Abstract
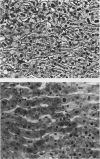
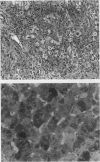
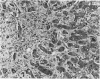
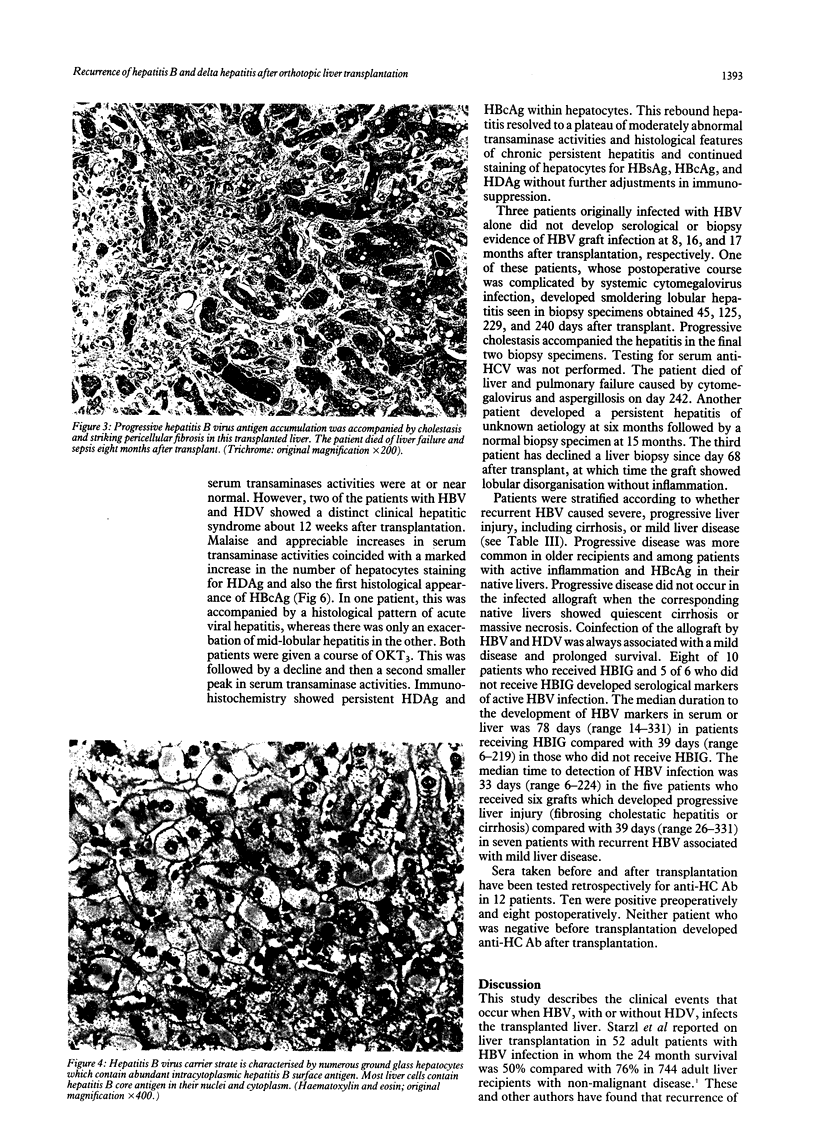
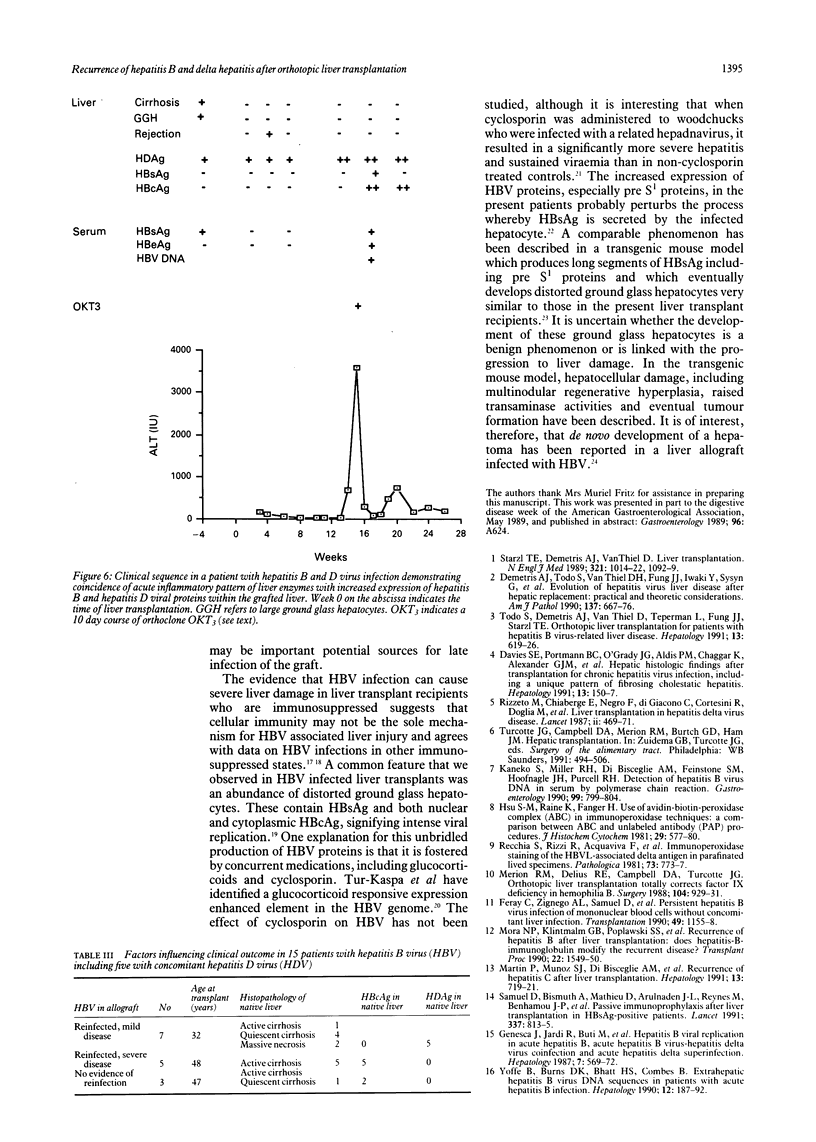
The clinical course of 10 liver transplant recipients who had hepatitis B virus (HBV) and five recipients with HBV and D (delta) infection before transplantation is described. Six patients who underwent eight transplants died. The estimated one and two year survival rates in patients with HBV only before transplantation were 74% and 67% respectively. The estimated one and two year survival in patients with HBV and HDV infection beforehand was 100%. Graft infection by HBV occurred in 8 of 10 patients infected with HBV only; and in 4 of 5 patients with previous HBV and HDV infection. There was a widely variable time from transplantation to the appearance of HBV markers in liver or serum, ranging from 6-331 days. Hepatitis D antigen (HDAg) appeared in three grafts very rapidly after transplantation at 4, 8, and 37 days respectively. Graft infection by HBV was accompanied by significant liver injury in six allografts in five recipients. In particular, there was a striking morphological appearance in five infected livers in which the hepatocytes became progressively enlarged and distorted as they accumulated huge amounts of hepatitis B surface and core antigens (HBsAg, HBcAg). These features were accompanied by pericellular fibrosis and cholestasis but little associated inflammation. This syndrome carried a poor prognosis. A gradual progression to cirrhosis occurred in one additional liver. Finally, recurrent HBV infection was a principal or a contributing factor in all deaths. The presence of HBcAg and inflammation in he native liver increased the risk of HBV induced tissue damaged in the graft whereas HDV infection in the host liver seemed to reduce the risk of significant HBV induced tissue damage in the allograft. These data suggest that post transplant HBV infection is accompanied by a variety of changes in the liver allograft, some of which are unique to the transplanted liver and may result in impaired allograft function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davies S. E., Portmann B. C., O'Grady J. G., Aldis P. M., Chaggar K., Alexander G. J., Williams R. Hepatic histological findings after transplantation for chronic hepatitis B virus infection, including a unique pattern of fibrosing cholestatic hepatitis. Hepatology. 1991 Jan;13(1):150–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degos F., Lugassy C., Degott C., Debure A., Carnot F., Theirs V., Tiollais P., Kreis H., Brechot C. Hepatitis B virus and hepatitis B-related viral infection in renal transplant recipients. A prospective study of 90 patients. