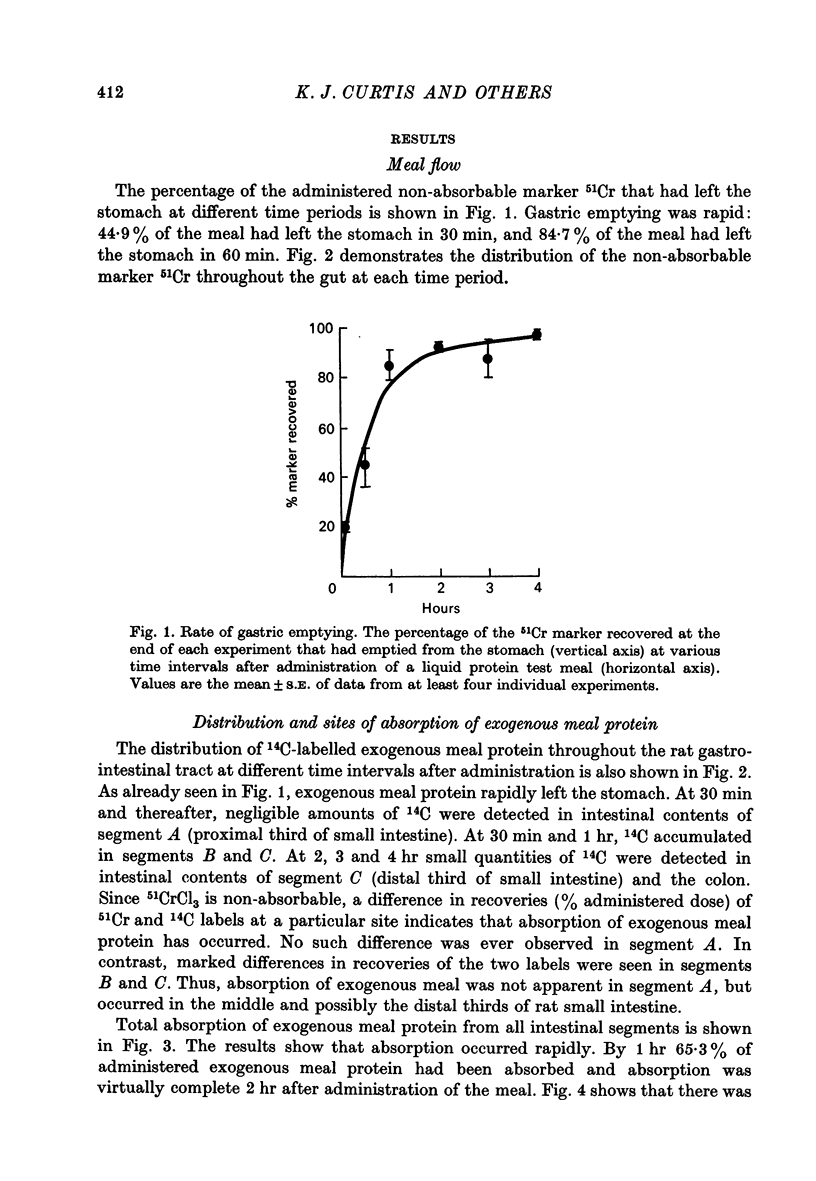
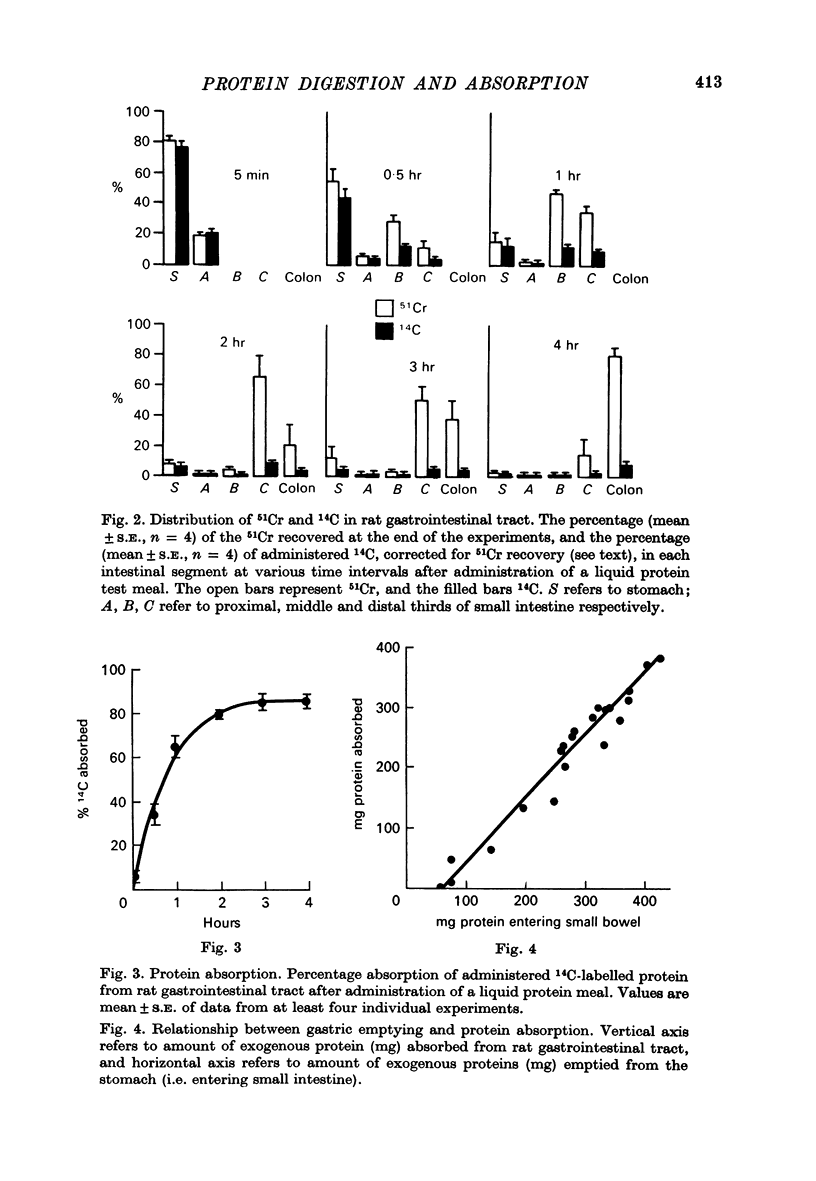
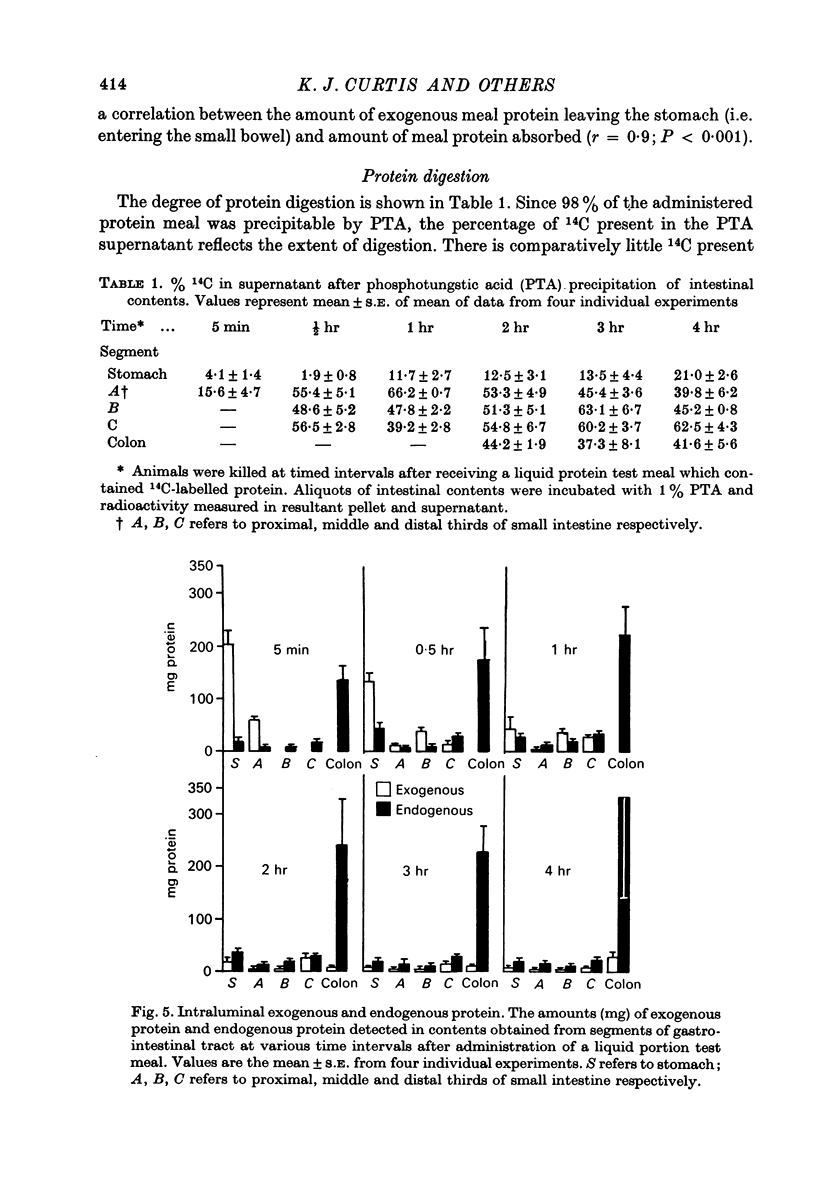
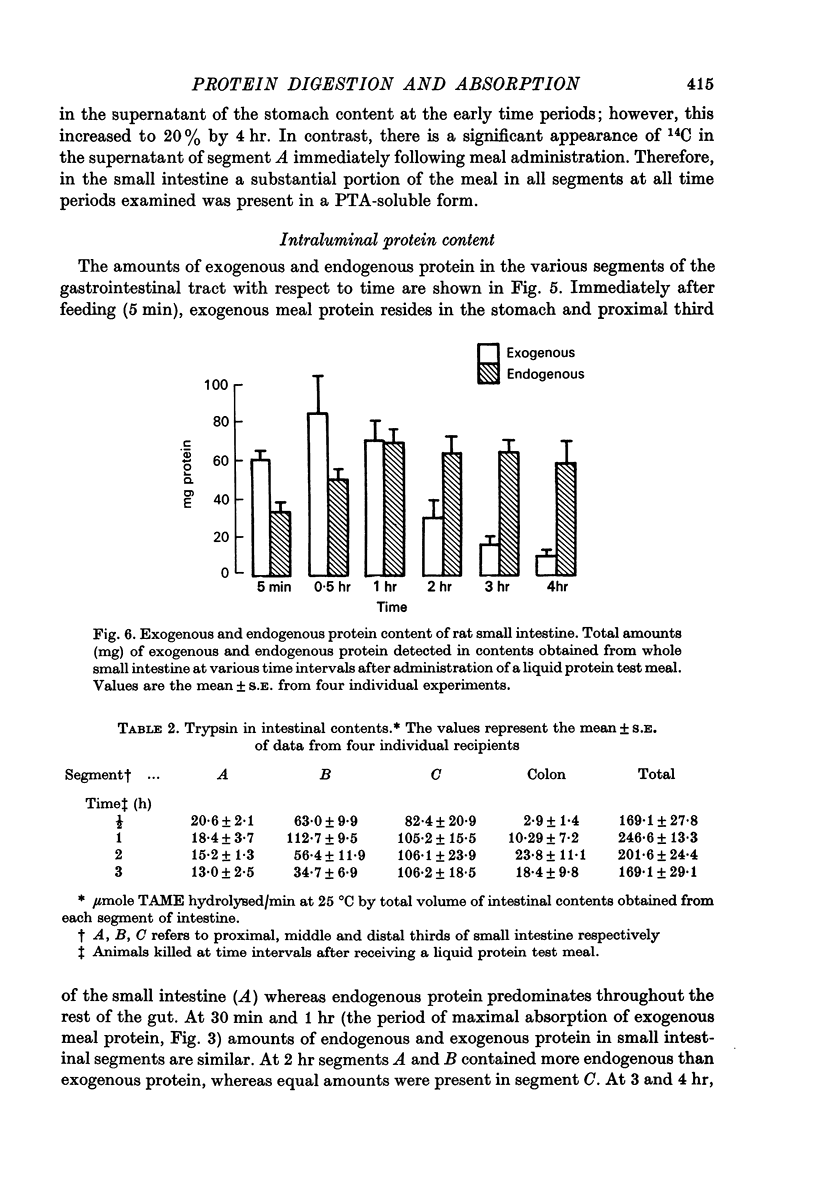
Abstract
1. A randomly labelled 14C protein was synthesized in order to investigate the site and rate of digestion and absorption of dietary protein in the rat. 2. A liquid test meal consisting of protein and a non-absorbable marker, 51CrCl3, was administered to rats which were then sacrificed at intervals up to 4 hr after ingestion of the meal. Analysis of intestinal contents showed that as gastric emptying proceeded, the meal moved rapidly to the distal two thirds of the small intestine. 3. Protein digestion and absorption occurred predominantly in this area over a period of 1-2 hr. 4. Amounts of endogenous protein present in the small intestine never exceeded amounts of exogenous protein during maximum absorption of exogenous protein (0-1 hr). At later time periods (2-4 hr), however, more endogenous than exogenous protein was detected in the intestinal lumen. 5. It is concluded that the digestion and absorption of dietary protein is a rapid process, taking place in the distal two-thirds of the small intestine. Endogenous protein levels do not exceed exogenous protein levels until after the bulk of exogeneous protein is absorbed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adibi S. A. Intestinal transport of dipeptides in man: relative importance of hydrolysis and intact absorption. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2266–2275. doi: 10.1172/JCI106724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adibi S. A., Mercer D. W. Protein digestion in human intestine as reflected in luminal, mucosal, and plasma amino acid concentrations after meals. