Abstract
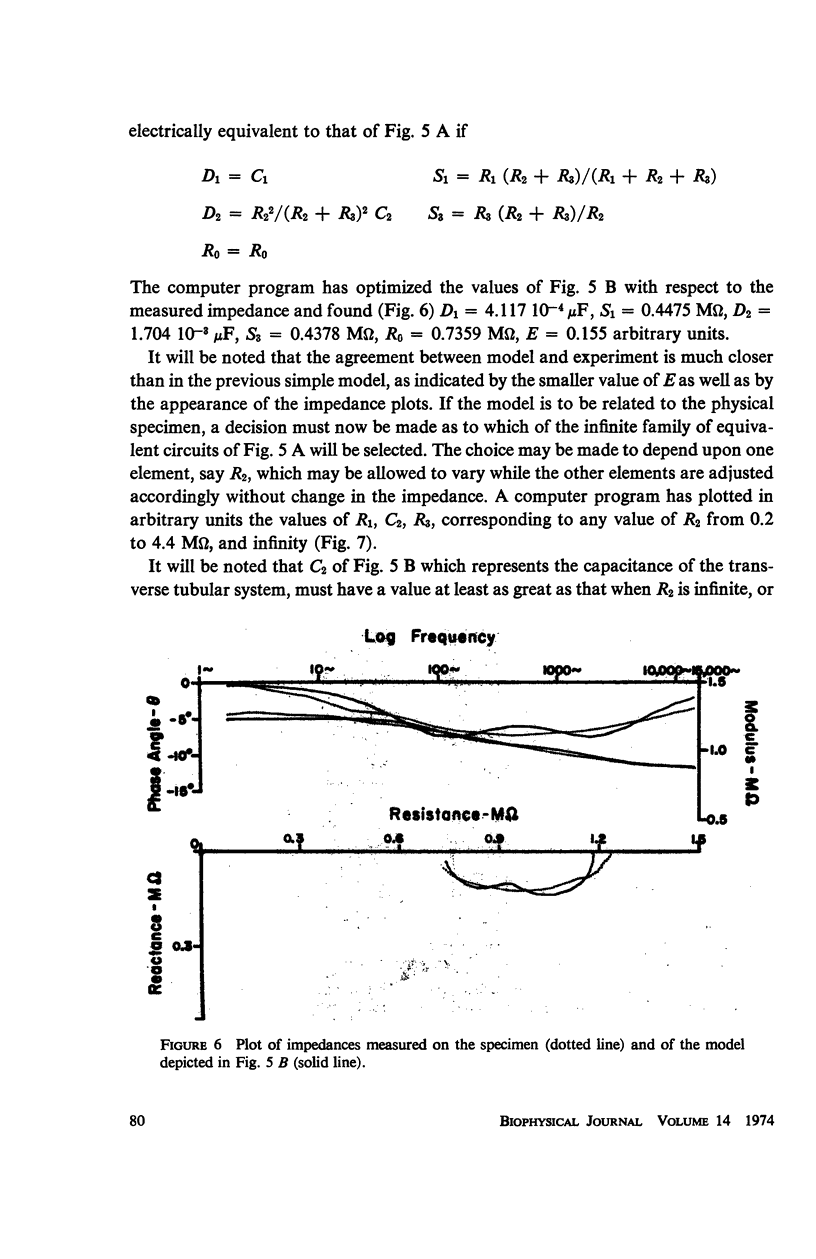
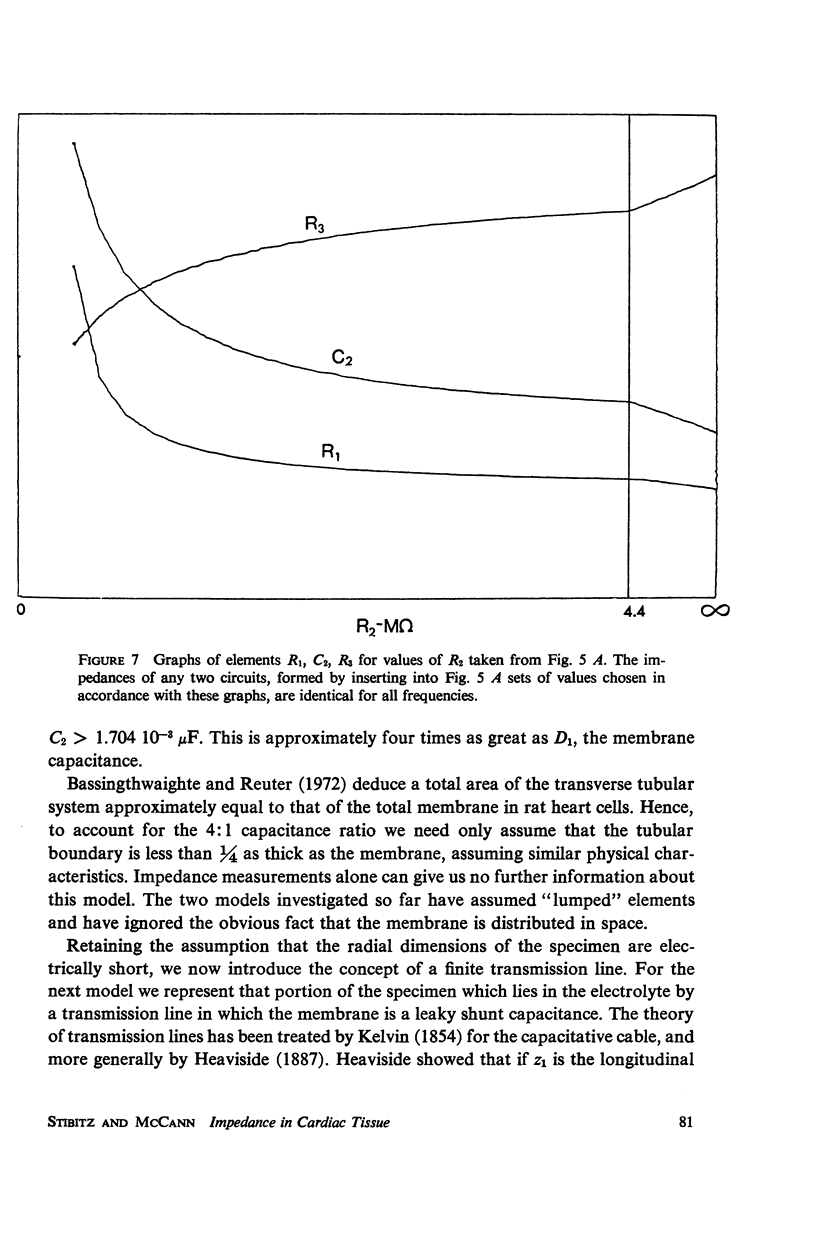
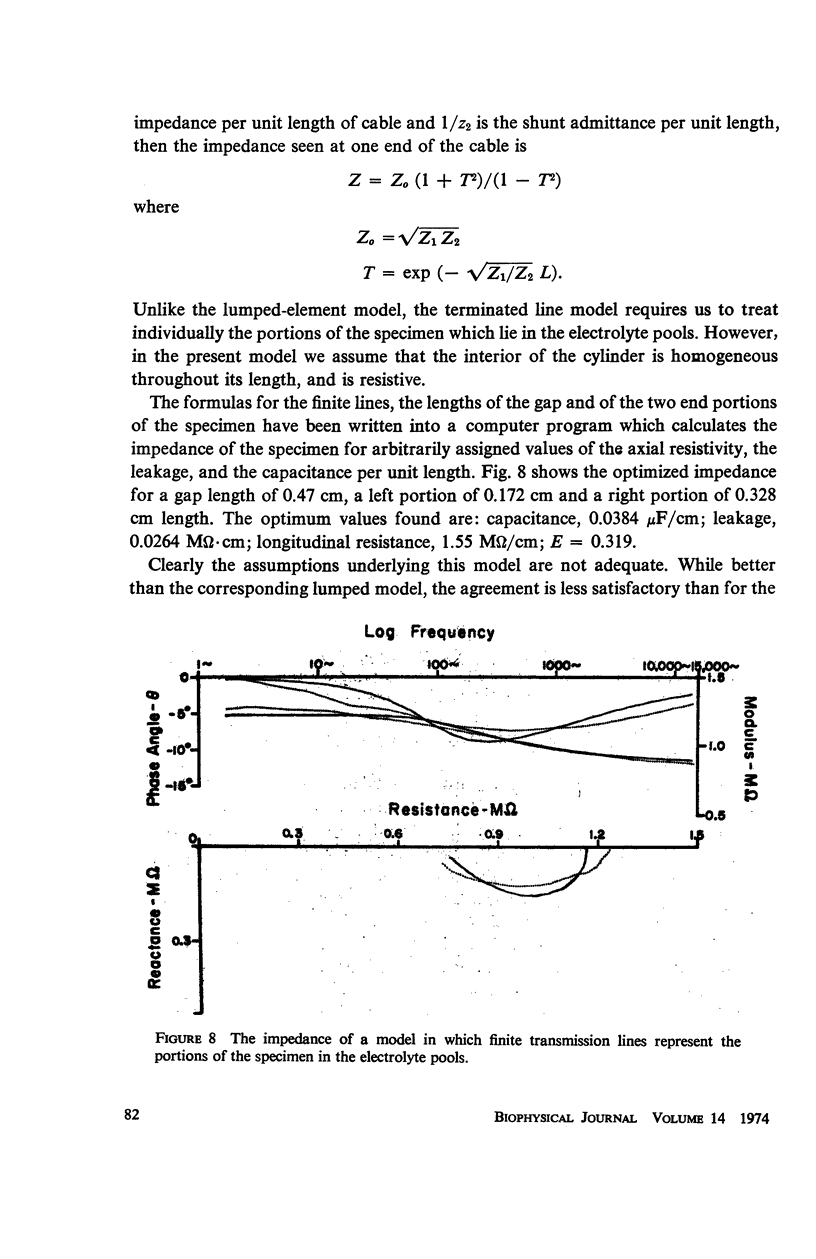
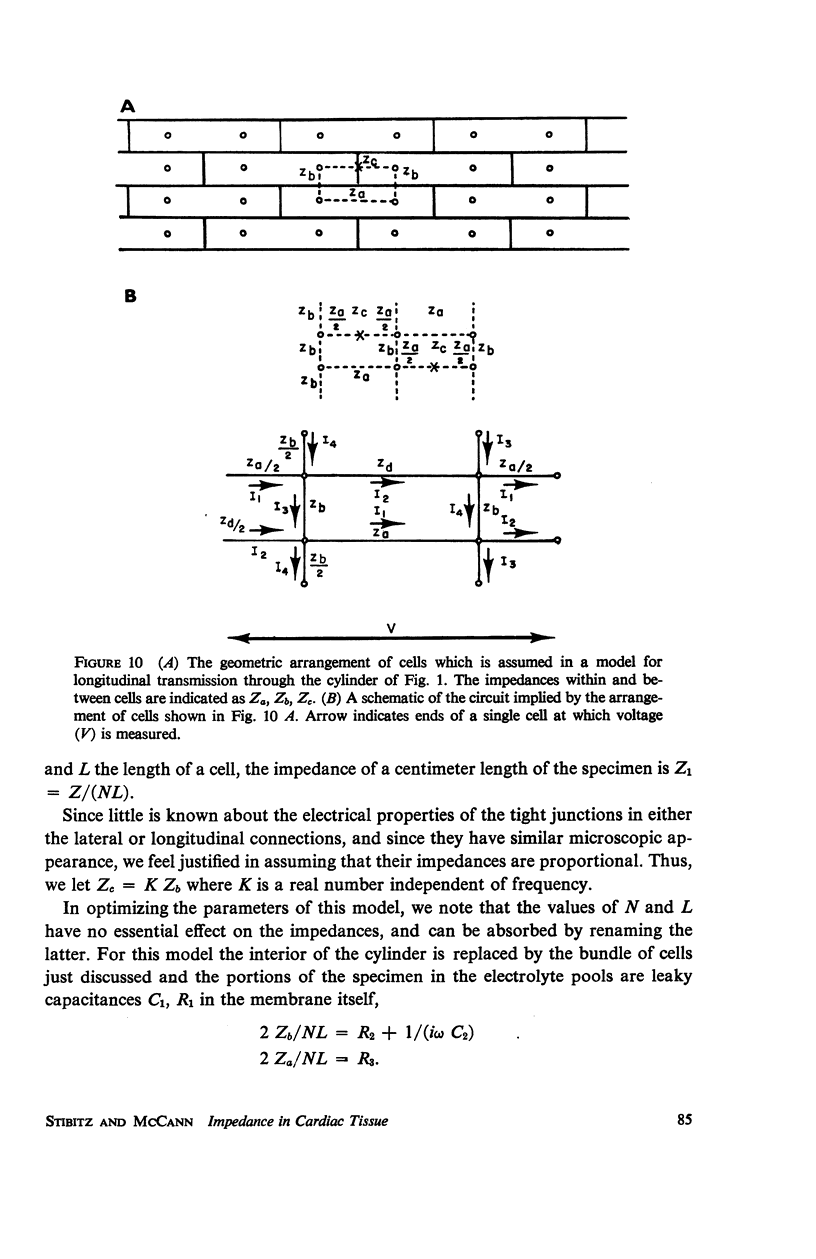
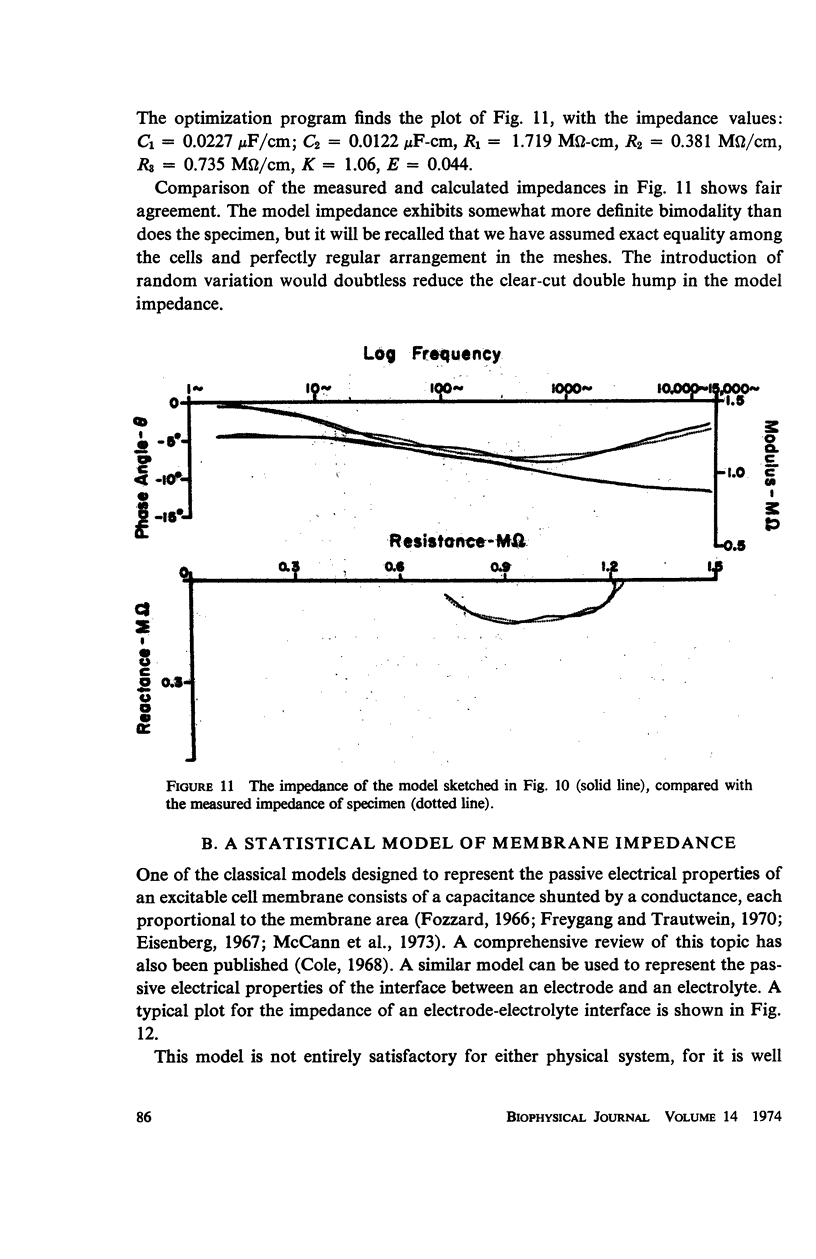
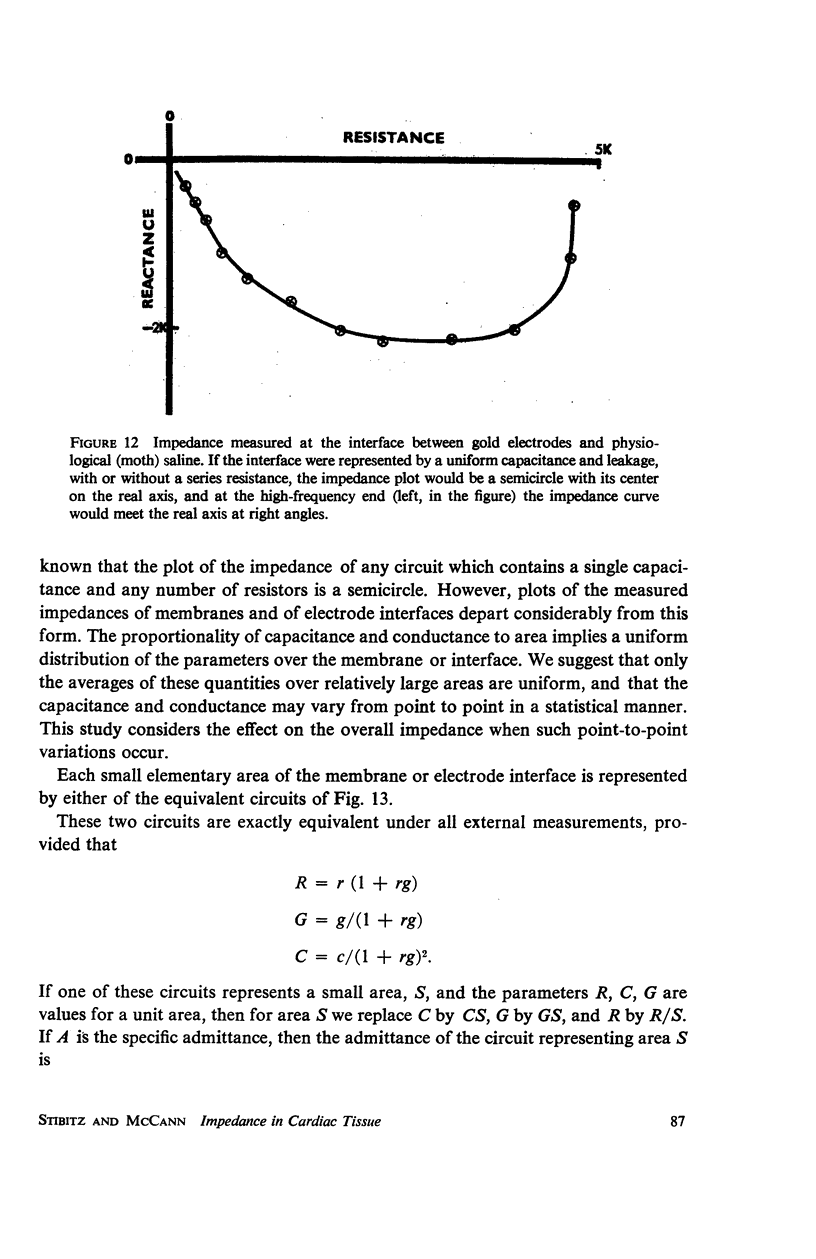
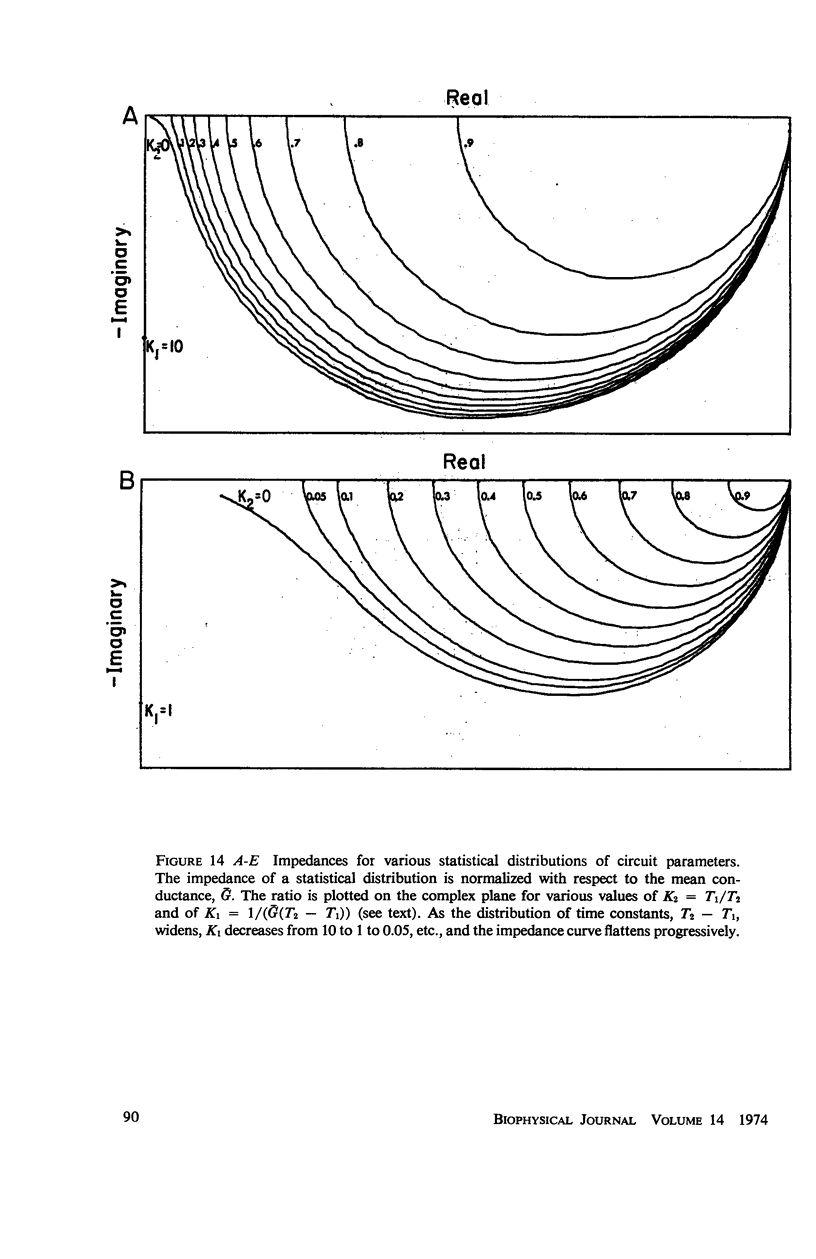
