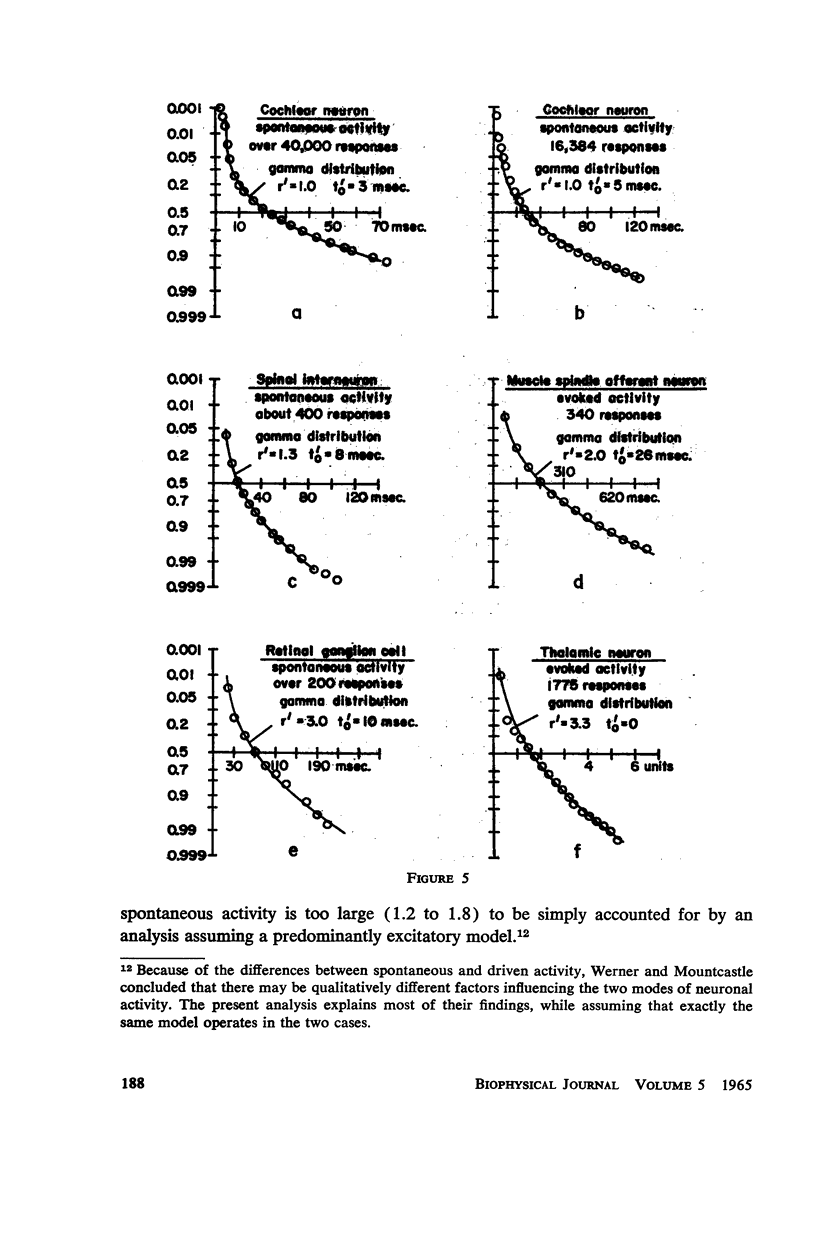
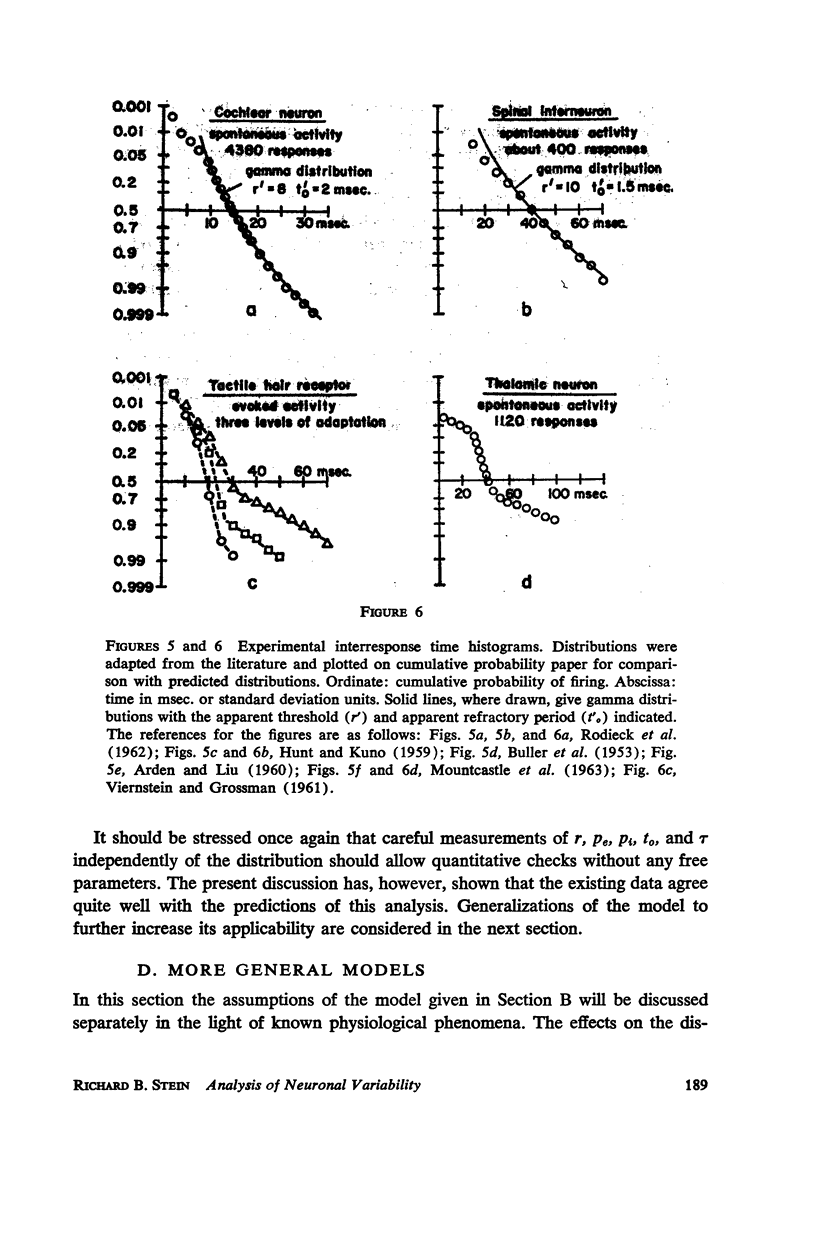
Abstract
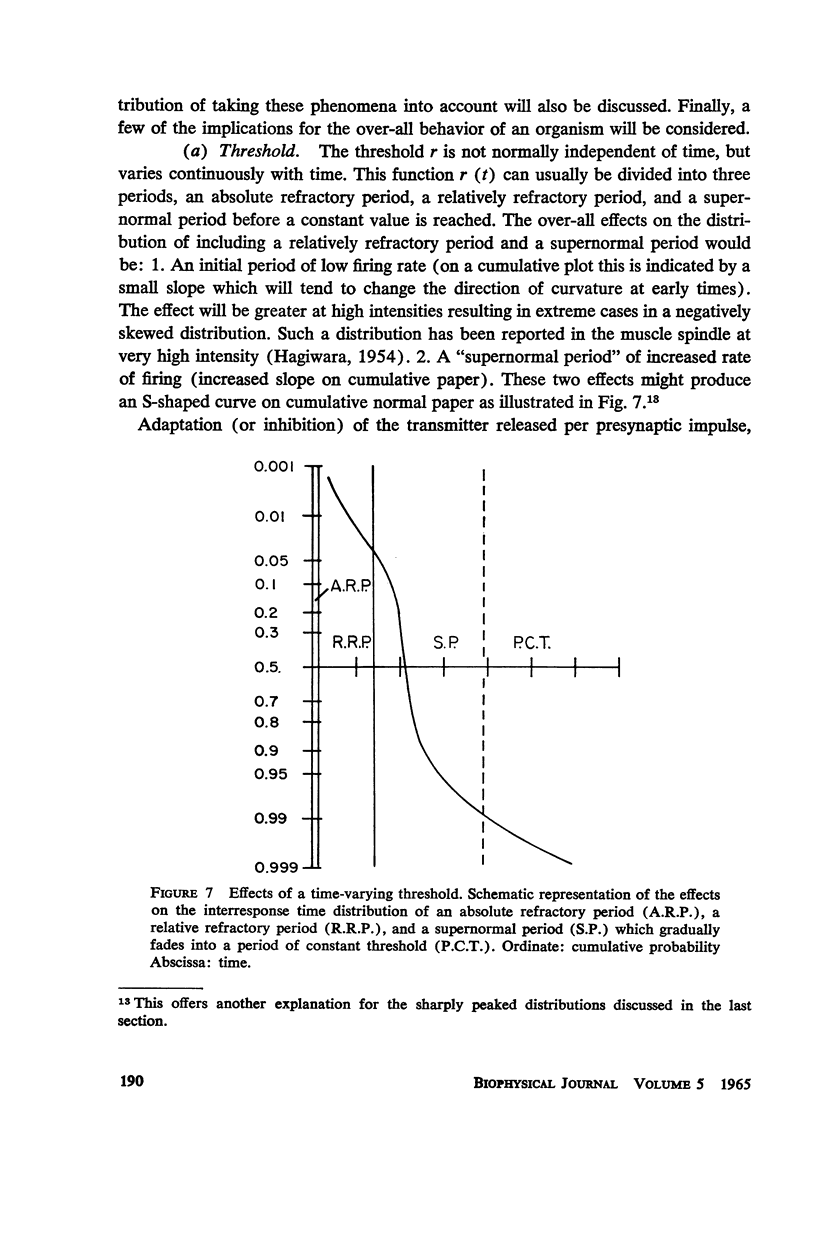
A simple neuronal model is assumed in which, after a refractory period, excitatory and inhibitory exponentially decaying inputs of constant size occur at random intervals and sum until a threshold is reached. The distribution of time intervals between successive neuronal firings (interresponse time histogram), the firing rate as a function of input frequency, the variability in the time course of depolarization from trial to trial, and the strength-duration curve are derived for this model. The predictions are compared with data from the literature and good qualitative agreement is found. All parameters are experimentally measurable and a direct test of the theory is possible with present techniques. The assumptions of the model are relaxed and the effects of such experimentally found phenomena as relative refractory and supernormal periods, adaptation, potentiation, and rhythmic slow potentials are discussed. Implications for gross behavior studies are considered briefly.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARDEN G., LIU Y. M. Some types of response of single cells in the rabbit lateral geniculate body to stimulation of the retina by light and to electrical stimulation of the optic nerve. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Jan 30;48:36–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKMAN J. G., GINSBORG B. L., RAY C. On the quantal release of the transmitter at a sympathetic synapse. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167:402–415. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., NICHOLLS J. G., STROM G. Spontaneous fluctuations of excitability in the muscle spindle of the frog. J Physiol. 