Abstract
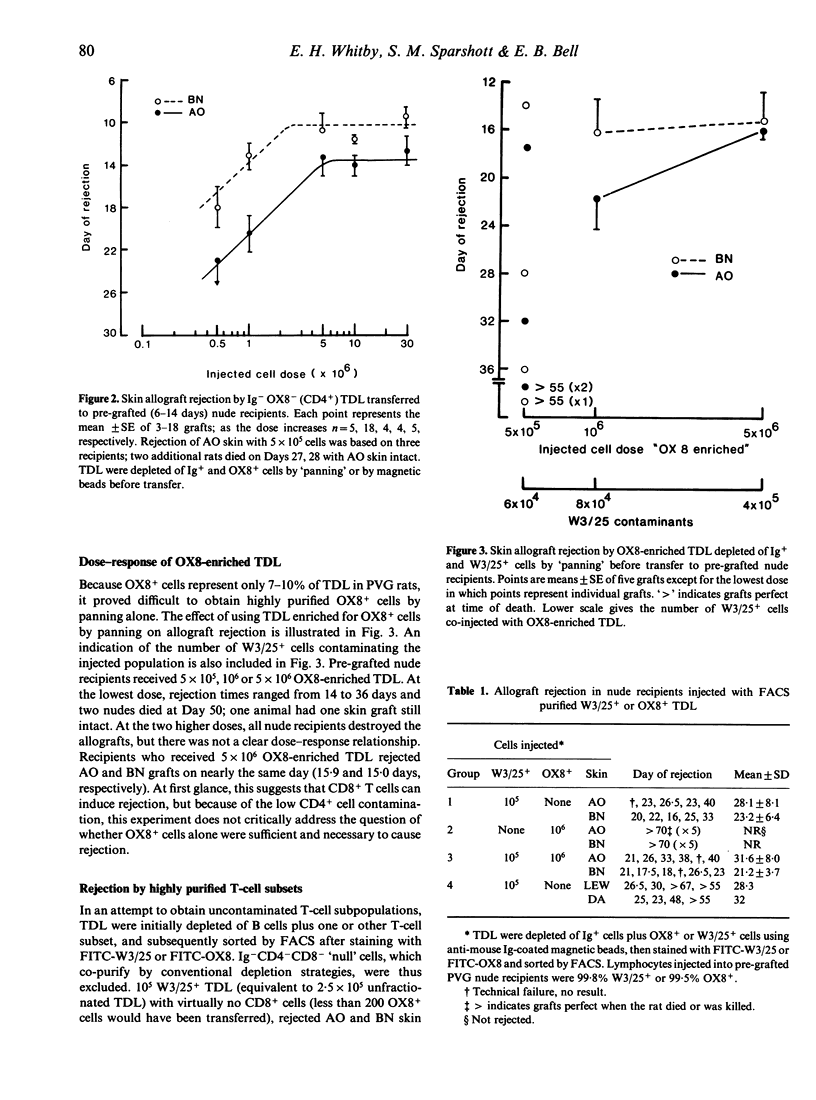
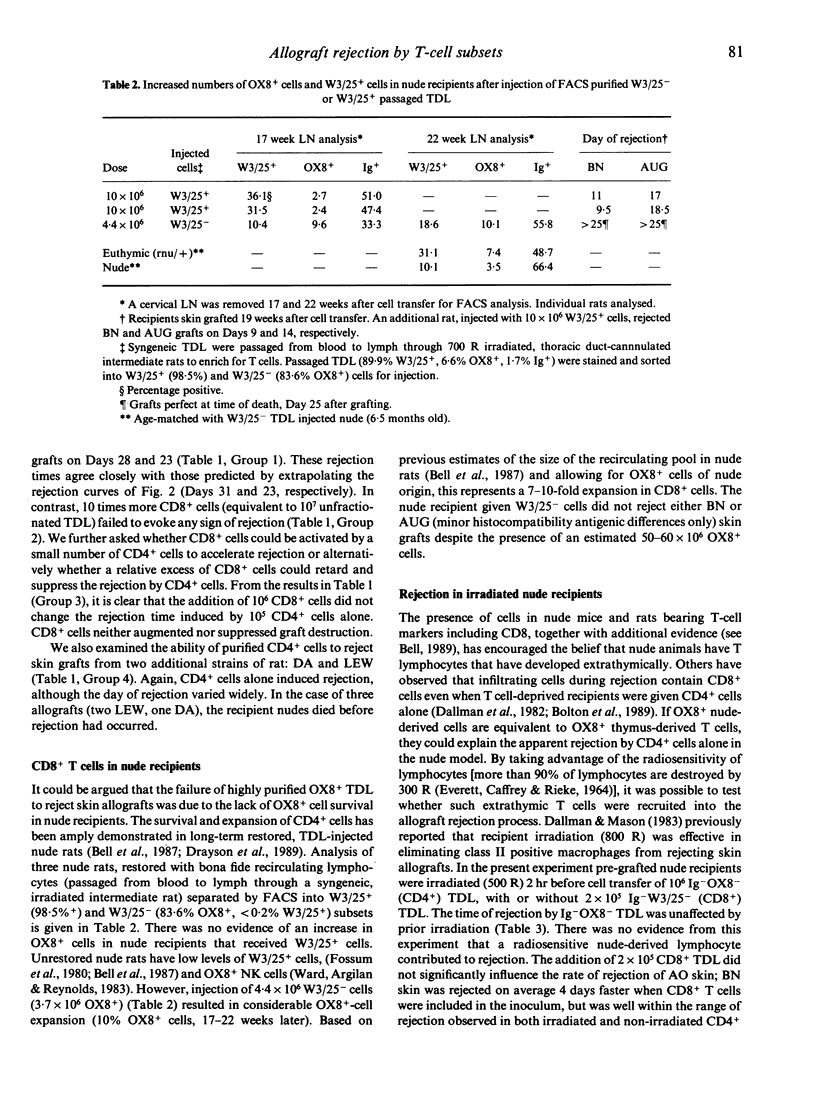
PVG.rnu/rnu nude rats were pre-grafted with two allogeneic skin grafts, AO(RTlu) and BN(RTln), 6-14 days in advance of cell transfer. Cellular requirements for rejection were established by transferring graded numbers of B cell-depleted (Ig-) thoracic duct lymphocytes (TDL) or purified W3/25+ (CD4+) or OX8+ (CD8+) TDL subsets. Allografts were rejected by 10(5) to 5 x 10(6) Ig- TDL in a dose-dependent fashion. A similar dose-response relationship was found by transferring 5 x 10(5) to 5 x 10(6) Ig- OX8- TDL (purified by depletion of B cells and OX8+ cells). Larger numbers of Ig- OX8- TDL (10-30 x 10(6)) did not significantly accelerate rejection. W3/25+ TDL alone (10(5)), highly purified by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS), were sufficient to induce allograft rejection in this athymic nude rat model. In contrast, 10 times more FACS purified OX8+ TDL (10(6)) were unable to initiate skin graft rejection despite the complete class I and class II MHC incompatibilities. Furthermore, the addition of 10(6) OX8+ cells did not accelerate or retard the rejection induced by 10(5) W3/25+ cells alone. Pre-grafted nude recipients, irradiated (500 R) 2 hr before W3/25+ TDL injection, in order to eliminate putative nude T cells, rejected allografts on the same day as unirradiated controls. We conclude that when confronted with complete MHC disparities, CD4+ T cells are necessary and sufficient to induce skin allograft rejection whereas CD8+ T cells do not appear to contribute.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ager A., Fajumi J., Sparshott S. M., Ford W. L., Butcher G. W. Major histocompatibility complex control of NK-related allogeneic lymphocyte cytotoxicity in rats. The contributions of strong and medial transplantation antigens. Transplantation. 1988 Nov;46(5):762–767. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198811000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. B., Sparshott S. M., Drayson M. T., Ford W. L. The stable and permanent expansion of functional T lymphocytes in athymic nude rats after a single injection of mature T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1379–1384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. B., Sparshott S. M., Drayson M. T., Hunt S. V. The origin of T cells in permanently reconstituted old athymic nude rats. Analysis using chromosome or allotype markers. Immunology. 1989 Dec;68(4):547–556. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton E. M., Gracie J. A., Briggs J. D., Kampinga J., Bradley J. A. Cellular requirements for renal allograft rejection in the athymic nude rat. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1931–1946. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born W., Wekerle H. Lympho-stromal interactions in the thymus: medullary thymocytes react with I-A determinants on autochthonous thymic stimulator cells. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jan;12(1):51–59. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold S. P., Jayasuriya A., Nash A., Prospero T. D., Waldmann H. Therapy with monoclonal antibodies by elimination of T-cell subsets in vivo. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):548–551. doi: 10.1038/312548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold S., Waldmann H. Skin allograft rejection by L3/T4+ and Lyt-2+ T cell subsets. Transplantation. 1986 May;41(5):634–639. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198605000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayson M. T., Sparshott S. M., Bell E. B. Fidelity of the repertoire in T cell reconstituted athymic nude rats. Preservation of a deficit in alloresponsiveness over one year. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):691–702. