Abstract
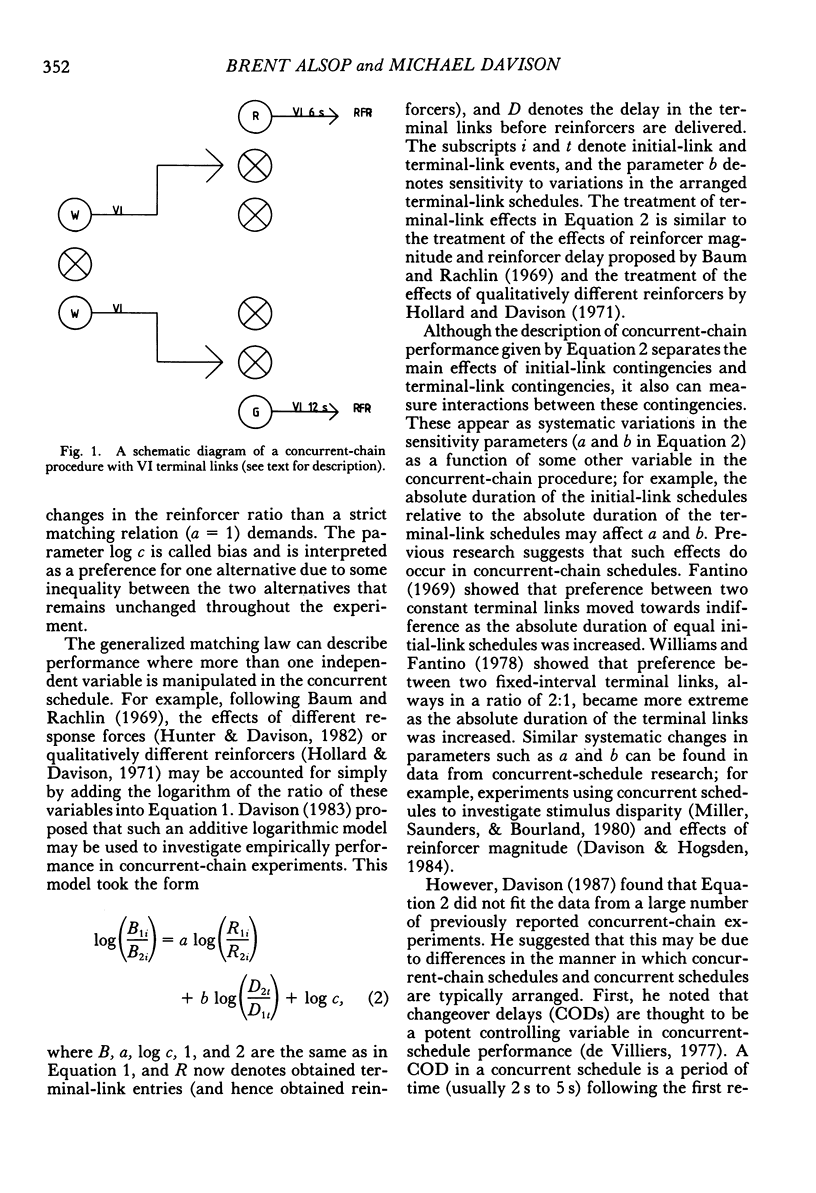
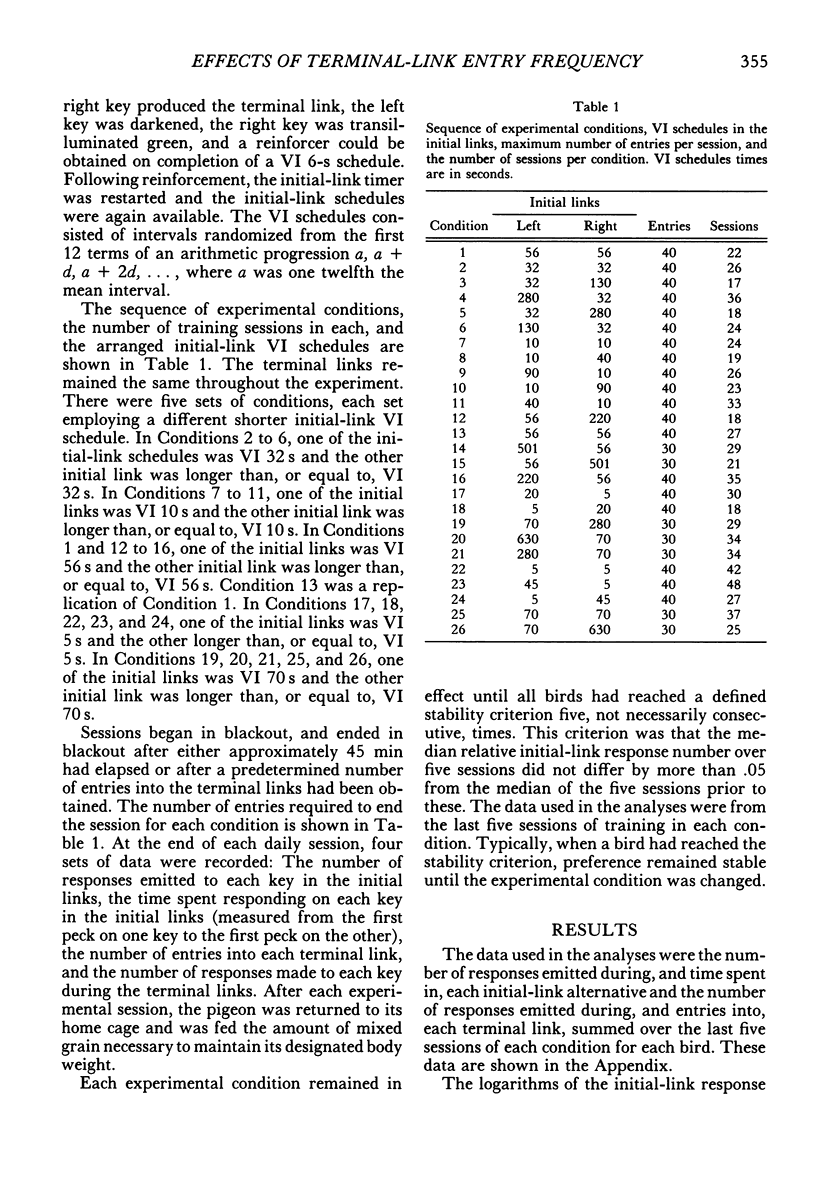
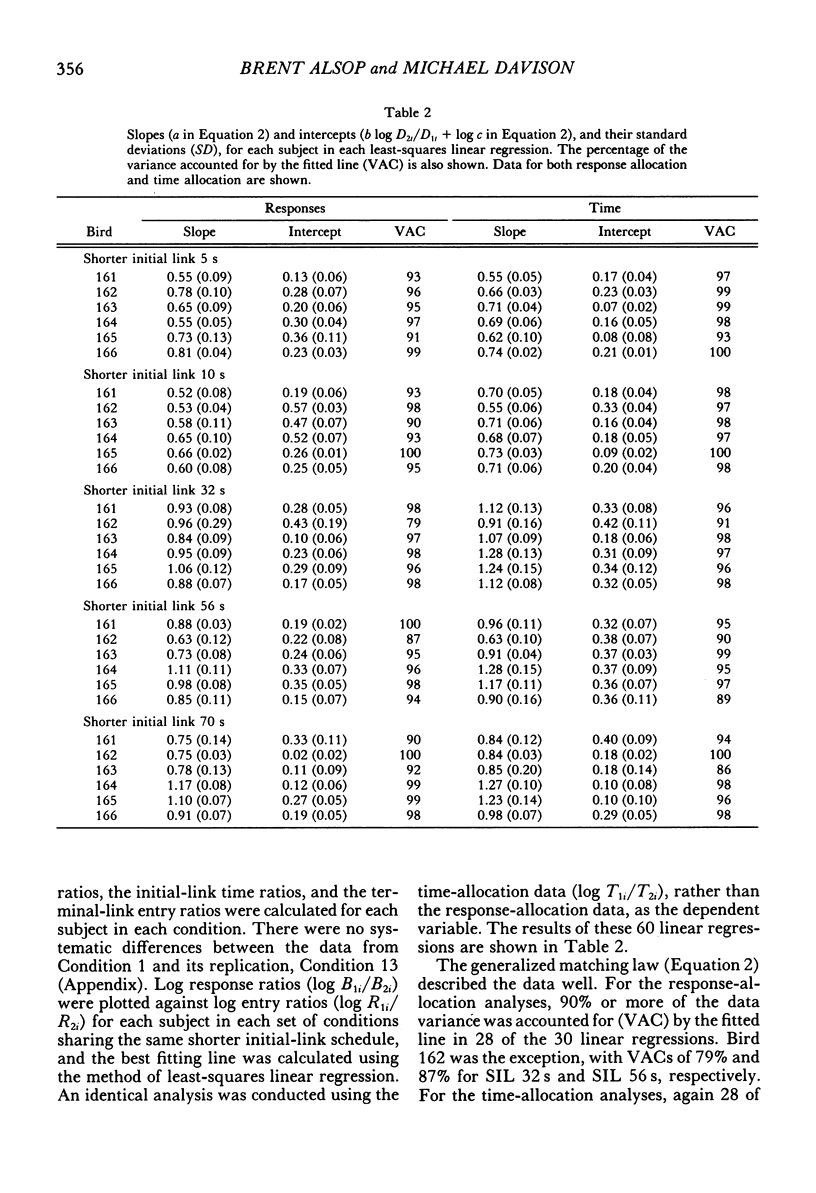
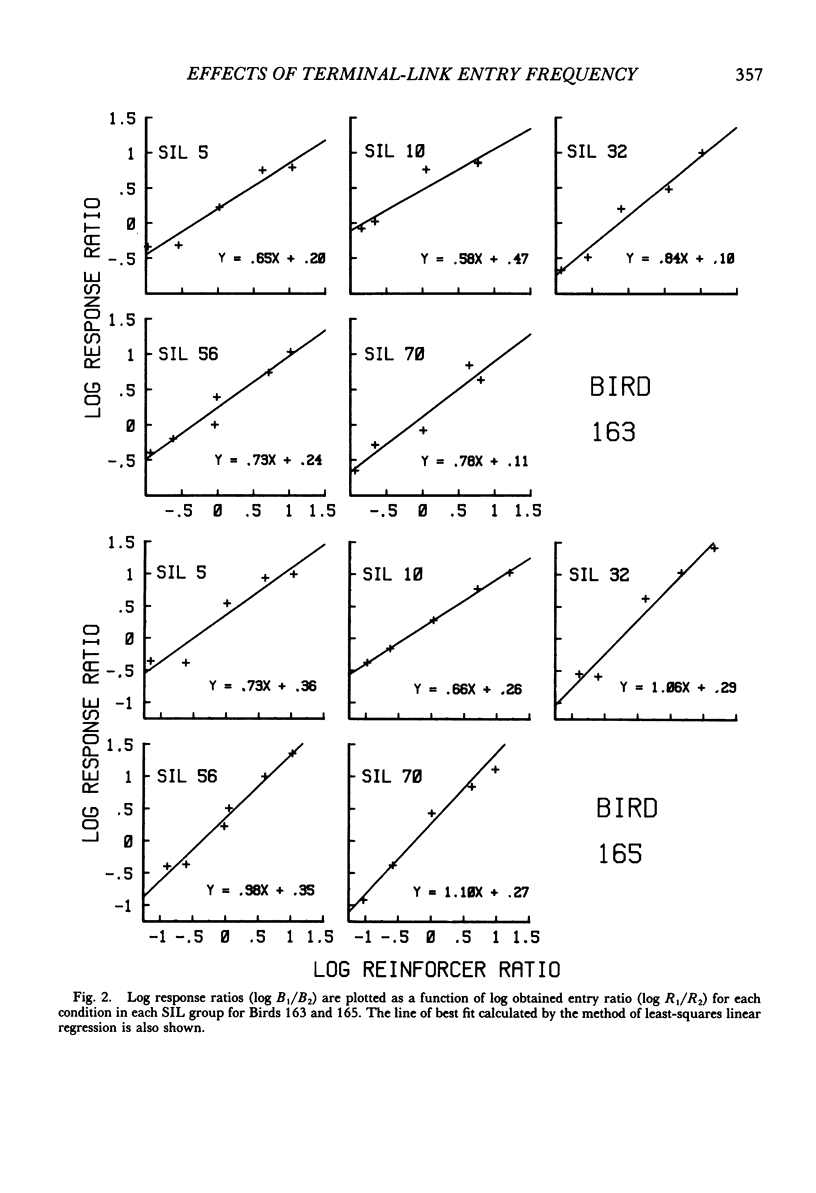
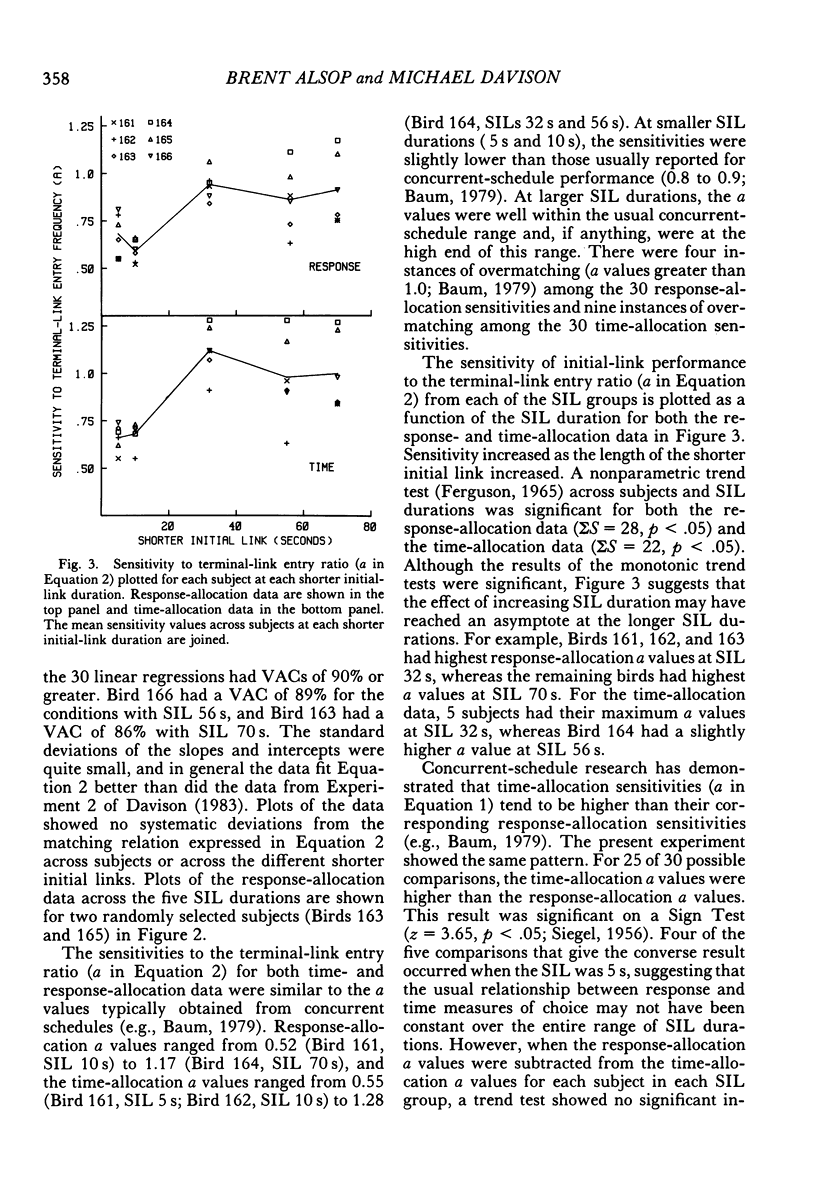
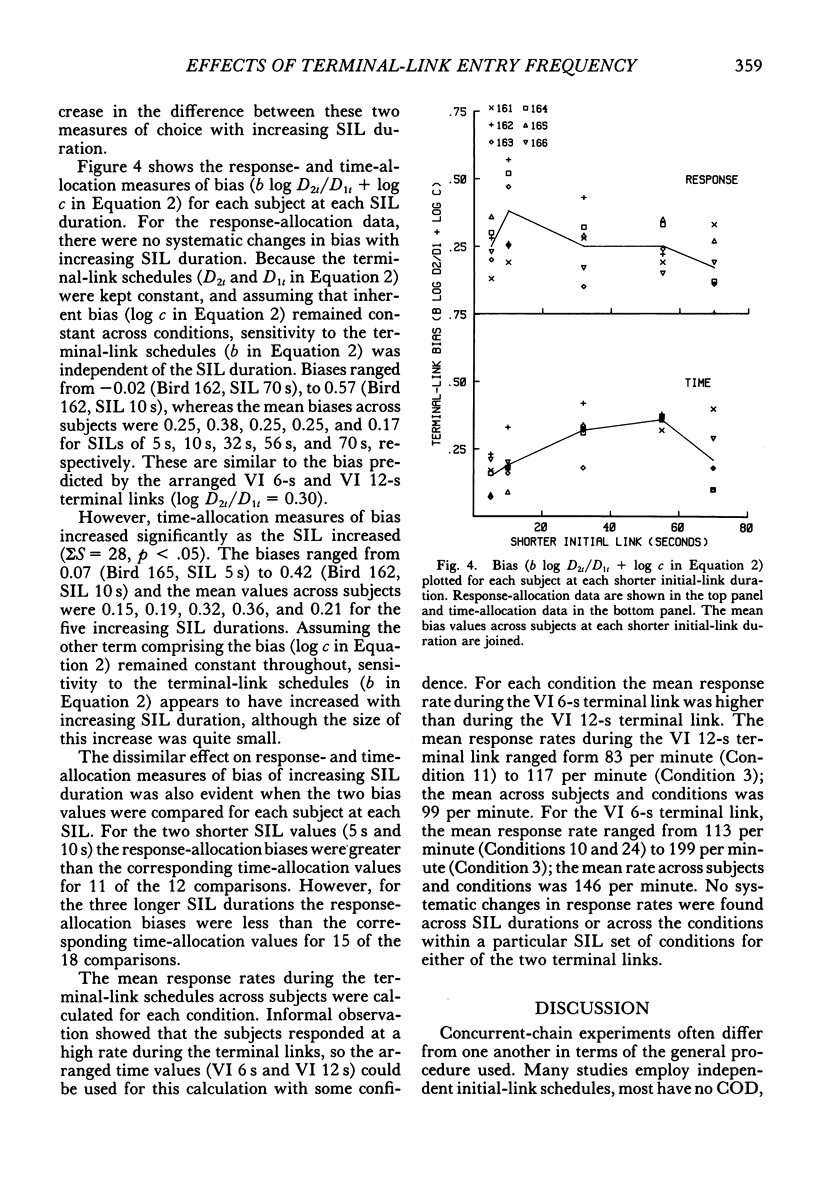
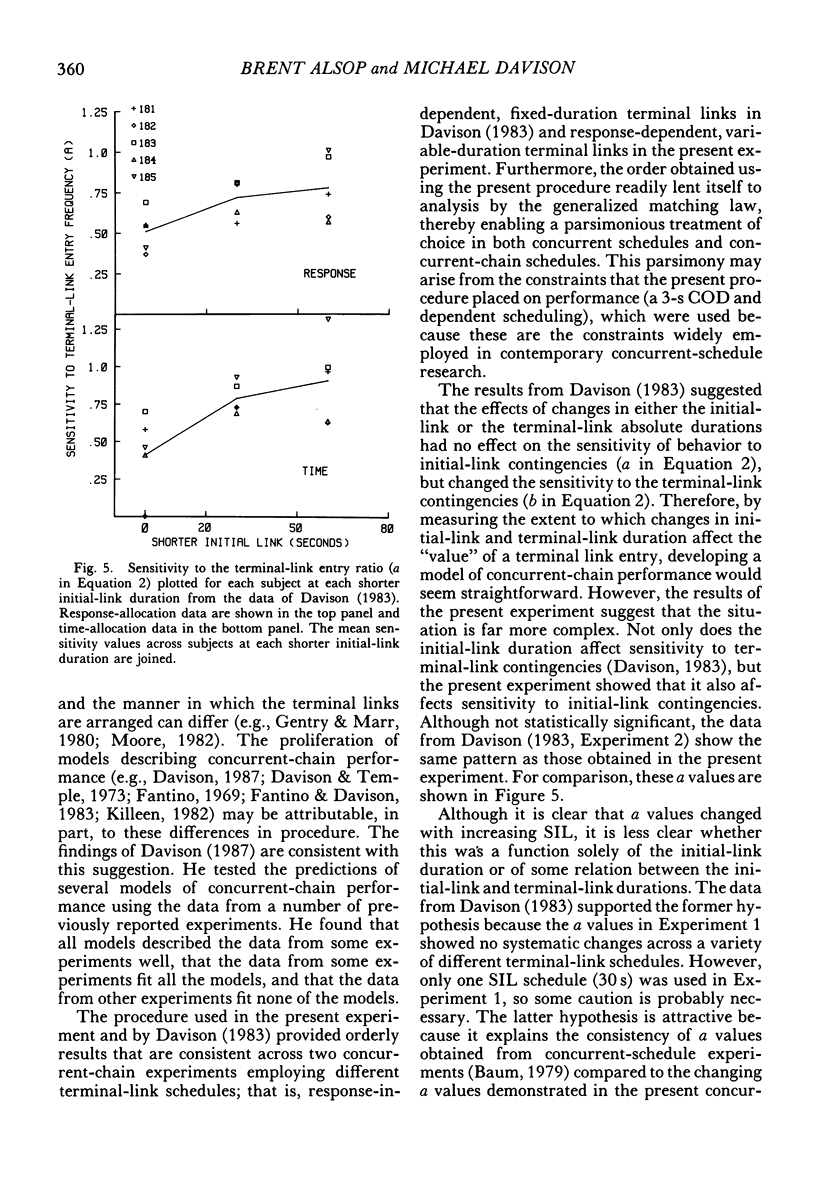
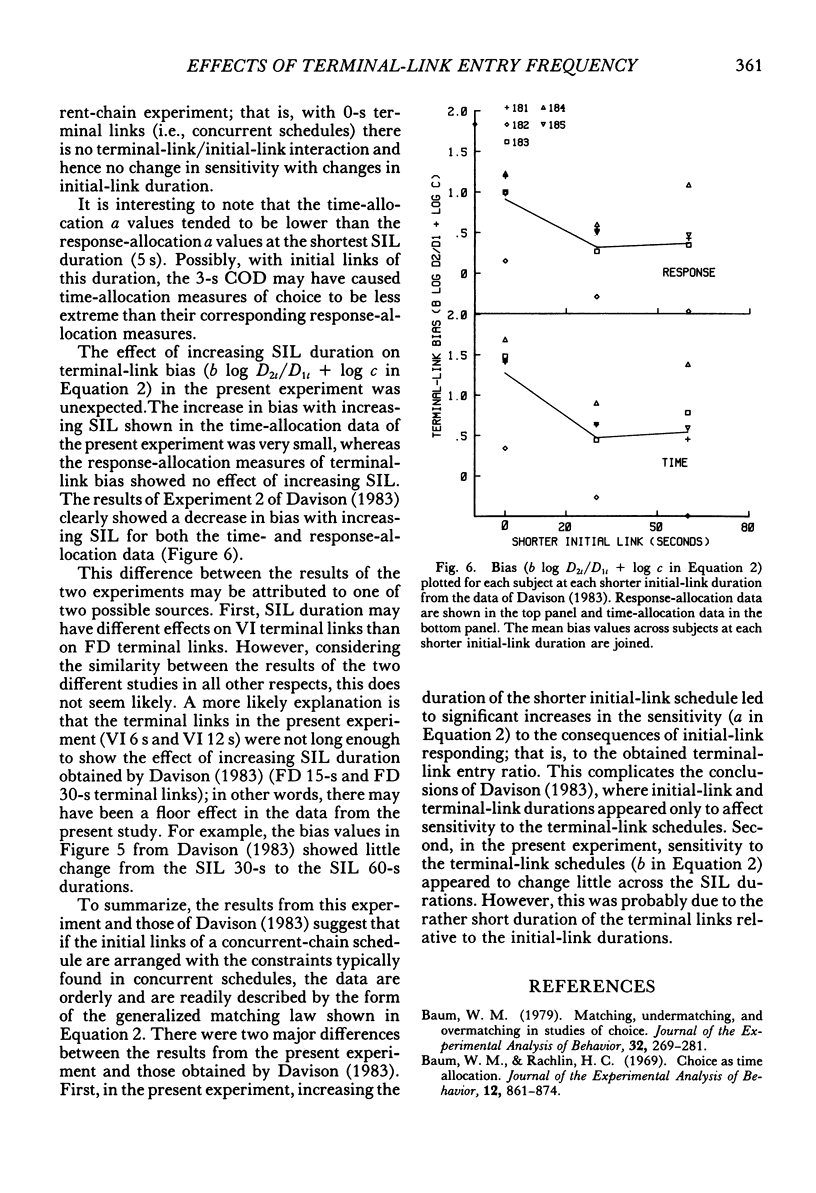
Six pigeons were trained in a concurrent-chain procedure with constant variable-interval 6-s variable-interval 12-s terminal links. Five groups of conditions were arranged. Within a group of conditions, the duration of one initial-link schedule was held constant and the duration of the other initial link was varied. The duration of the varied initial link was always longer than, or equal to, the constant initial-link duration. The duration of the shorter