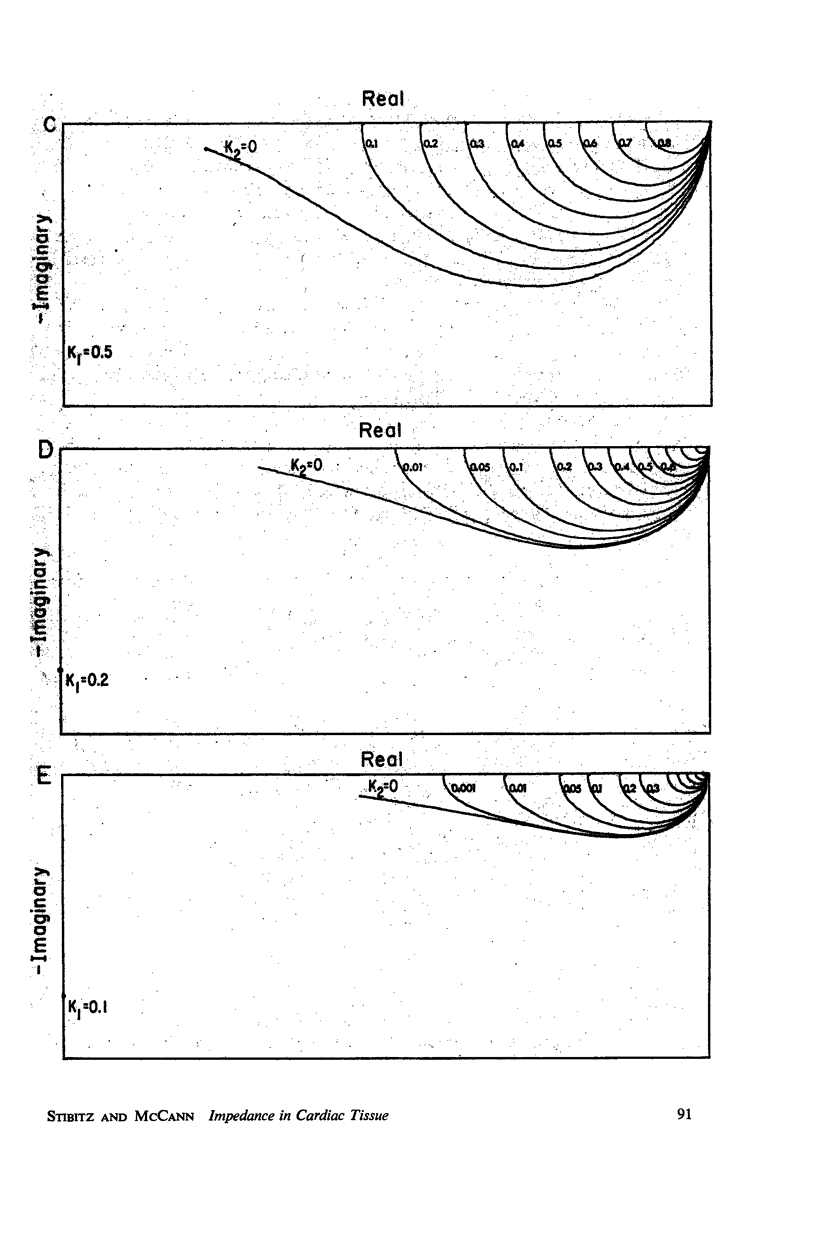
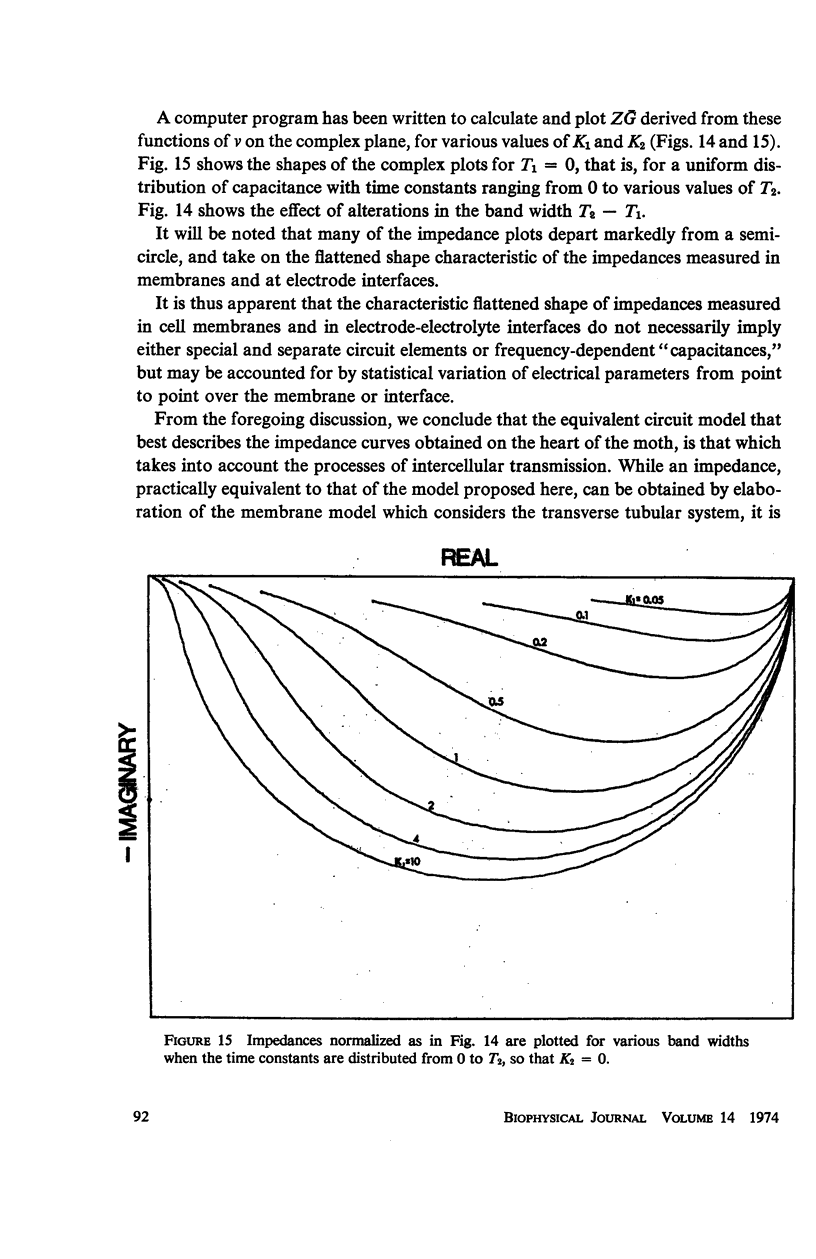
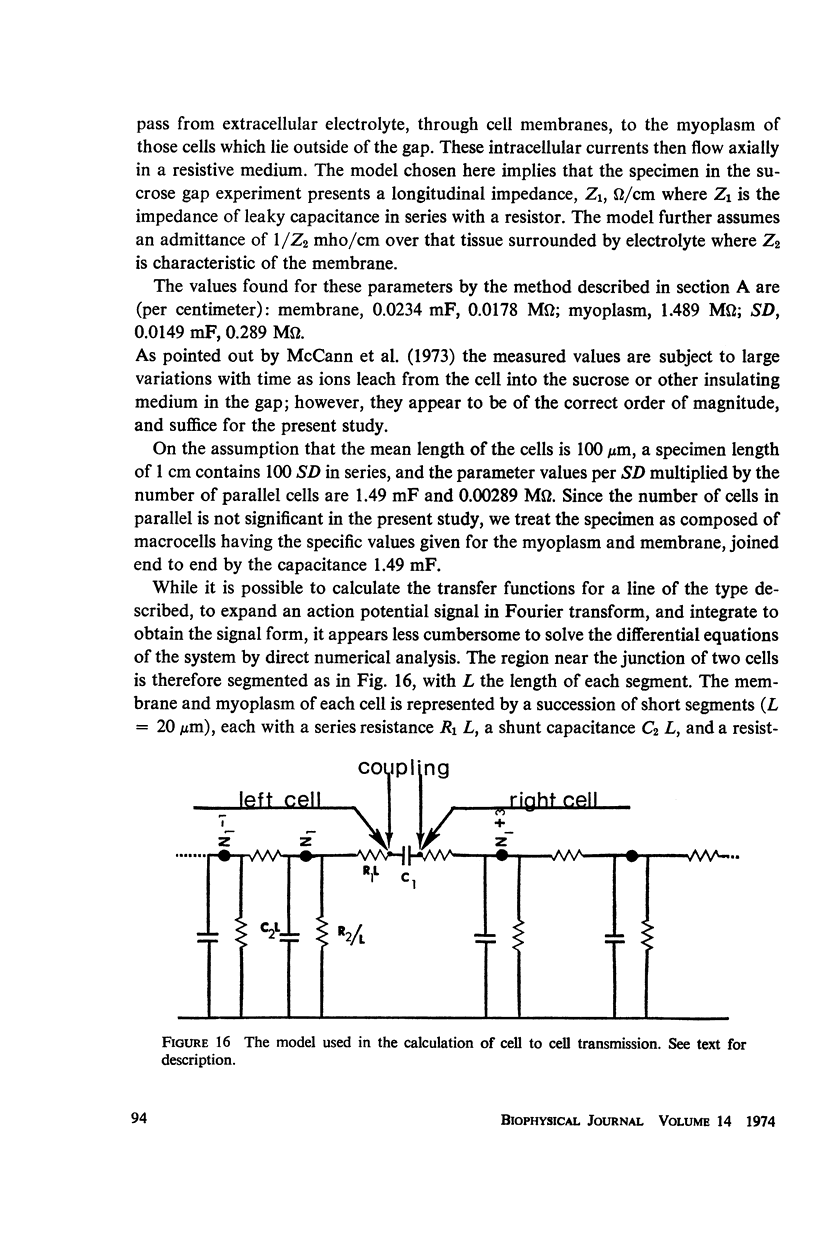
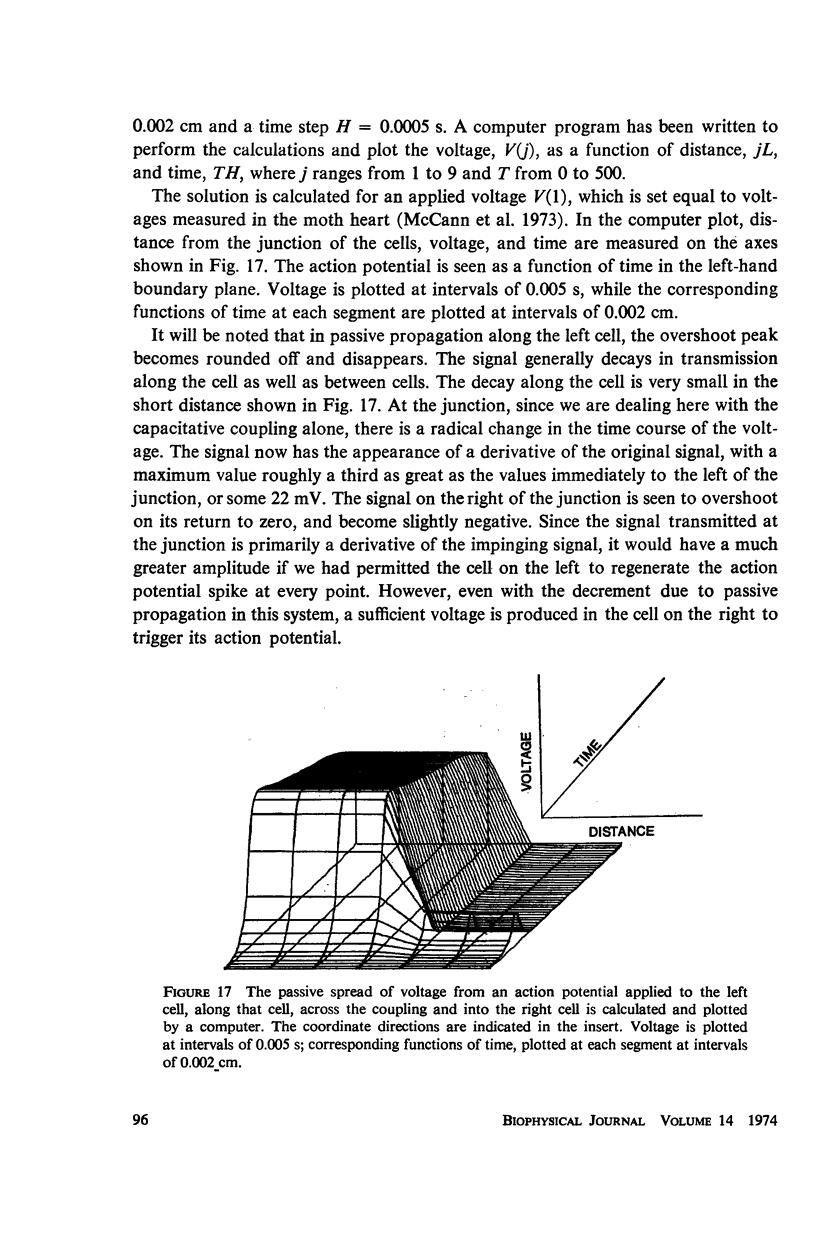
The impedance measured in a strip of heart tissue from the moth Hyalophora cecropia is fitted by circuit models of several configurations. The