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVERETT N. B., CAFFREY R. W., RIEKE W. O. RADIOAUTOGRAPHIC STUDIES OF THE EFFECT OF IRRADIATION ON THE LONG-LIVED LYMPHOCYTE OF THE RAT. Radiat Res. 1964 Mar;21:383–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossum S., Ager A., Rolstad B. Specific inhibition of natural killer (NK) activity against different alloantigens. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(6):329–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00343700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossum S., Smith M. E., Bell E. B., Ford W. L. The architecture of rat lymph nodes. III. The lymph nodes and lymph-borne cells of the congenitally athymic nude rat (rnu). Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(5):421–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Union N. A., Baker P. E., Smith K. A. The in vitro generation and sustained culture of nude mouse cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1460–1476. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. M., Dorsch S., Roser B. The cellular basis of allograft rejection in vivo. I. The cellular requirements for first-set rejection of heart grafts. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):878–889. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. M., Dorsch S., Roser B. The cellular basis of allograft rejection in vivo. II. The nature of memory cells mediating second set heart graft rejection. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):890–902. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. M., de Saxe I., Dorsch S. E. The cellular basis of allograft rejection in vivo. III. Restoration of first-set rejection of heart grafts by T helper cells in irradiated rats. Transplantation. 1983 Dec;36(6):700–705. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198336060-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T., Bevan M. J. Specificity of cytotoxic T cells from athymic mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):688–702. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindred B. Nude mice in immunology. Prog Allergy. 1979;26:137–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishihara K., Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Mak T. W., Nomoto K. Functional alpha and beta T cell chain receptor messages can be detected in old but not in young athymic mice. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Apr;17(4):477–482. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung J. T. Impaired clonal expansion in athymic nude CD8+CD4- T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3727–3735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung J. T., Thomas C. A., 3rd Athymic nude CD4+8- T cells produce IL-2 but fail to proliferate in response to mitogenic stimuli. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3691–3696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawetzky A., Hünig T. Analysis of CD3 and antigen receptor expression on T cell subpopulations of aged athymic mice. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Mar;18(3):409–416. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFrancois L., Bevan M. J. A reexamination of the role of LYT-2-positive T cells in murine skin graft rejection. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):57–67. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo O., Foo M., Forman J., Shivakumar S., Rabinowitz R., Bluestone J. A. Selective expression of the Ly-6C.2 epitope on Lyt-2+ T cells that can develop in the absence of thymic influence. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveland B. E., Hogarth P. M., Ceredig R., McKenzie I. F. Cells mediating graft rejection in the mouse. I. Lyt-1 cells mediate skin graft rejection. