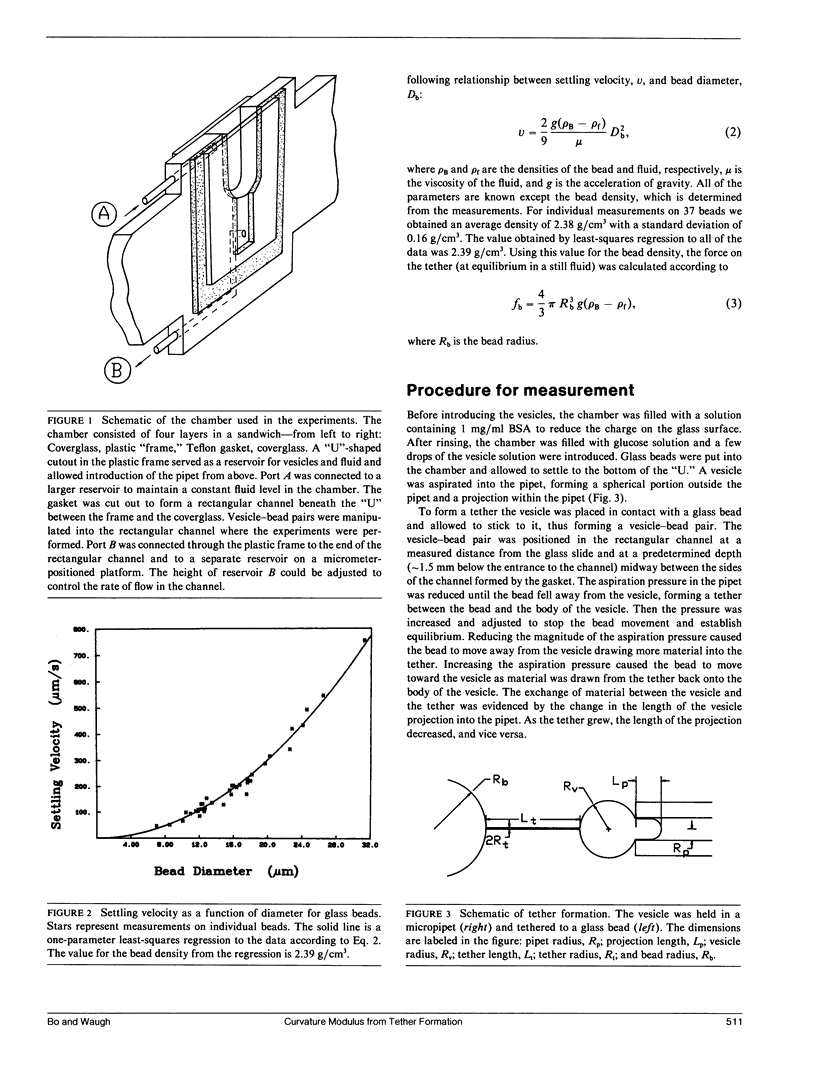
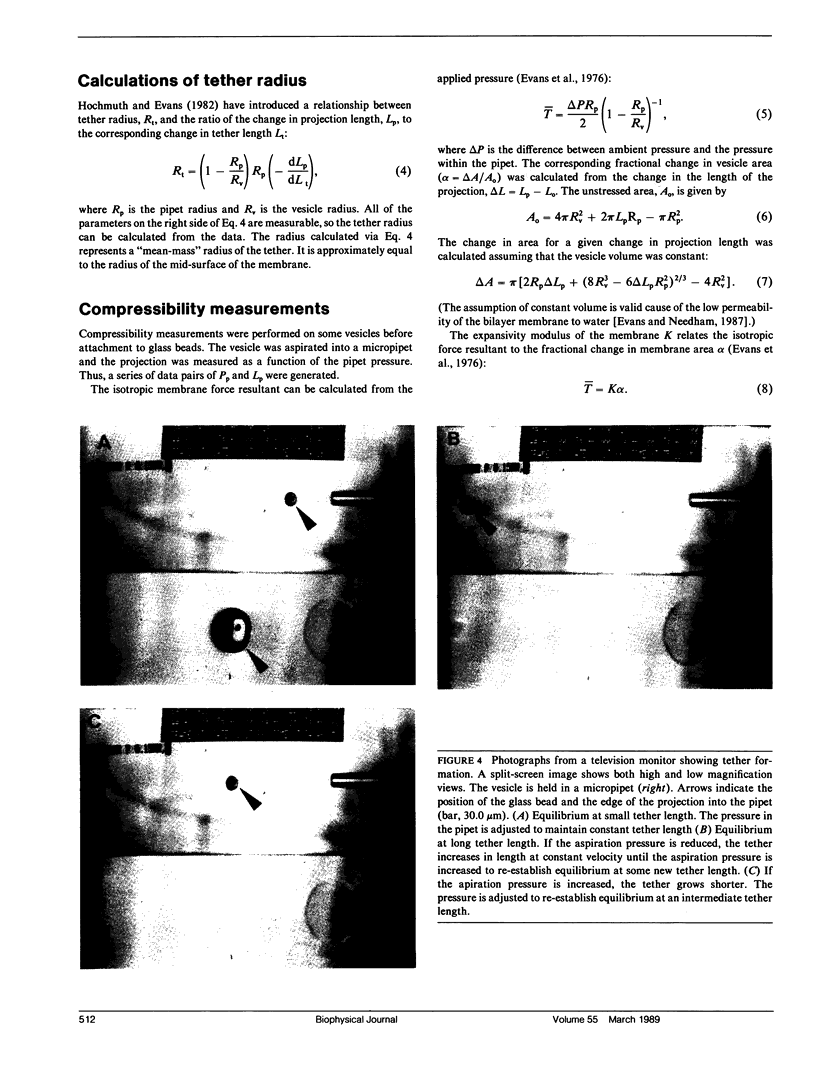
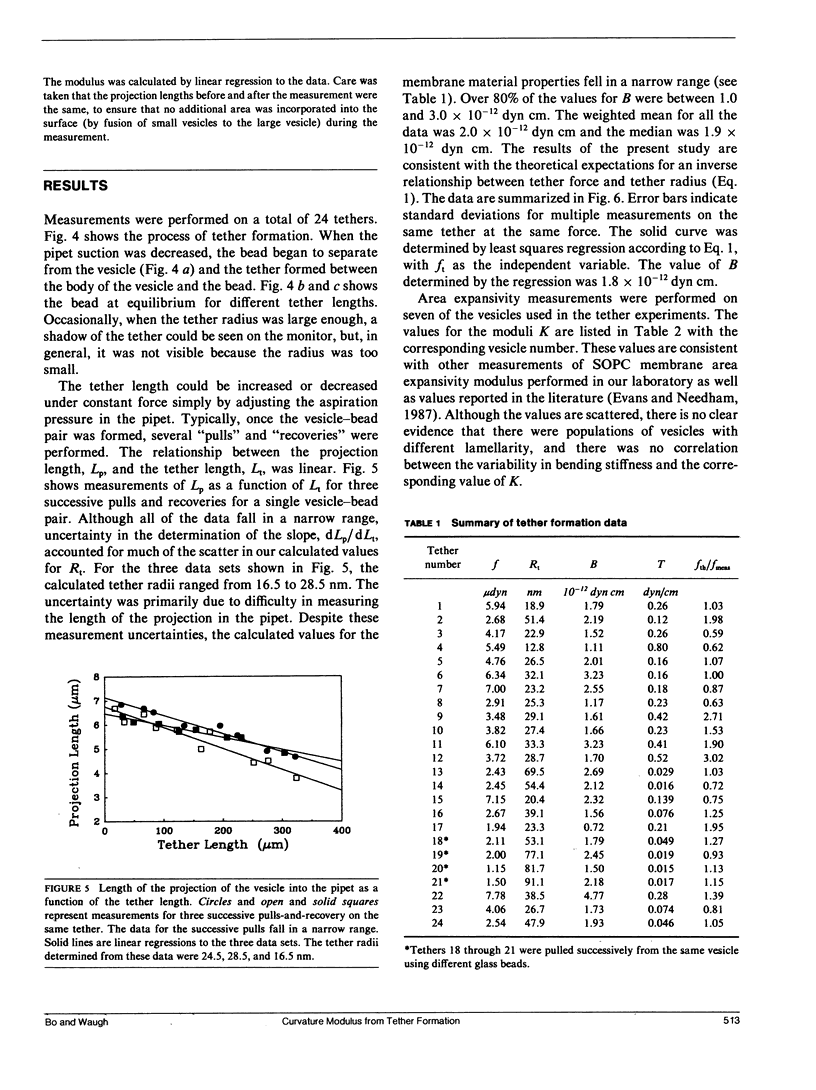
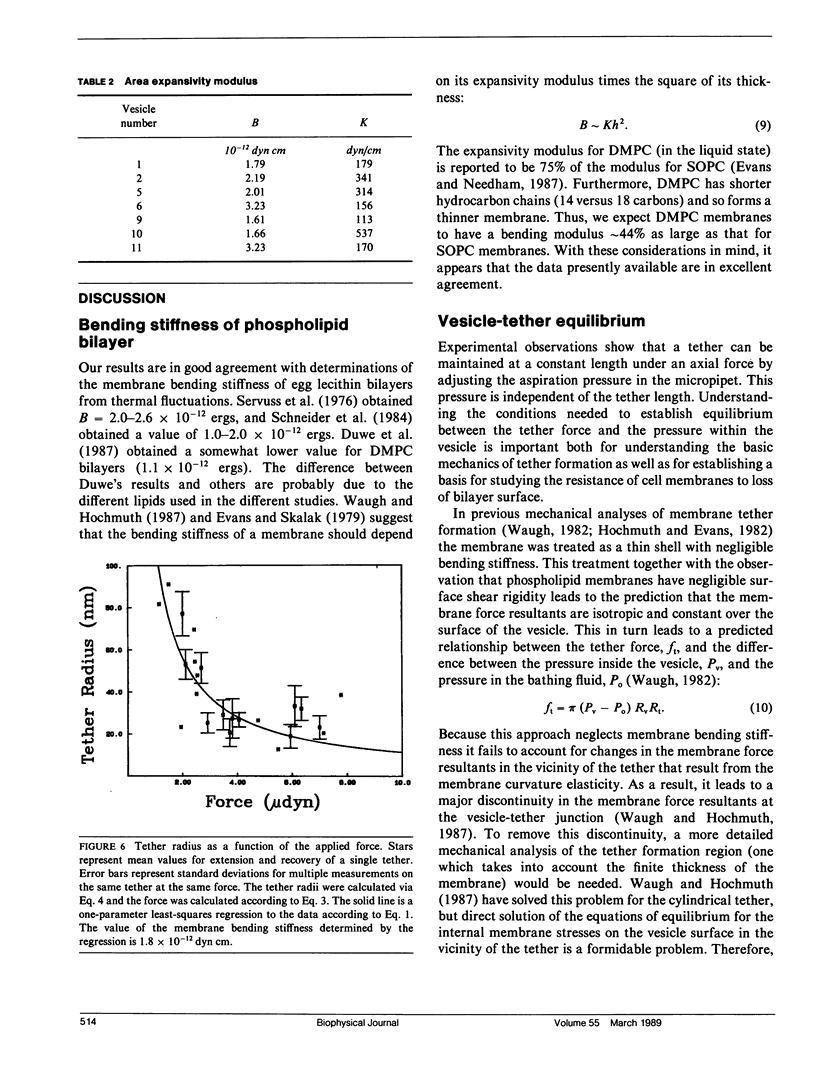
Abstract
The curvature elastic modulus (bending stiffness) of stearoyloleoyl phosphatidylcholine (SOPC) bilayer membrane is determined from membrane tether formation experiments. R. E. Waugh and R. M. Hochmuth 1987. Biophys. J. 52:391-400) have shown that the radius of a bilayer cylinder (tether) is inversely related to the force supported along its axis. The coefficient that relates the axial force on the tether to the tether radius is the membrane bending stiffness. Thus, the bending stiffness can be calculated directly from measurements of the tether radius as a function of force. Giant (10-50-microns diam) thin-walled vesicles were aspirated into a micropipette and a tether was pulled out of the surface by gravitational forces on small glass beads that had adhered to the vesicle surface. Because the vesicle keeps constant surface area and volume, formation of the tether requires displacement of material from the projection of the vesicle in the pipette. Tethers can be made to grow longer or shorter or to maintain equilibrium by adjusting the aspiration pressure in the micropipette at constant tether force. The ratio of the change in the length of the tether to the change in the projection length is proportional to the ratio of the pipette radius to the tether radius. Thus, knowing the density and diameter of the glass beads and measuring the displacement of the projection as a function of tether length, independent determinations of the force on