Abstract
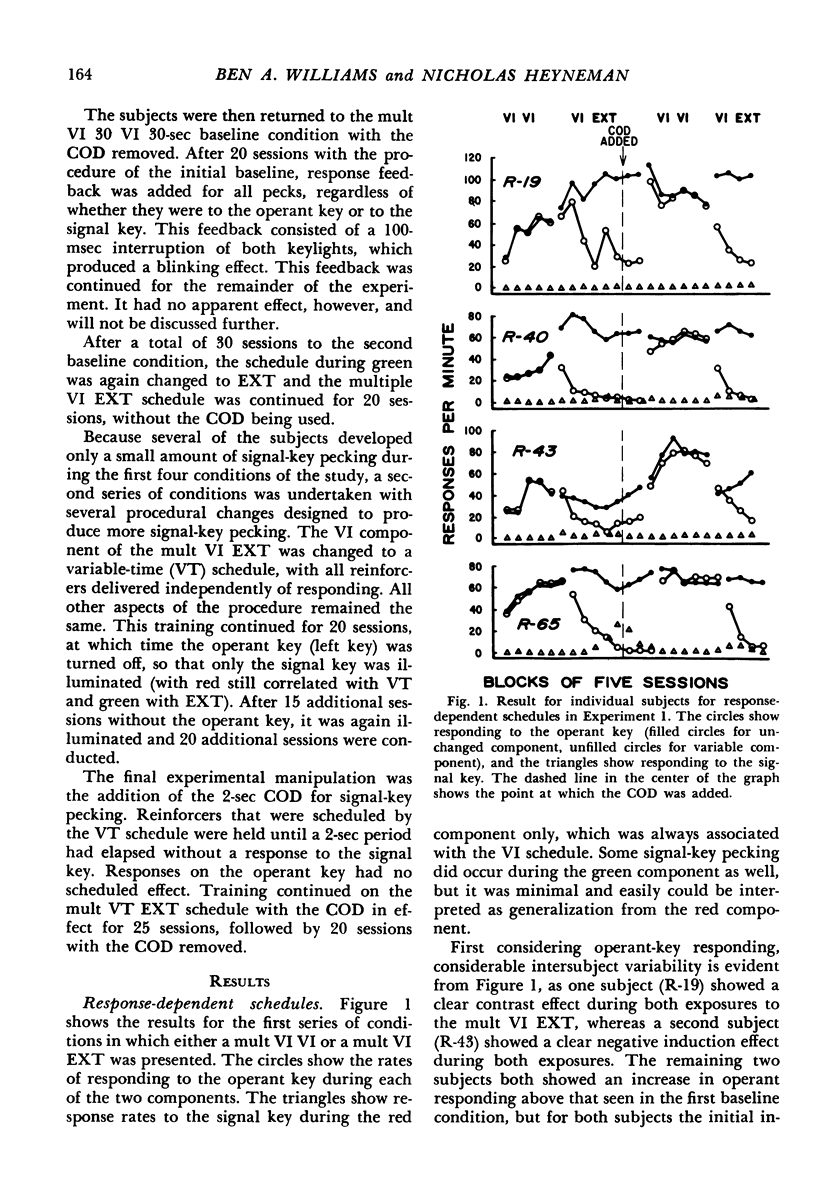
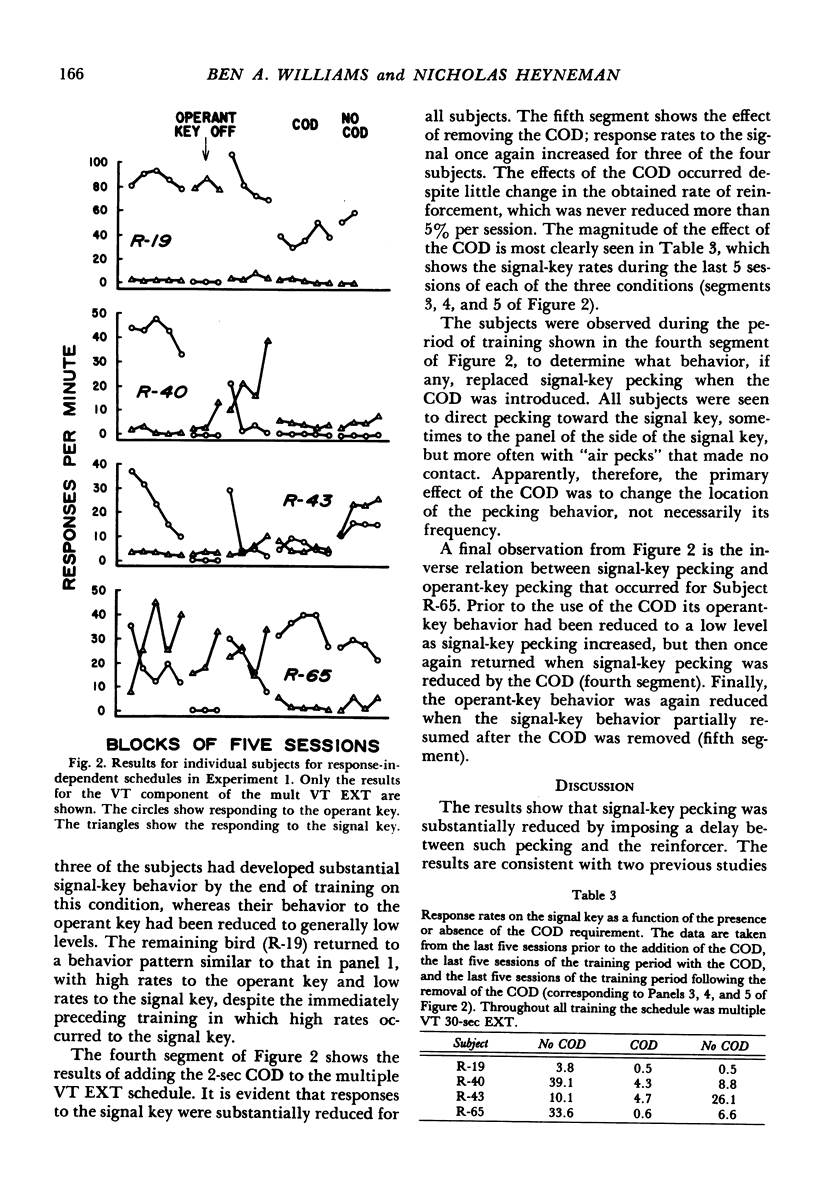
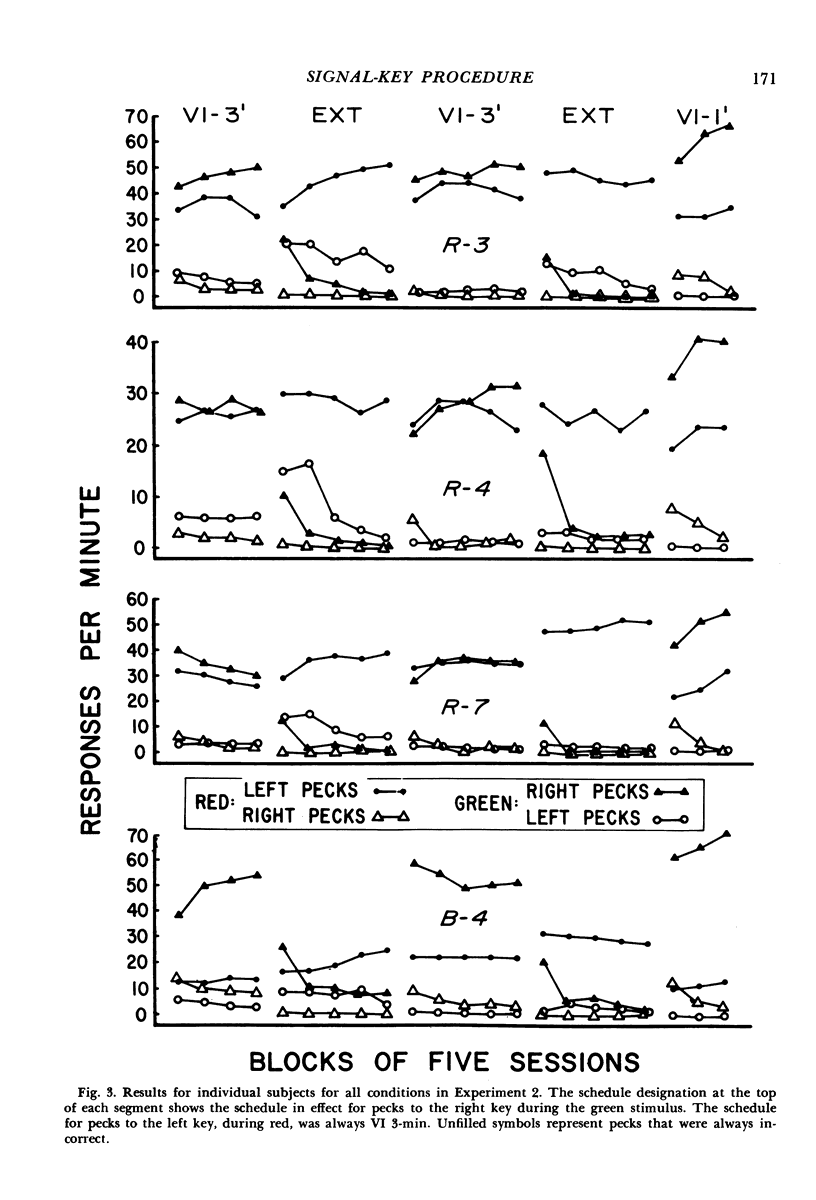
Two experiments are reported that challenge the interpretation of previous results with the signal-key procedure, in which the discriminative stimuli are located on a response key different from the key associated with the operant response requirement. Experiment 1 replicated the procedure of Keller (1974), and found that contrast effects on the operant key occurred reliably for only one of four subjects. High rates to the signal key initially occurred for only one subject, but modifications of the procedure produced substantial rates to the signal key for all subjects. In all cases, however, signal-key behavior was greatly reduced by the addition of a changeover delay which prevented reinforcement within 2 seconds of the last peck to the signal key, suggesting that signal-key pecking was maintained primarily by adventitious reinforcement. Experiment 2 modified the signal-key procedure by using three response keys, so that the discriminative stimuli on the signal key controlled different responses during all phases of training. With this modification, reliable contrast effects on the operant key occurred for all subjects, suggesting that the failure to find contrast in previous studies has been due to the confounding of changes in the discrimination requirements with changes in relative rate of reinforcement. The results challenge the additivity theory of contrast, and suggest that “elicited” behavior plays a minor role, if any, in the determination of contrast effects in multiple schedules.
Keywords: signal-key procedure, additivity theory, multiple schedules, behavioral contrast, key peck, pigeons