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1044–1057. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry R. P., Gurley K. E., Forbes R. D. Immune mechanisms in organ allograft rejection. I. Delayed-type hypersensitivity and lymphocytotoxicity in heart graft rejection. Transplantation. 1983 Oct;36(4):391–401. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198310000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Lees R. K., Bron C., Sordat B., Miescher G. T cell antigen receptor expression in athymic (nu/nu) mice. Evidence for an oligoclonal beta chain repertoire. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):195–209. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Lees R. K., Sordat B., Zaech P., Maryanski J. L., Bron C. Age-associated increase in expression of the T cell surface markers Thy-1, Lyt-1, and Lyt-2 in congenitally athymic (nu/nu) mice: analysis by flow microfluorometry. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):865–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Dallman M. J., Arthur R. P., Morris P. J. Mechanisms of allograft rejection: the roles of cytotoxic T-cells and delayed-type hypersensitivity. Immunol Rev. 1984;77:167–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Morris P. J. Effector mechanisms in allograft rejection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:119–145. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Simmonds S. J. The autonomy of CD8+ T cells in vitro and in vivo. Immunology. 1988 Oct;65(2):249–257. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolstad B., Fossum S., Bazin H., Kimber I., Marshall J., Sparshott S. M., Ford W. L. The rapid rejection of allogeneic lymphocytes by a non-adaptive, cell-mediated mechanism (NK activity). Immunology. 1985 Jan;54(1):127–138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. S., Mizuochi T., Sharrow S. O., Singer A. Phenotype, specificity, and function of T cell subsets and T cell interactions involved in skin allograft rejection. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1296–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. S., Mizuochi T., Singer A. Analysis of T-cell subsets in rejection of Kb mutant skin allografts differing at class I MHC. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):829–831. doi: 10.1038/322829a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J., Schaefer M., Lo D., Korngold R. Properties of purified T cell subsets. II. In vivo responses to class I vs. class II H-2 differences. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):998–1011. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmuller D. Which T cells mediate allograft rejection? Transplantation. 1985 Sep;40(3):229–233. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198509000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaessen L. M., Broekhuizen R., Rozing J., Vos J. G., Schuurman H. J. T-cell development during ageing in congenitally athymic (nude) rats. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Aug;24(2):223–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vliet E., Jenkinson E. J., Kingston R., Owen J. J., Van Ewijk W. Stromal cell types in the developing thymus of the normal and nude mouse embryo. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jul;15(7):675–681. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., Argilan F., Reynolds C. W. Immunoperoxidase localization of large granular lymphocytes in normal tissues and lesions of athymic nude rats. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):132–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wortis H. H., Nehlsen S., Owen J. J. Abnormal development of the thymus in "nude" mice. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):681–692. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