the tether and the tether radius were obtained. The bending stiffness for an SOPC bilayer obtained from these data is approximately 2.0 x 10(-12) dyn cm, for tether radii in the range of 20-100 nm. An equilibrium relationship between pressure and tether force is derived which closely matches experimental observation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Evans E. A. Bending elastic modulus of red blood cell membrane derived from buckling instability in micropipet aspiration tests. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84319-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Skalak R. Mechanics and thermodynamics of biomembranes: part 2. CRC Crit Rev Bioeng. 1979 Nov;3(4):331–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Waugh R., Melnik L. Elastic area compressibility modulus of red cell membrane. Biophys J. 1976 Jun;16(6):585–595. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85713-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Waugh R. Osmotic correction to elastic area compressibility measurements on red cell membrane. Biophys J. 1977 Dec;20(3):307–313. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85551-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochmuth R. M., Evans E. A. Extensional flow of erythrocyte membrane from cell body to elastic tether. I. Analysis. Biophys J. 1982 Jul;39(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84492-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochmuth R. M., Mohandas N., Blackshear P. L., Jr Measurement of the elastic modulus for red cell membrane using a fluid mechanical technique. Biophys J. 1973 Aug;13(8):747–762. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)86021-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochmuth R. M., Wiles H. C., Evans E. A., McCown J. T. Extensional flow of erythrocyte membrane from cell body to elastic tether. II. Experiment. Biophys J. 1982 Jul;39(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84493-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P., Dowben R. M. Formation and properties of thin-walled phospholipid vesicles. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Feb;73(1):49–60. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040730108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. B., Jenkins J. T., Webb W. W. Thermal fluctuations of large cylindrical phospholipid vesicles. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):891–899. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84235-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servuss R. M., Harbich W., Helfrich W. Measurement of the curvature-elastic modulus of egg lecithin bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 15;436(4):900–903. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh R. E., Hochmuth R. M. Mechanical equilibrium of thick, hollow, liquid membrane cylinders. Biophys J. 1987 Sep;52(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83227-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh R. E. Surface viscosity measurements from large bilayer vesicle tether formation. I. Analysis. Biophys J. 1982 Apr;38(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84526-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