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Catania A. C. Reinforcement schedules: the role of responses preceding the one that produces the reinforcer. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 May;15(3):271–287. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamzu E., Schwartz B. The maintenance of key pecking by stimulus-contingent and response-independent food presentation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jan;19(1):65–72. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Sutterer J. R., Brush F. R. Positive and negative behavioral contrast in the rat. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 May;23(3):377–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.23-377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller K. The role of elicited responding in behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Mar;21(2):249–257. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. A yoked-chamber comparison of concurrent and multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):13–22. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander D. G., Irwin R. J. Multiple schedules: effects of the distribution of reinforcements between component on the distribution of responses between conponents. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):517–524. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. On the form of the relation between response rates in a multiple schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Mar;21(2):237–248. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Some limitations on behavioral contrast and induction during successive discrimination. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jan;6:131–139. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. Discriminative stimulus location as a determinant of positive and negative behavioral contrast in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Mar;23(2):167–176. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.23-167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B., Hamilton B., Silberberg A. Behavioral contrast in the pigeon: a study of the duration of key pecking maintained on multiple schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Sep;24(2):199–206. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. Stimulus-reinforcer contingencies and local behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Mar;29(2):297–308. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P., Wheatley K. L. Matching to relative reinforcement frequency in multiple schedules with a short component duration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Mar;15(2):205–210. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spealman R. D., Gollub L. R. Behavioral interactions in multiple variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Nov;22(3):471–481. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spealman R. D. Interactions in multiple schedules: the role of the stimulus-reinforcer contingency. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Jul;26(1):79–93. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spealman R. D., Katz J. L., Witkin J. M. Drug effects on responding maintained by stimulus-reinforcer and response-reinforcer contingencies. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Sep;30(2):187–196. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.30-187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A. Contrast, component duration, and the following schedule of reinforcement. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 1979 Oct;5(4):379–396. doi: 10.1037//0097-7403.5.4.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


