Abstract
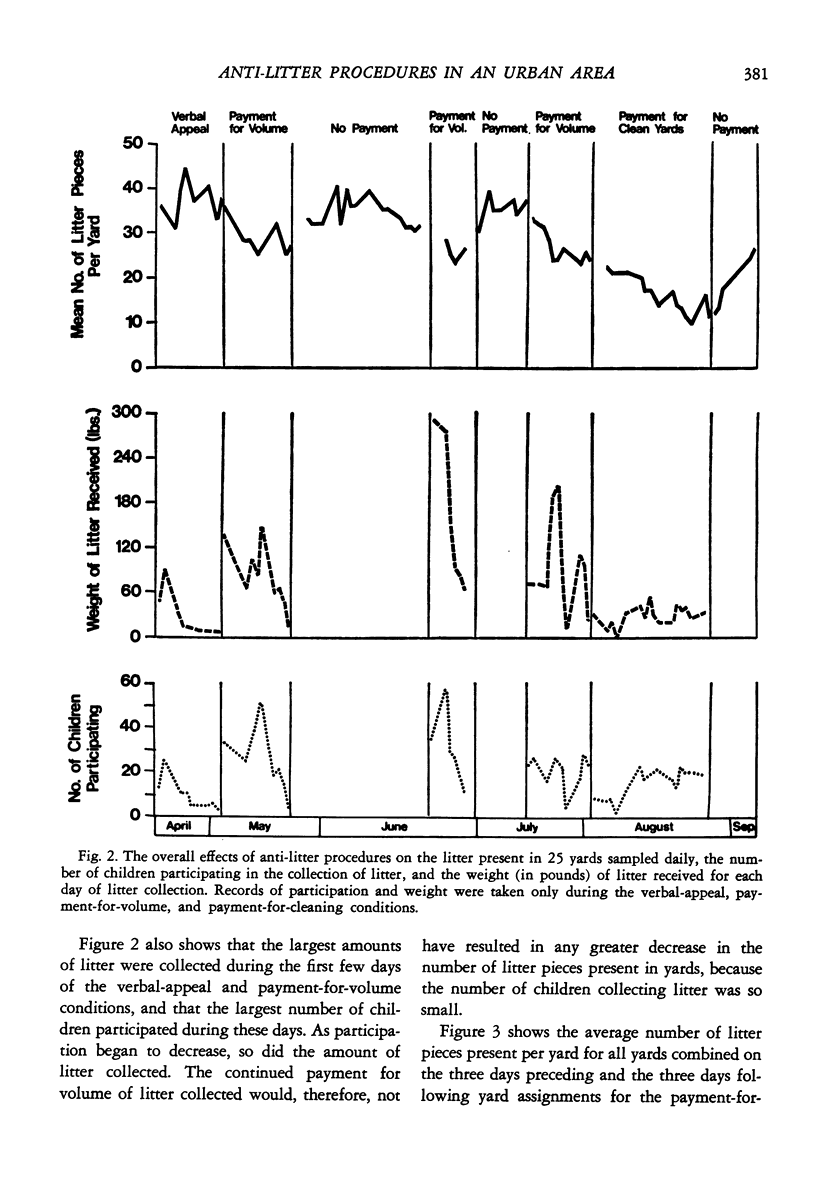
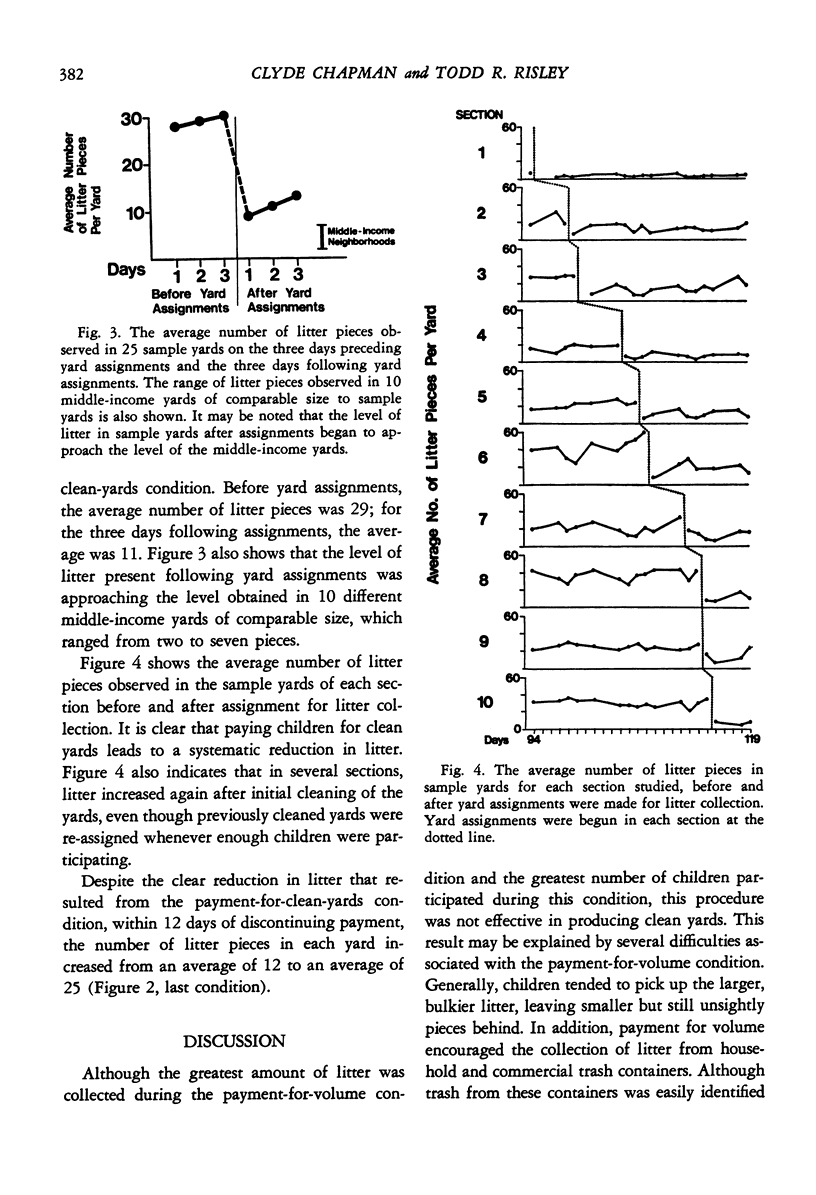
In urban high-density areas, litter has become an increasingly obvious and pervasive problem. In the present study, repeated measures of the amount of litter on randomly selected yards in an urban low-income housing project were used to evaluate the effectiveness of a series of anti-litter procedures directed at the children residing in the project. Paying children for volume of trash collected resulted in only a small decrease in the number of litter pieces present. Paying them for cleaning assigned yards markedly decreased the level of litter in all sampled yards. Thus, children can be employed to maintain a clean neighborhood in spite of the rapid accumulation of new litter in urban yards.
Full text
PDF