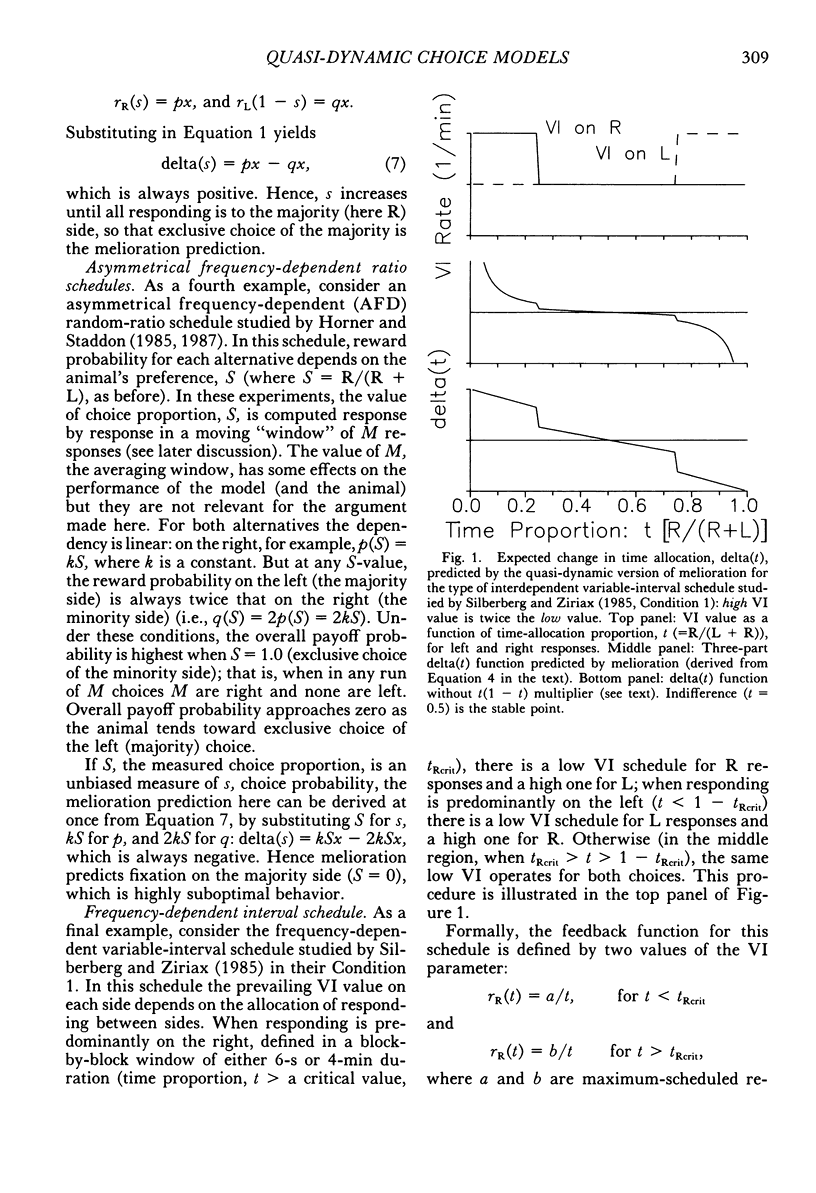
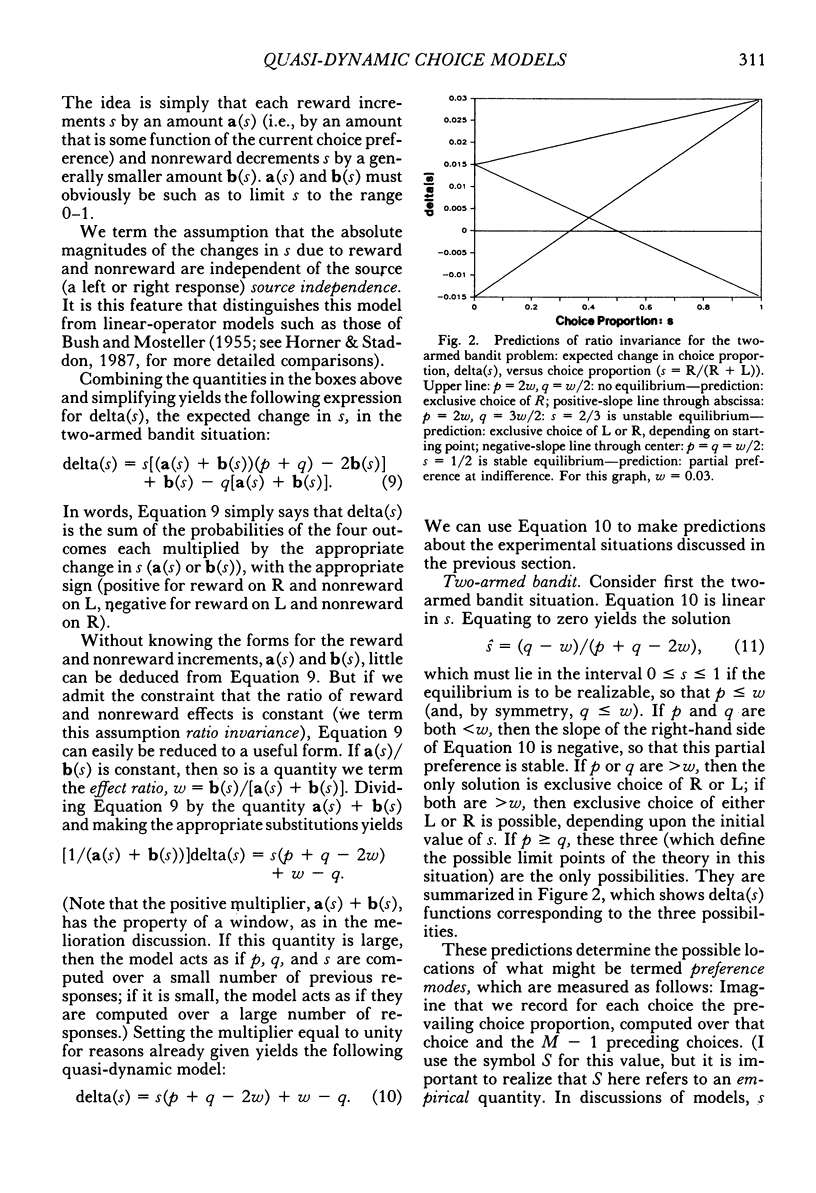
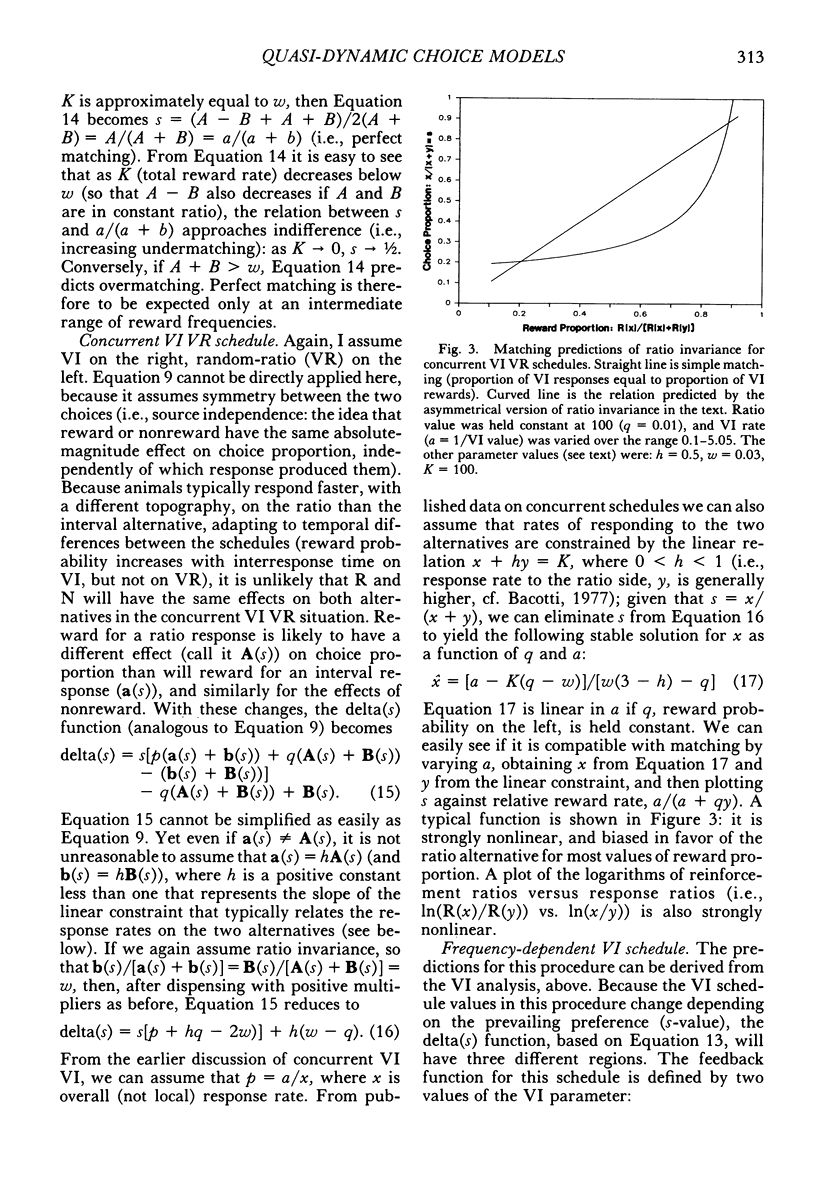
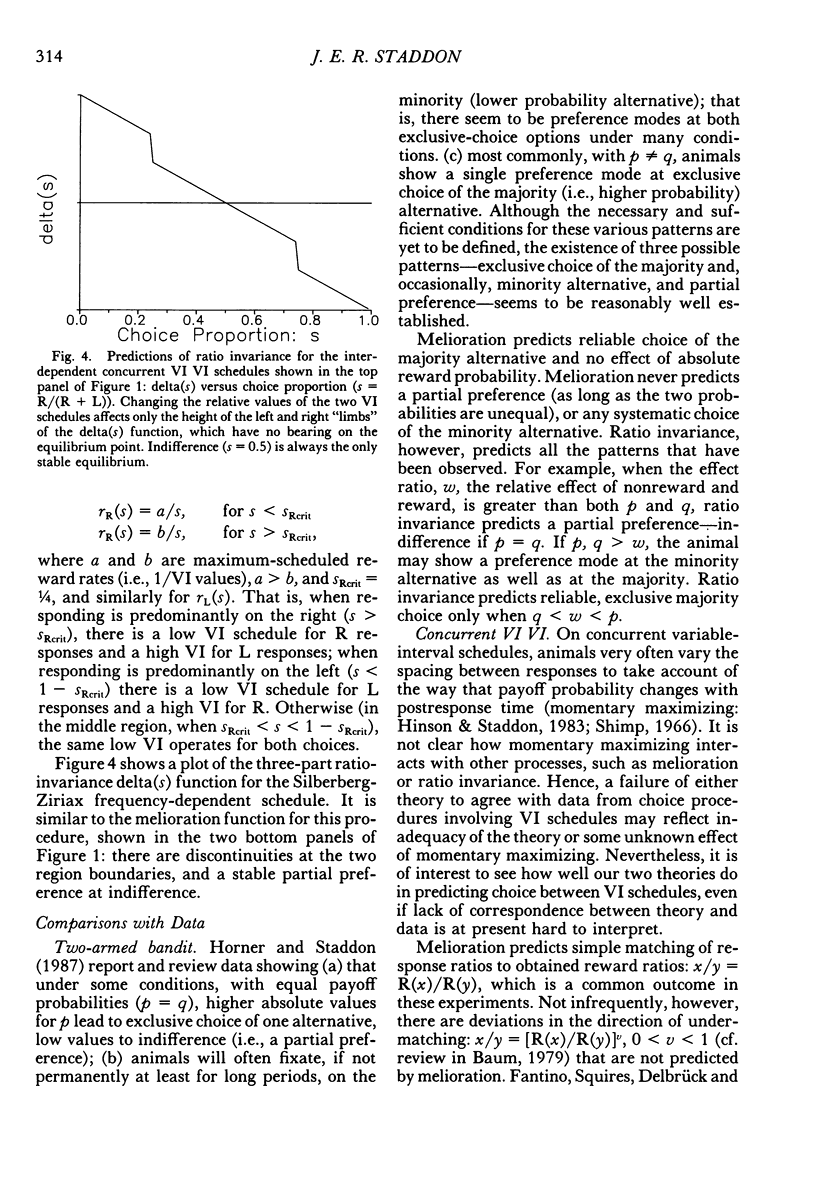
Abstract
There is continuing controversy about the behavioral process or processes that underlie the major regularities of free-operant choice such as molar matching and systematic deviations therefrom. A recent interchange between Vaughan and Silberberg and Ziriax concerned the relative merits of melioration, and a computer simulation of molecular maximizing. There are difficulties in evaluating theories expressed as computer programs because many arbitrary decisions must often be made in order to get the programs to operate. I therefore propose an alternative form of model that I term quasi-dynamic as a useful intermediate form of theory appropriate to our current state of knowledge about free-operant choice. Quasi-dynamic models resemble the game-theoretic analyses now commonplace in biology in that they can predict stable and unstable equilibria but not dynamic properties such as learning curves. It is possible to interpret melioration as a quasi-dynamic model. An alternative quasi-dynamic model for probabilistic choice, ratio invariance, has been proposed by Horner and Staddon. The present paper compares the predictions of melioration and ratio invariance for five experimental situations: concurrent variable-interval variable-interval schedules, concurrent variable-interval