1953 Nov 28;122(2):409–418. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUORTES M. G., MANTEGAZZINI F. Interpretation of the repetitive firing of nerve cells. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Jul;45:1163–1179. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.6.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERSTEIN G. L., MANDELBROT B. RANDOM WALK MODELS FOR THE SPIKE ACTIVITY OF A SINGLE NEURON. Biophys J. 1964 Jan;4:41–68. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(64)86768-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., KERNELL D., SHORTESS G. K. QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF REPETITIVE FIRING OF MAMMALIAN MOTONEURONES, CAUSED BY INJECTED CURRENTS. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:911–931. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., RENKIN B. Net depolarization and discharge rate of motoneurones, as measured by recurrent inhibition. J Physiol. 1961 Oct;158:461–475. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S. Analysis of interval fluctuation of the sensory nerve impulse. Jpn J Physiol. 1954 Sep 1;4(3):234–240. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.4.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C., KUNO M. Properties of spinal interneurones. J Physiol. 1959 Sep 2;147:346–363. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B. Depolarization of sensory terminals and the initiation of impulses in the muscle spindle. J Physiol. 1950 Oct 16;111(3-4):261–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1950.sp004479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. A STUDY OF SPONTANEOUS MINIATURE POTENTIALS IN SPINAL MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:389–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., FITZHUGH R., BARLOW H. B. Maintained activity in the cat's retina in light and darkness. J Gen Physiol. 1957 May 20;40(5):683–702. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.5.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS P. B. THE RESPONSE OF DE-EFFERENTED MUSCLE SPINDLE RECEPTORS TO STRETCHING AT DIFFERENT VELOCITIES. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:660–678. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUNTCASTLE V. B., POGGIO G. F., WERNER G. THE RELATION OF THALAMIC CELL RESPONSE TO PERIPHERAL STIMULI VARIED OVER AN INTENSIVE CONTINUUM. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Sep;26:807–834. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.5.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. H. The response of a single end organ. J Physiol. 1931 Jan 21;71(1):64–110. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1931.sp002718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODIECK R. W., KIANG N. Y., GERSTEIN G. L. Some quantitative methods for the study of spontaneous activity of single neurons. Biophys J. 1962 Jul;2:351–368. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86860-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERNER G., MOUNTCASTLE V. B. THE VARIABILITY OF CENTRAL NEURAL ACTIVITY IN A SENSORY SYSTEM, AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR THE CENTRAL REFLECTION OF SENSORY EVENTS. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Nov;26:958–977. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.6.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


