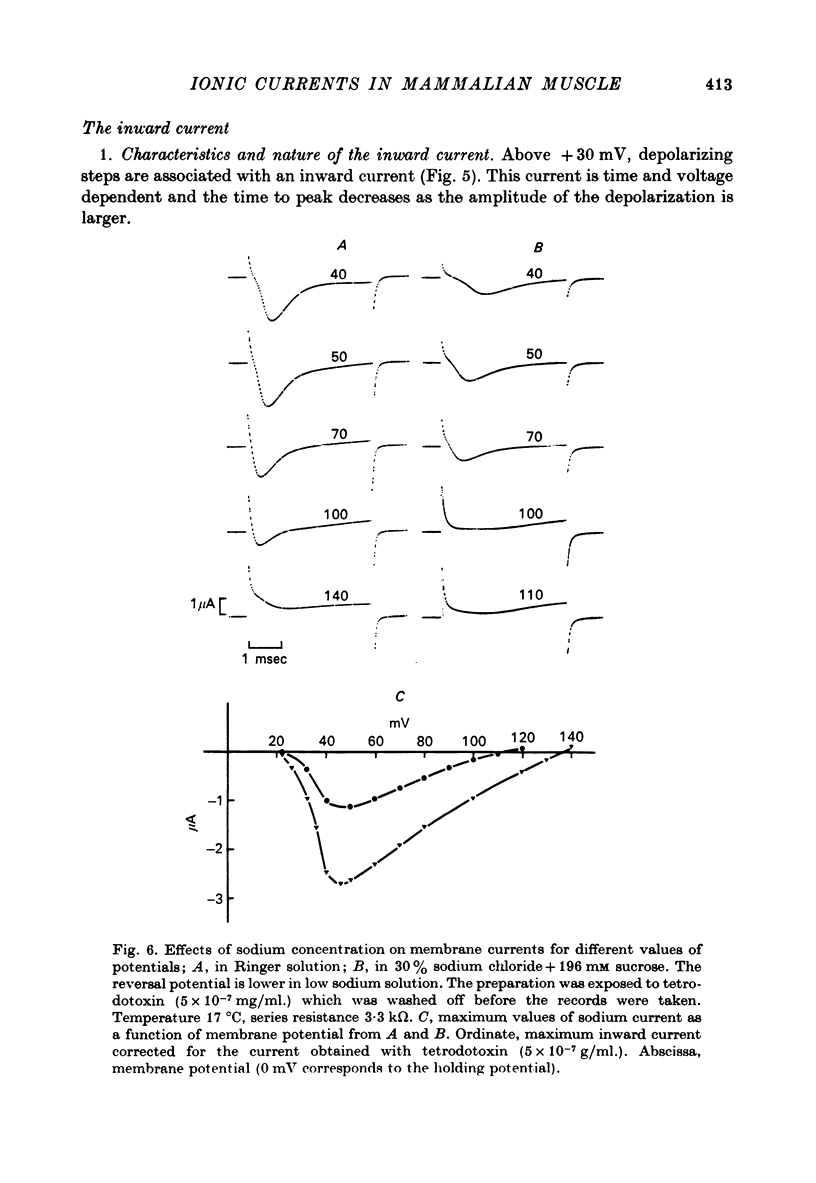
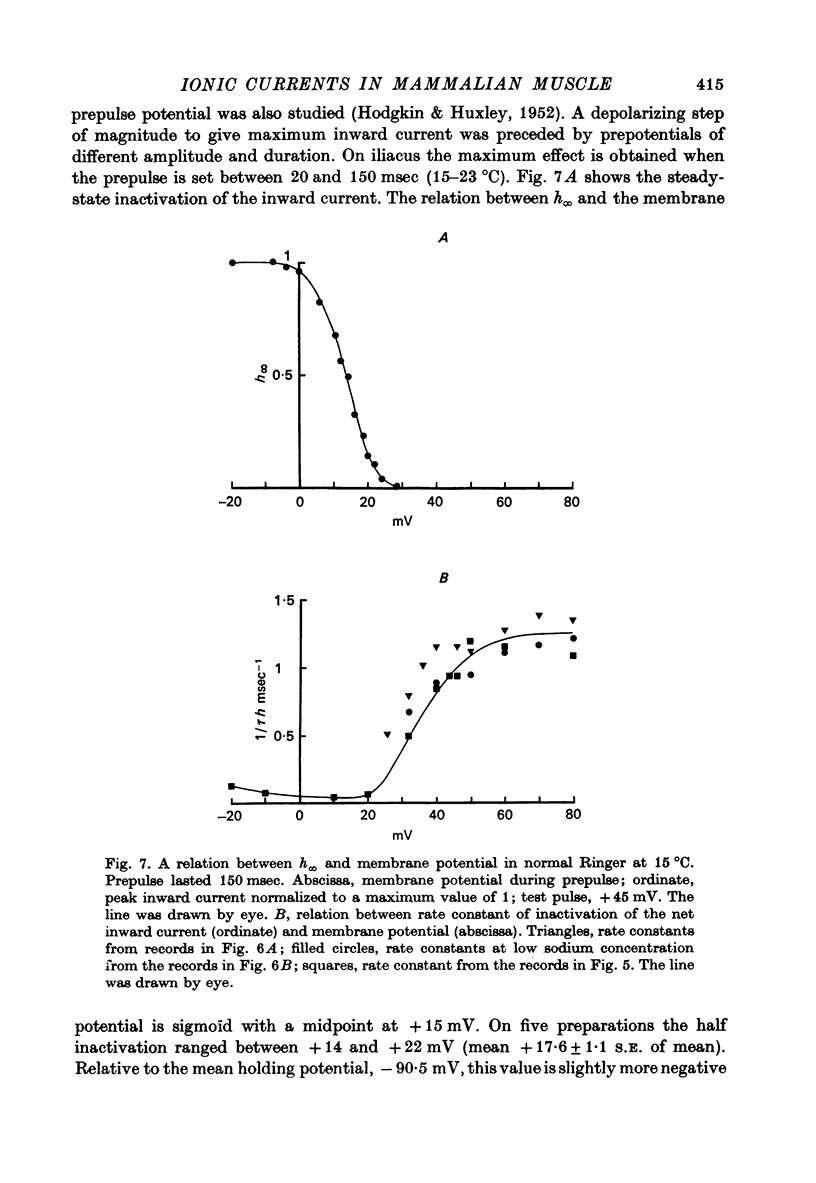
- Adrian R. H., Bryant S. H. On the repetitive discharge in myotonic muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(2):505–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
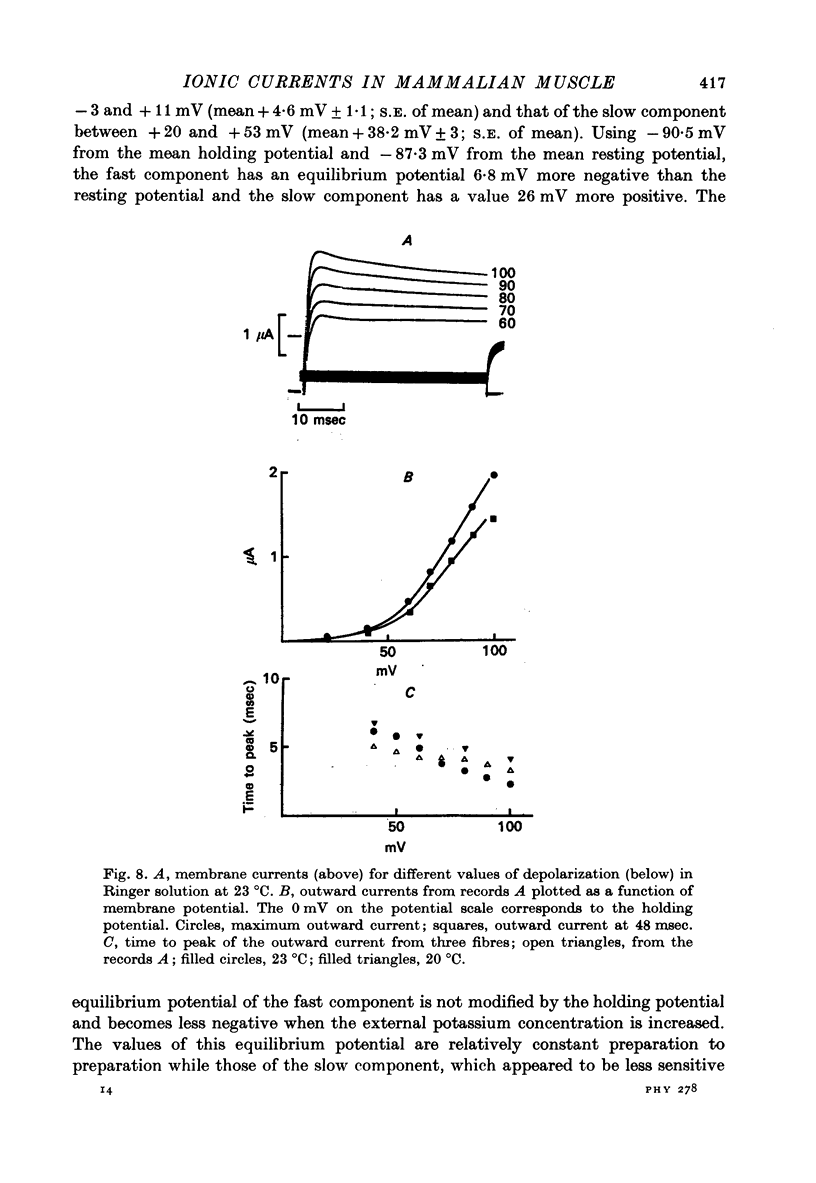
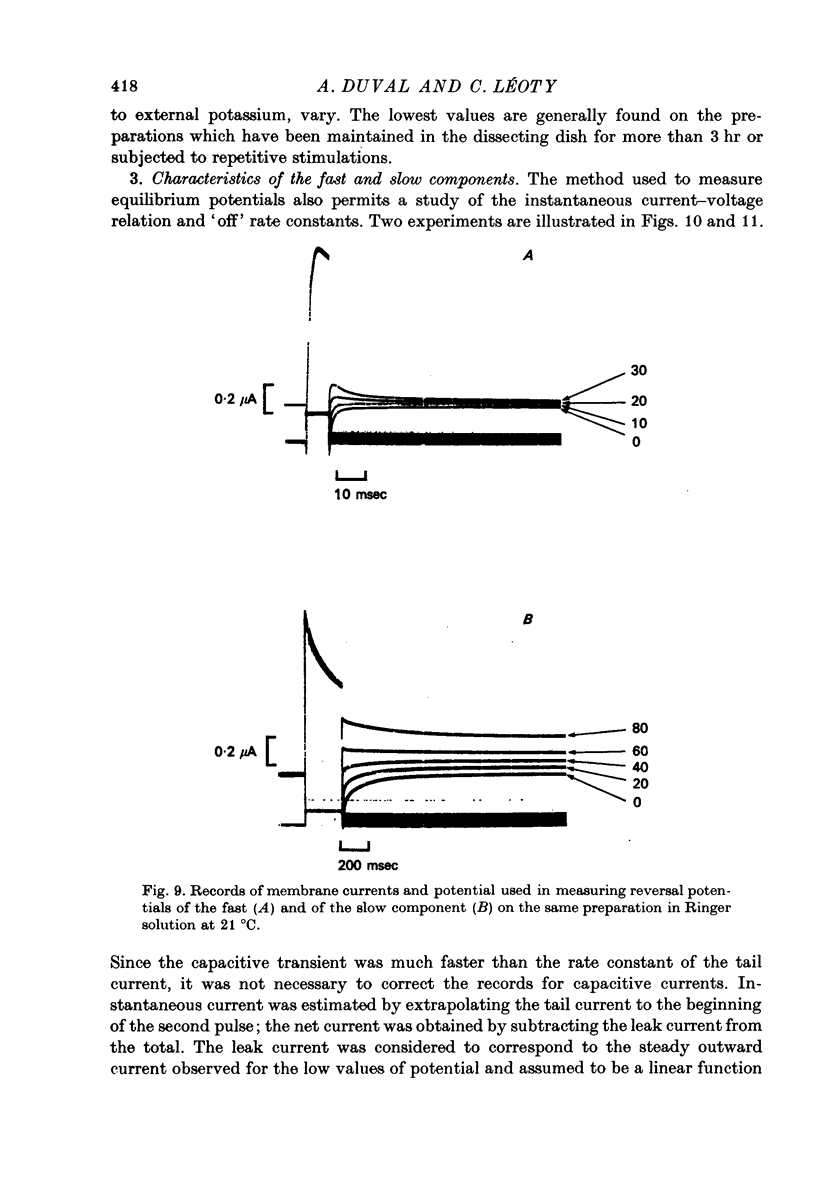
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Slow changes in potassium permeability in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):645–668. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1966 Oct;186(2):51P–52P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1968 May 1;51(5):188–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Costantin L. L., Peachey L. D. Radial spread of contraction in frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):231–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Freygang W. H. The potassium and chloride conductance of frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):61–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Marshall M. W. Sodium currents in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(1):223–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD I. A., MARTIN A. R. Membrane constants of mammalian muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:450–457. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Levine D. N., Tsairis P., Zajac F. E., 3rd Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastrocnemius. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):723–748. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLOSE R. DYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF FAST AND SLOW SKELETAL MUSCLES OF THE RAT DURING DEVELOPMENT. J Physiol. 1964 Sep;173:74–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L. The role of sodium current in the radial spread of contraction in frog muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jun;55(6):703–715. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.6.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval A., Leoty C. Voltage-clamp studies in rat fast skeletal muscle [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;270(1):45P–46P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg B. R., Kuda A. M. Discrimination between fiber populations in mammalian skeletal muscle by using ultrastructural parameters. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Jan;54(1):76–88. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Gage P. W. Frog skeletal muscle fibers: changes in electrical properties after disruption of transverse tubular system. Science. 1967 Dec 29;158(3809):1700–1701. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3809.1700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Howell J. N., Vaughan P. C. The maintenance of resting potentials in glycerol-treated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1971 May;215(1):95–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK G., FATT P. LINEAR ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF STRIATED MUSCLE FIBRES OBSERVED WITH INTRACELLULAR ELECTRODES. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Apr 14;160:69–123. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freygang W. H., Jr, Rapoport S. I., Peachey L. D. Some relations between changes in the linear electrical properties of striated muscle fibers and changes in ultrastructure. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Nov;50(10):2437–2458. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.10.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Eisenberg R. S. Capacitance of the surface and transverse tubular membrane of frog sartorius muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):265–278. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess A. Vertebrate slow muscle fibers. Physiol Rev. 1970 Jan;50(1):40–62. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Campbell D. T. An improved vaseline gap voltage clamp for skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):265–293. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ildefonse M., Rougier O. Voltage-clamp analysis of the early current in frog skeletal muscle fibre using the double sucrose-gap method. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):373–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. Y., Stanfield P. R. Actions of some anions on electrical properties and mechanical threshold of frog twitch muscle. J Physiol. 1968 Sep;198(2):291–309. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyohara T., Sato M. Membrane constants of red and white muscle fibers in the rat. Jpn J Physiol. 1967 Dec 15;17(6):720–725. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.17.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. M. The effect of denervation on the mechanical and electrical responses of fast and slow mammalian twitch muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(1):51–75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léoty C., Alix J. Some technical improvements for the voltage clamp with the double sucrose gap. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Sep 3;365(1):95–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00583633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léoty C., Poindessault J. P. Proceedings: Effects and compensation of the series resistance in voltage-clamp experiments using double sucrose-gap technique. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):108P–109P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Hodgkin A. L. Effect of diameter on the electrical constants of frog skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1970 Sep 5;227(5262):1053–1055. doi: 10.1038/2271053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poindessault J. P., Duval A., Léoty C. Voltage clamp with double sucrose gap technique. External series resistance compensation. Biophys J. 1976 Feb;16(2 Pt 1):105–120. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(76)85668-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. Electrical properties of white and red muscle fibres of the elasmobranch fish Scyliorhinus canicula. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(1):161–186. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The differential effects of tetraethylammonium and zinc ions on the resting conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):231–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The effect of the tetraethylammonium ion on the delayed currents of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):209–229. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The effect of the tetraethylammonium ion on the inwardly rectifying potassium channel of frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):2P–3P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdiosera R., Clausen C., Eisenberg R. S. Impedance of frog skeletal muscle fibers in various solutions. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Apr;63(4):460–491. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.4.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemura K. Resting and action potentials in red and white muscles of the rat. Jpn J Physiol. 1967 Dec 15;17(6):708–719. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.17.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