variable-ratio schedules, the two-armed bandit (concurrent random-ratio schedules), and two types of frequency-dependent schedule. Neither approach easily explains all the data, but ratio invariance seems to provide a better picture of pigeons' response to probabilistic choice procedures. Ratio invariance is also more adaptive (less susceptible to “traps”) and closer to the original expression of the law of effect than pure hill-climbing processes such as momentary maximizing and melioration, although such processes may come in to play on more complex procedures that provide opportunities for temporal discrimination.
Keywords: Bush-Mosteller, melioration, momentary maximizing, molecular maximizing, ratio invariance, source independence, matching
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alsop B., Elliffe D. Concurrent-schedule performance: Effects of relative and overall reinforcer rate. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 Jan;49(1):21–36. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.49-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacotti A. V. Matching under concurrent fixed-ratio variable-interval schedules of food presentation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Jan;27(1):171–182. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. Matching, undermatching, and overmatching in studies of choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1979 Sep;32(2):269–281. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.32-269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Reynolds G. S. A quantitative analysis of the responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3 Suppl):327–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-s327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Squires N., Delbrück N., Peterson C. Choice behavior and the accessibility of the reinforcer. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):35–43. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J., Heyman G. M. Is matching compatible with reinforcement maximization on concurrent variable interval variable ratio? J Exp Anal Behav. 1979 Mar;31(2):209–223. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.31-209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinson J. M., Staddon J. E. Matching, maximizing, and hill-climbing. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Nov;40(3):321–331. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.40-321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May R. M. Simple mathematical models with very complicated dynamics. Nature. 1976 Jun 10;261(5560):459–467. doi: 10.1038/261459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H. A molar theory of reinforcement schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Nov;30(3):345–360. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.30-345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMON H. A. Rational choice and the structure of the environment. Psychol Rev. 1956 Mar;63(2):129–138. doi: 10.1037/h0042769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P. Probabilistically reinforced choice behavior in pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jul;9(4):443–455. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberberg A., Ziriax J. M. Molecular maximizing characterizes choice on Vaughan's (1981) procedure. J Exp Anal Behav. 1985 Jan;43(1):83–96. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1985.43-83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. E., Hinson J. M., Kram R. Optimal choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 May;35(3):397–412. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.35-397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan W. Choice: A local analysis. J Exp Anal Behav. 1985 May;43(3):383–405. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1985.43-383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan W. Melioration, matching, and maximization. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 Sep;36(2):141–149. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.36-141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan W. Reply to silberberg and ziriax. J Exp Anal Behav. 1987 Sep;48(2):333–340. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1987.48-333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