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1586–1594. doi: 10.1172/JCI107335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORGSTROM B., DAHLQVIST A., GUSTAFSSON B. E., LUNDH G., MALMQUIST J. Trypsin, invertase and amylase content of feces of germfree rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Oct;102:154–155. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORGSTROM B., DAHLQVIST A., LUNDH G., SJOVALL J. Studies of intestinal digestion and absorption in the human. J Clin Invest. 1957 Oct;36(10):1521–1536. doi: 10.1172/JCI103549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE C. W., NEUBERGER A. The digestion and absorption of protein by normal man. Biochem J. 1960 Feb;74:313–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0740313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke R. J., Williams J. A. The value of phenol red and chromic chloride as nonabsorbable gastric indicators. Gut. 1971 May;12(5):389–392. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.5.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crampton R. F., Lis M. T., Matthews D. M. Sites of maximal absorption and hydrolysis of two dipeptides by rat small intestine in vivo. Clin Sci. 1973 Jun;44(6):583–594. doi: 10.1042/cs0440583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton D. W., Nesheim M. C. Amino acid patterns during digestion in the small intestine of ducks. J Nutr. 1969 Sep;99(1):43–50. doi: 10.1093/jn/99.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R., HOLDSWORTH E. S. An investigation into protein digestion with 14C-labelled protein. 