circuits include: (a) a single R-C circuit (b) a double R-C circuit (c) terminated transmission lines, and (d) a pattern of cells with cell-to-cell transmission paths. The last of these is found to give the best fit. Calculation of the model impedances and optimization of element values are performed by a computer. The possibility that the mechanism of cell-to-cell transmission may be capacitative rather than conductive is explored using values of capacitance derived from the circuit models to calculate the effect of capacitative coupling alone on signal transmission. The calculations show that sufficient voltage can be transmitted from the excited cell to an adjacent cell to effect excitation.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barr L. Electrical transmission between the cells of vertebrate cardiac muscle. Experientia Suppl. 1969;15:102–110. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6800-6_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWEY M. M., BARR L. A STUDY OF THE STRUCTURE AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE NEXUS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Dec;23:553–585. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.3.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
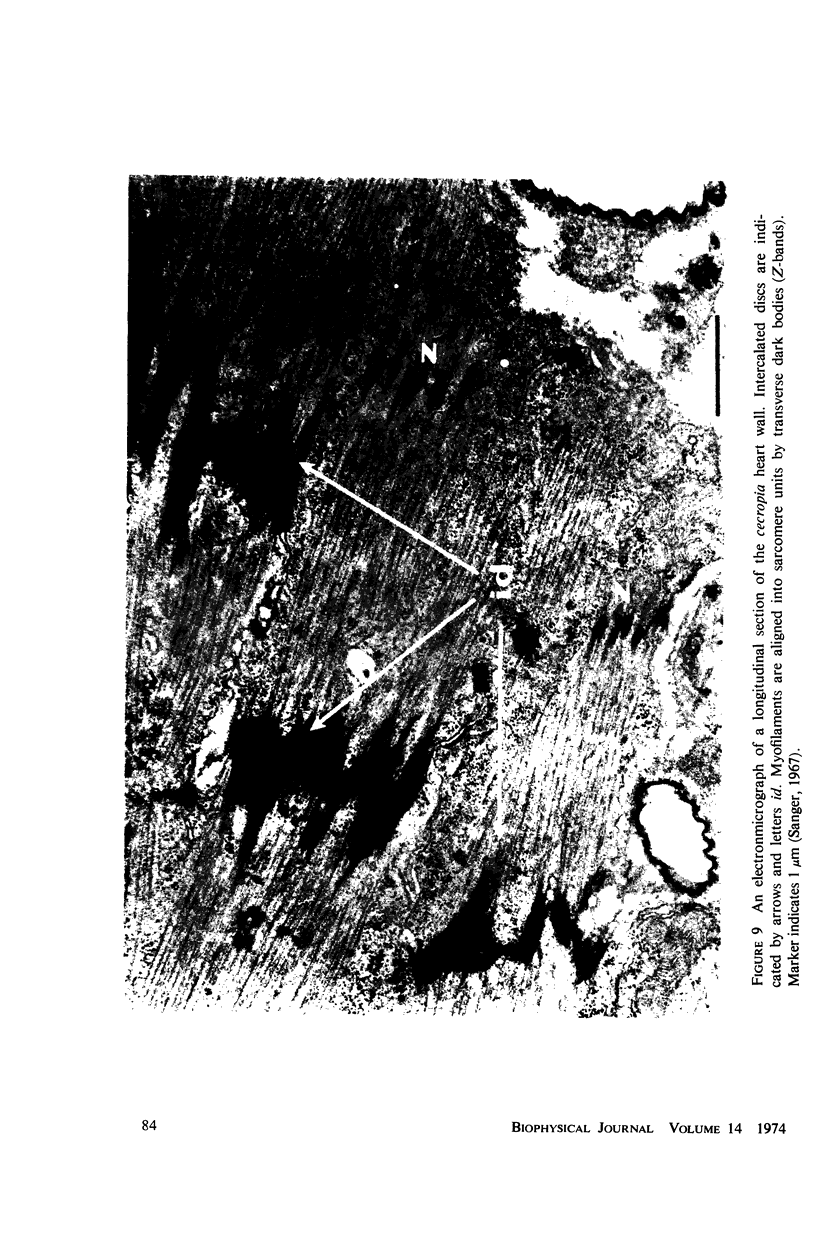
- Sanger J. W., McCann F. V. Ultrastructure of the myocardium of the moth, Hyalophora cecropia. J Insect Physiol. 1968 Aug;14(8):1105–1111. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(68)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARR M., SPERELAKIS N. WEAK ELECTROTONIC INTERACTION BETWEEN CONTIGUOUS CARDIAC CELLS. Am J Physiol. 1964 Sep;207:691–700. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.3.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]