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jan;94(1):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90623-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demetris A. J., Todo S., Van Thiel D. H., Fung J. J., Iwaki Y., Sysyn G., Ming W., Trager J., Starzl T. E. Evolution of hepatitis B virus liver disease after hepatic replacement. Practical and theoretical considerations. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):667–676. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Féray C., Zignego A. L., Samuel D., Bismuth A., Reynes M., Tiollais P., Bismuth H., Brechot C. Persistent hepatitis B virus infection of mononuclear blood cells without concomitant liver infection. The liver transplantation model. Transplantation. 1990 Jun;49(6):1155–1158. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199006000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genesca J., Jardi R., Buti M., Vives L., Prat S., Esteban J. I., Esteban R., Guardia J. Hepatitis B virus replication in acute hepatitis B, acute hepatitis B virus-hepatitis delta virus coinfection and acute hepatitis delta superinfection. Hepatology. 1987 May-Jun;7(3):569–572. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Miller R. H., Di Bisceglie A. M., Feinstone S. M., Hoofnagle J. H., Purcell R. H. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum by polymerase chain reaction. Application for clinical diagnosis. Gastroenterology. 1990 Sep;99(3):799–804. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90971-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luketic V. A., Shiffman M. L., McCall J. B., Posner M. P., Mills A. S., Carithers R. L., Jr Primary hepatocellular carcinoma after orthotopic liver transplantation for chronic hepatitis B infection. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Feb 1;114(3):212–213. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-3-212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Muñoz S. J., Di Bisceglie A. M., Rubin R., Waggoner J. G., Armenti V. T., Moritz M. J., Jarrell B. E., Maddrey W. C. Recurrence of hepatitis C virus infection after orthotopic liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1991 Apr;13(4):719–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merion R. M., Delius R. E., Campbell D. A., Jr, Turcotte J. G. Orthotopic liver transplantation totally corrects factor IX deficiency in hemophilia B. Surgery. 