1. The general pattern of 14C incorporation in body tissues and fluids of the rat up to 3 h after feeding. Br J Nutr. 1962;16:13–25. doi: 10.1079/bjn19620002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. M., Jr, Barreras R. F. Intestinal absorption of trace quantities of chromium. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Sep;68(3):484–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. M., Jr Role of enteric microorganisms in malabsorption. Fed Proc. 1967 Sep;26(5):1426–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. M., Cooper H. L. Protein digestion and absorption. Gastroenterology. 1971 Oct;61(4):535–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL B. C. A modified spectrophotometric determination of chymotrypsin, trypsin, and thrombin. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Dec;37:1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Accumulation of endogenous protein in the cecum of the germfree rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Nov;129(2):380–384. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. M., Kim Y. S. Changes in sucrase, enterokinase, and peptide hydrolase after intestinal resection. The association of cellular hyperplasia and adaptation. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):942–951. doi: 10.1172/JCI107259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasset E. S. Amino acid homeostasis in the gut lumen and its nutritional significance. World Rev Nutr Diet. 1972;14:134–153. doi: 10.1159/000392735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon S. E., Mawer G. E. The digestion and absorption of protein in man. 2. The form in which digested protein is absorbed. Br J Nutr. 1970 Mar;24(1):241–258. doi: 10.1079/bjn19700024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa-Solano A., Gitler C. Digestion and absorption of ingested and secreted proteins labeled with 75Se-selenomethionine and 35S-methionine in the gastrointestinal tract of the rat. J Nutr. 1968 Feb;94(2):249–255. doi: 10.1093/jn/94.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKINS R. A., DIMITRIADOU A., BOOTH C. C. The rates and sites of absorption of 131 I-labelled albumin and sodium 131 I in the rat. Clin Sci. 1960 Nov;19:595–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PELOT D., GROSSMAN M. I. Distribution and fate of pancreatic enzymes in small intestine of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1962 Feb;202:285–288. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter D. N., Coates M. E. The influence of the microflora of the alimentary tract on protein digestion in the chick. Br J Nutr. 1971 Jul;26(1):55–69. doi: 10.1079/bjn19710008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk D. B. Progress report. Peptide absorption in man. Gut. 1974 Jun;15(6):494–501. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.6.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk D. B., Webb J. P., Lane A. E., Clark M. L., Dawson A. M. Functional differentiation of human jejunum and ileum: a comparison of the handling of glucose, peptides, and amino acids. Gut. 1974 Jun;15(6):444–449. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.6.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