initial link was varied across groups of conditions from 5 s to 70 s. The data from each group were well described by the generalized matching law. Sensitivity (a) to the terminal-link entry ratio increased as the shorter initial-link duration increased, but appeared to reach an asymptote at shorter initial-link durations greater than 32 s. Terminal-link bias did not change with changes in shorter initial-link duration for the response-allocation data, but showed a small increase with increasing shorter initial-link duration for the time-allocation data.
Keywords: concurrent-chain schedules, generalized matching law, sensitivity to entry frequency, bias, response allocation, time allocation, key peck, pigeons
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M. Matching, undermatching, and overmatching in studies of choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1979 Sep;32(2):269–281. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.32-269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M., Rachlin H. C. Choice as time allocation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):861–874. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C., Temple W. Preference for fixed-interval schedules: an alternative model. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):393–403. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. Bias and sensitivity to reinforcement in a concurrent-chain schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Jul;40(1):15–34. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.40-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M., Hogsden I. Concurrent variable-interval schedule performance: Fixed versus mixed reinforcer durations. J Exp Anal Behav. 1984 Mar;41(2):169–182. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1984.41-169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B., Fantino E. Choice for periodic schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jul;14(1):73–86. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E. Choice and rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):723–730. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Davison M. Choice: Some quantitative relations. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Jul;40(1):1–13. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.40-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Royalty P. A molecular analysis of choice on concurrent-chains schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1987 Jul;48(1):145–159. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1987.48-145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry G. D., Marr M. J. Choice and reinforcement delay. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Jan;33(1):27–37. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.33-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollard V., Davison M. C. Preference for qualitatively different reinforcers. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Nov;16(3):375–380. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter I., Davison M. Independence of response force and reinforcement rate on concurrent variable-interval schedule performance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 Mar;37(2):183–197. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.37-183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. R. Incentive theory: II. Models for choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 Sep;38(2):217–232. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.38-217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. Choice and multiple reinforcers. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 Jan;37(1):115–122. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.37-115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J. Delayed reinforcement versus reinforcement after a fixed interval. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 May;12(3):375–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman M. Delay and amount of reward in a concurrent chain. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 May;39(3):437–447. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires N., Fantino E. A model for choice in simple concurrent and concurrent-chains schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Jan;15(1):27–38. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs D. A., Pliskoff S. S. Concurrent responding with fixed relative rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):887–895. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A., Fantino E. Effects on choice of reinforcement delay and conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Jan;29(1):77–86. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