1988 Nov;104(5):929–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mora N. P., Klintmalm G. B., Poplawski S. S., Cofer J. B., Husberg B. S., Gonwa T. A., Goldstein R. M. Recurrence of hepatitis B after liver transplantation: does hepatitis-B-immunoglobulin modify the recurrent disease? Transplant Proc. 1990 Aug;22(4):1549–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Inhibition of secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen by a related presurface polypeptide. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1388–1391. doi: 10.1126/science.3787251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recchia S., Rizzi R., Acquaviva F., Rizzetto M., Tison V., Bonino F., Verme G. Immunoperoxidase staining of the HBV-associated delta antigen in paraffinated liver specimens. Pathologica. 1981 Sep-Oct;73(1027):773–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzetto M., Macagno S., Chiaberge E., Verme G., Negro F., Marinucci G., di Giacomo C., Alfani D., Cortesini R., Milazzo F. Liver transplantation in hepatitis delta virus disease. Lancet. 1987 Aug 29;2(8557):469–471. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91789-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roingeard P., Lu S. L., Sureau C., Freschlin M., Arbeille B., Essex M., Romet-Lemonne J. L. Immunocytochemical and electron microscopic study of hepatitis B virus antigen and complete particle production in hepatitis B virus DNA transfected HepG2 cells. Hepatology. 1990 Feb;11(2):277–285. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Demetris A. J., Van Thiel D. Liver transplantation (1). N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 12;321(15):1014–1022. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910123211505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todo S., Demetris A. J., Van Thiel D., Teperman L., Fung J. J., Starzl T. E. Orthotopic liver transplantation for patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver disease. Hepatology. 1991 Apr;13(4):619–626. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tur-Kaspa R., Burk R. D., Shaul Y., Shafritz D. A. Hepatitis B virus DNA contains a glucocorticoid-responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1627–1631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Chura C. M., Roll F. J., Maddrey W. C. Serial studies of hepatitis-associated antigen and antibody in patients receiving antitumor chemotherapy for myeloproliferative and lymphoproliferative disorders. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jan;68(1):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoffe B., Burns D. K., Bhatt H. S., Combes B. Extrahepatic hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in patients with acute hepatitis B infection. Hepatology. 1990 Aug;12(2):187–192. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]